Abstract
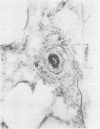
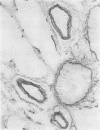
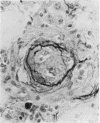
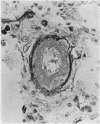
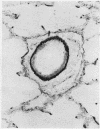
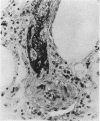
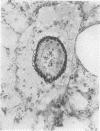
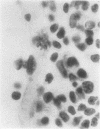
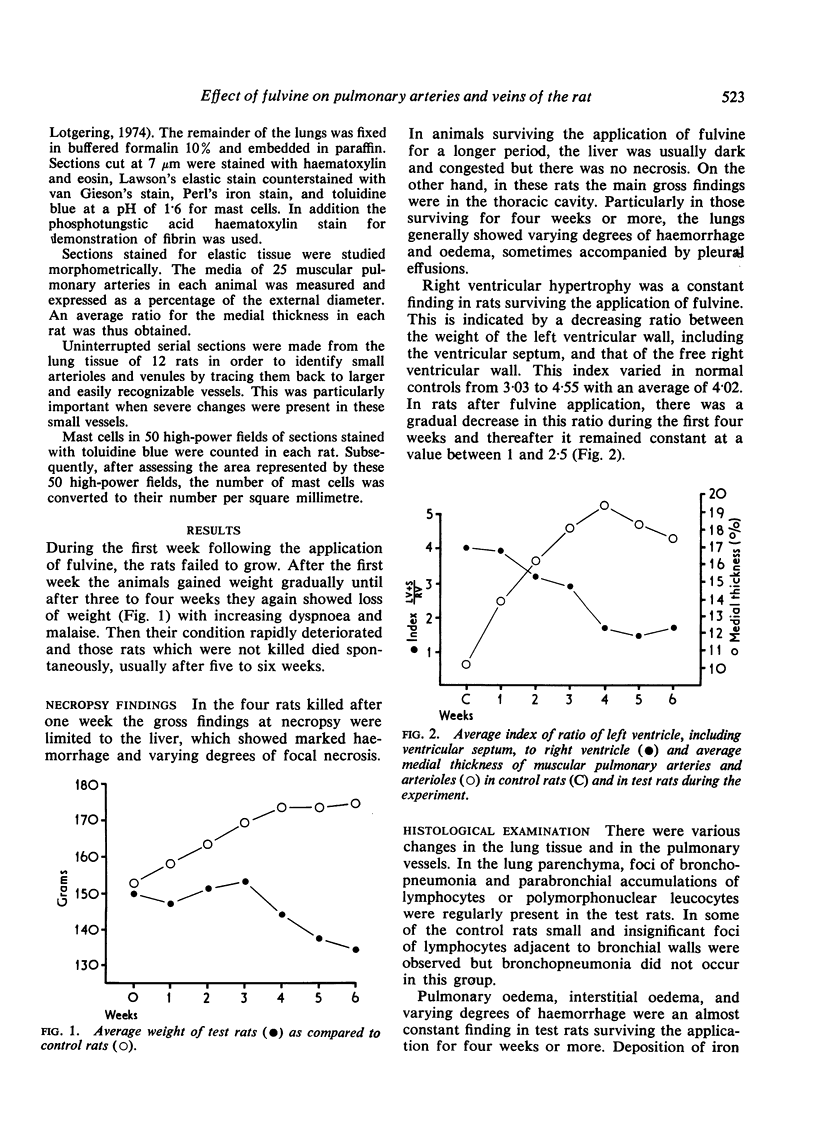
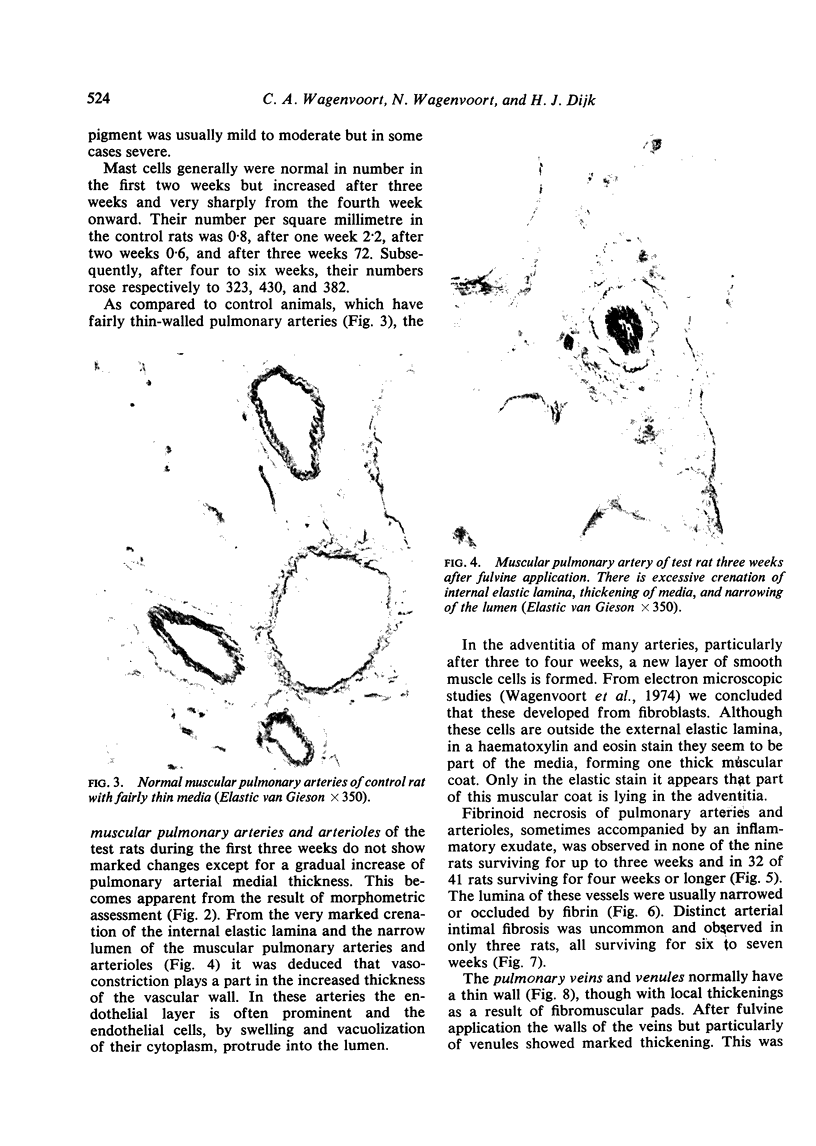
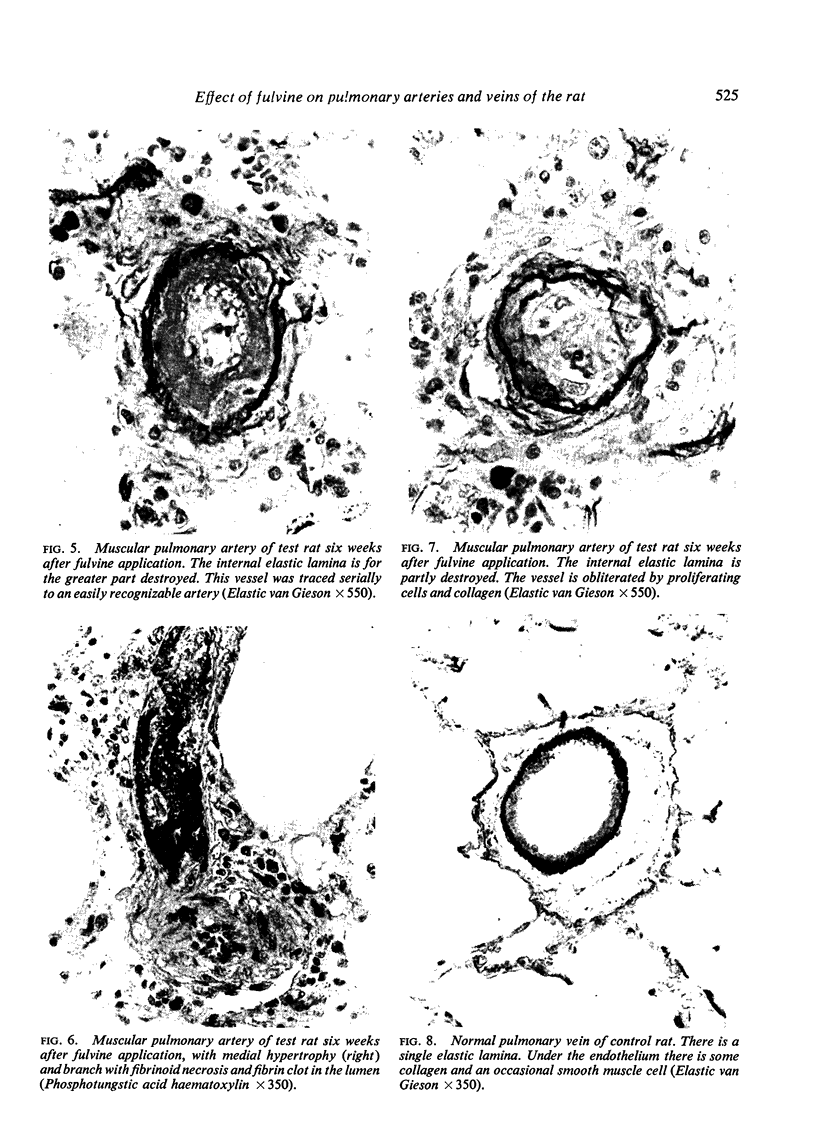
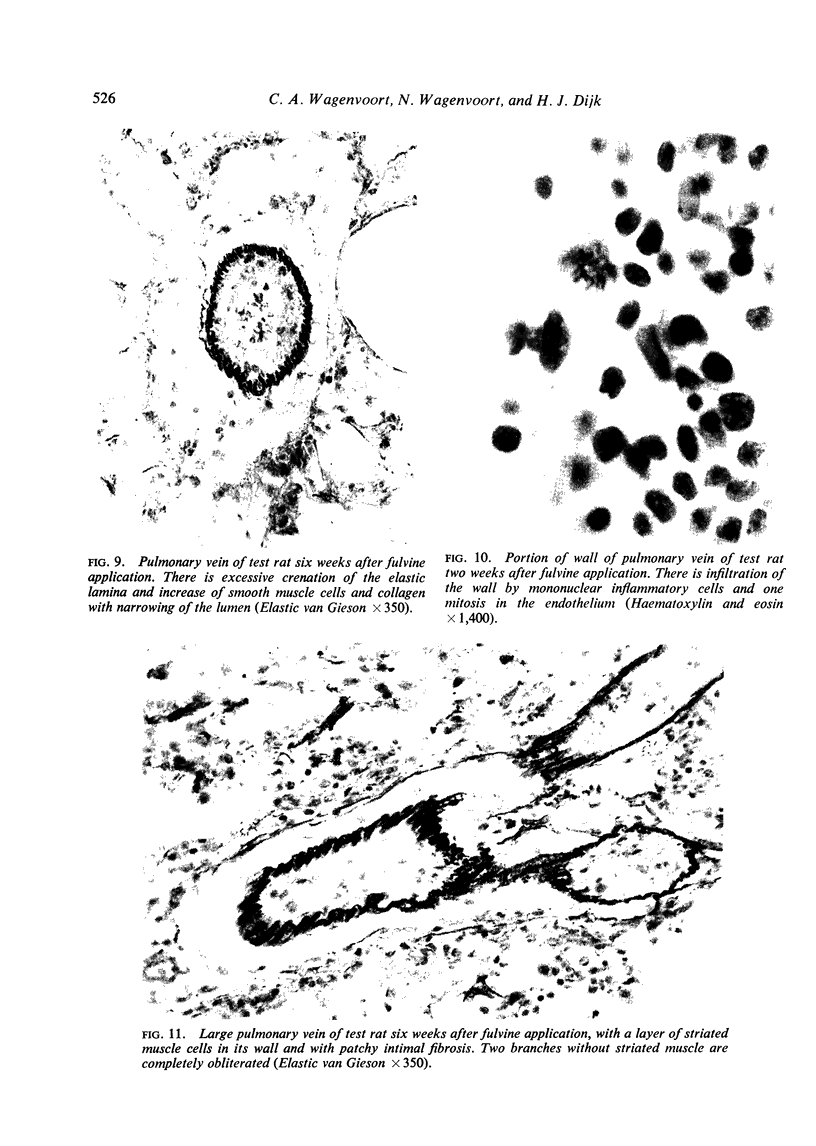
Wagenvoort, C. A., Wagenvoort, N., and Dijk, H. J. (1974).Thorax, 29, 522-529. Effect of fulvine on pulmonary arteries and veins of the rat. Fulvine, one of the pyrrolizidine alkaloids from the Crotalaria group, was administered to rats in a single dose. Vasoconstriction and medial hypertrophy of pulmonary arteries and right ventricular hypertrophy developed gradually, starting after one week. Smooth muscle fibres developed in the arterial adventitia. Fibrinoid necrosis and arteritis of these arteries were common. In