Abstract
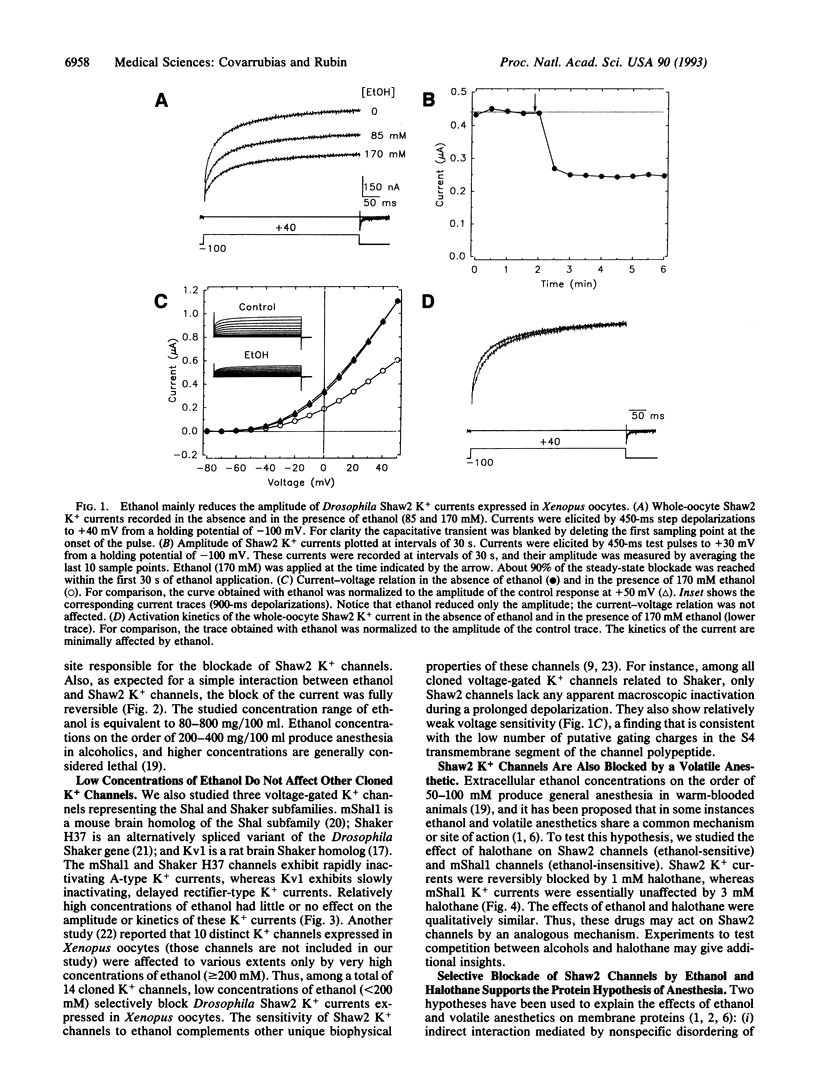
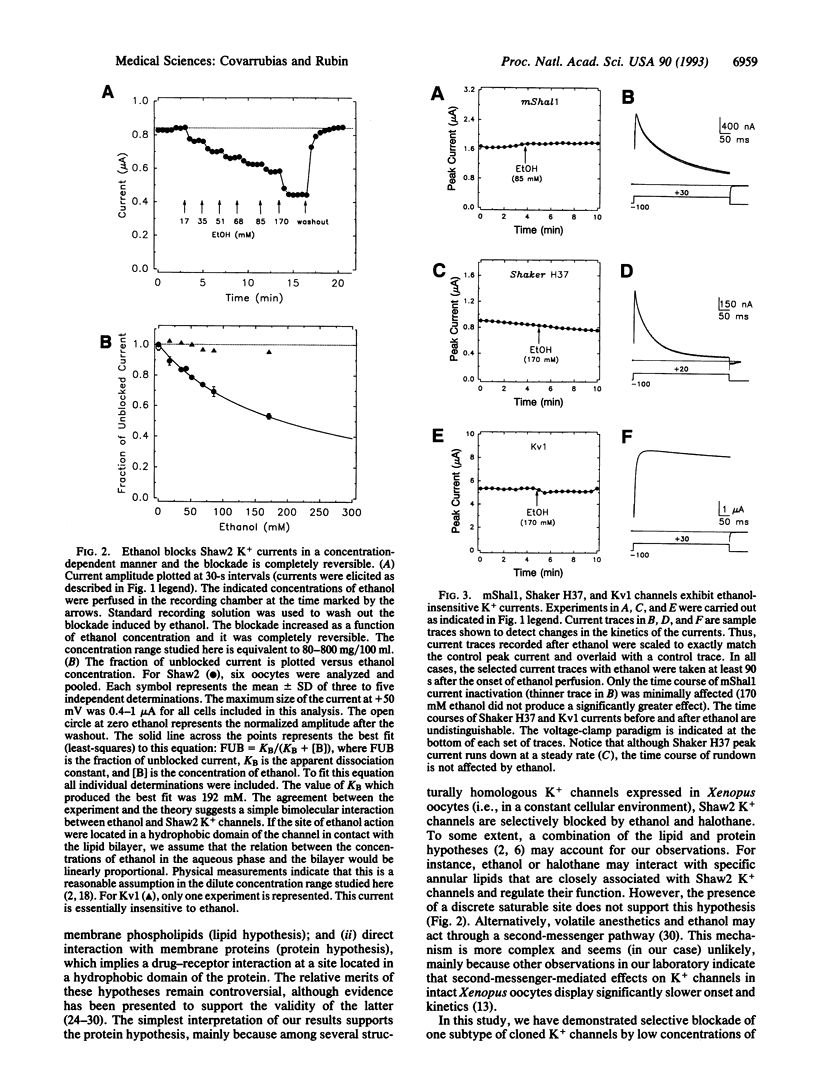
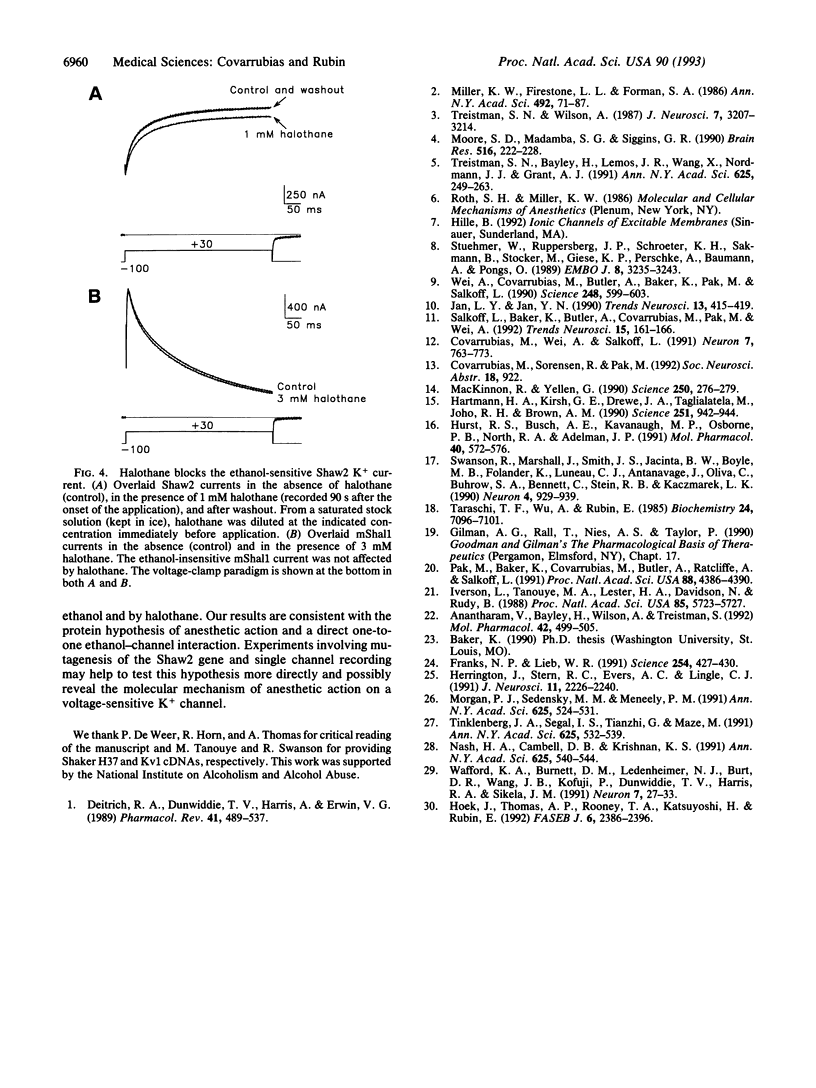
There is presently a debate regarding the relative merits of lipid-based and protein-based theories of anesthesia and the action of ethanol in the central nervous system. Voltage-sensitive K+ channels play a key role as regulators of neuronal electrical activity and are potential targets of ethanol and other anesthetic agents. We investigated the action of low concentrations of ethanol on four structurally homologous cloned K+ channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. We report that only the Drosophila Shaw2 channel, which does not inactivate upon prolonged depolarization, is rapidly and reversibly blocked by ethanol in a concentration-dependent manner (17-170 mM). The concentration dependence of the blockade can be explained by assuming a bimolecular interaction between ethanol and the channel. We also found that Shaw2 K+ channels were selectively blocked by halothane (1 mM). Our results support the "protein hypothesis" of ethanol and anesthetic action. These findings open ways to elucidate directly the molecular mechanism of interaction between general anesthetics and a voltage-sensitive K+ channel.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anantharam V., Bayley H., Wilson A., Treistman S. N. Differential effects of ethanol on electrical properties of various potassium channels expressed in oocytes. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Sep;42(3):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covarrubias M., Wei A. A., Salkoff L. Shaker, Shal, Shab, and Shaw express independent K+ current systems. Neuron. 1991 Nov;7(5):763–773. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90279-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitrich R. A., Dunwiddie T. V., Harris R. A., Erwin V. G. Mechanism of action of ethanol: initial central nervous system actions. Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Dec;41(4):489–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Stereospecific effects of inhalational general anesthetic optical isomers on nerve ion channels. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):427–430. doi: 10.1126/science.1925602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann H. A., Kirsch G. E., Drewe J. A., Taglialatela M., Joho R. H., Brown A. M. Exchange of conduction pathways between two related K+ channels. Science. 1991 Feb 22;251(4996):942–944. doi: 10.1126/science.2000495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrington J., Stern R. C., Evers A. S., Lingle C. J. Halothane inhibits two components of calcium current in clonal (GH3) pituitary cells. J Neurosci. 1991 Jul;11(7):2226–2240. