Abstract
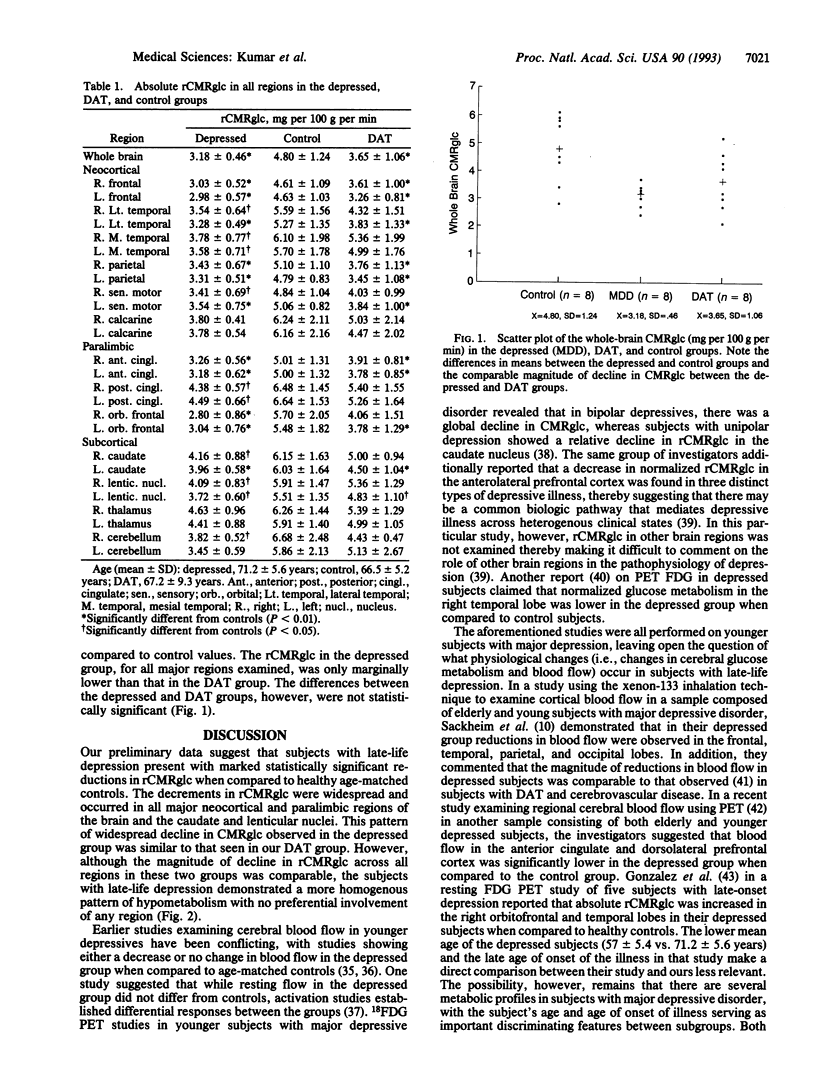
Eight subjects with late-life depression, eight subjects with probable Alzheimer disease, and eight healthy age-matched controls were studied using 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography in the resting state with their eyes open and ears unoccluded. The depressed subjects showed widespread reductions in the regional cerebral metabolic rate for glucose in most major neocortical, subcortical, and paralimbic regions that were significantly different from control values (P < 0.01). The metabolic decrements in the depressed group were comparable in magnitude to those seen in the Alzheimer disease group. These data demonstrate widespread nonfocal decline in glucose metabolism in late-life depression that is comparable to the hypometabolism seen in Alzheimer disease. These findings have pathophysiological implications in major depressive disorder in the elderly.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alavi A., Hirsch L. J. Studies of central nervous system disorders with single photon emission computed tomography and positron emission tomography: evolution over the past 2 decades. Semin Nucl Med. 1991 Jan;21(1):58–81. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(05)80079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander G. E., DeLong M. R., Strick P. L. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:357–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexopoulos G. S., Young R. C., Meyers B. S., Abrams R. C., Shamoian C. A. Late-onset depression. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1988 Mar;11(1):101–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter L. R., Jr, Phelps M. E., Mazziotta J. C., Schwartz J. M., Gerner R. H., Selin C. E., Sumida R. M. Cerebral metabolic rates for glucose in mood disorders. Studies with positron emission tomography and fluorodeoxyglucose F 18. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1985 May;42(5):441–447. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1985.01790280019002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter L. R., Jr, Schwartz J. M., Phelps M. E., Mazziotta J. C., Guze B. H., Selin C. E., Gerner R. H., Sumida R. M. Reduction of prefrontal cortex glucose metabolism common to three types of depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1989 Mar;46(3):243–250. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1989.01810030049007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bench C. J., Friston K. J., Brown R. G., Scott L. C., Frackowiak R. S., Dolan R. J. The anatomy of melancholia--focal abnormalities of cerebral blood flow in major depression. Psychol Med. 1992 Aug;22(3):607–615. doi: 10.1017/s003329170003806x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blazer D., Hughes D. C., George L. K. The epidemiology of depression in an elderly community population. Gerontologist. 1987 Jun;27(3):281–287. doi: 10.1093/geront/27.3.281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. M., Crane A. M., Goldman P. S. Regional distribution of monoamines in the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures of the rhesus monkey: concentrations and in vivo synthesis rates. Brain Res. 1979 May 18;168(1):133–150. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey C. E., Figiel G. S., Djang W. T., Cress M., Saunders W. B., Weiner R. D. Leukoencephalopathy in elderly depressed patients referred for ECT. Biol Psychiatry. 1988 Jun;24(2):143–161. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(88)90270-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey C. E., Figiel G. S., Djang W. T., Saunders W. B., Weiner R. D. White matter hyperintensity on magnetic resonance imaging: clinical and neuroanatomic correlates in the depressed elderly. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1989 Spring;1(2):135–144. doi: 10.1176/jnp.1.2.