The crystal structures of two chromone derivatives are described, one of which has two independent molecules in the asymmetric unit. A comparison of the dihedral angles between the mean planes of the central chromone core with those of the substituents shows that each molecule differs significantly from the others.
Keywords: crystal structure, drug design, chromone, conformation supramolecular structure
Abstract
The crystal structures of two chromone derivatives, viz. ethyl 6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate, C19H16O4, (1), and ethyl 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate C18H13FO4, (2), have been determined: (1) crystallizes with two molecules in the asymmetric unit. A comparison of the dihedral angles beween the mean planes of the central chromone core with those of the substituents, an ethyl ester moiety at the 2-position and a para-substituted phenyl ring at the 6-position shows that each molecule differs significantly from the others, even the two independent molecules (a and b) of (1). In all three molecules, the carbonyl groups of the chromone and the carboxylate are trans-related. The supramolecular structure of (1) involves only weak C—H⋯π interactions between H atoms of the substituent phenyl group and the phenyl group, which link molecules into a chain of alternating molecules a and b, and weak π–π stacking interactions between the chromone units. The packing in (2) involves C—H⋯O interactions, which form a network of two intersecting ladders involving the carbonyl atom of the carboxylate group as the acceptor for H atoms at the 7-position of the chromone ring and from an ortho-H atom of the exocyclic benzene ring. The carbonyl atom of the chromone acts as an acceptor from a meta-H atom of the exocyclic benzene ring. π–π interactions stack the molecules by unit translation along the a axis.
Chemical context
Benzopyran derivatives represent a large class of natural and synthetic heterocycles that are often linked to a broad array of biological activities, (Gaspar et al., 2014 ▸, 2015 ▸). Within this vast class of compounds, the chromone core has emerged as a privileged structure for drug discovery and development programs (Welsch et al., 2010 ▸). Chemically, the chromone scaffold is a rigid benzoannelated γ-pyrone ring, which can be modulated by diversity-oriented synthesis, (Gaspar et al., 2015 ▸; Welsch et al., 2010 ▸; Ko et al., 2006 ▸; Nicolaou et al., 2000 ▸), exhibiting a diversity of pharmacological properties such as anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial and anticancer among others (Gaspar et al., 2015 ▸). The application of chromones as a valid scaffold for the development of therapeutic solutions for aging-related diseases is still an emerging field, even though the data acquired indicate their importance in the development of new drug candidates for targets ascribed with respect to Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases, namely as adenosine receptors ligands (Cagide et al., 2015a
▸) and/or as monoamino oxidase B inhibitors, (Cagide et al., 2015b
▸).
Within this framework, our project has been focused on the discovery of new chemical entities based on a chromone scaffold. Herein we describe the crystal structures of two new chromone derivatives, viz. ethyl-6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate (1) and ethyl-6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate (2).
Molecular Geometry
Ellipsoid plots of the molecules are given in Figs. 1 ▸ and 2 ▸. Compound (1) crystallizes with two molecules (a and b) in the asymmetric unit.
Figure 1.
A view of the asymmetric unit of (1), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 70% probability level.
Figure 2.
A view of the asymmetric unit of (2), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 70% probability level.
The molecules consist of a central chromone core with an ethylester substituent at the 2-position and a p-substituted phenyl group at the 6-position of the chromone ring system. Those constitutive fragments are essentially planar, therefore the major contribution to the definition of the molecular conformations are the rotations around the C—C bonds that connect the substituents to the chromone ring. As such, the analysis of the molecular geometry will be based on the values for the dihedral angles between the mean planes of the chromone and the phenyl ring (θChr–Phe) and the chromone and the ethyl carboxylate moiety (θChr–carboxlylate), Table 1 ▸. As can be seen, the dihedral angles for molecules a and b of (1) are significantly different from each other. An overlay fit using the quaternion transformation method (Mackay, 1984 ▸) shows that molecule i inverts on molecule ii where the weighted/unit weight r.m.s. fits are 0.090/0.089 Å for 23 atoms. The largest individual displacement is 0.169 Å (O14/O24 pair). The r.m.s. bond fit is 0.0021 Å and the r.m.s. angle fit is 0.376°. These values show that, in spite of the large differences in the dihedral angles, the molecules are quite similar overall.
Table 1. Selected dihedral angles (°).
θChr–C3ring is the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the chromene and the phenyl ring. θChr–C6ester is the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the chromone ring and the plane defined by the ester atoms attached to C2 but not including it. θChr–OCO is the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the chromone ring and the OCO atoms of the ester.
| Compound | θChr–Phe | θChr–carboxylate | θChr–OCO |
|---|---|---|---|
| (1) molecule a | 32.8754) | 23.23 (7) | 21.16 (16) |
| (1) molecule b | 24.14 (5) | 14.191 (7) | 12.16 (17) |
| (2) | 36.05 (5) | 9.52 (6) | 12.97 (13) |
Considering the relative position of the ethyl carboxylate residue with respect to the chromone ring as may be seen in Fig. 3 ▸, the molecules may have any conformation between two possible extremes: conformation A where the carbonyl groups are trans-related and conformation B where they are cis-related. A theoretical calculation made with Gaussian03 (Frisch et al., 2004 ▸) at the B3LYP /631++(d,p) level shows that the energy associated with each of the boundary conformations is similar in adiabatic conditions [see supporting information; the B3LYP model combines the hybrid exchange functional of Becke (1997 ▸) with the gradient-correlation functional of Lee et al. (1988 ▸) and the split-valence polarized 6-311+G(d, p) basis set (Hehre et al., 1986 ▸)]. Thus the adopted conformation in the solid state, with a geometry closer to A where the degree of twist lies between 9 and 21° (as measured by dihedral angles) may be due to packing factors. Preliminary results for the structures of similar compounds such as 6-(phenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate, 6-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate and 6-(4-3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate indicate that the major components have the same trans conformation as described above. These structures are imprecisely determined (the crystal quality was poor and the structures appeared to be intractably disordered).
Figure 3.
The relative position of the ethyl carboxylate residue with respect to the chromone ring. Molecules may have any conformation between two possible extremes: conformation A where the carbonyl groups are trans-related and conformation B where they are cis-related.
The rotation around the C(phenyl)—C(chromone) bond is higher than the rotation around the C(chromone)—C(carboxyethyl) bond for all of the three molecules. This rotation may also contribute to the molecular packing since, in the absence of electronically crowded substituents in the o- or m- positions, the phenyl substituent does not impose steric hindrance with respect to the chromone ring.
Supramolecular structures
In the absence of strong hydrogen-bond donors, the supramolecular structures depend on weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π and very weak π–π interactions.
In (1) there are no weak C—H⋯O interactions and aromatic interactions appear to play the major role in the establishment of the packing. There are two T-shaped C—H⋯π interactions, one between C162 and the centroid of the phenyl ring with pivot atom C261, Cg(C261) within the selected asymmetric unit, and the other between C262 and the centroid of the phenyl ring with pivot atom C161, Cg(C161)(x,  − y, −
− y, − + z), Table 2 ▸. This forms a chain of alternating glide-related asymmetric units which runs parallel to the c axis. Within the asymmetric unit, the shortest packing contact is between the rings containing C15 and C25 and has a value of 4.2901 (9) Å, with an average perpendicular distance between the planes of 3.5350 Å and an angle between the planes of 6.46 (7)°, suggesting a possible very weak π–π interaction. Centrosymmetrically related pairs of molecule i form π–π stacked pairs, as do centrosymmetric pairs of molecule ii, Table 3 ▸. These base-paired units form a column of molecule along the a axis, Fig. 4 ▸.
+ z), Table 2 ▸. This forms a chain of alternating glide-related asymmetric units which runs parallel to the c axis. Within the asymmetric unit, the shortest packing contact is between the rings containing C15 and C25 and has a value of 4.2901 (9) Å, with an average perpendicular distance between the planes of 3.5350 Å and an angle between the planes of 6.46 (7)°, suggesting a possible very weak π–π interaction. Centrosymmetrically related pairs of molecule i form π–π stacked pairs, as do centrosymmetric pairs of molecule ii, Table 3 ▸. These base-paired units form a column of molecule along the a axis, Fig. 4 ▸.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (1) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C162—H162⋯Cg(C261) | 0.95 | 2.85 | 3.4914 (15) | 126 |
| C262—H262⋯Cg(C161)i | 0.95 | 2.84 | 3.5408 (4) | 131 |
Symmetry code: (i)  .