addition, however, changes were observed in pulmonary veins and venules which showed thickening of their walls by constriction, proliferation of muscle fibres, and increase of collagen, leading to luminal occlusion. Apparently fulvine is angiotoxic not only for pulmonary arteries but also for pulmonary veins. This detracts from the usefulness of fulvine in the experimental production of pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNES J. M., MAGEE P. N., SCHOENTAL R. LESIONS IN THE LUNGS AND LIVERS OF RATS POISONED WITH THE PYRROLIZIDINE ALKALOID FULVINE AND ITS N-OXIDE. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:521–531. doi: 10.1002/path.1700880215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAS G., BERRY D. M., GYORGY P. Plants as aetiological factor in veno-occlusive disease of the liver. Lancet. 1957 May 11;272(6976):960–962. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)91283-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesney C. F., Allen J. R. Animal model: pulmonary hypertension, cor pulmonale and endocardial fibroelastosis in monocrotaline-intoxicated nonhuman primates. Am J Pathol. 1973 Mar;70(3):489–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Hussa J. F., Lalich J. J. Cor pulmonale in rats. Lab Invest. 1967 Jun;16(6):875–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Harris P., Heath D. Pulmonary hypertension produced in rats by ingestion of Crotalaria spectabilis seeds. Thorax. 1967 Mar;22(2):176–179. doi: 10.1136/thx.22.2.176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Heath D. Observations on the pulmonary arteries and heart weight of rats fed on Crotalaria spectabilis seeds. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1966 Oct;92(2):385–394. doi: 10.1002/path.1700920216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay J. M., Heath D., Smith P., Bras G., Summerell J. Fulvine and the pulmonary circulation. Thorax. 1971 May;26(3):249–261. doi: 10.1136/thx.26.3.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LALICH J. J., MERKOW L. Pulmonary arteritis produced in rat by feeding Crotalaria spectabilis. Lab Invest. 1961 Jul-Aug;10:744–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P., Kay J. M., Heath D. Hypertensive pulmonary vascular disease in rats after prolonged feeding with Crotalaria spectabilis seeds. J Pathol. 1970 Oct;102(2):97–106. doi: 10.1002/path.1711020205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stötzer H., Herbst M., Reichl R., Köllmer H. Zur Pathogenese der experimentellen pulmonalen Hypertonie. Modellversuche mit Crotalaria spectabilis an Ratten. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1972;356(4):331–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TURNER J. H., LALICH J. J. EXPERIMENTAL COR PULMONALE IN THE RAT. Arch Pathol. 1965 Apr;79:409–418. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagenvoort C. A., Dingemans K. P., Lotgering G. G. Electron microscopy of pulmonary vasculature after application of fulvine. Thorax. 1974 Sep;29(5):511–521. doi: 10.1136/thx.29.5.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]