Abstract
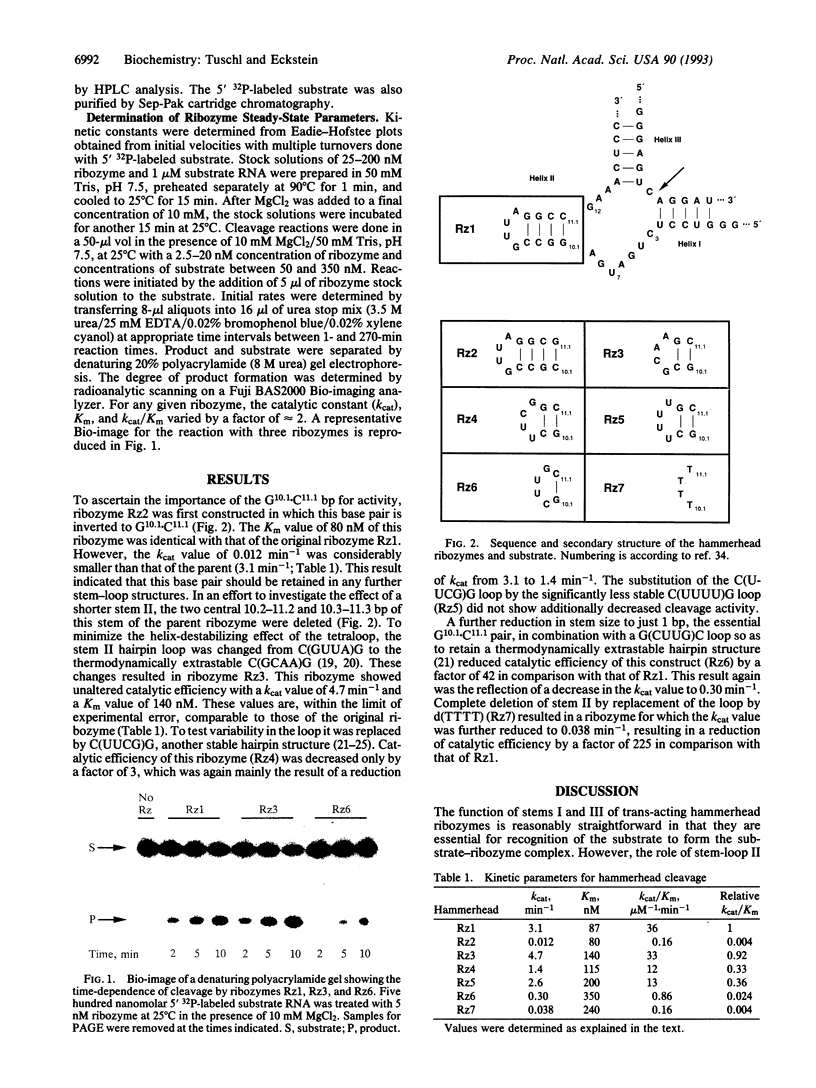
The activity of several hammerhead ribozyme constructs with constant lengths of stems I and III of 5 nt each but with variously shortened stems II is reported. Stems with 2 bp rather than the conventional 4 bp show essentially unaltered catalytic activity, independent of the composition of the tetraloop. Further reduction in size to 1 bp or 0 bp decreases activity drastically. Inversion of the G10.1.C11.1 bp next to the invariant core leads to a loss in activity, even when the stem consists of 4 bp. Thus, the minimal structural requirement for stem-loop II is a 2-bp stem with a conserved G.C bp. The reduction in catalytic activity is predominantly a result of a decrease of catalytic constant kcat, whereas Km is only slightly affected. Thus, the structural requirement for optimal activity in these constructs where the chemical-cleavage step is rate limiting is determined by the stabilization of the transition state.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antao V. P., Lai S. Y., Tinoco I., Jr A thermodynamic study of unusually stable RNA and DNA hairpins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5901–5905. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheong C., Varani G., Tinoco I., Jr Solution structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin, 5'GGAC(UUCG)GUCC. Nature. 1990 Aug 16;346(6285):680–682. doi: 10.1038/346680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Uhlenbeck O. C. Kinetics of intermolecular cleavage by hammerhead ribozymes. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 8;31(48):12042–12054. doi: 10.1021/bi00163a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedor M. J., Uhlenbeck O. C. Substrate sequence effects on "hammerhead" RNA catalytic efficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1668–1672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu D. J., McLaughlin L. W. Importance of specific adenosine N7-nitrogens for efficient cleavage by a hammerhead ribozyme. A model for magnesium binding. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 17;31(45):10941–10949. doi: 10.1021/bi00160a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu D. J., McLaughlin L. W. Importance of specific purine amino and hydroxyl groups for efficient cleavage by a hammerhead ribozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3985–3989. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertel K. J., Pardi A., Uhlenbeck O. C., Koizumi M., Ohtsuka E., Uesugi S., Cedergren R., Eckstein F., Gerlach W. L., Hodgson R. Numbering system for the hammerhead. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3252–3252. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heus H. A., Pardi A. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the hammerhead ribozyme domain. Secondary structure formation and magnesium ion dependence. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 5;217(1):113–124. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90615-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heus H. A., Pardi A. Structural features that give rise to the unusual stability of RNA hairpins containing GNRA loops. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):191–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1712983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heus H. A., Uhlenbeck O. C., Pardi A. Sequence-dependent structural variations of hammerhead RNA enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1103–1108. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Turner D. H., Zuker M. Improved predictions of secondary structures for RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7706–7710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall M. J., Hendry P., Jennings P. A. Minimal sequence requirements for ribozyme activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 1;89(13):5710–5714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.13.5710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odai O., Kodama H., Hiroaki H., Sakata T., Tanaka T., Uesugi S. Synthesis and NMR study of ribo-oligonucleotides forming a hammerhead-type RNA enzyme system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):5955–5960. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.5955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen D. B., Benseler F., Aurup H., Pieken W. A., Eckstein F. Study of a hammerhead ribozyme containing 2'-modified adenosine residues. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9735–9741. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolella G., Sproat B. S., Lamond A. I. Nuclease resistant ribozymes with high catalytic activity. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1913–1919. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05244.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pease A. C., Wemmer D. E. Characterization of the secondary structure and melting of a self-cleaved RNA hammerhead domain by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 25;29(38):9039–9046. doi: 10.1021/bi00490a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreault J. P., Labuda D., Usman N., Yang J. H., Cedergren R. Relationship between 2'-hydroxyls and magnesium binding in the hammerhead RNA domain: a model for ribozyme catalysis. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 23;30(16):4020–4025. doi: 10.1021/bi00230a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perreault J. P., Wu T. F., Cousineau B., Ogilvie K. K., Cedergren R. Mixed deoxyribo- and ribo-oligonucleotides with catalytic activity. Nature. 1990 Apr 5;344(6266):565–567. doi: 10.1038/344565a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieken W. A., Olsen D. B., Benseler F., Aurup H., Eckstein F. Kinetic characterization of ribonuclease-resistant 2'-modified hammerhead ribozymes. Science. 1991 Jul 19;253(5017):314–317. doi: 10.1126/science.1857967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffner D. E., Stormo G. D., Uhlenbeck O. C. Sequence requirements of the hammerhead RNA self-cleavage reaction. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 27;29(47):10695–10702. doi: 10.1021/bi00499a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakata T., Hiroaki H., Oda Y., Tanaka T., Ikehara M., Uesugi S. Studies on the structure and stabilizing factor of the CUUCGG hairpin RNA using chemically synthesized oligonucleotides. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3831–3839. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SantaLucia J., Jr, Kierzek R., Turner D. H. Context dependence of hydrogen bond free energy revealed by substitutions in an RNA hairpin. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):217–219. doi: 10.1126/science.1373521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SantaLucia J., Jr, Kierzek R., Turner D. H. Effects of GA mismatches on the structure and thermodynamics of RNA internal loops. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 18;29(37):8813–8819. doi: 10.1021/bi00489a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slim G., Gait M. J. Configurationally defined phosphorothioate-containing oligoribonucleotides in the study of the mechanism of cleavage of hammerhead ribozymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1183–1188. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slim G., Gait M. J. The role of the exocyclic amino groups of conserved purines in hammerhead ribozyme cleavage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Mar 16;183(2):605–609. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)90525-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symons R. H. Small catalytic RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:641–671. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuerk C., Gauss P., Thermes C., Groebe D. R., Gayle M., Guild N., Stormo G., d'Aubenton-Carafa Y., Uhlenbeck O. C., Tinoco I., Jr CUUCGG hairpins: extraordinarily stable RNA secondary structures associated with various biochemical processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1364–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. H., Sugimoto N., Freier S. M. RNA structure prediction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:167–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani G., Cheong C., Tinoco I., Jr Structure of an unusually stable RNA hairpin. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 2;30(13):3280–3289. doi: 10.1021/bi00227a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams D. M., Pieken W. A., Eckstein F. Function of specific 2'-hydroxyl groups of guanosines in a hammerhead ribozyme probed by 2' modifications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):918–921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. H., Usman N., Chartrand P., Cedergren R. Minimum ribonucleotide requirement for catalysis by the RNA hammerhead domain. Biochemistry. 1992 Jun 2;31(21):5005–5009. doi: 10.1021/bi00136a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Tol H., Buzayan J. M., Feldstein P. A., Eckstein F., Bruening G. Two autolytic processing reactions of a satellite RNA proceed with inversion of configuration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18(8):1971–1975. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.8.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