.
Table 3. Selected π–π contacts and short intermolecular contacts (Å, °).
In compound (1), Cg1, Cg2, Cg5 and Cg6 are the centroids of the rings containing atoms O11, C15, O21 and C25, respectively. In compound (2), Cg1, Cg2 and Cg6 are the centroids of the rings containing atoms O1, C5 and C61. Values marked with an asterisk are average perpendicular distances and angles between the planes.
| Compound | contacts | distance | perp. distance | slippage/angle* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | Cg1⋯Cg2i | 3.7338 (8) | 3.503* | 0.45* |
| Cg2⋯Cg2i | 3.7226 (8) | 3.5040 (6) | 1.257 | |
| Cg5⋯Cg6ii | 3.6743 (9) | 3.824* | 0.98* | |
| Cg6⋯Cg6ii | 3.9299 (9) | 3.5762 (6) | 1.630 | |
| (2) | Cg1⋯Cg1iii | 3.8521 (7) | 3.3989 (4) | 1.813 |
| Cg2⋯Cg2iii | 3.8521 (7) | 3.3957 (4) | 1.819 | |
| Cg3⋯Cg3iii’ | 3.8521 (7) | 3.5811 (5) | 1.419 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (ii) 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z; (iii) 1 + x, y, z.
Figure 4.
A view showing the stacking of the molecules along the a axis. Symmetry codes: (*) −x, −y + 1, −z + 1; (#) −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1. H atoms are omitted.
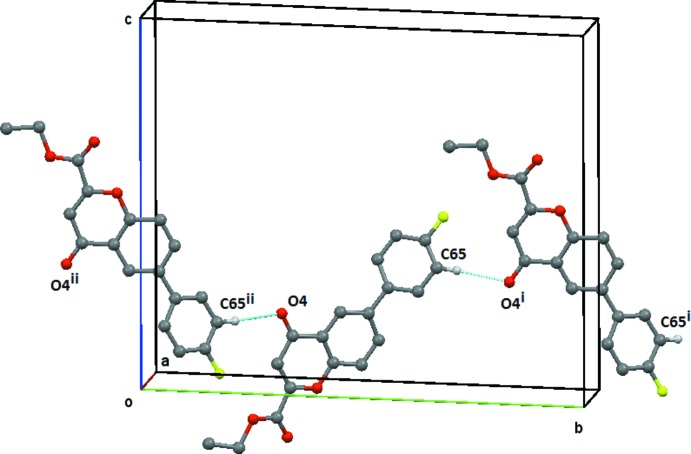
In contrast, compound (2) has a more intricate supramolecular structure, based on C—H⋯O and π–π interactions (Tables 3 ▸ and 4 ▸). Both carboxylic oxygen atoms (O21 and O4) act as acceptors of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. Atom O21 is involved in two centrosymmetrically linked ring structures. In one of these, the C7—H7⋯O21(−x, −y + 1, −z + 1) hydrogen bond forms an  (16) ring, Fig. 5 ▸, and in the other the C66—H66⋯O21(−x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1) hydrogen bond forms an
(16) ring, Fig. 5 ▸, and in the other the C66—H66⋯O21(−x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1) hydrogen bond forms an  (22) ring (Fig. 6 ▸). These interactions combine to link the molecules into zigzag chains of rings which run parallel to the a axis, Fig. 7 ▸. These are linked to form a three-dimensional network by the C65—H65⋯O4(−x + 2, y +
(22) ring (Fig. 6 ▸). These interactions combine to link the molecules into zigzag chains of rings which run parallel to the a axis, Fig. 7 ▸. These are linked to form a three-dimensional network by the C65—H65⋯O4(−x + 2, y +  , −z + 3/2) weak hydrogen bond formed by the action of the twofold screw axis at (1, y, 3/4), Fig. 8 ▸. The molecules are π–π stacked above each other with unit translation along the a axis, Table 3 ▸ and Fig. 9 ▸.
, −z + 3/2) weak hydrogen bond formed by the action of the twofold screw axis at (1, y, 3/4), Fig. 8 ▸. The molecules are π–π stacked above each other with unit translation along the a axis, Table 3 ▸ and Fig. 9 ▸.
Table 4. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °) for (2) .
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C7—H7⋯O21i | 0.95 | 2.47 | 3.1977 (13) | 133 |
| C65—H65⋯O4ii | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.4447 (13) | 175 |
| C66—H66⋯O21iii | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.4425 (13) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Figure 5.
Compound (2), view of the C7—H7⋯O21 centrosymetric  (16) ring structure centred on (0, ½, ½). Atoms labelelled with a postscript,(i), are in molecules at (−x, −y + 1, −z + 1). Hydrogen atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonding are omitted.
(16) ring structure centred on (0, ½, ½). Atoms labelelled with a postscript,(i), are in molecules at (−x, −y + 1, −z + 1). Hydrogen atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonding are omitted.
Figure 6.
Compound (2), view of the C66—H66⋯O21 centrosymetric  (22) ring structure centred on (½, ½, ½). Symmetry code: (i) = −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1. H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonding are omitted.
(22) ring structure centred on (½, ½, ½). Symmetry code: (i) = −x + 1, −y + 1, −z + 1. H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonding are omitted.
Figure 7.
Compound (2), the combined ring structure formed by the combination of the ring structures in Figs. 4 ▸ and 5 ▸. This chain of rings extends along the a axis. H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonding are omitted.
Figure 8.
Compound (2), the simple C9 chain formed by the C65—H65⋯O4 weak hydrogen bond. This chain of rings extends along the a axis and is generated by the twofold screw axis at (1, y,  ). Symmetry codes: (i) −x + 2, y +
). Symmetry codes: (i) −x + 2, y +  , −z +
, −z +  ; (ii) −x + 2, y −
; (ii) −x + 2, y −  , −z +
, −z +  . H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonding are omitted.
. H atoms not involved in the hydrogen bonding are omitted.
Figure 9.
A view showing the stacking of the molecules along the a axis. Symmetry codes: (*) x − 1, y, z; (#) x + 1, y, z + 1. H atoms are omitted.
The intermolecular interactions probably account for the significant difference (about 36 K) in the melting points for these compounds [411–418 K for (1) and 446–455 K for (2)]. They also may have an influence in the conformations of the molecules since in (2) the atoms in the carboxyethyl group are involved either as donors or acceptors; these interactions may constrain the conformation of the orientation of the carboxyethyl moiety.
Synthesis and crystallization
Compounds (1) and (2) were obtained, in moderate yields, by a two-step synthetic procedure. In the first step, the required phenylacetophenone derivatives were obtained from 5′-bromo-2′-hydroxyacetophenone by a Suzuki C–C cross-coupling reaction assisted by microwave (MW) heating (Soares et al., 2015 ▸). In the second step, the phenylacetophenone derivatives were converted in the corresponding chromones via an intramolecular Claisen condensation reaction accomplished with diethyl oxalate in the presence of ethanolic sodium ethoxide and cyclization under acidic conditions of the intermediate formed in situ.
Ethyl 6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate (1). Overall yield 50.7%; m.p. 411–418 K. Crystallization: ethyl acetate to form colourless prisms.
Ethyl 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate (2). Overall yield 55.9%; m.p. 446–455 K. Crystallization: ethyl acetate, to form colourless needles.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 5 ▸. H atoms were treated as riding atoms with C—H(aromatic) = 0.95 Å, with U iso = 1.2U eq(C) and C—H(methyl) = 0.98 Å with U iso = 1.5U eq(C).
Table 5. Experimental details.
