Abstract
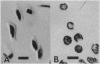
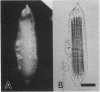
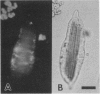
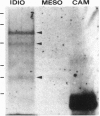
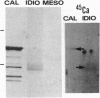
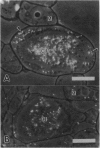
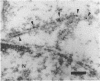
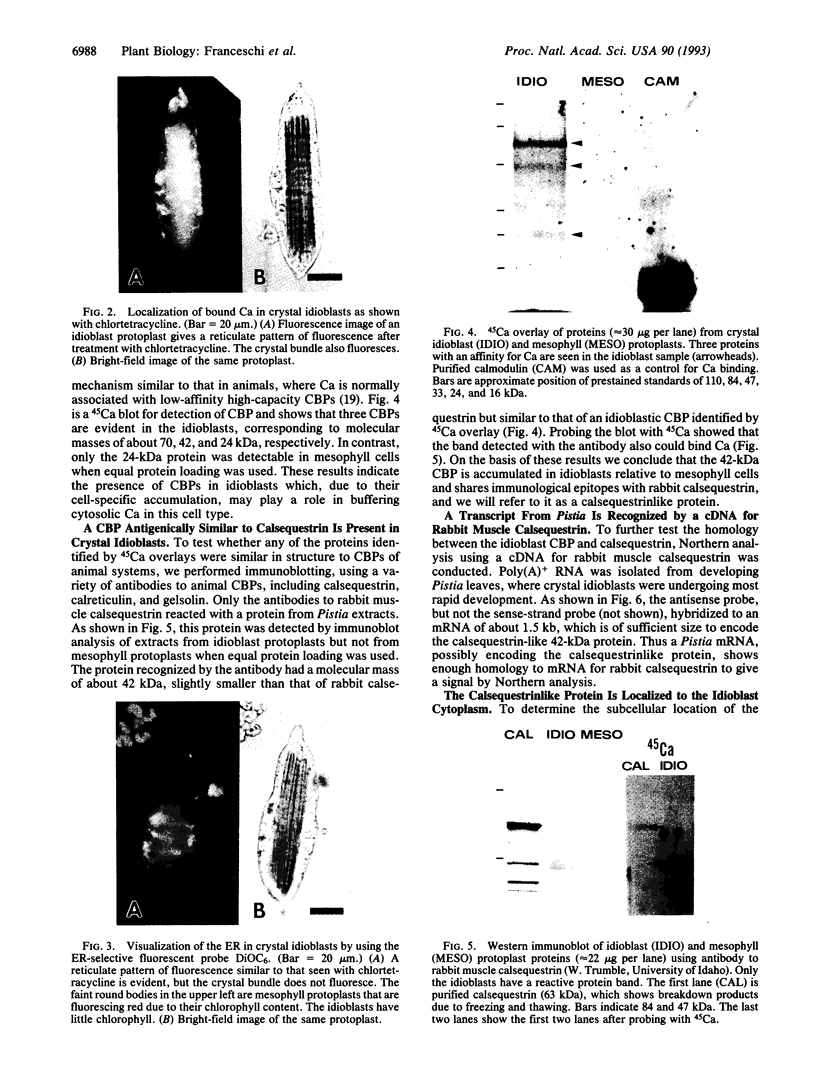
To contend with high calcium (Ca) levels in the environment, many plant species contain crystal idioblasts, specialized cells which accumulate large amounts of Ca as oxalate crystals. The biochemical processes involved in the accumulation of Ca in crystal idioblasts are unknown, as these cells constitute only a minor proportion of the total plant tissue. To address how crystal idioblasts buffer cytosolic Ca during crystal formation, we purified these cells from water lettuce and assessed their biochemistry. We show here that crystal idioblast cells contain three Ca-binding proteins not detectable in mesophyll cells. One of the Ca-binding proteins shares antigenicity with rabbit calsequestrin, a high-capacity low-affinity Ca-binding protein, and is encoded by related nucleotide sequences. Immunocytochemical localization studies further demonstrate that a calsequestrinlike protein is present primarily in crystal idioblasts and is preferentially localized in the endoplasmic reticulum, an organelle enriched in Ca as evidenced by vital staining. We thus conclude that crystal idioblasts possess a buffering system involving calsequestrinlike proteins, a process that likely plays an essential role in the bulk control of Ca in plant cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Choi E. S., Clegg D. O. Identification and developmental expression of a chicken calsequestrin homolog. Dev Biol. 1990 Nov;142(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90160-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou M., Krause K. H., Campbell K. P., Jensen K. G., Sjolund R. D. Antibodies against the Calcium-Binding Protein: Calsequestrin from Streptanthus tortuosus (Brassicaceae). Plant Physiol. 1989 Dec;91(4):1259–1261. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.4.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg D. O., Helder J. C., Hann B. C., Hall D. E., Reichardt L. F. Amino acid sequence and distribution of mRNA encoding a major skeletal muscle laminin binding protein: an extracellular matrix-associated protein with an unusual COOH-terminal polyaspartate domain. J Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;107(2):699–705. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.2.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damiani E., Spamer C., Heilmann C., Salvatori S., Margreth A. Endoplasmic reticulum of rat liver contains two proteins closely related to skeletal sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca-ATPase and calsequestrin. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):340–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fliegel L., Ohnishi M., Carpenter M. R., Khanna V. K., Reithmeier R. A., MacLennan D. H. Amino acid sequence of rabbit fast-twitch skeletal muscle calsequestrin deduced from cDNA and peptide sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1167–1171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto S., Bruno B., Lew D. P., Pozzan T., Volpe P., Meldolesi J. Immunocytochemistry of calciosomes in liver and pancreas. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 2):2523–2531. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson J. H., Begg D. A., Beaulieu S. M., Fishkind D. J., Bonder E. M., Terasaki M., Lebeche D., Kaminer B. A calsequestrin-like protein in the endoplasmic reticulum of the sea urchin: localization and dynamics in the egg and first cell cycle embryo. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):149–161. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jande S. S., Maler L., Lawson D. E. Immunohistochemical mapping of vitamin D-dependent calcium-binding protein in brain. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):765–767. doi: 10.1038/294765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly L. E. Purification and properties of a 23 kDa Ca2(+)-binding protein from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochem J. 1990 Nov 1;271(3):661–666. doi: 10.1042/bj2710661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause K. H., Chou M., Thomas M. A., Sjolund R. D., Campbell K. P. Plant cells contain calsequestrin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 15;264(8):4269–4272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. X., Franceschi V. R. Distribution of peroxisomes and glycolate metabolism in relation to calcium oxalate formation in Lemna minor L. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;51(1):9–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Wong P. T. Isolation of a calcium-sequestering protein from sarcoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1231–1235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Mikawa T., Ebashi S. Detection of calcium binding proteins by 45Ca autoradiography on nitrocellulose membrane after sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. J Biochem. 1984 Feb;95(2):511–519. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsawa K., Ebata N. Silver stain for detecting 10-femtogram quantities of protein after polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):409–415. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90703-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrobon D., Di Virgilio F., Pozzan T. Structural and functional aspects of calcium homeostasis in eukaryotic cells. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):599–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19378.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poovaiah B. W., Reddy A. S. Calcium messenger system in plants. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci. 1987;6(1):47–103. doi: 10.1080/07352688709382247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer R., Charman M., Wilson P., Lawson E. Vitamin d-stimulated intestinal calcium absorption may not involve calcium-binding protein directly. Nature. 1976 Sep 9;263(5573):161–163. doi: 10.1038/263161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]