Abstract
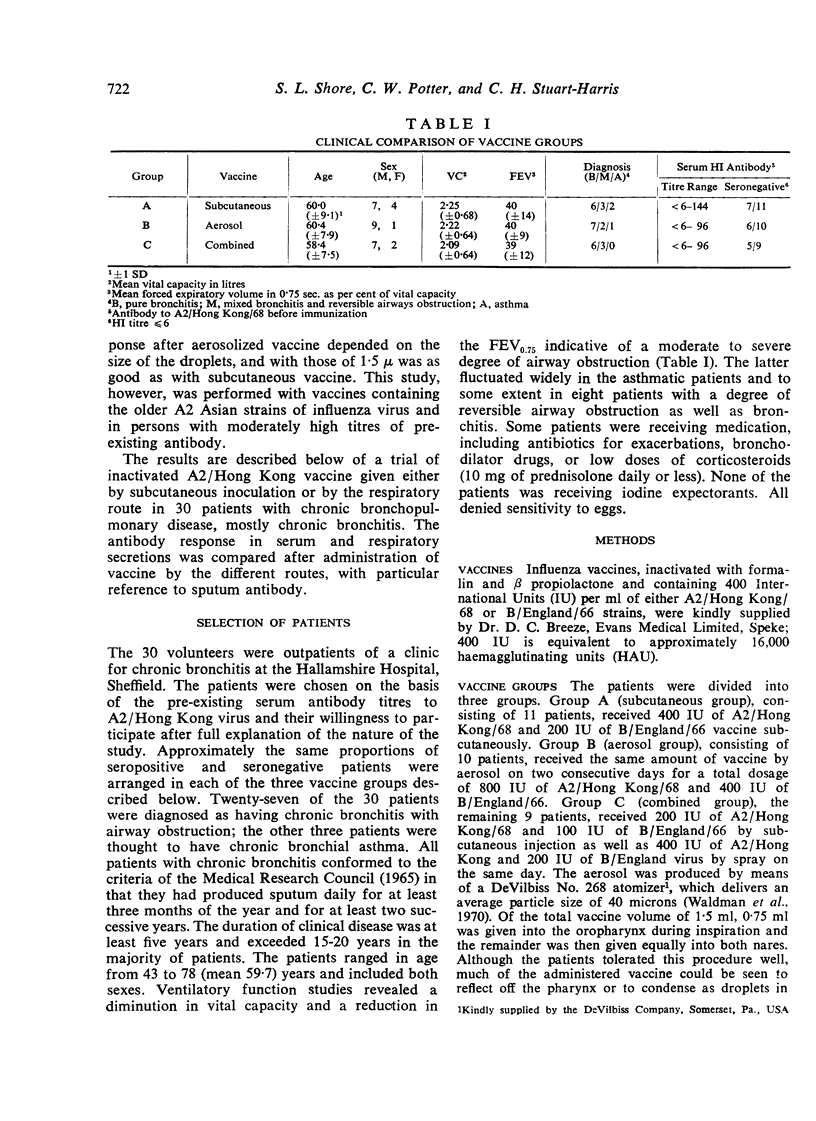
Shore, S. L., Potter, C. W., and Stuart-Harris, C. H. (1973).Thorax,28, 721-728. Antibody response to inactivated influenza vaccine given by different routes in patients with chronic bronchopulmonary disease. A comparison was made of the effects of administering inactivated bivalent influenza vaccine to 30 patients with chronic chest disease by various routes. The vaccine was given by subcutaneous injection to one group, by intranasal and intraoral spray on two successive days to a second group, and by both subcutaneous and intranasal routes to a third group of patients. Most of the patients suffered from chronic bronchitis with airways obstruction but three had asthma. The composition of the groups was adjusted in order that approximately the same number was present in each group of those with or without antibodies to influenza virus A2/Hong Kong/68. The titre of antibodies to this virus was measured in the serum and in sputum before and after immunization.