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal data | ||
| Chemical formula | C19H16O4 | C18H13FO4 |
| M r | 308.32 | 312.28 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 100 | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 14.7129 (11), 18.9613 (13), 11.3031 (6) | 3.8521 (2), 20.6970 (15), 17.5478 (11) |
| β (°) | 111.632 (7) | 91.546 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 2931.2 (4) | 1398.52 (15) |
| Z | 8 | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.10 | 0.11 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.20 × 0.09 × 0.05 | 0.42 × 0.02 × 0.01 |
| Data collection | ||
| Diffractometer | Rigaku Saturn724+ | Rigaku Saturn724+ |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrystalClear-SM Expert; Rigaku, 20112) | Multi-scan CrystalClear-SM Expert (Rigaku, 20112) |
| T min, T max | 0.981, 0.995 | 0.954, 0.999 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 22133, 6680, 5311 | 16479, 3177, 2725 |
| R int | 0.033 | 0.035 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.649 | 0.650 |
| Refinement | ||
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.038, 0.104, 1.11 | 0.031, 0.087, 0.98 |
| No. of reflections | 6680 | 3176 |
| No. of parameters | 419 | 209 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.33, −0.23 | 0.31, −0.20 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) general, 1, 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb7543sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 1. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb75431sup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb75432sup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb75431sup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb75432sup5.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb7543sup6.pdf
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the staff at the National Crystallographic Service, University of Southampton, for the data collection, help and advice (Coles & Gale, 2012 ▸), and the Foundation for Science and Technology (FCT) of Portugal (QUI/UI0081/2015) for financial support. CF (SFRH/BD/98519/2013) and AG (SFRH/BPD/93331/2013) are supported by FCT, POPH and QREN.
supplementary crystallographic information
(1) Ethyl 6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Crystal data
| C19H16O4 | F(000) = 1296 |
| Mr = 308.32 | Dx = 1.397 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 14.7129 (11) Å | Cell parameters from 18061 reflections |
| b = 18.9613 (13) Å | θ = 3.0–27.5° |
| c = 11.3031 (6) Å | µ = 0.10 mm−1 |
| β = 111.632 (7)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 2931.2 (4) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.20 × 0.09 × 0.05 mm |
(1) Ethyl 6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn724+ (2x2 bin mode) diffractometer | 6680 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Rotating Anode | 5311 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Confocal monochromator | Rint = 0.033 |
| Detector resolution: 28.5714 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.0° |
| profile data from ω–scans | h = −17→19 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear-SM Expert; Rigaku, 20112) | k = −17→24 |
| Tmin = 0.981, Tmax = 0.995 | l = −14→14 |
| 22133 measured reflections |
(1) Ethyl 6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.104 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0504P)2 + 0.4579P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.11 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 6680 reflections | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 419 parameters | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
(1) Ethyl 6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
(1) Ethyl 6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O11 | 0.13984 (7) | 0.39931 (4) | 0.51267 (8) | 0.0167 (2) | |
| O14 | 0.14523 (8) | 0.46234 (5) | 0.86202 (8) | 0.0239 (2) | |
| O121 | 0.18698 (7) | 0.26721 (4) | 0.47772 (8) | 0.0186 (2) | |
| O122 | 0.13729 (7) | 0.23141 (4) | 0.63468 (8) | 0.0162 (2) | |
| C12 | 0.14765 (9) | 0.35255 (6) | 0.60658 (11) | 0.0153 (3) | |
| C13 | 0.14901 (9) | 0.37041 (6) | 0.72208 (11) | 0.0161 (3) | |
| H13 | 0.1540 | 0.3344 | 0.7827 | 0.019* | |
| C14 | 0.14293 (10) | 0.44401 (6) | 0.75658 (11) | 0.0166 (3) | |
| C14A | 0.13289 (9) | 0.49463 (6) | 0.65301 (11) | 0.0150 (2) | |
| C15 | 0.12422 (9) | 0.56769 (6) | 0.66738 (11) | 0.0156 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.1247 | 0.5855 | 0.7462 | 0.019* | |
| C16 | 0.11494 (9) | 0.61435 (6) | 0.56912 (11) | 0.0147 (2) | |
| C17 | 0.11434 (10) | 0.58625 (6) | 0.45309 (11) | 0.0171 (3) | |
| H17 | 0.1084 | 0.6175 | 0.3849 | 0.021* | |
| C18 | 0.12206 (10) | 0.51512 (7) | 0.43612 (11) | 0.0176 (3) | |
| H18 | 0.1209 | 0.4972 | 0.3571 | 0.021* | |
| C18A | 0.13157 (9) | 0.46978 (6) | 0.53635 (11) | 0.0150 (3) | |
| C121 | 0.15961 (9) | 0.27911 (6) | 0.56400 (11) | 0.0152 (3) | |
| C122 | 0.16128 (10) | 0.15886 (6) | 0.61422 (11) | 0.0173 (3) | |
| H12A | 0.2328 | 0.1535 | 0.6384 | 0.021* | |
| H12B | 0.1288 | 0.1457 | 0.5235 | 0.021* | |
| C123 | 0.12554 (11) | 0.11295 (6) | 0.69613 (12) | 0.0222 (3) | |
| H12C | 0.1445 | 0.0639 | 0.6900 | 0.033* | |
| H12D | 0.0542 | 0.1162 | 0.6671 | 0.033* | |
| H12E | 0.1546 | 0.1287 | 0.7848 | 0.033* | |
| C161 | 0.10558 (9) | 0.69191 (6) | 0.58084 (11) | 0.0141 (2) | |
| C162 | 0.14423 (9) | 0.73832 (6) | 0.51543 (11) | 0.0160 (3) | |
| H162 | 0.1776 | 0.7200 | 0.4645 | 0.019* | |
| C163 | 0.13461 (9) | 0.81085 (6) | 0.52375 (11) | 0.0168 (3) | |
| H163 | 0.1612 | 0.8412 | 0.4779 | 0.020* | |
| C164 | 0.08671 (9) | 0.83989 (6) | 0.59792 (11) | 0.0162 (3) | |
| C165 | 0.04831 (9) | 0.79352 (6) | 0.66303 (11) | 0.0164 (3) | |
| H165 | 0.0150 | 0.8120 | 0.7140 | 0.020* | |
| C166 | 0.05741 (9) | 0.72085 (6) | 0.65533 (11) | 0.0157 (3) | |
| H166 | 0.0306 | 0.6906 | 0.7011 | 0.019* | |
| C167 | 0.07977 (10) | 0.91884 (6) | 0.60848 (12) | 0.0208 (3) | |
| H16A | 0.0176 | 0.9310 | 0.6167 | 0.031* | |
| H16B | 0.0831 | 0.9412 | 0.5320 | 0.031* | |
| H16C | 0.1341 | 0.9356 | 0.6836 | 0.031* | |
