Abstract
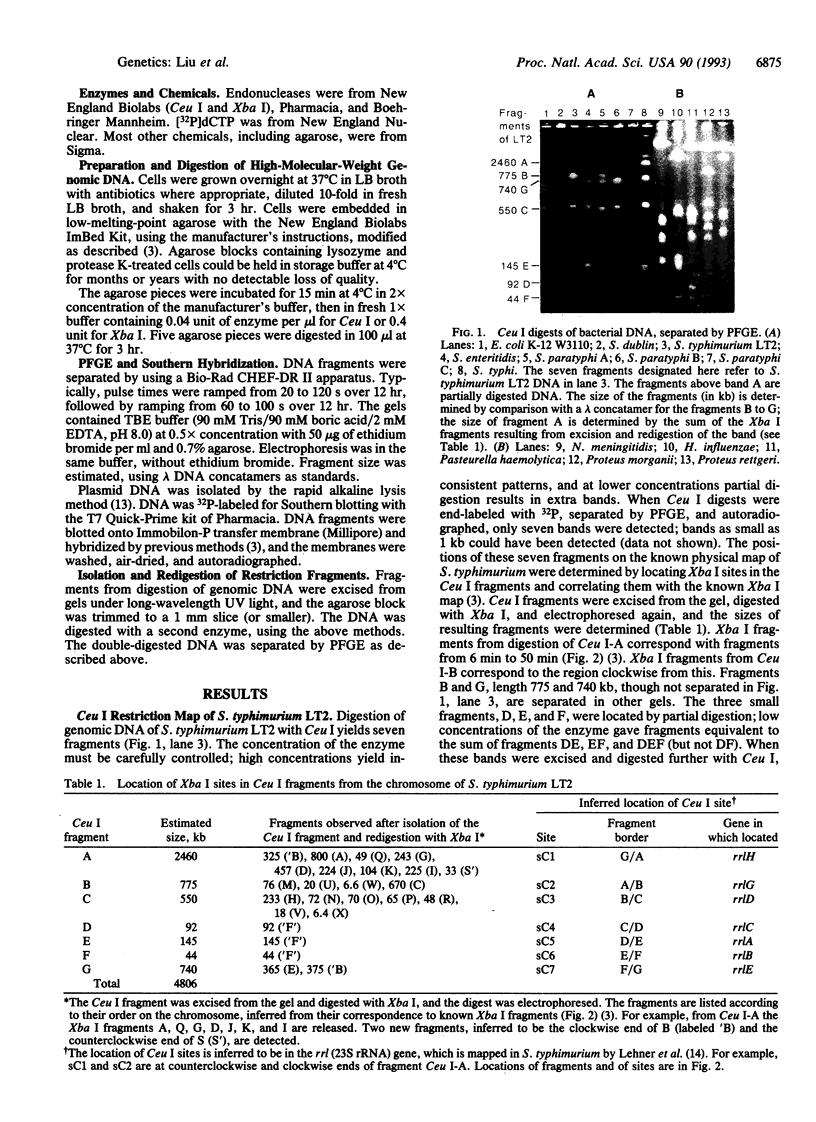
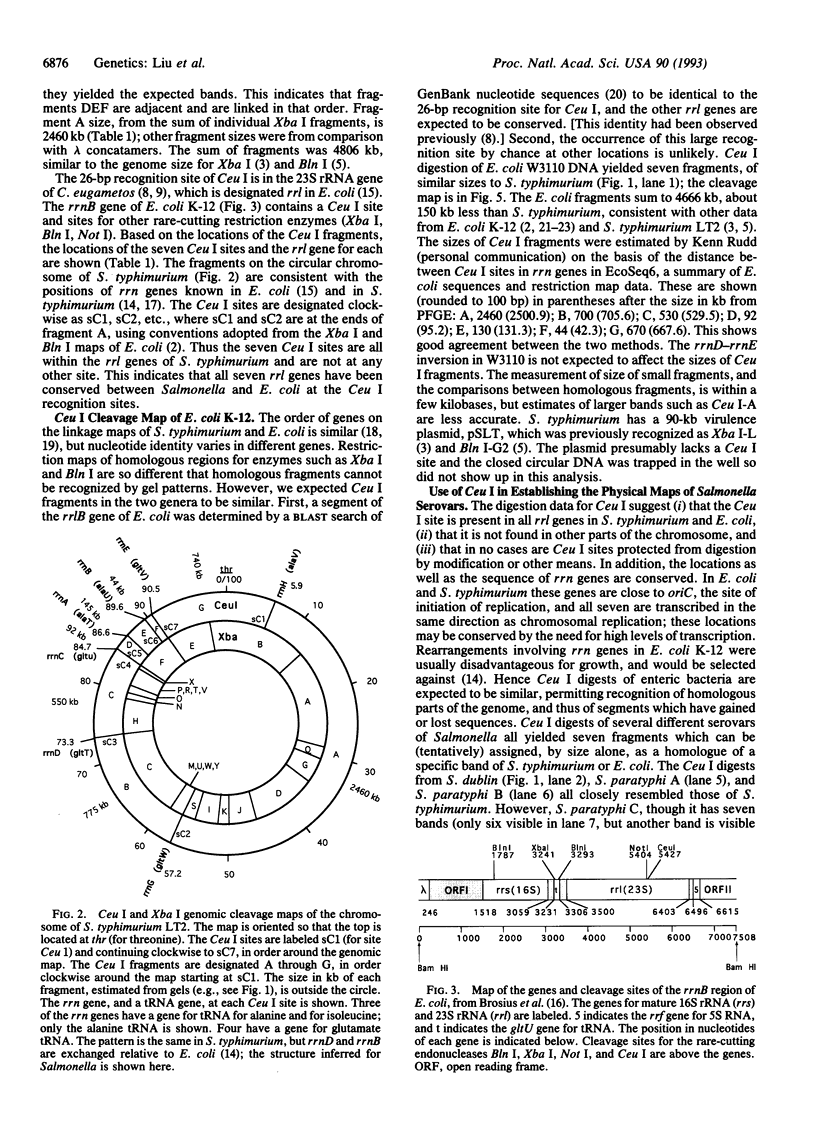
Construction of physical maps of genomes by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis requires enzymes which cut the genome into an analyzable number of fragments; most produce too many fragments. The enzyme I-Ceu I, encoded by a mobile intron in the chloroplast 23S ribosomal RNA (rrl) gene of Chlamydomonas eugametos, cuts a 26-bp site in the rrl gene. This enzyme digests DNA of Salmonella typhimurium at seven sites, each corresponding to one of the rrl genes of the rrn operons, but at no other site. These seven fragments were located on the previously determined Xba I physical map, and the I-Ceu I sites, and thus the rrn genes of S. typhimurium, were mapped on the 4800-kb chromosome. Escherichia coli K-12 also yields seven fragments of sizes similar to those of S. typhimurium, indicating conservation of rrn genes and their location, and a chromosome size of 4600 kb. The sizes of the E. coli fragments are close to the size predicted from restriction maps and nucleotide sequence. The I-Ceu I maps of Salmonella enteritidis, Salmonella paratyphi A, B, C, and Salmonella typhi were deduced after digesting genomic DNA and I-Ceu I and probing with DNA of S. typhimurium; the data indicated strong conservation of rrn gene number and position and genome sizes up to 4950 kb. Digestion of DNA of other bacteria (species of Haemophilus, Neisseria, Proteus, and Pasteurella) suggested that only rrn genes are cut in all these species. I-Ceu I digestion followed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool for determining genome structure and evolution.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beltran P., Plock S. A., Smith N. H., Whittam T. S., Old D. C., Selander R. K. Reference collection of strains of the Salmonella typhimurium complex from natural populations. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Mar;137(3):601–606. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-3-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bihimaier A., Römling U., Meyer T. F., Tümmler B., Gibbs C. P. Physical and genetic map of the Neisseria gonorrhoeae strain MS11-N198 chromosome. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Oct;5(10):2529–2539. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. W., Kuspa A., Keseler I. M., Shimkets L. J. Physical map of the Myxococcus xanthus chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):2109–2115. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.2109-2115.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards M. F., Stocker B. A. Construction of delta aroA his delta pur strains of Salmonella typhi. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):3991–3995. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.3991-3995.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier A., Turmel M., Lemieux C. A group I intron in the chloroplast large subunit rRNA gene of Chlamydomonas eugametos encodes a double-strand endonuclease that cleaves the homing site of this intron. Curr Genet. 1991 Jan;19(1):43–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00362086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawiec S., Riley M. Organization of the bacterial chromosome. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):502–539. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.502-539.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehner A. F., Harvey S., Hill C. W. Mapping and spacer identification of rRNA operons of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):682–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.682-686.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Sanderson K. E. A physical map of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 genome made by using XbaI analysis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1662–1672. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1662-1672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall P., Lemieux C. Cleavage pattern of the homing endonuclease encoded by the fifth intron in the chloroplast large subunit rRNA-encoding gene of Chlamydomonas eugametos. Gene. 1991 Aug 15;104(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90256-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Jones R., Patel Y., Nelson M. Restriction endonucleases for pulsed field mapping of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5985–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd K. E., Miller W., Ostell J., Benson D. A. Alignment of Escherichia coli K12 DNA sequences to a genomic restriction map. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 25;18(2):313–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E. Genetic relatedness in the family Enterobacteriaceae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:327–349. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.001551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VII. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):485–532. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.485-532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., McClelland M. A BlnI restriction map of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 genome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1656–1661. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1656-1661.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]