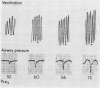
Abstract
Maranetra, N. and Pain, M. C. F. (1974). Thorax, 29, 578-581. Ventilatory drive and ventilatory response during rebreathing. The increase in inspiratory airway pressure generated against a transiently occluded airway during rebreathing is proposed as a simple index of ventilatory drive (ΔP/ΔPco2). A study of this index in 12 normal subjects and 50 patients with chronic airways obstruction demonstrated no significant difference between normals and patients in ΔP/ΔPco2 despite an overall reduction in the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide (ΔV̇e/ΔPco2) in the patients. A significant association was demonstrated between the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide, ΔP/ΔPco2 and the degree of airways obstruction. Patients with a low ΔP/ΔPco2 showed greater hypoxaemia, hypercapnia, and polycythaemia than patients with a higher ΔP/ΔPco2 for the same degree of airways obstruction.
Full text
PDF
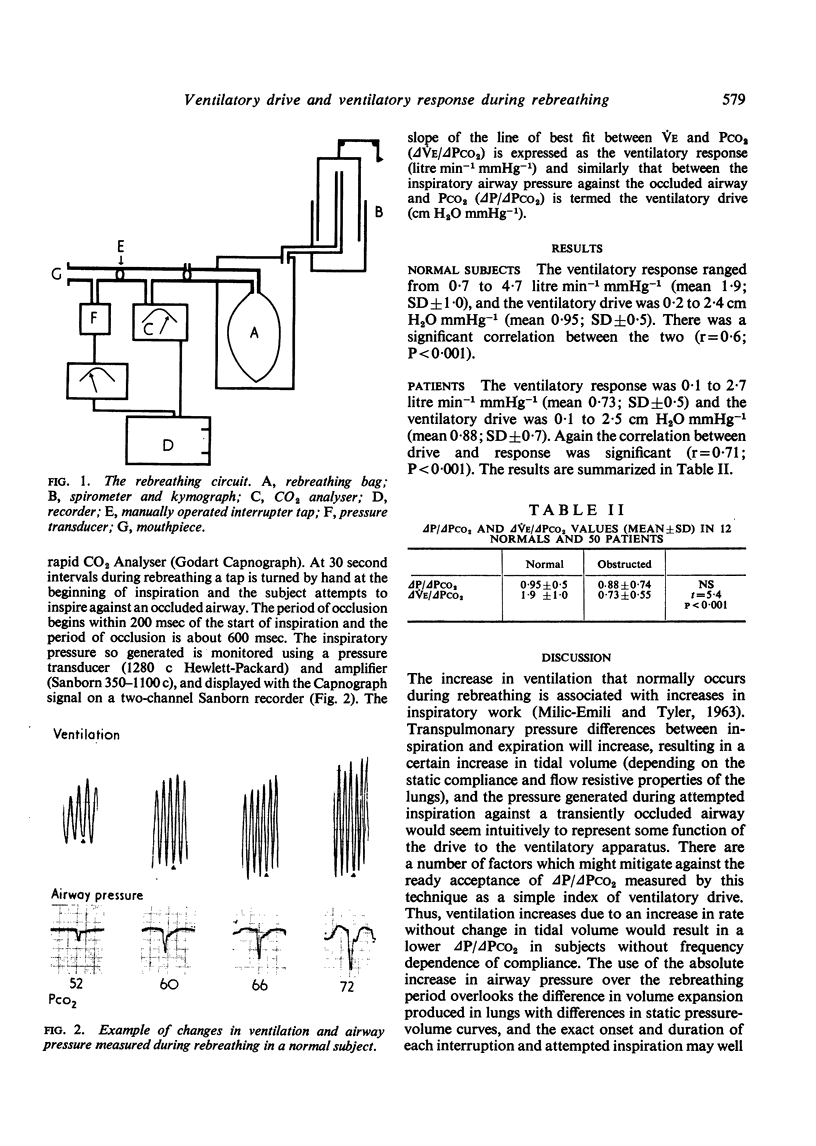
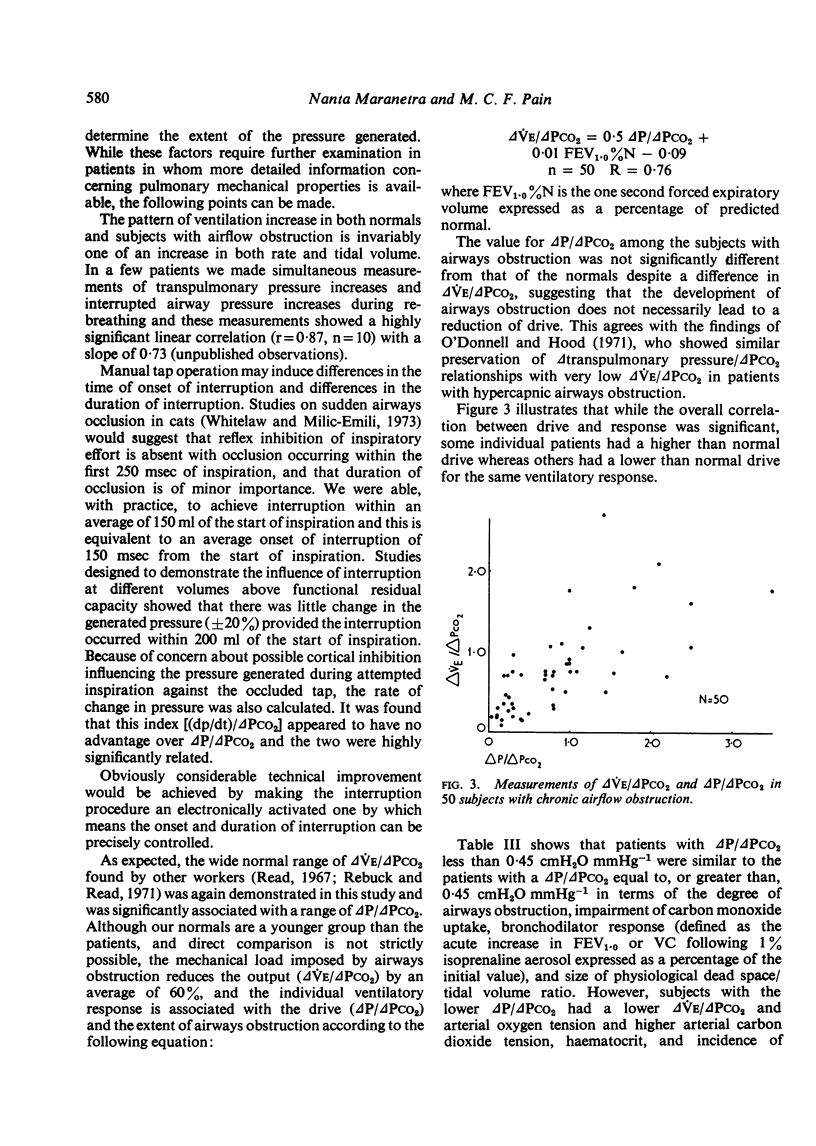
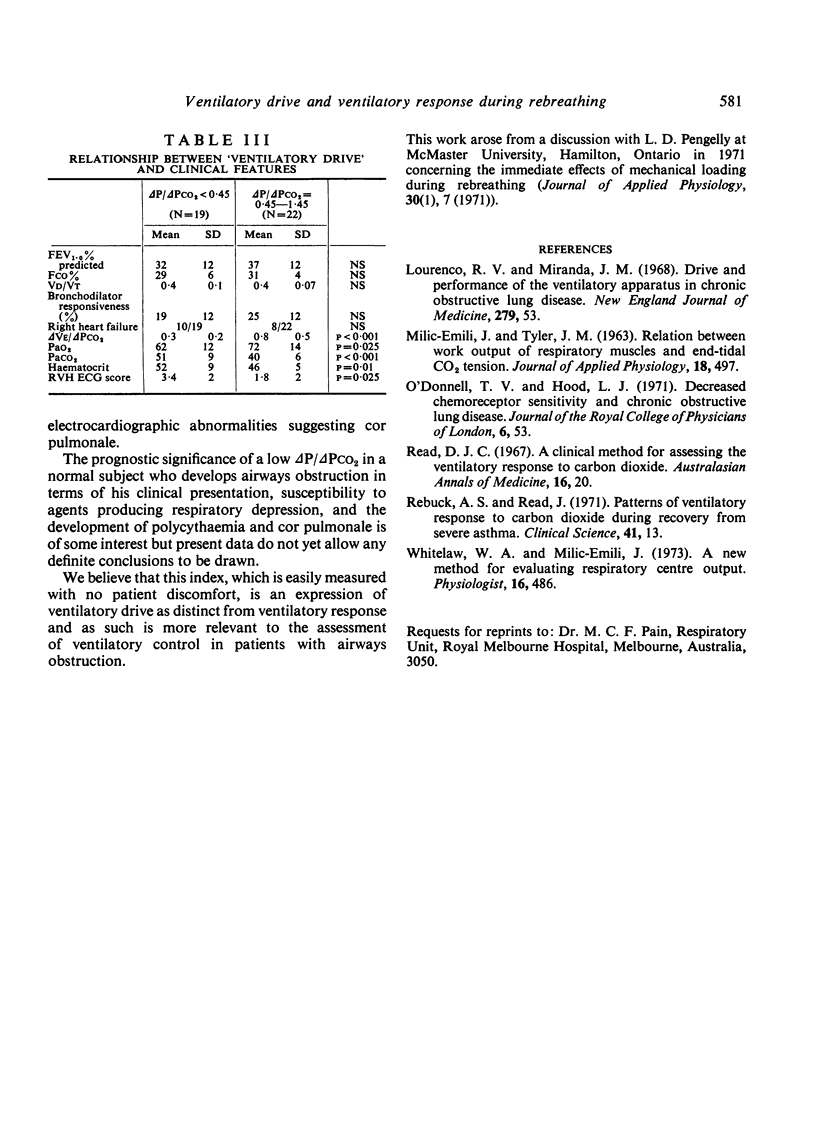
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lourenço R. V., Miranda J. M. Drive and performance of the ventilatory apparatus in chronic obstructive lung disease. N Engl J Med. 1968 Jul 11;279(2):53–59. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196807112790201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read D. J. A clinical method for assessing the ventilatory response to carbon dioxide. Australas Ann Med. 1967 Feb;16(1):20–32. doi: 10.1111/imj.1967.16.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebuck A. S., Read J. Patterns of ventilatory response to carbon dioxide during recovery from severe asthma. Clin Sci. 1971 Jul;41(1):13–21. doi: 10.1042/cs0410013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]