| O21 | 0.36690 (7) | 0.39338 (4) | 0.38688 (8) | 0.0173 (2) | |
| O24 | 0.39990 (8) | 0.46146 (5) | 0.74405 (8) | 0.0256 (2) | |
| O221 | 0.34285 (7) | 0.25860 (4) | 0.32365 (8) | 0.0197 (2) | |
| O222 | 0.39836 (7) | 0.22764 (4) | 0.53103 (8) | 0.0170 (2) | |
| C22 | 0.37715 (9) | 0.34766 (6) | 0.48321 (11) | 0.0151 (3) | |
| C23 | 0.38783 (9) | 0.36726 (6) | 0.60153 (11) | 0.0166 (3) | |
| H23 | 0.3942 | 0.3321 | 0.6639 | 0.020* | |
| C24 | 0.38986 (10) | 0.44161 (6) | 0.63652 (11) | 0.0170 (3) | |
| C24A | 0.37849 (9) | 0.49097 (6) | 0.53085 (11) | 0.0152 (3) | |
| C25 | 0.37738 (9) | 0.56447 (6) | 0.54600 (11) | 0.0155 (3) | |
| H25 | 0.3850 | 0.5832 | 0.6270 | 0.019* | |
| C26 | 0.36546 (9) | 0.61053 (6) | 0.44566 (11) | 0.0154 (3) | |
| C27 | 0.35322 (10) | 0.58073 (6) | 0.32652 (12) | 0.0182 (3) | |
| H27 | 0.3446 | 0.6111 | 0.2564 | 0.022* | |
| C28 | 0.35334 (10) | 0.50898 (7) | 0.30850 (12) | 0.0190 (3) | |
| H28 | 0.3444 | 0.4901 | 0.2271 | 0.023* | |
| C28A | 0.36677 (9) | 0.46452 (6) | 0.41131 (11) | 0.0159 (3) | |
| C221 | 0.37034 (9) | 0.27309 (6) | 0.43493 (11) | 0.0156 (3) | |
| C222 | 0.38561 (10) | 0.15314 (6) | 0.49520 (11) | 0.0187 (3) | |
| H22A | 0.4129 | 0.1431 | 0.4289 | 0.022* | |
| H22B | 0.3154 | 0.1405 | 0.4615 | 0.022* | |
| C223 | 0.43928 (11) | 0.11188 (7) | 0.61367 (12) | 0.0211 (3) | |
| H22C | 0.4313 | 0.0613 | 0.5947 | 0.032* | |
| H22D | 0.4127 | 0.1233 | 0.6791 | 0.032* | |
| H22E | 0.5089 | 0.1240 | 0.6446 | 0.032* | |
| C261 | 0.36521 (9) | 0.68856 (6) | 0.46004 (11) | 0.0146 (3) | |
| C262 | 0.31923 (9) | 0.73240 (6) | 0.35536 (11) | 0.0163 (3) | |
| H262 | 0.2869 | 0.7120 | 0.2738 | 0.020* | |
| C263 | 0.31995 (9) | 0.80523 (6) | 0.36846 (11) | 0.0167 (3) | |
| H263 | 0.2885 | 0.8336 | 0.2955 | 0.020* | |
| C264 | 0.36574 (9) | 0.83778 (6) | 0.48628 (11) | 0.0165 (3) | |
| C265 | 0.41121 (10) | 0.79387 (6) | 0.59067 (11) | 0.0175 (3) | |
| H265 | 0.4428 | 0.8144 | 0.6723 | 0.021* | |
| C266 | 0.41138 (9) | 0.72107 (7) | 0.57822 (11) | 0.0166 (3) | |
| H266 | 0.4434 | 0.6928 | 0.6512 | 0.020* | |
| C267 | 0.36524 (11) | 0.91687 (6) | 0.49995 (12) | 0.0211 (3) | |
| H26A | 0.3662 | 0.9391 | 0.4221 | 0.032* | |
| H26B | 0.4231 | 0.9316 | 0.5725 | 0.032* | |
| H26C | 0.3061 | 0.9313 | 0.5141 | 0.032* |
(1) Ethyl 6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O11 | 0.0239 (5) | 0.0110 (4) | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0018 (4) | 0.0083 (4) | 0.0015 (3) |
| O14 | 0.0381 (6) | 0.0187 (5) | 0.0180 (4) | −0.0004 (4) | 0.0138 (4) | −0.0006 (4) |
| O121 | 0.0209 (5) | 0.0164 (4) | 0.0209 (4) | 0.0001 (4) | 0.0103 (4) | −0.0004 (3) |
| O122 | 0.0215 (5) | 0.0103 (4) | 0.0174 (4) | 0.0006 (3) | 0.0079 (4) | 0.0009 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0135 (6) | 0.0129 (6) | 0.0182 (6) | −0.0002 (5) | 0.0044 (5) | 0.0023 (4) |
| C13 | 0.0154 (7) | 0.0149 (6) | 0.0175 (6) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0053 (5) | 0.0023 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0173 (7) | 0.0157 (6) | 0.0168 (6) | −0.0006 (5) | 0.0063 (5) | −0.0002 (5) |
| C14A | 0.0131 (6) | 0.0145 (6) | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0002 (5) | 0.0047 (5) | 0.0006 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0155 (6) | 0.0157 (6) | 0.0155 (6) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0058 (5) | −0.0015 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0123 (6) | 0.0138 (6) | 0.0170 (6) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0042 (5) | −0.0010 (4) |
| C17 | 0.0210 (7) | 0.0138 (6) | 0.0163 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0065 (5) | 0.0023 (4) |
| C18 | 0.0228 (7) | 0.0158 (6) | 0.0149 (6) | 0.0022 (5) | 0.0076 (5) | −0.0006 (5) |
| C18A | 0.0145 (7) | 0.0111 (6) | 0.0190 (6) | 0.0008 (5) | 0.0059 (5) | −0.0011 (4) |
| C121 | 0.0123 (6) | 0.0139 (6) | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0001 (5) | 0.0033 (5) | 0.0005 (5) |
| C122 | 0.0224 (7) | 0.0106 (6) | 0.0186 (6) | 0.0017 (5) | 0.0071 (5) | −0.0009 (4) |
| C123 | 0.0317 (8) | 0.0125 (6) | 0.0231 (6) | 0.0001 (6) | 0.0109 (6) | 0.0015 (5) |
| C161 | 0.0136 (6) | 0.0125 (6) | 0.0140 (5) | 0.0001 (5) | 0.0024 (5) | −0.0006 (4) |
| C162 | 0.0161 (7) | 0.0165 (6) | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0015 (5) | 0.0065 (5) | −0.0012 (5) |
| C163 | 0.0180 (7) | 0.0146 (6) | 0.0172 (6) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0059 (5) | 0.0008 (5) |
| C164 | 0.0152 (7) | 0.0136 (6) | 0.0155 (6) | 0.0007 (5) | 0.0005 (5) | −0.0020 (4) |
| C165 | 0.0155 (7) | 0.0177 (6) | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0014 (5) | 0.0047 (5) | −0.0032 (5) |
| C166 | 0.0155 (7) | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0140 (5) | −0.0009 (5) | 0.0042 (5) | −0.0003 (4) |
| C167 | 0.0241 (8) | 0.0141 (6) | 0.0237 (6) | 0.0007 (5) | 0.0084 (6) | −0.0017 (5) |
| O21 | 0.0246 (5) | 0.0114 (4) | 0.0164 (4) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0082 (4) | 0.0010 (3) |
| O24 | 0.0415 (7) | 0.0190 (5) | 0.0152 (4) | −0.0008 (4) | 0.0091 (4) | −0.0007 (3) |
| O221 | 0.0232 (5) | 0.0172 (5) | 0.0163 (4) | 0.0007 (4) | 0.0046 (4) | −0.0006 (3) |
| O222 | 0.0224 (5) | 0.0109 (4) | 0.0163 (4) | 0.0013 (4) | 0.0053 (4) | 0.0008 (3) |
| C22 | 0.0137 (6) | 0.0134 (6) | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0025 (4) |
| C23 | 0.0160 (7) | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0166 (6) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0037 (5) | 0.0028 (5) |
| C24 | 0.0169 (7) | 0.0168 (6) | 0.0154 (6) | −0.0008 (5) | 0.0036 (5) | 0.0012 (5) |
| C24A | 0.0130 (6) | 0.0152 (6) | 0.0156 (6) | 0.0000 (5) | 0.0031 (5) | 0.0011 (4) |
| C25 | 0.0155 (7) | 0.0155 (6) | 0.0147 (5) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0047 (5) | −0.0018 (4) |
| C26 | 0.0126 (6) | 0.0162 (6) | 0.0174 (6) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0055 (5) | −0.0008 (5) |
| C27 | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0149 (6) | 0.0188 (6) | 0.0012 (5) | 0.0096 (5) | 0.0028 (5) |
| C28 | 0.0257 (7) | 0.0165 (6) | 0.0161 (6) | 0.0003 (5) | 0.0092 (5) | −0.0010 (5) |
