Abstract
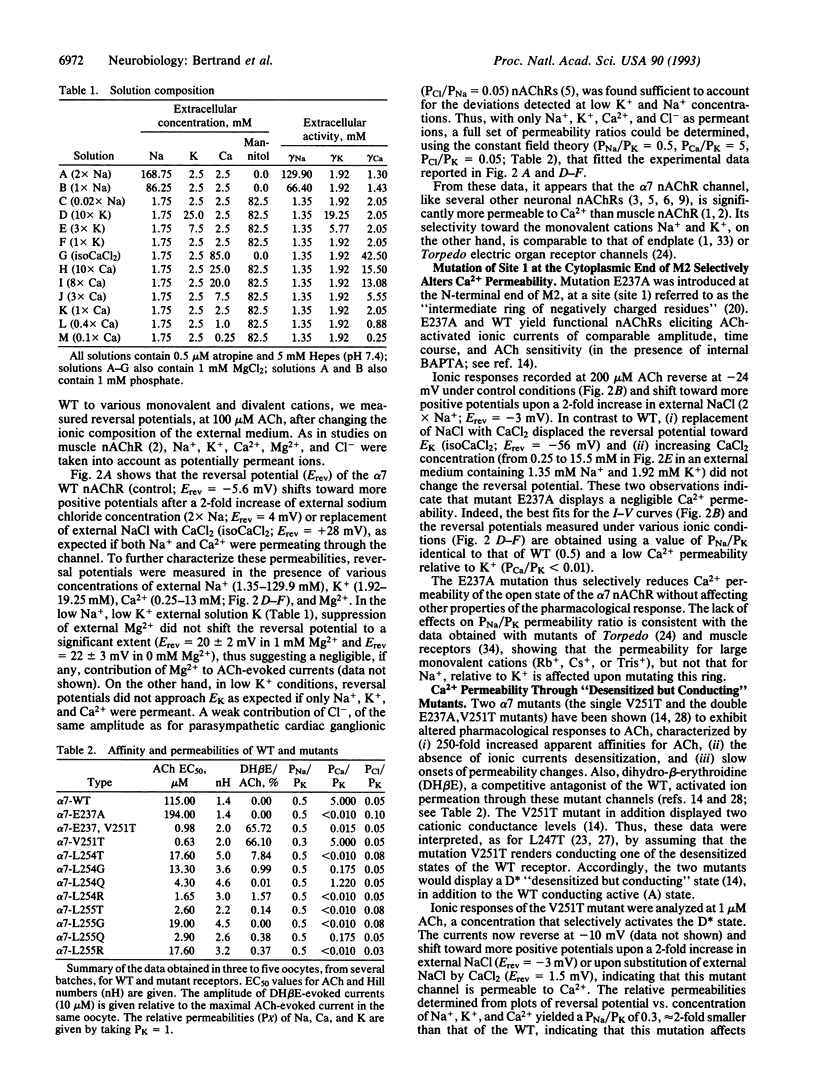
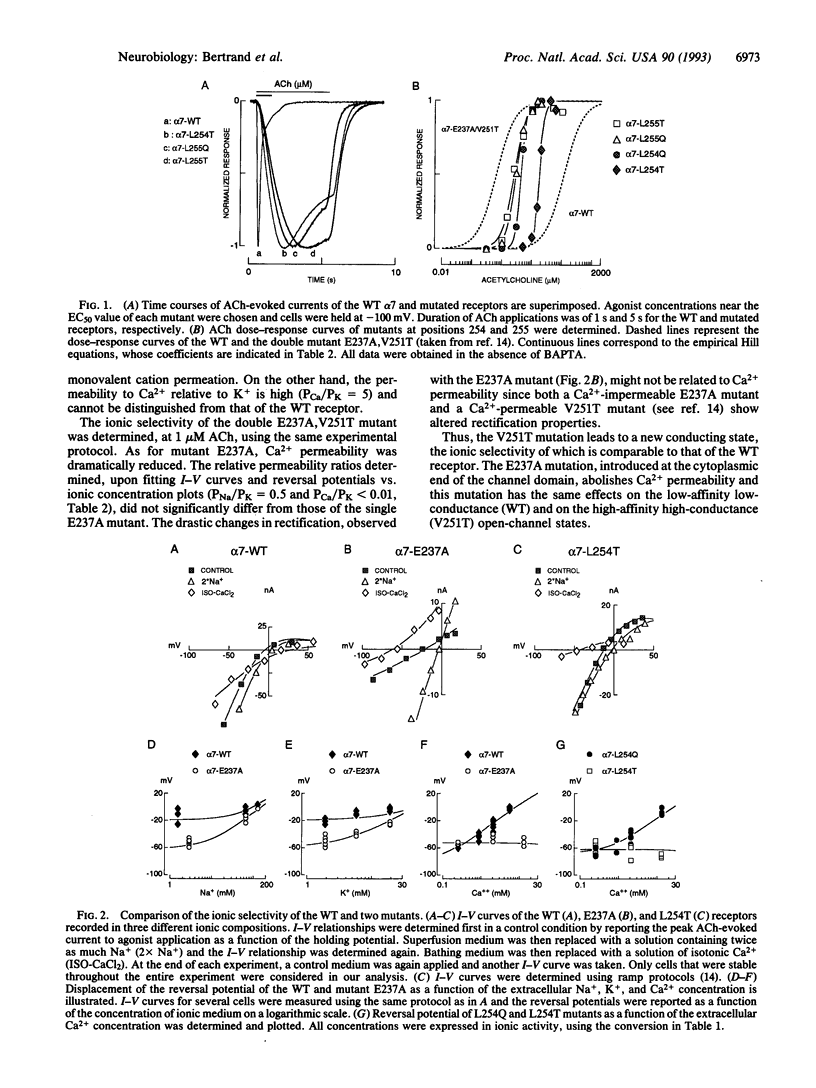
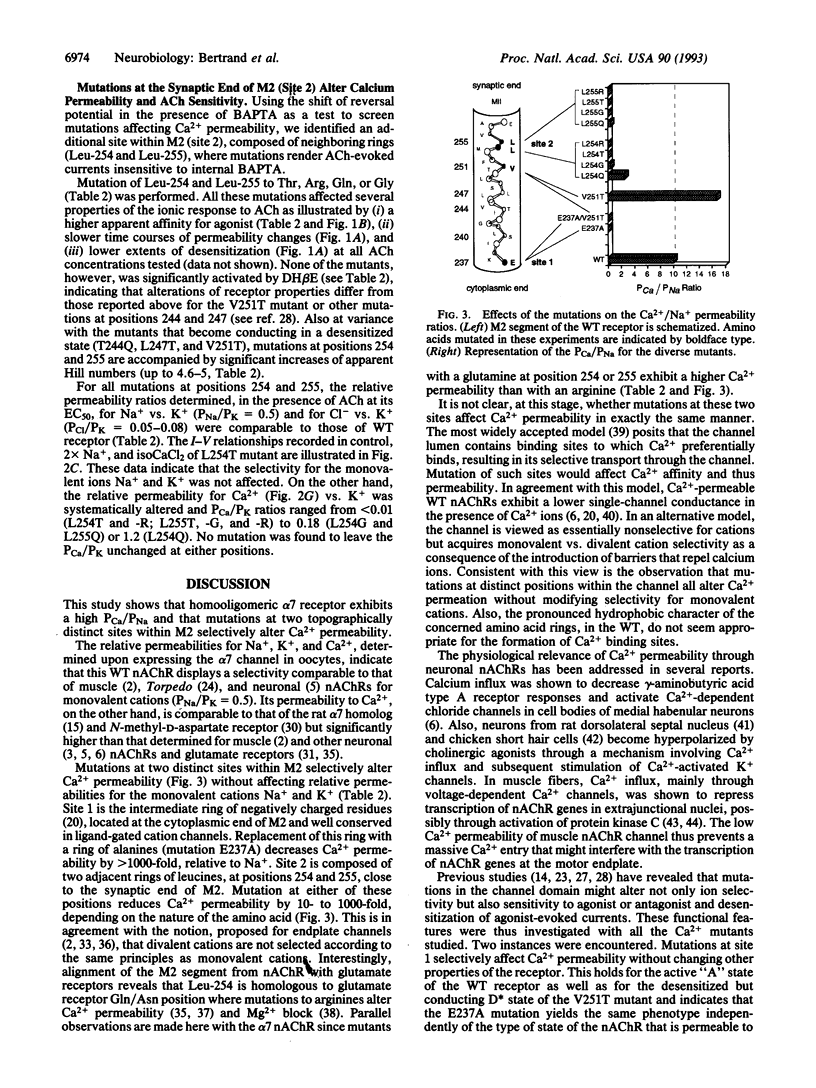
The relative permeability for sodium, potassium, and calcium of chicken alpha 7 neuronal nicotinic receptor was investigated by mutagenesis of the channel domain M2. Mutations in the "intermediate ring" of negatively charged residues, located at the cytoplasmic end of M2 (site 1), reduce calcium permeability without significantly modifying other functional properties (activation and desensitization) of the receptor; a similar change of ion selectivity is also noticed when mutations at site 1 are done in the context of a receptor mutant that conducts ions in a desensitized state. Moreover, mutations of two adjacent rings of leucines at the synaptic end of M2 (site 2) have multiple effects. They abolish calcium permeability, increase the apparent affinity for acetylcholine by 10- to 100-fold, augment Hill numbers (up to 4.6-5.0) of acetylcholine dose-response relationships, slow rates of ionic response onset, and lower the extent of desensitization. Mutations at these two topographically distinct sites within M2 selectively alter calcium transport without affecting the relative permeabilities for sodium and potassium.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. J., Dwyer T. M., Hille B. The permeability of endplate channels to monovalent and divalent metal cations. J Gen Physiol. 1980 May;75(5):493–510. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.5.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand D., Devillers-Thiéry A., Revah F., Galzi J. L., Hussy N., Mulle C., Bertrand S., Ballivet M., Changeux J. P. Unconventional pharmacology of a neuronal nicotinic receptor mutated in the channel domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1261–1265. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bregestovski P. D., Miledi R., Parker I. Calcium conductance of acetylcholine-induced endplate channels. Nature. 1979 Jun 14;279(5714):638–639. doi: 10.1038/279638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnashev N., Schoepfer R., Monyer H., Ruppersberg J. P., Günther W., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Control by asparagine residues of calcium permeability and magnesium blockade in the NMDA receptor. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1415–1419. doi: 10.1126/science.1382314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changeux J. P., Galzi J. L., Devillers-Thiéry A., Bertrand D. The functional architecture of the acetylcholine nicotinic receptor explored by affinity labelling and site-directed mutagenesis. Q Rev Biophys. 1992 Nov;25(4):395–432. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500004352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. N., Labarca C., Czyzyk L., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Tris+/Na+ permeability ratios of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are reduced by mutations near the intracellular end of the M2 region. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Apr;99(4):545–572. doi: 10.1085/jgp.99.4.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier S., Bertrand D., Matter J. M., Hernandez M. C., Bertrand S., Millar N., Valera S., Barkas T., Ballivet M. A neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit (alpha 7) is developmentally regulated and forms a homo-oligomeric channel blocked by alpha-BTX. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):847–856. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90344-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier S., Erkman L., Valera S., Rungger D., Bertrand S., Boulter J., Ballivet M., Bertrand D. Alpha 5, alpha 3, and non-alpha 3. Three clustered avian genes encoding neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-related subunits. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17560–17567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani J. A., Eisenman G. Monovalent and divalent cation permeation in acetylcholine receptor channels. Ion transport related to structure. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jun;89(6):959–983. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.6.959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deneris E. S., Connolly J., Rogers S. W., Duvoisin R. Pharmacological and functional diversity of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1991 Jan;12(1):34–40. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(91)90486-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiéry A., Galzi J. L., Bertrand S., Changeux J. P., Bertrand D. Stratified organization of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channel. Neuroreport. 1992 Nov;3(11):1001–1004. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199211000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvoisin R. M., Deneris E. S., Patrick J., Heinemann S. The functional diversity of the neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors is increased by a novel subunit: beta 4. Neuron. 1989 Oct;3(4):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Heinemann S. F. Ca2+ permeability of unedited and edited versions of the kainate selective glutamate receptor GluR6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fieber L. A., Adams D. J. Acetylcholine-evoked currents in cultured neurones dissociated from rat parasympathetic cardiac ganglia. J Physiol. 1991 Mar;434:215–237. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs P. A., Murrow B. W. Cholinergic inhibition of short (outer) hair cells of the chick's cochlea. J Neurosci. 1992 Mar;12(3):800–809. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-03-00800.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzi J. L., Devillers-Thiéry A., Hussy N., Bertrand S., Changeux J. P., Bertrand D. Mutations in the channel domain of a neuronal nicotinic receptor convert ion selectivity from cationic to anionic. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):500–505. doi: 10.1038/359500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic G. P., Heinemann S. Determinants of the calcium permeation of ligand-gated cation channels. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;4(4):670–677. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90088-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giraudat J., Dennis M., Heidmann T., Chang J. Y., Changeux J. P. Structure of the high-affinity binding site for noncompetitive blockers of the acetylcholine receptor: serine-262 of the delta subunit is labeled by [3H]chlorpromazine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2719–2723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess P., Tsien R. W. Mechanism of ion permeation through calcium channels. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):453–456. doi: 10.1038/309453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. F., Tong J., Schmidt J. Protein kinase C couples membrane excitation to acetylcholine receptor gene inactivation in chick skeletal muscle. Neuron. 1992 Oct;9(4):671–678. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90030-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hucho F., Oberthür W., Lottspeich F. The ion channel of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is formed by the homologous helices M II of the receptor subunits. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):137–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80881-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto K., Busch C., Sakmann B., Mishina M., Konno T., Nakai J., Bujo H., Mori Y., Fukuda K., Numa S. Rings of negatively charged amino acids determine the acetylcholine receptor channel conductance. Nature. 1988 Oct 13;335(6191):645–648. doi: 10.1038/335645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto K., Konno T., Nakai J., Wang F., Mishina M., Numa S. A ring of uncharged polar amino acids as a component of channel constriction in the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 9;289(2):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81068-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto K., Methfessel C., Sakmann B., Mishina M., Mori Y., Konno T., Fukuda K., Kurasaki M., Bujo H., Fujita Y. Location of a delta-subunit region determining ion transport through the acetylcholine receptor channel. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):670–674. doi: 10.1038/324670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarsfeld A., Laufer R., Fontaine B., Devillers-Thiéry A., Dubreuil C., Changeux J. P. Regulation of muscle AChR alpha subunit gene expression by electrical activity: involvement of protein kinase C and Ca2+. Neuron. 1989 Mar;2(3):1229–1236. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(89)90307-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konno T., Busch C., Von Kitzing E., Imoto K., Wang F., Nakai J., Mishina M., Numa S., Sakmann B. Rings of anionic amino acids as structural determinants of ion selectivity in the acetylcholine receptor channel. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 May 22;244(1310):69–79. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. J., Labarca C. G., Charnet P., Davidson N., Lester H. A. Evidence that the M2 membrane-spanning region lines the ion channel pore of the nicotinic receptor. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2462281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. A. Ion-concentration dependence of the reversal potential and the single channel conductance of ion channels at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1979 Jan;286:417–445. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1979.sp012629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis C. A., Stevens C. F. Acetylcholine receptor channel ionic selectivity: ions experience an aqueous environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6110–6113. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luetje C. W., Patrick J. Both alpha- and beta-subunits contribute to the agonist sensitivity of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Neurosci. 1991 Mar;11(3):837–845. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-03-00837.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L. Permeation and block of N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor channels by divalent cations in mouse cultured central neurones. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:501–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R. Intracellular calcium and desensitization of acetylcholine receptors. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1980 Sep 26;209(1176):447–452. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1980.0106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Chloride current induced by injection of calcium into Xenopus oocytes. J Physiol. 1984 Dec;357:173–183. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori H., Masaki H., Yamakura T., Mishina M. Identification by mutagenesis of a Mg(2+)-block site of the NMDA receptor channel. Nature. 1992 Aug 20;358(6388):673–675. doi: 10.1038/358673a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulle C., Choquet D., Korn H., Changeux J. P. Calcium influx through nicotinic receptor in rat central neurons: its relevance to cellular regulation. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90115-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulle C., Vidal C., Benoit P., Changeux J. P. Existence of different subtypes of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in the rat habenulo-interpeduncular system. J Neurosci. 1991 Aug;11(8):2588–2597. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-08-02588.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi S. Molecular diversity of glutamate receptors and implications for brain function. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):597–603. doi: 10.1126/science.1329206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nooney J. M., Peters J. A., Lambert J. J. A patch clamp study of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor of bovine adrenomedullary chromaffin cells in culture. J Physiol. 1992 Sep;455:503–527. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revah F., Bertrand D., Galzi J. L., Devillers-Thiéry A., Mulle C., Hussy N., Bertrand S., Ballivet M., Changeux J. P. Mutations in the channel domain alter desensitization of a neuronal nicotinic receptor. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):846–849. doi: 10.1038/353846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revah F., Galzi J. L., Giraudat J., Haumont P. Y., Lederer F., Changeux J. P. The noncompetitive blocker [3H]chlorpromazine labels three amino acids of the acetylcholine receptor gamma subunit: implications for the alpha-helical organization of regions MII and for the structure of the ion channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4675–4679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sands S. B., Barish M. E. Calcium permeability of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor channels in PC12 cells. Brain Res. 1991 Sep 27;560(1-2):38–42. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91211-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent P. B. The diversity of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1993;16:403–443. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.16.030193.002155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigel E., Baur R., Trube G., Möhler H., Malherbe P. The effect of subunit composition of rat brain GABAA receptors on channel function. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguéla P., Wadiche J., Dineley-Miller K., Dani J. A., Patrick J. W. Molecular cloning, functional properties, and distribution of rat brain alpha 7: a nicotinic cation channel highly permeable to calcium. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):596–604. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00596.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernino S., Amador M., Luetje C. W., Patrick J., Dani J. A. Calcium modulation and high calcium permeability of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90114-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan S., Pugh P. C., Zhang Z. W., Rathouz M. M., Berg D. K. Nicotinic receptors that bind alpha-bungarotoxin on neurons raise intracellular free Ca2+. Neuron. 1992 Feb;8(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90301-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villarroel A., Herlitze S., Koenen M., Sakmann B. Location of a threonine residue in the alpha-subunit M2 transmembrane segment that determines the ion flow through the acetylcholine receptor channel. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Jan 22;243(1306):69–74. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong L. A., Gallagher J. P. Pharmacology of nicotinic receptor-mediated inhibition in rat dorsolateral septal neurones. J Physiol. 1991 May;436:325–346. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