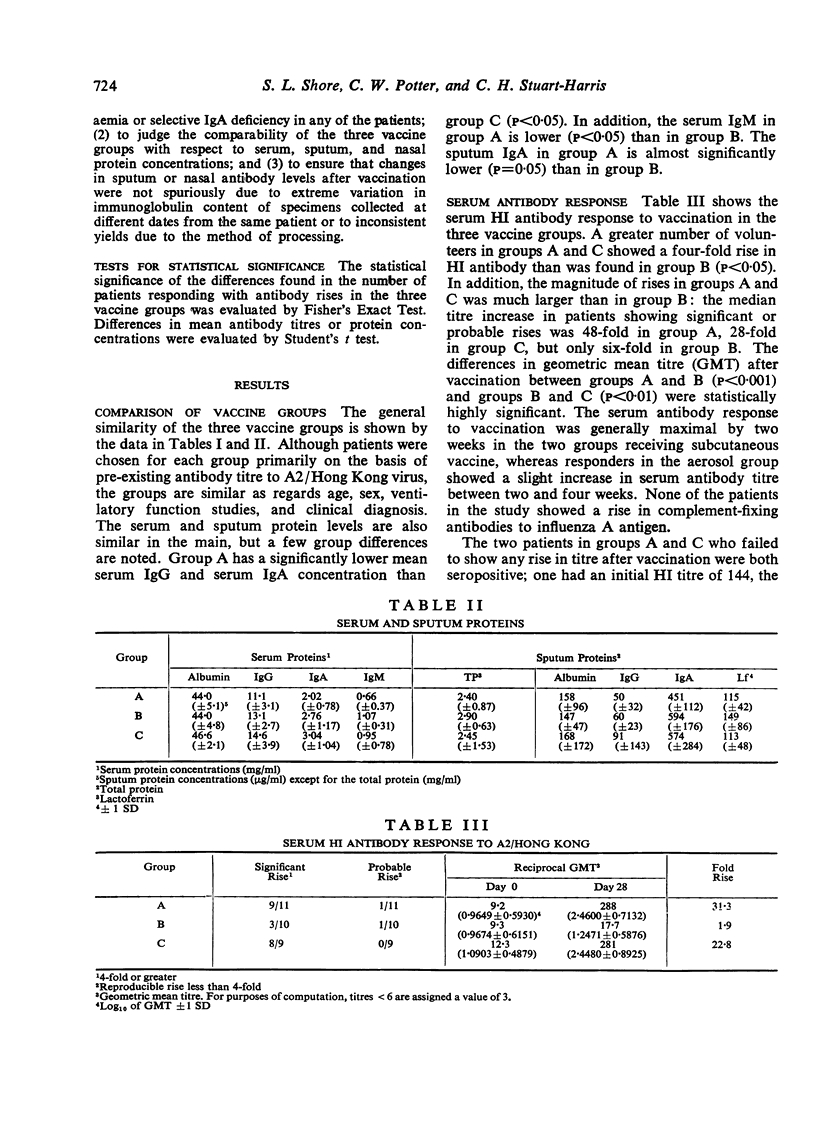
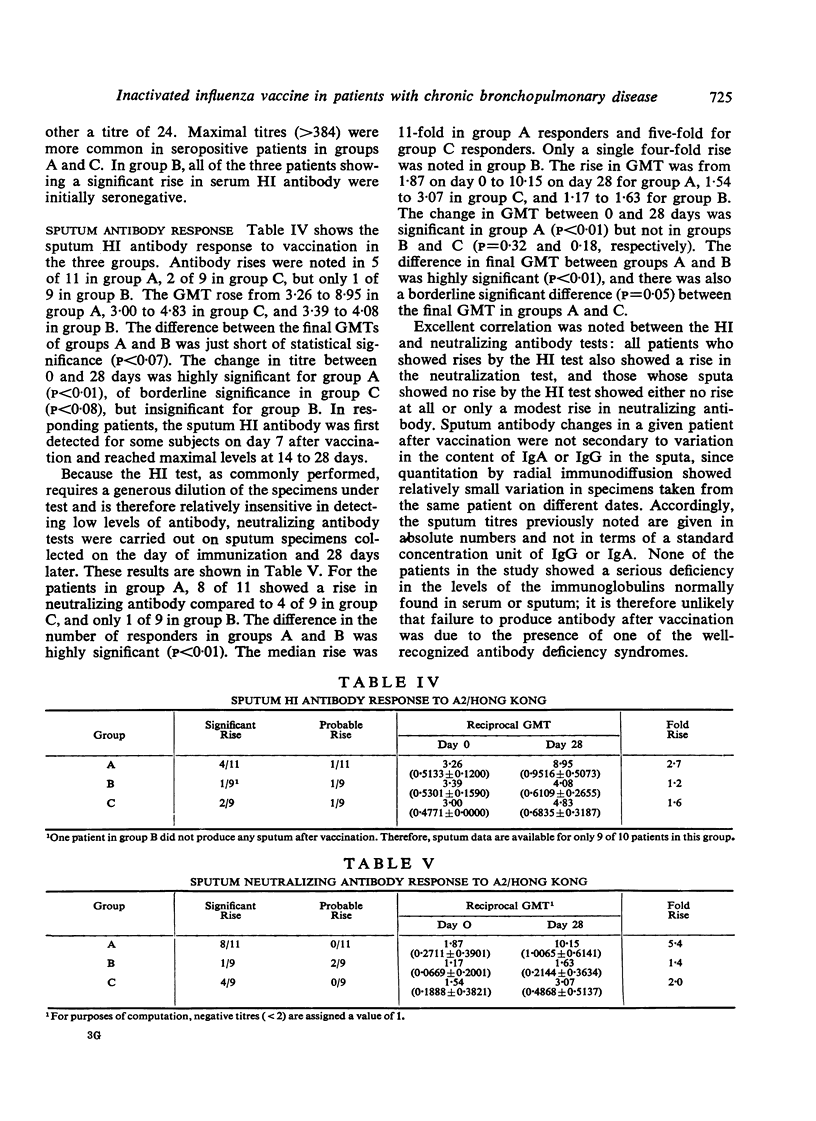
The results were clearcut in that a greater proportion of those receiving subcutaneous vaccine with or without intranasal vaccine achieved a rise in HI antibodies and a higher titre of serum antibodies than those receiving vaccine purely by the respiratory route. Sputum antibodies were measured by both HI and tissue culture neutralization tests. The best sputum antibody responses were achieved by those receiving a single dose of subcutaneous vaccine. Those receiving vaccine by the respiratory route only achieved the poorest result and the third group immunized by both routes produced intermediate titres of sputum antibodies, thus suggesting an impairment of the local antibody response. These results are discussed with reference to the method of immunization against influenza of patients with chronic bronchitis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Downie J. C., Stuart-Harris C. H. The production of neutralizing activity in serum and nasal secretion following immunization with influenza B virus. J Hyg (Lond) 1970 Jun;68(2):233–244. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400028709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finter N. B. Quantitative hemadsorption, a new assay technique. II. Assay of neutralizing antibodies to hemadsorbing viruses. J Immunol. 1967 Jan;98(1):88–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Edmondson W. P., Jr, Rothenberg R., White P. W. A comparison of subcutaneous, nasal, and combined influenza vaccination. I. Antigenicity. Am J Epidemiol. 1971 Jun;93(6):472–479. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B. G. Isolation of crystalline lactoferrin from human milk. Acta Chem Scand. 1969;23(2):683–684. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.23-0683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONTREUIL J., TONNELAT J., MULLET S. [Preparation and properties of lactosiderophilin (lactotransferrin) of human milk]. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Dec 18;45:413–421. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91478-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medici T. C., Buergi H. The role of immunoglobulin A in endogenous bronchial defense mechanisms in chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Jun;103(6):784–791. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.6.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostow S. R., Schoenbaum S. C., Dowdle W. R., Coleman M. T., Kaye H. S., Hierholzer J. C. Studies on inactivated influenza vaccines. II. Effect of increasing dosage on antibody response and adverse reactions in man. Am J Epidemiol. 1970 Oct;92(4):248–256. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a121204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips D. J., Shore S. L., Maddison S. E., Gordon D. S., Reimer C. B. Comparative evaluation of commercial precipitating antisera against human IgA. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Apr;77(4):639–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. W., Oxford J. S., Shore S. L., McLaren C., Stuart-Harris C. Immunity to influenza in ferrets. I. Response to live and killed virus. Br J Exp Pathol. 1972 Apr;53(2):153–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer C. B., Phillips D. J., Maddison S. E., Shore S. L. Comparative evaluation of commercial precipitating antisera against human IgM and IgM. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Dec;76(6):949–960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore S. L., Phillips D. J., Reimer C. B. Umbrella effect: pitfall in analysis of specificity of antisera to immunoglobulins. Immunochemistry. 1971 Jun;8(6):562–565. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90408-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart-Harris C. H. Control of influenza: lack of knowledge versus lack of application of knowledge. Arch Environ Health. 1970 Sep;21(3):276–285. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1970.10667239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasi T. B., Jr, Bienenstock J. Secretory immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1968;9:1–96. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60441-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