| C28A | 0.0154 (7) | 0.0130 (6) | 0.0196 (6) | 0.0008 (5) | 0.0068 (5) | −0.0006 (5) |
| C221 | 0.0130 (6) | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0186 (6) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0055 (5) | 0.0014 (5) |
| C222 | 0.0235 (7) | 0.0114 (6) | 0.0202 (6) | −0.0015 (5) | 0.0070 (5) | −0.0021 (5) |
| C223 | 0.0280 (8) | 0.0142 (6) | 0.0222 (6) | 0.0005 (5) | 0.0107 (6) | 0.0024 (5) |
| C261 | 0.0139 (6) | 0.0138 (6) | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0006 (5) | 0.0082 (5) | −0.0001 (4) |
| C262 | 0.0149 (7) | 0.0181 (6) | 0.0157 (6) | −0.0011 (5) | 0.0056 (5) | −0.0021 (5) |
| C263 | 0.0158 (7) | 0.0170 (6) | 0.0168 (6) | 0.0019 (5) | 0.0056 (5) | 0.0029 (5) |
| C264 | 0.0151 (7) | 0.0158 (6) | 0.0207 (6) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0090 (5) | −0.0013 (5) |
| C265 | 0.0174 (7) | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0171 (6) | −0.0009 (5) | 0.0057 (5) | −0.0039 (5) |
| C266 | 0.0157 (7) | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0159 (6) | 0.0014 (5) | 0.0054 (5) | 0.0020 (5) |
| C267 | 0.0253 (8) | 0.0148 (6) | 0.0228 (6) | 0.0002 (5) | 0.0085 (6) | −0.0023 (5) |
(1) Ethyl 6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O11—C12 | 1.3551 (14) | O21—C22 | 1.3561 (14) |
| O11—C18A | 1.3769 (14) | O21—C28A | 1.3770 (14) |
| O14—C14 | 1.2299 (14) | O24—C24 | 1.2282 (14) |
| O121—C121 | 1.2057 (14) | O221—C221 | 1.2025 (14) |
| O122—C121 | 1.3258 (14) | O222—C221 | 1.3274 (14) |
| O122—C122 | 1.4597 (14) | O222—C222 | 1.4625 (14) |
| C12—C13 | 1.3418 (16) | C22—C23 | 1.3403 (16) |
| C12—C121 | 1.5046 (17) | C22—C221 | 1.5056 (17) |
| C13—C14 | 1.4606 (17) | C23—C24 | 1.4615 (17) |
| C13—H13 | 0.9500 | C23—H23 | 0.9500 |
| C14—C14A | 1.4785 (16) | C24—C24A | 1.4777 (16) |
| C14A—C18A | 1.3936 (16) | C24A—C28A | 1.3911 (16) |
| C14A—C15 | 1.4061 (16) | C24A—C25 | 1.4049 (17) |
| C15—C16 | 1.3869 (16) | C25—C26 | 1.3904 (17) |
| C15—H15 | 0.9500 | C25—H25 | 0.9500 |
| C16—C17 | 1.4126 (16) | C26—C27 | 1.4095 (16) |
| C16—C161 | 1.4875 (16) | C26—C261 | 1.4885 (16) |
| C17—C18 | 1.3729 (17) | C27—C28 | 1.3757 (17) |
| C17—H17 | 0.9500 | C27—H27 | 0.9500 |
| C18—C18A | 1.3877 (16) | C28—C28A | 1.3895 (17) |
| C18—H18 | 0.9500 | C28—H28 | 0.9500 |
| C122—C123 | 1.5001 (17) | C222—C223 | 1.4998 (17) |
| C122—H12A | 0.9900 | C222—H22A | 0.9900 |
| C122—H12B | 0.9900 | C222—H22B | 0.9900 |
| C123—H12C | 0.9800 | C223—H22C | 0.9800 |
| C123—H12D | 0.9800 | C223—H22D | 0.9800 |
| C123—H12E | 0.9800 | C223—H22E | 0.9800 |
| C161—C166 | 1.3973 (17) | C261—C266 | 1.3989 (16) |
| C161—C162 | 1.3979 (17) | C261—C262 | 1.3995 (16) |
| C162—C163 | 1.3893 (17) | C262—C263 | 1.3885 (17) |
| C162—H162 | 0.9500 | C262—H262 | 0.9500 |
| C163—C164 | 1.3924 (17) | C263—C264 | 1.3952 (17) |
| C163—H163 | 0.9500 | C263—H263 | 0.9500 |
| C164—C165 | 1.3930 (17) | C264—C265 | 1.3968 (17) |
| C164—C167 | 1.5083 (16) | C264—C267 | 1.5079 (17) |
| C165—C166 | 1.3901 (17) | C265—C266 | 1.3875 (17) |
| C165—H165 | 0.9500 | C265—H265 | 0.9500 |
| C166—H166 | 0.9500 | C266—H266 | 0.9500 |
| C167—H16A | 0.9800 | C267—H26A | 0.9800 |
| C167—H16B | 0.9800 | C267—H26B | 0.9800 |
| C167—H16C | 0.9800 | C267—H26C | 0.9800 |
| C12—O11—C18A | 118.08 (9) | C22—O21—C28A | 118.25 (9) |
| C121—O122—C122 | 114.80 (9) | C221—O222—C222 | 115.53 (9) |
| C13—C12—O11 | 124.30 (11) | C23—C22—O21 | 124.14 (11) |
| C13—C12—C121 | 125.68 (11) | C23—C22—C221 | 126.14 (11) |
| O11—C12—C121 | 109.95 (10) | O21—C22—C221 | 109.67 (9) |
| C12—C13—C14 | 121.37 (11) | C22—C23—C24 | 121.38 (11) |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.3 | C22—C23—H23 | 119.3 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.3 | C24—C23—H23 | 119.3 |
| O14—C14—C13 | 123.11 (11) | O24—C24—C23 | 123.13 (11) |
| O14—C14—C14A | 122.88 (11) | O24—C24—C24A | 122.83 (11) |
| C13—C14—C14A | 114.01 (10) | C23—C24—C24A | 114.04 (10) |
| C18A—C14A—C15 | 118.18 (11) | C28A—C24A—C25 | 118.24 (11) |
| C18A—C14A—C14 | 119.48 (11) | C28A—C24A—C24 | 119.56 (11) |
| C15—C14A—C14 | 122.34 (10) | C25—C24A—C24 | 122.19 (11) |
| C16—C15—C14A | 121.49 (11) | C26—C25—C24A | 121.82 (11) |
| C16—C15—H15 | 119.3 | C26—C25—H25 | 119.1 |
| C14A—C15—H15 | 119.3 | C24A—C25—H25 | 119.1 |
| C15—C16—C17 | 117.90 (11) | C25—C26—C27 | 117.43 (11) |
| C15—C16—C161 | 122.99 (10) | C25—C26—C261 | 122.68 (11) |
| C17—C16—C161 | 119.11 (10) | C27—C26—C261 | 119.89 (10) |
| C18—C17—C16 | 121.85 (11) | C28—C27—C26 | 122.09 (11) |
| C18—C17—H17 | 119.1 | C28—C27—H27 | 119.0 |
| C16—C17—H17 | 119.1 | C26—C27—H27 | 119.0 |
| C17—C18—C18A | 118.90 (11) | C27—C28—C28A | 118.93 (11) |
| C17—C18—H18 | 120.6 | C27—C28—H28 | 120.5 |
| C18A—C18—H18 | 120.6 | C28A—C28—H28 | 120.5 |
| O11—C18A—C18 | 115.60 (10) | O21—C28A—C28 | 115.91 (10) |
| O11—C18A—C14A | 122.73 (10) | O21—C28A—C24A | 122.62 (10) |
| C18—C18A—C14A | 121.67 (11) | C28—C28A—C24A | 121.47 (11) |
| O121—C121—O122 | 126.18 (11) | O221—C221—O222 | 126.22 (11) |
| O121—C121—C12 | 123.04 (11) | O221—C221—C22 | 123.05 (11) |
| O122—C121—C12 | 110.77 (10) | O222—C221—C22 | 110.73 (10) |
| O122—C122—C123 | 106.78 (10) | O222—C222—C223 | 106.56 (10) |
| O122—C122—H12A | 110.4 | O222—C222—H22A | 110.4 |
| C123—C122—H12A | 110.4 | C223—C222—H22A | 110.4 |
| O122—C122—H12B | 110.4 | O222—C222—H22B | 110.4 |
| C123—C122—H12B | 110.4 | C223—C222—H22B | 110.4 |
| H12A—C122—H12B | 108.6 | H22A—C222—H22B | 108.6 |
| C122—C123—H12C | 109.5 | C222—C223—H22C | 109.5 |
| C122—C123—H12D | 109.5 | C222—C223—H22D | 109.5 |
| H12C—C123—H12D | 109.5 | H22C—C223—H22D | 109.5 |
| C122—C123—H12E | 109.5 | C222—C223—H22E | 109.5 |
| H12C—C123—H12E | 109.5 | H22C—C223—H22E | 109.5 |
| H12D—C123—H12E | 109.5 | H22D—C223—H22E | 109.5 |
| C166—C161—C162 | 117.85 (11) | C266—C261—C262 | 117.31 (11) |
| C166—C161—C16 | 121.74 (11) | C266—C261—C26 | 121.49 (11) |
| C162—C161—C16 | 120.40 (11) | C262—C261—C26 | 121.20 (11) |
| C163—C162—C161 | 121.06 (11) | C263—C262—C261 | 121.22 (11) |
| C163—C162—H162 | 119.5 | C263—C262—H262 | 119.4 |
| C161—C162—H162 | 119.5 | C261—C262—H262 | 119.4 |
| C162—C163—C164 | 121.27 (11) | C262—C263—C264 | 121.58 (11) |