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-07-02226.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoek J. B., Thomas A. P., Rooney T. A., Higashi K., Rubin E. Ethanol and signal transduction in the liver. FASEB J. 1992 Apr;6(7):2386–2396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurst R. S., Busch A. E., Kavanaugh M. P., Osborne P. B., North R. A., Adelman J. P. Identification of amino acid residues involved in dendrotoxin block of rat voltage-dependent potassium channels. Mol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;40(4):572–576. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson L. E., Tanouye M. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Rudy B. A-type potassium channels expressed from Shaker locus cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5723–5727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N. How might the diversity of potassium channels be generated? Trends Neurosci. 1990 Oct;13(10):415–419. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90123-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Yellen G. Mutations affecting TEA blockade and ion permeation in voltage-activated K+ channels. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):276–279. doi: 10.1126/science.2218530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller K. W., Firestone L. L., Forman S. A. General anesthetic and specific effects of ethanol on acetylcholine receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;492:71–87. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb48656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. D., Madamba S. G., Siggins G. R. Ethanol diminishes a voltage-dependent K+ current, the M-current, in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1990 May 21;516(2):222–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90922-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan P. G., Sedensky M. M., Meneely P. M. The genetics of response to volatile anesthetics in Caenorhabditis elegans. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;625:524–531. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Campbell D. B., Krishnan K. S. New mutants of Drosophila that are resistant to the anesthetic effects of halothane. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;625:540–544. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33885.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pak M. D., Baker K., Covarrubias M., Butler A., Ratcliffe A., Salkoff L. mShal, a subfamily of A-type K+ channel cloned from mammalian brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4386–4390. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkoff L., Baker K., Butler A., Covarrubias M., Pak M. D., Wei A. An essential 'set' of K+ channels conserved in flies, mice and humans. Trends Neurosci. 