Abstract
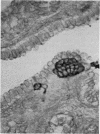
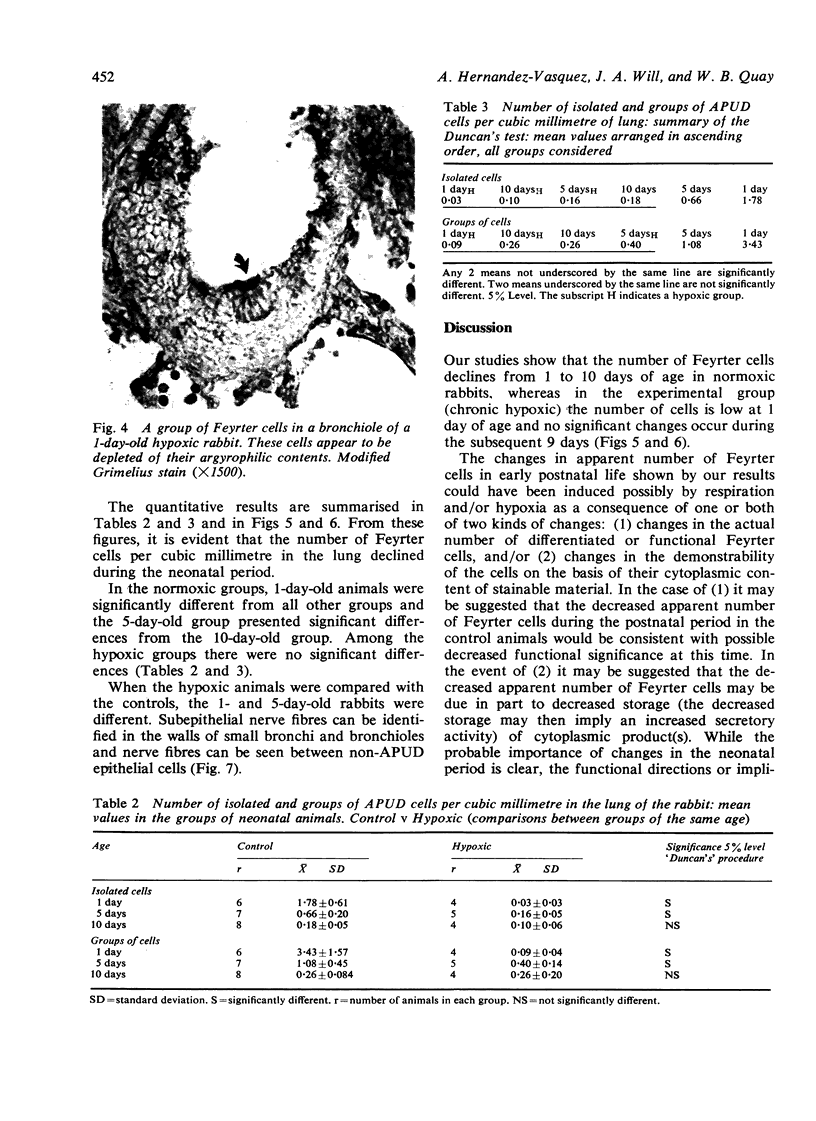
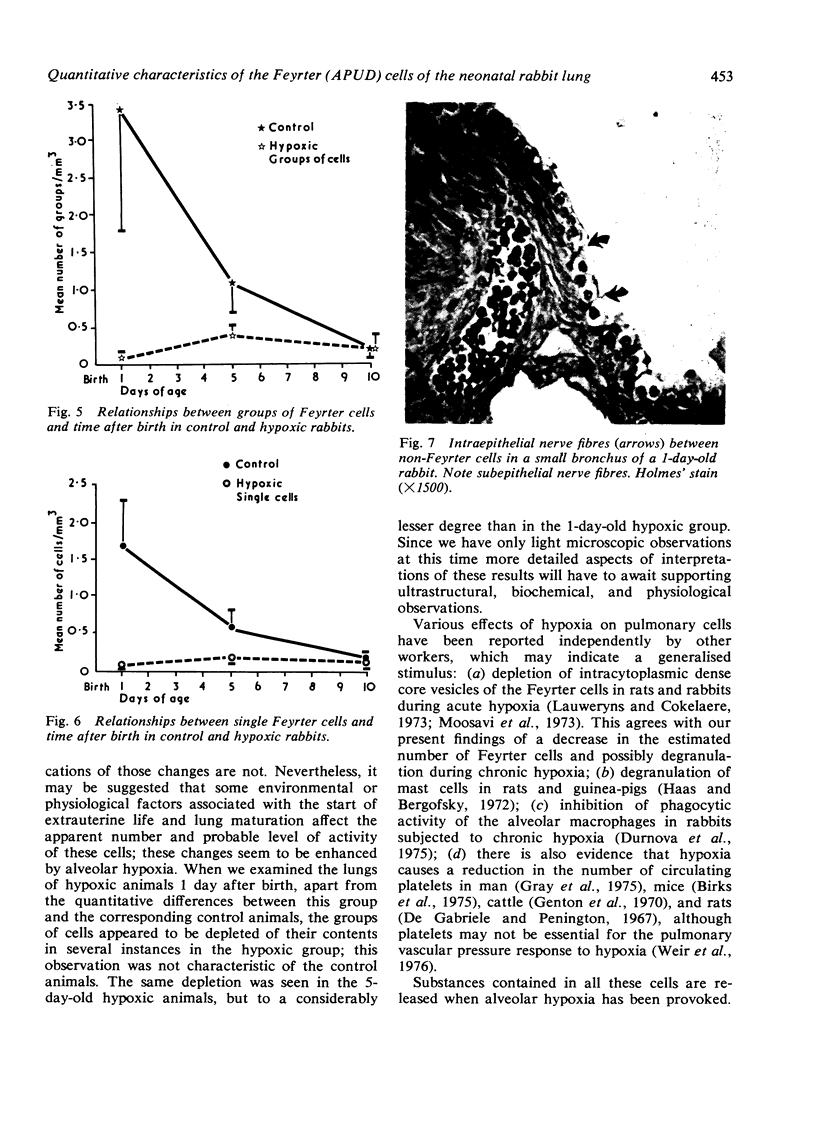
Our studies show that the apparent number of Feyrter cells in the lung declines during the neonatal period in normoxic rabbits, and that in hypoxic animals a uniformly and significantly lower number of cells occurs as compared with the normoxic rabbits. There is some indication of degranulation of cells in the hypoxic groups. It is suggested that environmental and/or physiological factors associated with the start of extrauterine life, or lung development, may affect the apparent number and probable level of activity of these cells. These changes seem to be enhanced by hypoxia. Mast cells are scarce, and Feyrter cells are relatively more numerous along the airways. These cell types could possibly represent storage sites for 5-hydroxytryptamine, as suggested also by other investigators. Intraepithelial nerve fibres in bronchi and bronchioles were found but they were not limited to innervations of Feyrter cells or related cell bodies.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensch K. G., Gordon G. B., Miller L. R. Studies on the bronchial counterpart of the Kultschitzky (argentaffin) cell and innervation of bronchial glands. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Jun;12(5):668–686. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensch K. G., Gordon G. B., Miller L. R. Studies on the bronchial counterpart of the Kultschitzky (argentaffin) cell and innervation of bronchial glands. J Ultrastruct Res. 1965 Jun;12(5):668–686. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(65)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birks J. W., Klassen L. W., Gurney C. W. Hypoxia-induced thrombocytopenia in mice. J Lab Clin Med. 1975 Aug;86(2):230–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cronau L. H., Kerstein M. D., Mandel S., Gillis C. N. 5-Hydroxytryptamine extraction by the lung. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976 Jul;143(1):51–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutz E., Chan W., Wong V., Conen P. E. Endocrine cells in rat fetal lungs. Ultrastructural and histochemical study. Lab Invest. 1974 Apr;30(4):458–464. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutz E., Chan W., Wong V., Conen P. E. Ultrastructure and fluorescence histochemistry of endocrine (APUD-type) cells in tracheal mucosa of human and various animal species. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 May 20;158(4):425–437. doi: 10.1007/BF00220210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cutz E., Conen P. E. Endocrine-like cells in human fetal lungs: an electron microscopic study. Anat Rec. 1972 May;173(1):115–122. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091730110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Gabriele G., Penington D. G. Physiology of the regulation of platelet production. Br J Haematol. 1967 Mar;13(2):202–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1967.tb08732.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis C. N., Cronau L. H., Greene N. M., Hammond G. L. Removal of 5-hydroxytryptamine and norepinephrine from the pulmonary vascular space of man: influence of cardiopulmonary bypass and pulmonary arterial pressure on these processes. Surgery. 