| C162—C163—H163 | 119.4 | C262—C263—H263 | 119.2 |
| C164—C163—H163 | 119.4 | C264—C263—H263 | 119.2 |
| C163—C164—C165 | 117.54 (11) | C263—C264—C265 | 117.07 (11) |
| C163—C164—C167 | 120.28 (11) | C263—C264—C267 | 121.25 (11) |
| C165—C164—C167 | 122.16 (11) | C265—C264—C267 | 121.68 (11) |
| C166—C165—C164 | 121.70 (11) | C266—C265—C264 | 121.70 (11) |
| C166—C165—H165 | 119.2 | C266—C265—H265 | 119.1 |
| C164—C165—H165 | 119.2 | C264—C265—H265 | 119.1 |
| C165—C166—C161 | 120.59 (11) | C265—C266—C261 | 121.12 (11) |
| C165—C166—H166 | 119.7 | C265—C266—H266 | 119.4 |
| C161—C166—H166 | 119.7 | C261—C266—H266 | 119.4 |
| C164—C167—H16A | 109.5 | C264—C267—H26A | 109.5 |
| C164—C167—H16B | 109.5 | C264—C267—H26B | 109.5 |
| H16A—C167—H16B | 109.5 | H26A—C267—H26B | 109.5 |
| C164—C167—H16C | 109.5 | C264—C267—H26C | 109.5 |
| H16A—C167—H16C | 109.5 | H26A—C267—H26C | 109.5 |
| H16B—C167—H16C | 109.5 | H26B—C267—H26C | 109.5 |
| C18A—O11—C12—C13 | −0.81 (19) | C28A—O21—C22—C23 | −0.43 (19) |
| C18A—O11—C12—C121 | −177.93 (10) | C28A—O21—C22—C221 | 177.20 (10) |
| O11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.6 (2) | O21—C22—C23—C24 | −0.4 (2) |
| C121—C12—C13—C14 | 176.04 (12) | C221—C22—C23—C24 | −177.63 (12) |
| C12—C13—C14—O14 | −179.03 (13) | C22—C23—C24—O24 | −179.71 (13) |
| C12—C13—C14—C14A | 1.46 (18) | C22—C23—C24—C24A | 0.44 (18) |
| O14—C14—C14A—C18A | 179.54 (12) | O24—C24—C24A—C28A | −179.56 (13) |
| C13—C14—C14A—C18A | −0.96 (17) | C23—C24—C24A—C28A | 0.29 (18) |
| O14—C14—C14A—C15 | −0.7 (2) | O24—C24—C24A—C25 | −0.7 (2) |
| C13—C14—C14A—C15 | 178.85 (12) | C23—C24—C24A—C25 | 179.18 (12) |
| C18A—C14A—C15—C16 | −0.24 (19) | C28A—C24A—C25—C26 | −0.31 (19) |
| C14—C14A—C15—C16 | 179.95 (12) | C24—C24A—C25—C26 | −179.21 (12) |
| C14A—C15—C16—C17 | 0.05 (19) | C24A—C25—C26—C27 | 0.75 (19) |
| C14A—C15—C16—C161 | 179.98 (12) | C24A—C25—C26—C261 | −179.29 (12) |
| C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.36 (19) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | −0.3 (2) |
| C161—C16—C17—C18 | −179.57 (12) | C261—C26—C27—C28 | 179.72 (12) |
| C16—C17—C18—C18A | −0.6 (2) | C26—C27—C28—C28A | −0.5 (2) |
| C12—O11—C18A—C18 | −178.91 (11) | C22—O21—C28A—C28 | −178.28 (11) |
| C12—O11—C18A—C14A | 1.31 (18) | C22—O21—C28A—C24A | 1.20 (18) |
| C17—C18—C18A—O11 | −179.42 (11) | C27—C28—C28A—O21 | −179.49 (12) |
| C17—C18—C18A—C14A | 0.4 (2) | C27—C28—C28A—C24A | 1.0 (2) |
| C15—C14A—C18A—O11 | 179.80 (11) | C25—C24A—C28A—O21 | 179.94 (11) |
| C14—C14A—C18A—O11 | −0.39 (19) | C24—C24A—C28A—O21 | −1.13 (19) |
| C15—C14A—C18A—C18 | 0.03 (19) | C25—C24A—C28A—C28 | −0.60 (19) |
| C14—C14A—C18A—C18 | 179.84 (12) | C24—C24A—C28A—C28 | 178.33 (12) |
| C122—O122—C121—O121 | 8.49 (18) | C222—O222—C221—O221 | −5.78 (19) |
| C122—O122—C121—C12 | −170.74 (10) | C222—O222—C221—C22 | 174.17 (10) |
| C13—C12—C121—O121 | −156.97 (13) | C23—C22—C221—O221 | 165.68 (13) |
| O11—C12—C121—O121 | 20.10 (17) | O21—C22—C221—O221 | −11.89 (17) |
| C13—C12—C121—O122 | 22.30 (18) | C23—C22—C221—O222 | −14.27 (18) |
| O11—C12—C121—O122 | −160.63 (10) | O21—C22—C221—O222 | 168.16 (10) |
| C121—O122—C122—C123 | −176.76 (10) | C221—O222—C222—C223 | 168.94 (11) |
| C15—C16—C161—C166 | −33.27 (18) | C25—C26—C261—C266 | 24.15 (19) |
| C17—C16—C161—C166 | 146.65 (12) | C27—C26—C261—C266 | −155.89 (12) |
| C15—C16—C161—C162 | 147.55 (12) | C25—C26—C261—C262 | −156.33 (12) |
| C17—C16—C161—C162 | −32.53 (18) | C27—C26—C261—C262 | 23.63 (18) |
| C166—C161—C162—C163 | −0.31 (18) | C266—C261—C262—C263 | 0.30 (18) |
| C16—C161—C162—C163 | 178.90 (11) | C26—C261—C262—C263 | −179.24 (11) |
| C161—C162—C163—C164 | 0.36 (19) | C261—C262—C263—C264 | −0.47 (19) |
| C162—C163—C164—C165 | −0.32 (18) | C262—C263—C264—C265 | 0.19 (18) |
| C162—C163—C164—C167 | 178.21 (12) | C262—C263—C264—C267 | −179.32 (12) |
| C163—C164—C165—C166 | 0.26 (18) | C263—C264—C265—C266 | 0.26 (19) |
| C167—C164—C165—C166 | −178.24 (11) | C267—C264—C265—C266 | 179.76 (12) |
| C164—C165—C166—C161 | −0.23 (19) | C264—C265—C266—C261 | −0.4 (2) |
| C162—C161—C166—C165 | 0.25 (18) | C262—C261—C266—C265 | 0.14 (19) |
| C16—C161—C166—C165 | −178.95 (11) | C26—C261—C266—C265 | 179.68 (12) |
(1) Ethyl 6-(4-methylphenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C162—H162···Cg(C261) | 0.95 | 2.85 | 3.4914 (15) | 126 |
| C262—H262···Cg(C161)i | 0.95 | 2.84 | 3.5408 (4) | 131 |
Symmetry code: (i) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
(2) Ethyl 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Crystal data
| C18H13FO4 | F(000) = 648 |
| Mr = 312.28 | Dx = 1.483 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| a = 3.8521 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 15331 reflections |
| b = 20.6970 (15) Å | θ = 2.3–27.5° |
| c = 17.5478 (11) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| β = 91.546 (1)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1398.52 (15) Å3 | Needle, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.42 × 0.02 × 0.01 mm |
(2) Ethyl 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn724+ (2x2 bin mode) diffractometer | 3177 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: Sealed Tube | 2725 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite Monochromator monochromator | Rint = 0.035 |
| Detector resolution: 28.5714 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.3° |
| profile data from ω–scans | h = −4→4 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan CrystalClear-SM Expert (Rigaku, 20112) | k = −26→26 |
| Tmin = 0.954, Tmax = 0.999 | l = −22→22 |
| 16479 measured reflections |
(2) Ethyl 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.031 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.087 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0482P)2 + 0.4787P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 0.98 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3176 reflections | Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3 |
| 209 parameters | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
(2) Ethyl 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