1992 May;15(5):161–166. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(92)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Ruppersberg J. P., Schröter K. H., Sakmann B., Stocker M., Giese K. P., Perschke A., Baumann A., Pongs O. Molecular basis of functional diversity of voltage-gated potassium channels in mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3235–3244. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R., Marshall J., Smith J. S., Williams J. B., Boyle M. B., Folander K., Luneau C. J., Antanavage J., Oliva C., Buhrow S. A. Cloning and expression of cDNA and genomic clones encoding three delayed rectifier potassium channels in rat brain. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):929–939. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90146-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taraschi T. F., Wu A., Rubin E. Phospholipid spin probes measure the effects of ethanol on the molecular order of liver microsomes. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7096–7101. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinklenberg J. A., Segal I. S., Guo T. Z., Maze M. Analysis of anesthetic action on the potassium channels of the Shaker mutant of Drosophila. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;625:532–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33884.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treistman S. N., Bayley H., Lemos J. R., Wang X. M., Nordmann J. J., Grant A. J. Effects of ethanol on calcium channels, potassium channels, and vasopressin release. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1991;625:249–263. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1991.tb33844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treistman S. N., Wilson A. Effects of ethanol on early potassium currents in Aplysia: cell specificity and influence of channel state. J Neurosci. 1987 Oct;7(10):3207–3214. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-10-03207.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wafford K. A., Burnett D. M., Leidenheimer N. J., Burt D. R., Wang J. B., Kofuji P., Dunwiddie T. V., Harris R. A., Sikela J. M. Ethanol sensitivity of the GABAA receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes requires 8 amino acids contained in the gamma 2L subunit. Neuron. 1991 Jul;7(1):27–33. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei A., Covarrubias M., Butler A., Baker K., Pak M., Salkoff L. K+ current diversity is produced by an extended gene family conserved in Drosophila and mouse. Science. 1990 May 4;248(4955):599–603. doi: 10.1126/science.2333511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



