Abstract
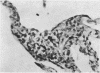
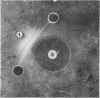
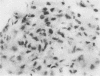
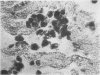
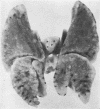
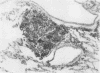
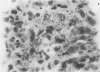
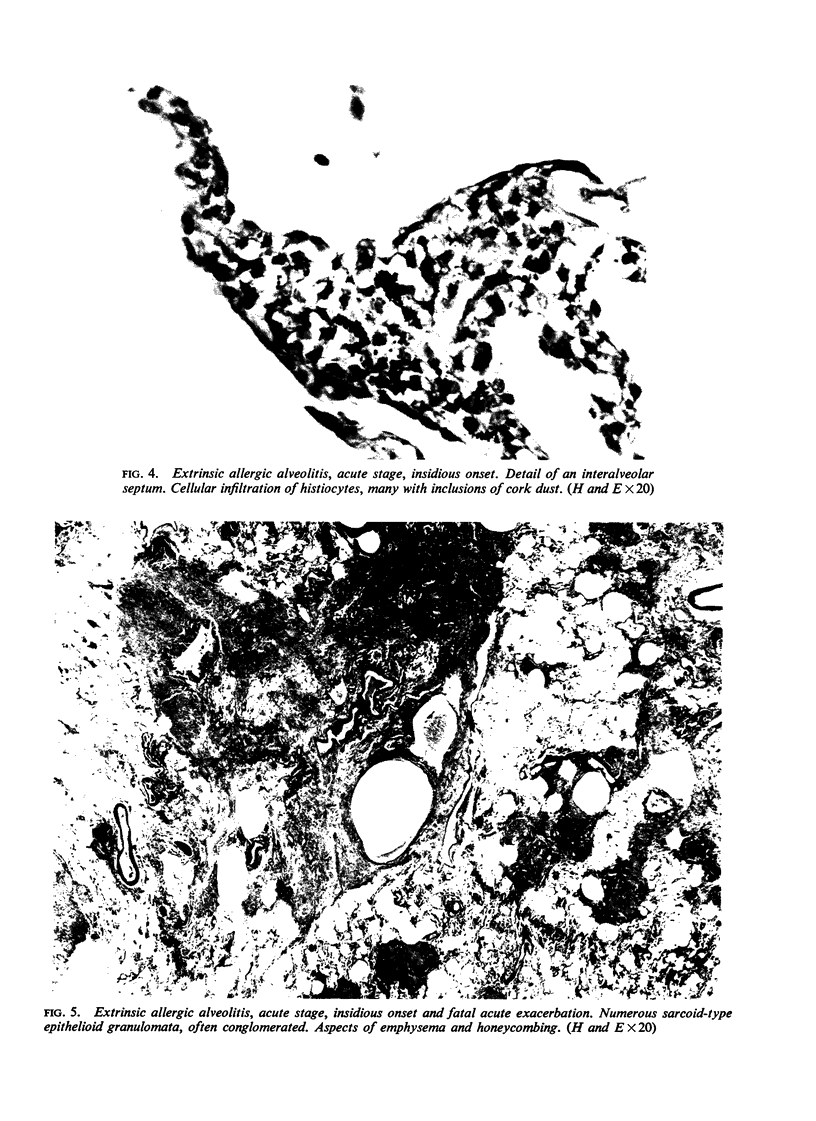
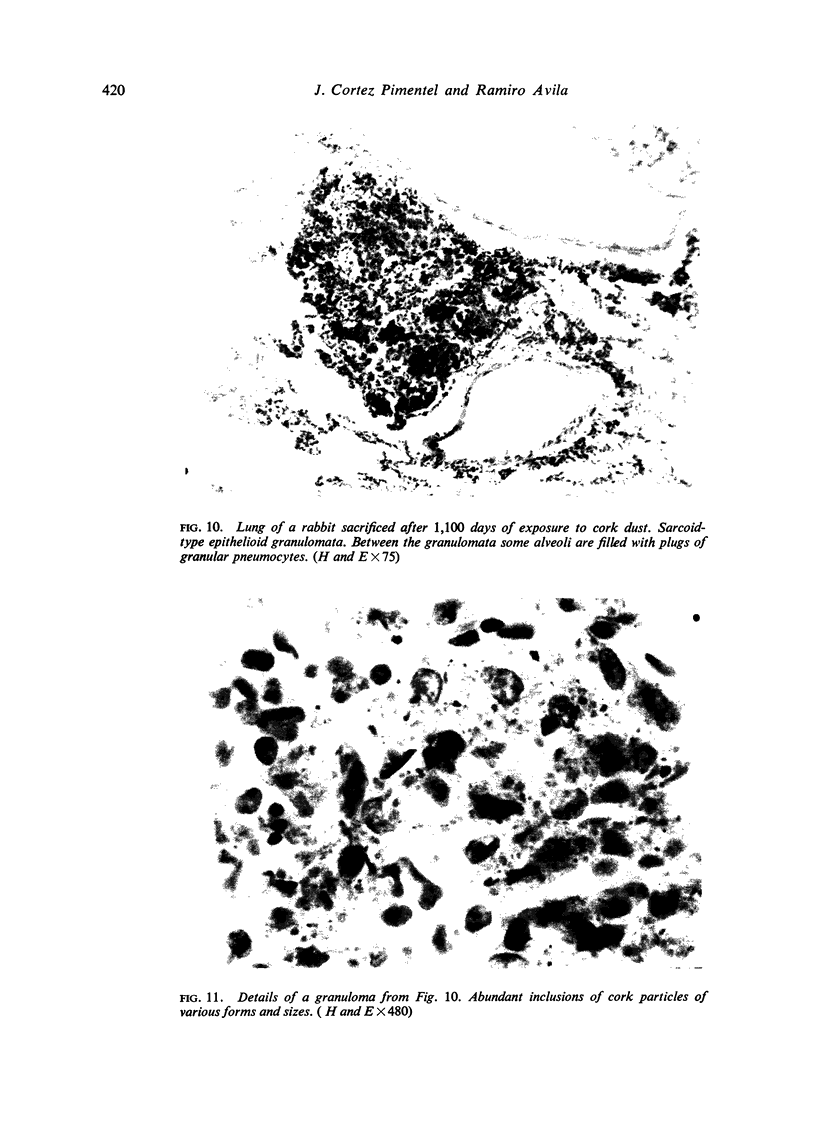
Pimentel, J. Cortez, and Avila, Ramiro (1973).Thorax, 28, 409-423. Respiratory disease in cork workers (`suberosis'). A clinical, immunological, and histological study of 63 workers in the cork industry with bronchopulmonary manifestations is described. From this study, it was possible to recognize three types of reaction to the inhalation of cork dust: asthma-like syndromes, extrinsic allergic alveolitis, and chronic bronchitis with bronchiectasis. The place of histological (lung biopsy and scalene node biopsy) and immunological methods in the diagnosis of these different forms of the disease is evaluated. The high incidence of precipitins to Penicillium frequentans is stressed because the antigens produced by this fungus seem to be more pathogenic than those produced by the mouldy cork itself. The histological studies have demonstrated extrapulmonary foci of disease and have also revealed for the first time, abnormalities in the lungs of symptomless subjects. Pathological changes present in the lungs of patients with the chronic form of extrinsic allergic alveolitis, long after removal from exposure to cork dust, are also described. The experimental material of Horta and Cancella (1956) is reviewed in the light of present knowledge, and the similarity between the lesions produced in animals and those found in cork workers is noted. Finally, especial importance is attached to the finding of cork dust within the lesions, the technique for its identification and staining being described.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avila R., Villar T. G. Suberosis. Respiratory disease in cork workers. Lancet. 1968 Mar 23;1(7543):620–621. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91239-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrowcliff D. F., Arblaster P. G. Farmer's lung: a study of an early acute fatal case. Thorax. 