(2) Ethyl 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C2 | 0.3562 (3) | 0.34130 (5) | 0.52749 (6) | 0.0141 (2) | |
| C3 | 0.5254 (3) | 0.30718 (5) | 0.58218 (6) | 0.0155 (2) | |
| H3 | 0.5714 | 0.2626 | 0.5741 | 0.019* | |
| C4 | 0.6397 (3) | 0.33746 (5) | 0.65381 (6) | 0.0149 (2) | |
| C5 | 0.6674 (3) | 0.44460 (5) | 0.72144 (6) | 0.0138 (2) | |
| H5 | 0.7882 | 0.4245 | 0.7630 | 0.017* | |
| C4A | 0.5615 (3) | 0.40718 (5) | 0.65824 (6) | 0.0135 (2) | |
| C6 | 0.5990 (3) | 0.51041 (5) | 0.72442 (6) | 0.0137 (2) | |
| C7 | 0.4184 (3) | 0.53915 (5) | 0.66195 (6) | 0.0145 (2) | |
| H7 | 0.3699 | 0.5841 | 0.6633 | 0.017* | |
| C8 | 0.3108 (3) | 0.50362 (5) | 0.59912 (6) | 0.0147 (2) | |
| H8 | 0.1891 | 0.5237 | 0.5577 | 0.018* | |
| C8A | 0.3843 (3) | 0.43766 (5) | 0.59763 (6) | 0.0134 (2) | |
| C21 | 0.2302 (3) | 0.31555 (5) | 0.45161 (6) | 0.0143 (2) | |
| C22 | 0.2530 (3) | 0.22857 (5) | 0.36482 (6) | 0.0175 (2) | |
| H22A | 0.3781 | 0.2496 | 0.3230 | 0.021* | |
| H22B | 0.0005 | 0.2343 | 0.3553 | 0.021* | |
| C23 | 0.3417 (3) | 0.15775 (5) | 0.36840 (6) | 0.0193 (2) | |
| H23A | 0.2795 | 0.1373 | 0.3195 | 0.029* | |
| H23B | 0.2120 | 0.1372 | 0.4091 | 0.029* | |
| H23C | 0.5914 | 0.1526 | 0.3789 | 0.029* | |
| C61 | 0.7187 (3) | 0.55070 (5) | 0.79004 (6) | 0.0142 (2) | |
| C62 | 0.7275 (3) | 0.52672 (5) | 0.86460 (6) | 0.0169 (2) | |
| H62 | 0.6491 | 0.4840 | 0.8740 | 0.020* | |
| C63 | 0.8493 (3) | 0.56456 (5) | 0.92520 (6) | 0.0193 (2) | |
| H63 | 0.8535 | 0.5483 | 0.9759 | 0.023* | |
| C64 | 0.9640 (3) | 0.62638 (5) | 0.90974 (6) | 0.0182 (2) | |
| C65 | 0.9542 (3) | 0.65260 (5) | 0.83766 (6) | 0.0179 (2) | |
| H65 | 1.0299 | 0.6956 | 0.8290 | 0.021* | |
| C66 | 0.8302 (3) | 0.61423 (5) | 0.77786 (6) | 0.0161 (2) | |
| H66 | 0.8207 | 0.6315 | 0.7277 | 0.019* | |
| F64 | 1.0940 (2) | 0.66280 (3) | 0.96871 (4) | 0.02586 (17) | |
| O1 | 0.27388 (19) | 0.40483 (3) | 0.53315 (4) | 0.01485 (17) | |
| O4 | 0.7946 (2) | 0.30785 (4) | 0.70522 (4) | 0.02071 (19) | |
| O21 | 0.0372 (2) | 0.34557 (4) | 0.40948 (4) | 0.02041 (18) | |
| O22 | 0.3576 (2) | 0.25727 (4) | 0.43820 (4) | 0.01680 (17) |
(2) Ethyl 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C2 | 0.0153 (5) | 0.0131 (5) | 0.0141 (5) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0014 (4) | −0.0013 (4) |
| C3 | 0.0180 (5) | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0151 (5) | 0.0016 (4) | −0.0001 (4) | −0.0010 (4) |
| C4 | 0.0163 (5) | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0141 (5) | 0.0011 (4) | 0.0001 (4) | 0.0009 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0141 (5) | 0.0151 (5) | 0.0121 (5) | −0.0001 (4) | −0.0001 (4) | 0.0018 (4) |
| C4A | 0.0134 (5) | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0132 (5) | 0.0004 (4) | 0.0012 (4) | 0.0005 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0130 (5) | 0.0155 (5) | 0.0126 (5) | −0.0014 (4) | 0.0011 (4) | −0.0006 (4) |
| C7 | 0.0151 (5) | 0.0126 (4) | 0.0157 (5) | 0.0002 (4) | 0.0012 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| C8 | 0.0154 (5) | 0.0150 (5) | 0.0138 (5) | 0.0013 (4) | −0.0005 (4) | 0.0020 (4) |
| C8A | 0.0140 (5) | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0113 (4) | −0.0014 (4) | 0.0005 (4) | −0.0011 (4) |
| C21 | 0.0154 (5) | 0.0144 (5) | 0.0133 (5) | −0.0012 (4) | 0.0014 (4) | 0.0006 (4) |
| C22 | 0.0198 (5) | 0.0194 (5) | 0.0130 (5) | 0.0002 (4) | −0.0033 (4) | −0.0046 (4) |
| C23 | 0.0193 (6) | 0.0183 (5) | 0.0203 (5) | 0.0004 (4) | −0.0002 (4) | −0.0050 (4) |
| C61 | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0152 (5) | 0.0139 (5) | 0.0013 (4) | 0.0001 (4) | −0.0015 (4) |
| C62 | 0.0201 (5) | 0.0143 (5) | 0.0161 (5) | −0.0008 (4) | 0.0006 (4) | 0.0004 (4) |
| C63 | 0.0250 (6) | 0.0199 (5) | 0.0130 (5) | 0.0004 (4) | −0.0004 (4) | 0.0007 (4) |
| C64 | 0.0197 (5) | 0.0198 (5) | 0.0149 (5) | −0.0013 (4) | −0.0010 (4) | −0.0065 (4) |
| C65 | 0.0199 (5) | 0.0149 (5) | 0.0190 (5) | −0.0019 (4) | 0.0020 (4) | −0.0017 (4) |
| C66 | 0.0180 (5) | 0.0159 (5) | 0.0144 (5) | 0.0004 (4) | 0.0009 (4) | 0.0005 (4) |
| F64 | 0.0363 (4) | 0.0244 (3) | 0.0167 (3) | −0.0080 (3) | −0.0025 (3) | −0.0070 (3) |
| O1 | 0.0197 (4) | 0.0123 (3) | 0.0123 (3) | 0.0017 (3) | −0.0030 (3) | −0.0008 (3) |
| O4 | 0.0290 (5) | 0.0163 (4) | 0.0165 (4) | 0.0055 (3) | −0.0062 (3) | 0.0002 (3) |
| O21 | 0.0265 (4) | 0.0183 (4) | 0.0161 (4) | 0.0045 (3) | −0.0046 (3) | 0.0003 (3) |
| O22 | 0.0204 (4) | 0.0154 (4) | 0.0143 (4) | 0.0026 (3) | −0.0039 (3) | −0.0039 (3) |
(2) Ethyl 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C2—C3 | 1.3457 (14) | C21—O22 | 1.3257 (12) |
| C2—O1 | 1.3568 (12) | C22—O22 | 1.4647 (12) |
| C2—C21 | 1.5025 (14) | C22—C23 | 1.5059 (15) |
| C3—C4 | 1.4617 (14) | C22—H22A | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C22—H22B | 0.9900 |
| C4—O4 | 1.2315 (13) | C23—H23A | 0.9800 |
| C4—C4A | 1.4766 (14) | C23—H23B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3886 (14) | C23—H23C | 0.9800 |
| C5—C4A | 1.4042 (14) | C61—C62 | 1.3989 (14) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C61—C66 | 1.4015 (14) |
| C4A—C8A | 1.3984 (14) | C62—C63 | 1.3920 (15) |
| C6—C7 | 1.4135 (14) | C62—H62 | 0.9500 |
| C6—C61 | 1.4851 (14) | C63—C64 | 1.3829 (16) |
| C7—C8 | 1.3797 (14) | C63—H63 | 0.9500 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C64—F64 | 1.3646 (12) |
| C8—C8A | 1.3948 (14) | C64—C65 | 1.3759 (15) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C65—C66 | 1.3903 (14) |
| C8A—O1 | 1.3774 (12) | C65—H65 | 0.9500 |
| C21—O21 | 1.2065 (13) | C66—H66 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C2—O1 | 124.47 (9) | O22—C22—H22A | 110.2 |
| C3—C2—C21 | 125.77 (9) | C23—C22—H22A | 110.2 |
| O1—C2—C21 | 109.76 (8) | O22—C22—H22B | 110.2 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.14 (9) | C23—C22—H22B | 110.2 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.4 | H22A—C22—H22B | 108.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C22—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| O4—C4—C3 | 123.05 (9) | C22—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| O4—C4—C4A | 122.91 (9) | H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C4A | 114.03 (9) | C22—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4A | 121.29 (9) | H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.4 | H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C4A—C5—H5 | 119.4 | C62—C61—C66 | 118.41 (9) |