1974 Oct;76(4):608–616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis C. N., Greene N. M., Cronau L. H., Hammond G. L. Pulmonary extraction of 5-hydroxytryptamine and norepinephrine before and after cardiopulmonary bypass in man. Circ Res. 1972 Jun;30(6):666–674. doi: 10.1161/01.res.30.6.666. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis C. N. Metabolism of vasoactive hormones by lung. Anesthesiology. 1973 Dec;39(6):626–632. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197312000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. W., Bryan A. C., Freedman M. H., Houston C. S., Lewis W. F., McFadden D. M., Newell G. Effect of altitude exposure on platelets. J Appl Physiol. 1975 Oct;39(4):648–652. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1975.39.4.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimelius L. A silver nitrate stain for alpha-2 cells in human pancreatic islets. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1968;73(5-6):243–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas F., Bergofsky E. H. Role of the mast cell in the pulmonary pressor response to hypoxia. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3154–3162. doi: 10.1172/JCI107142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hage E. Endocrine cells in the bronchial mucosa of human foetuses. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A. 1972;80(2):225–234. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1972.tb02169.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hage E. Histochemistry and fine structure of endocrine cells in foetal lungs of the rabbit, mouse and guinea-pig. Cell Tissue Res. 1974 Jun 24;149(4):513–524. doi: 10.1007/BF00223029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung K. S., Loosli C. G. Bronchiolar neuro-epithelial bodies in the neonatal mouse lungs. Am J Anat. 1974 Jun;140(2):191–199. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001400206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasawa Y., Gillis C. N., Aghajanian G. Hypothermic inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine and norepinephrine uptake by lung: cellular location of amines after uptake. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Sep;186(3):498–507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery P., Reid L. Intra-epithelial nerves in normal rat airways: a quantitative electron microscopic study. J Anat. 1973 Jan;114(Pt 1):35–45. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junod A. F. Metabolism, production, and release of hormones and mediators in the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Jul;112(1):93–108. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.112.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. S., McLelland J., Cook R. D., King D. Z., Walsh C. The ultrastructure of afferent nerve endings in the avian lung. Respir Physiol. 1974 Oct;22(1-2):21–40. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(74)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Cokelaere J., Theunynck P. Serotonin producing neuroepithelial bodies in rabbit respiratory mucosa. Science. 