Abstract
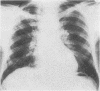
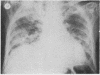
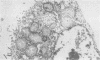
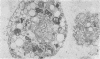
A case of alveolar lipoproteinosis associated with silicosis is reported. A 58-year-old man had been exposed to silica for seven years and died three years after the onset of symptoms. Light microscopy of biopsy and necropsy material showed small silicotic nodules, silica particles, and alveolar lipoproteinosis, and ultrastructural studies were performed to define changes in alveolar epithelium and macrophages. The case provides a further example of alveolar lipoproteinosis developing as a response of the lung to injury by an external agent.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buechner H. A., Ansari A. Acute silico-proteinosis. A new pathologic variant of acute silicosis in sandblasters, characterized by histologic features resembling alveolar proteinosis. Dis Chest. 1969 Apr;55(4):274–278. doi: 10.1378/chest.55.4.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corrin B., King E. Pathogenesis of experimental pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Thorax. 1970 Mar;25(2):230–236. doi: 10.1136/thx.25.2.230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson J. M., Macleod W. M. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Br J Dis Chest. 1969 Jan;63(1):13–28. doi: 10.1016/s0007-0971(69)80040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P., DeTreville R. T. Alveolar proteinosis. Its experimental production in rodents. Arch Pathol. 1968 Sep;86(3):255–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Wright N. A., Stewart J. A. Experimental alveolar lipo-proteinosis following the inhalation of silica. J Pathol. 1970 Aug;101(4):293–307. doi: 10.1002/path.1711010402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Young A. E. Alveolar lipo-proteinosis: an ultrastructural comparison of the experimental and human forms. J Pathol. 1972 Jun;107(2):107–117. doi: 10.1002/path.1711070205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn C., Györkey F., Levine B. E., Ramirez-Rivera J. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. A study using enzyme histochemistry, electron microscopy, and surface tension measurement. Lab Invest. 1966 Feb;15(2):492–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARSON R. K., GORDINIER R. PULMONARY ALVEOLAR PROTEINOSIS. REPORT OF SIX CASES, REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE, AND FORMULATION OF A NEW THEORY. Ann Intern Med. 1965 Feb;62:292–312. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-62-2-292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler W. A., Kay J. M., Hasleton P. S., Heath D. Busulphan lung. Thorax. 1969 Nov;24(6):639–655. doi: 10.1136/thx.24.6.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN S. H., CASTLEMAN B., LIEBOW A. A. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. N Engl J Med. 1958 Jun 5;258(23):1123–1142. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195806052582301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P., Heath D., Hasleton P. S. Electron microscopy of chlorphentermine lung. Thorax. 1973 Sep;28(5):559–566. doi: 10.1136/thx.28.5.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijeyaratnam G. S., Corrin B. Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis developing from desquamative interstitial pneumonia in long term toxicity studies of iprindole in the rat. Virchows Arch A Pathol Pathol Anat. 1973;358(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00555550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijeyaratnam G. S., Corrin B. Pulmonary histiocytosis simulating desquamative interstitial pneumonia in rats receiving oral iprindole. J Pathol. 1972 Oct;108(2):105–113. doi: 10.1002/path.1711080203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]