1968 Sep;23(5):490–500. doi: 10.1136/thx.23.5.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CANCELLA L. de C. On a special kind of pneumoconiosis: the suberosis; preliminary report. Med Contemp. 1955 May;73(5):235–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EMANUEL D. A., LAWTON B. R., WENZEL F. J. Maple-bark disease. Pneumonitis due to Coniosporium corticale. N Engl J Med. 1962 Feb 15;26:333–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hearn C. E., Holford-Strevens V. Immunological aspects of bagassosis. Br J Ind Med. 1968 Oct;25(4):283–292. doi: 10.1136/oem.25.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash E. S., Vogelpoel L., Becker W. B. Pigeon breeder's lung--a case report. S Afr Med J. 1967 Feb 25;41(8):191–193. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPYS J., JENKINS P. A., FESTENSTEIN G. N., GREGORY P. H., LACEY M. E., SKINNER F. A. FARMER'S LUNG. THERMOPHILIC ACTINOMYCETES AS A SOURCE OF "FARMER'S LUNG HAY" ANTIGEN. Lancet. 1963 Sep 21;2(7308):607–611. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(63)90398-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPYS J., JENKINS P. A. PRECIPITIN (F.L.H.) TEST IN FARMER'S LUNG. Thorax. 1965 Jan;20:21–35. doi: 10.1136/thx.20.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEPYS J., LONGBOTTOM J. L., JENKINS P. A. VEGETABLE DUST PNEUMOCONIOSES. IMMUNOLOGIC RESPONSES TO VEGETABLE DUSTS AND THEIR FLORA. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 Jun;89:842–858. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.89.6.842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pepys J., Longbottom J. L., Hargreave F. E., Faux J. Allergic reactions of the lungs to enzymes of Bacillus subtilis. Lancet. 1969 Jun 14;1(7607):1181–1184. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92166-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel F. J., Emanuel D. A., Lawton B. R. Pneumonitis due to Micromonospora vulgaris (farmer's lung). Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Apr;95(4):652–655. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.95.4.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]