| C8A—C4A—C5 | 118.51 (9) | C62—C61—C6 | 121.68 (9) |
| C8A—C4A—C4 | 119.79 (9) | C66—C61—C6 | 119.91 (9) |
| C5—C4A—C4 | 121.69 (9) | C63—C62—C61 | 120.93 (10) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 118.26 (9) | C63—C62—H62 | 119.5 |
| C5—C6—C61 | 121.65 (9) | C61—C62—H62 | 119.5 |
| C7—C6—C61 | 120.07 (9) | C64—C63—C62 | 118.27 (10) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 121.77 (9) | C64—C63—H63 | 120.9 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 119.1 | C62—C63—H63 | 120.9 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 119.1 | F64—C64—C65 | 118.67 (10) |
| C7—C8—C8A | 118.68 (9) | F64—C64—C63 | 118.35 (10) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.7 | C65—C64—C63 | 122.98 (10) |
| C8A—C8—H8 | 120.7 | C64—C65—C66 | 117.97 (10) |
| O1—C8A—C8 | 116.10 (9) | C64—C65—H65 | 121.0 |
| O1—C8A—C4A | 122.40 (9) | C66—C65—H65 | 121.0 |
| C8—C8A—C4A | 121.50 (9) | C65—C66—C61 | 121.41 (10) |
| O21—C21—O22 | 125.79 (10) | C65—C66—H66 | 119.3 |
| O21—C21—C2 | 122.64 (9) | C61—C66—H66 | 119.3 |
| O22—C21—C2 | 111.57 (9) | C2—O1—C8A | 118.08 (8) |
| O22—C22—C23 | 107.55 (8) | C21—O22—C22 | 115.51 (8) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.66 (17) | C3—C2—C21—O22 | −11.10 (15) |
| C21—C2—C3—C4 | 179.33 (10) | O1—C2—C21—O22 | 168.89 (8) |
| C2—C3—C4—O4 | 179.88 (11) | C5—C6—C61—C62 | −35.73 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—C4A | −1.71 (15) | C7—C6—C61—C62 | 145.98 (11) |
| C6—C5—C4A—C8A | 0.07 (15) | C5—C6—C61—C66 | 143.58 (11) |
| C6—C5—C4A—C4 | 178.64 (10) | C7—C6—C61—C66 | −34.71 (15) |
| O4—C4—C4A—C8A | −179.98 (10) | C66—C61—C62—C63 | −1.07 (16) |
| C3—C4—C4A—C8A | 1.60 (14) | C6—C61—C62—C63 | 178.25 (10) |
| O4—C4—C4A—C5 | 1.48 (16) | C61—C62—C63—C64 | −0.46 (17) |
| C3—C4—C4A—C5 | −176.94 (9) | C62—C63—C64—F64 | −177.91 (10) |
| C4A—C5—C6—C7 | 0.08 (15) | C62—C63—C64—C65 | 1.81 (18) |
| C4A—C5—C6—C61 | −178.24 (9) | F64—C64—C65—C66 | 178.21 (10) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.02 (16) | C63—C64—C65—C66 | −1.50 (17) |
| C61—C6—C7—C8 | 178.33 (10) | C64—C65—C66—C61 | −0.15 (16) |
| C6—C7—C8—C8A | −0.20 (16) | C62—C61—C66—C65 | 1.39 (16) |
| C7—C8—C8A—O1 | −179.34 (9) | C6—C61—C66—C65 | −177.94 (10) |
| C7—C8—C8A—C4A | 0.36 (16) | C3—C2—O1—C8A | 3.16 (15) |
| C5—C4A—C8A—O1 | 179.38 (9) | C21—C2—O1—C8A | −176.84 (8) |
| C4—C4A—C8A—O1 | 0.79 (15) | C8—C8A—O1—C2 | 176.53 (9) |
| C5—C4A—C8A—C8 | −0.30 (15) | C4A—C8A—O1—C2 | −3.17 (14) |
| C4—C4A—C8A—C8 | −178.89 (10) | O21—C21—O22—C22 | 0.82 (15) |
| C3—C2—C21—O21 | 168.95 (11) | C2—C21—O22—C22 | −179.12 (8) |
| O1—C2—C21—O21 | −11.05 (14) | C23—C22—O22—C21 | −165.47 (9) |
(2) Ethyl 6-(4-fluorophenyl)-4-oxo-4H-chromene-2-carboxylate . Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C7—H7···O21i | 0.95 | 2.47 | 3.1977 (13) | 133 |
| C65—H65···O4ii | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.4447 (13) | 175 |
| C66—H66···O21iii | 0.95 | 2.53 | 3.4425 (13) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (iii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
References
- Becke, A. D. (1997). J. Chem. Phys 107, 8554–8560.
- Cagide, F., Gaspar, A., Reis, J., Chavarria, D., Vilar, S., Hripcsak, S., Uriarte, E., Kachler, S., Klotz, K. N. & Borges, F. (2015a). RSC Adv. 5, 78572–78585.
- Cagide, F., Silva, T., Reis, J., Gaspar, A., Borges, F., Gomes, L. R. & Low, J. N. (2015b). Chem. Commun. 51, 2832–2835. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Coles, S. J. & Gale, P. A. (2012). Chem. Sci. 3, 683–689.
- Frisch, M. J., et al. (2004). GAUSSIAN 03. Gaussian, Inc., Wallingford, Connecticut, USA.
- Gaspar, A., Matos, M. J., Garrido, J., Uriarte, E. & Borges, F. (2014). Chem. Rev. 114, 4960–4992. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, A., Milhazes, N., Santana, L., Uriarte, E., Borges, F. & Matos, M. J. (2015). Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 15, 432–445. [PubMed]
- Hehre, W. J., Radom, L., Schleyer, P. V. R. & Pople, J. A. (1986). Ab Initio Molecular Orbital Theory. New York: Wiley.
- Hübschle, C. B., Sheldrick, G. M. & Dittrich, B. (2011). J. Appl. Cryst. 44, 1281–1284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ko, S. K., Jang, H. J., Kim, E. & Park, S. B. (2006). Chem. Commun. pp. 2962–2694. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lee, C., Yang, W. & Parr, G. R. (1988). Phys. Rev. B, 37, 785–789. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mackay, A. L. (1984). Acta Cryst. A40, 165–166.
- Macrae, C. F., Edgington, P. R., McCabe, P., Pidcock, E., Shields, G. P., Taylor, R., Towler, M. & van de Streek, J. (2006). J. Appl. Cryst. 39, 453–457.
- McArdle, P., Gilligan, K., Cunningham, D., Dark, R. & Mahon, M. (2004). CrystEngComm, 6, 303–309.
- Nicolaou, K. C., Pfefferkorn, J. A., Roecker, A. J., Cao, G. Q., Barluenga, S. & Mitchell, H. J. (2000). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 122, 9939–9953.
- Rigaku (2012). CrystalClear-SM Expert. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Soares, P., Fernandes, C., Chavarria, D. & Borges, F. (2015). J. Chem. Educ. 92, 575–578.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Welsch, M. E., Snyder, S. A. & Stockwell, B. R. (2010). Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 14, 347–361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) general, 1, 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb7543sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 1. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb75431sup2.hkl
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) 2. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb75432sup3.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb75431sup4.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb75432sup5.cml
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022781/hb7543sup6.pdf
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report