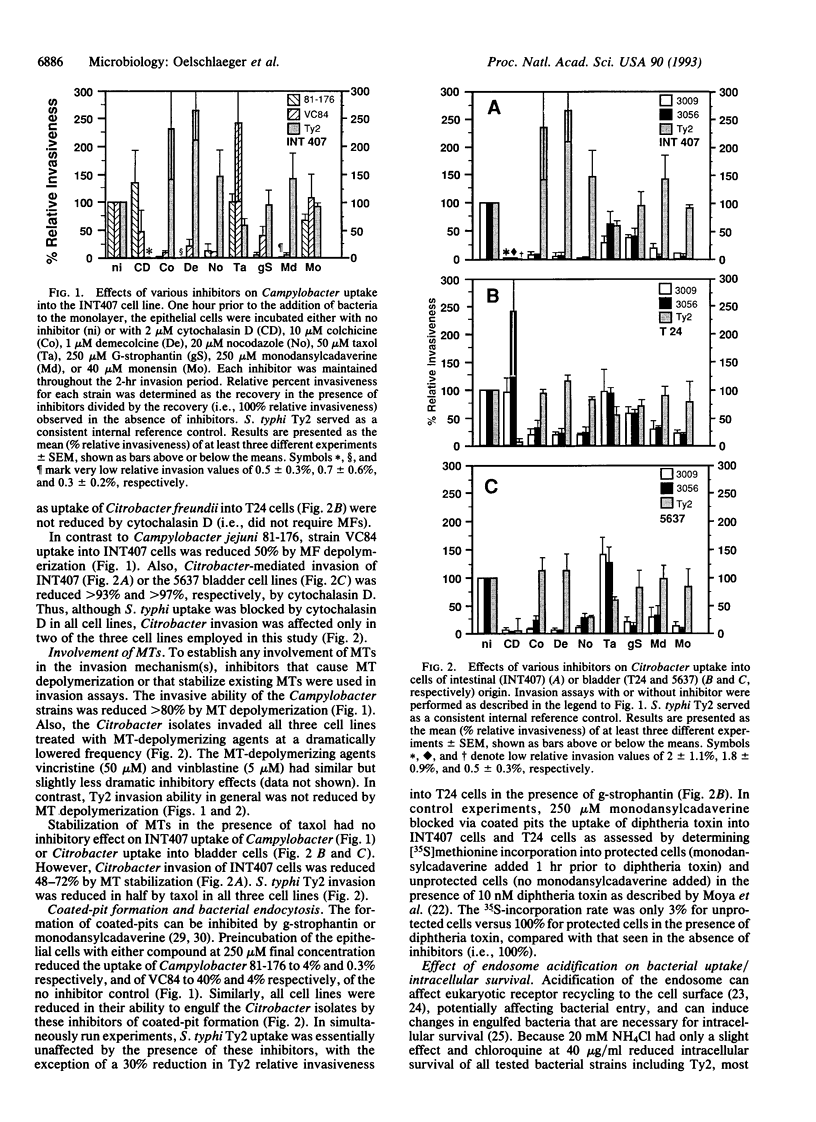
Abstract
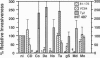
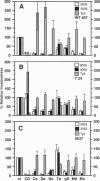
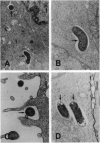
Bacterial invasion of six different human epithelial cell lines showed that some strains of the intestinal pathogen Campylobacter jejuni invaded intestinal cell lines at a level 10(2)-10(4) times higher than reported previously for other Campylobacter strains. Separately, urinary tract isolates of Citrobacter freundii triggered a high-efficiency invasion of bladder cells. Use of multiple inhibitors with known effects on eukaryotic cell structures/processes allowed us to define in these genetically distinct bacterial genera unusual bacterial invasion mechanisms that uniquely require microtubules but not microfilaments. Campylobacter jejuni strain 81-176 uptake into 407 intestinal cells and Citrobacter entry into T24 bladder cells was blocked by microtubule depolymerization and inhibitors of coated-pit formation but not by microfilament depolymerization. Inhibitors of endosome acidification had no significant impact on intracellular survival of Campylobacter jejuni or Citrobacter freundii, but monensin markedly reduced Citrobacter uptake. Epithelial cell invasion by both of these bacterial genera was dependent upon de novo bacterial protein synthesis but not upon de novo eukaryotic cell protein synthesis. In contrast to the T24 cell line-specific, strict microtubule-dependent uptake, Citrobacter entry into other cell lines was inhibited by both microtubule- and microfilament-depolymerization, suggesting that these bacteria encode two separate pathways for uptake (i, microtubule-dependent; ii, microfilament-dependent) that are cell line-specific and are recognized perhaps depending on the presence and abundance of appropriate eukaryotic receptors.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu S. K., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G., Brown M. S. Monensin interrupts the recycling of low density lipoprotein receptors in human fibroblasts. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):493–502. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90340-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black R. E., Levine M. M., Clements M. L., Hughes T. P., Blaser M. J. Experimental Campylobacter jejuni infection in humans. J Infect Dis. 1988 Mar;157(3):472–479. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.3.472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Sansonetti P. J. Entry of Shigella flexneri into HeLa cells: evidence for directed phagocytosis involving actin polymerization and myosin accumulation. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2681–2688. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2681-2688.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. J., Davies D. R., Levitzki A., Maxfield F. R., Milhaud P., Willingham M. C., Pastan I. H. Transglutaminase is essential in receptor-mediated endocytosis of alpha 2-macroglobulin and polypeptide hormones. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):162–167. doi: 10.1038/283162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Baron L. S., Kopecko D. J. Penetration of human intestinal epithelial cells by Salmonella: molecular cloning and expression of Salmonella typhi invasion determinants in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5173–5177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fauchere J. L., Rosenau A., Veron M., Moyen E. N., Richard S., Pfister A. Association with HeLa cells of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from human feces. Infect Immun. 1986 Nov;54(2):283–287. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.2.283-287.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. H., Headley V. L., Underwood J. L., Payne S. M., Berry L. J. The chicken embryo as a model for campylobacter invasion: comparative virulence of human isolates of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):118–125. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.118-125.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fincher R. M., Jackson M. W., Fischer A. Q. Citrobacter freundii: a newly reported cause of pyomyositis. Am J Med Sci. 1990 May;299(5):331–333. doi: 10.1097/00000441-199005000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Common themes in microbial pathogenicity. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Jun;53(2):210–230. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.2.210-230.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Falkow S. Comparison of the invasion strategies used by Salmonella cholerae-suis, Shigella flexneri and Yersinia enterocolitica to enter cultured animal cells: endosome acidification is not required for bacterial invasion or intracellular replication. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):1089–1099. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay B. B., Gumbiner B., Falkow S. Penetration of Salmonella through a polarized Madin-Darby canine kidney epithelial cell monolayer. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flegg P. J., Mandal B. K. Citrobacter freundii bacteraemia presenting as typhoid fever. J Infect. 1989 Mar;18(2):171–173. doi: 10.1016/s0163-4453(89)91234-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaillard J. L., Berche P., Mounier J., Richard S., Sansonetti P. In vitro model of penetration and intracellular growth of Listeria monocytogenes in the human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2822–2829. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2822-2829.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino A., Giannella R., Thompson M. R. Citrobacter freundii produces an 18-amino-acid heat-stable enterotoxin identical to the 18-amino-acid Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin (ST Ia). Infect Immun. 1989 Feb;57(2):649–652. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.2.649-652.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hale T. L., Morris R. E., Bonventre P. F. Shigella infection of henle intestinal epithelial cells: role of the host cell. Infect Immun. 1979 Jun;24(3):887–894. doi: 10.1128/iai.24.3.887-894.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey C. D., Montag D. M., Pittman F. E. Experimental infection of hamsters with Campylobacter jejuni. J Infect Dis. 1985 Mar;151(3):485–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/151.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel M. E., Babakhani F., Joens L. A. Invasion-related antigens of Campylobacter jejuni. J Infect Dis. 1990 Oct;162(4):888–895. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.4.888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konkel M. E., Joens L. A. Adhesion to and invasion of HEp-2 cells by Campylobacter spp. Infect Immun. 1989 Oct;57(10):2984–2990. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.10.2984-2990.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. M., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Anderson R. G. Depletion of intracellular potassium arrests coated pit formation and receptor-mediated endocytosis in fibroblasts. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):273–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90356-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moya M., Dautry-Varsat A., Goud B., Louvard D., Boquet P. Inhibition of coated pit formation in Hep2 cells blocks the cytotoxicity of diphtheria toxin but not that of ricin toxin. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):548–559. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rae C. E., Fazio A., Rosales J. P. Successful treatment of neonatal Citrobacter freundii meningitis with ceftriaxone. DICP. 1991 Jan;25(1):27–29. doi: 10.1177/106002809102500106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz A. L., Bolognesi A., Fridovich S. E. Recycling of the asialoglycoprotein receptor and the effect of lysosomotropic amines in hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):732–738. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker R. I., Caldwell M. B., Lee E. C., Guerry P., Trust T. J., Ruiz-Palacios G. M. Pathophysiology of Campylobacter enteritis. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Mar;50(1):81–94. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.1.81-94.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wileman T., Harding C., Stahl P. Receptor-mediated endocytosis. Biochem J. 1985 Nov 15;232(1):1–14. doi: 10.1042/bj2320001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]