1973 Apr 27;180(4084):410–413. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4084.410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Cokelaere M. Hypoxia-sensitive neuro-epithelial bodies. Intrapulmonary secretory neuroreceptors, modulated by the CNS. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Dec 21;145(4):521–540. doi: 10.1007/BF00306722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Cokelaere M., Theunynck P., Deleersnyder M. Neuroepithelial bodies in mammalian respiratory mucosa: light optical, histochemical an ultrastructural studies. Chest. 1974 Apr;65(Suppl):22S–29S. doi: 10.1378/chest.65.4_supplement.22s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Peuskens J. C. Argyrophil (kinin and amine producing?) cells in human infant airway epithelium. Life Sci. 1969 Jun 1;8(11):577–585. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90019-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauweryns J. M., Peuskens J. C. Neuro-epithelial bodies (neuroreceptor or secretory organs?) in human infant bronchial and bronchiolar epithelium. Anat Rec. 1972 Mar;172(3):471–481. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091720301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moosavi H., Smith P., Heath D. The Feyrter cell in hypoxia. Thorax. 1973 Nov;28(6):729–741. doi: 10.1136/thx.28.6.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G. The cytochemistry and ultrastructure of polypeptide hormone-producing cells of the APUD series and the embryologic, physiologic and pathologic implications of the concept. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 May;17(5):303–313. doi: 10.1177/17.5.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodin J. A. The ciliated cell. Ultrastructure and function of the human tracheal mucosa. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1966 Mar;93(3 Suppl):1–15. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1966.93.3P2.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Yoshida T., Kitamura S., Vreim C. Pulmonary alveolar hypoxia: release of prostaglandins and other humoral mediators. Science. 1974 Sep 27;185(4157):1181–1183. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4157.1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweisthal M. R., Frost C. C., Brinn J. E. Stains for A, B, and D cells in fetal rat islets. Stain Technol. 1975 May;50(3):161–170. doi: 10.3109/10520297509117053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solcia E., Capella C., Vassallo G. On the staining of the gastrin cell. Gastroenterology. 1971 Nov;61(5):794–796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir E. K., Seavy J., Mlczoch J., Genton E., Reeves J. T. Platelets are not essential for the pulmonary vascular pressor response to hypoxia. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Sep;88(3):412–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winckler J. Biogene Amine in Polypeptidhormon-bildenden Zellen. Due APUD-Zellen (Pearse) Klin Wochenschr. 1976 Jan 15;54(2):49–58. doi: 10.1007/BF01468770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]