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folstein M. F., Folstein S. E., McHugh P. R. "Mini-mental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975 Nov;12(3):189–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-3956(75)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster N. L., Chase T. N., Fedio P., Patronas N. J., Brooks R. A., Di Chiro G. Alzheimer's disease: focal cortical changes shown by positron emission tomography. Neurology. 1983 Aug;33(8):961–965. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.8.961. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedland R. P., Budinger T. F., Ganz E., Yano Y., Mathis C. A., Koss B., Ober B. A., Huesman R. H., Derenzo S. E. Regional cerebral metabolic alterations in dementia of the Alzheimer type: positron emission tomography with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1983 Aug;7(4):590–598. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198308000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gur R. E., Skolnick B. E., Gur R. C., Caroff S., Rieger W., Obrist W. D., Younkin D., Reivich M. Brain function in psychiatric disorders. II. Regional cerebral blood flow in medicated unipolar depressives. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1984 Jul;41(7):695–699. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1984.01790180065008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton M. Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness. Br J Soc Clin Psychol. 1967 Dec;6(4):278–296. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8260.1967.tb00530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz B., Duara R., Rapoport S. I. Intercorrelations of glucose metabolic rates between brain regions: application to healthy males in a state of reduced sensory input. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1984 Dec;4(4):484–499. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1984.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagust W. J., Budinger T. F., Reed B. R. The diagnosis of dementia with single photon emission computed tomography. Arch Neurol. 1987 Mar;44(3):258–262. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1987.00520150014011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagust W. J., Friedland R. P., Budinger T. F., Koss E., Ober B. Longitudinal studies of regional cerebral metabolism in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1988 Jun;38(6):909–912. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.6.909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karp J. S., Muehllehner G., MankofF D. A., Ordonez C. E., Ollinger J. M., Daube-Witherspoon M. E., Haigh A. T., Beerbohm D. J. Continuous-slice PENN-PET: a positron tomograph with volume imaging capability. J Nucl Med. 1990 May;31(5):617–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Schapiro M. B., Grady C., Haxby J. V., Wagner E., Salerno J. A., Friedland R. P., Rapoport S. I. High-resolution PET studies in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1991 Jan;4(1):35–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew R. J., Meyer J. S., Francis D. J., Semchuk K. M., Mortel K., Claghorn J. L. Cerebral blood flow in depression. Am J Psychiatry. 1980 Nov;137(11):1449–1450. doi: 10.1176/ajp.137.11.1449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberg H. S., Starkstein S. E., Peyser C. E., Brandt J., Dannals R. F., Folstein S. E. Paralimbic frontal lobe hypometabolism in depression associated with Huntington's disease. Neurology. 1992 Sep;42(9):1791–1797. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.9.1791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayberg H. S., Starkstein S. E., Sadzot B., Preziosi T., Andrezejewski P. L., Dannals R. F., Wagner H. N., Jr, Robinson R. G. Selective hypometabolism in the inferior frontal lobe in depressed patients with Parkinson's disease. Ann Neurol. 1990 Jul;28(1):57–64. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlson G. D., Rabins P. V., Burns A. Centrum semiovale white matter CT changes associated with normal ageing, Alzheimer's disease and late life depression with and without reversible dementia. Psychol Med. 1991 May;21(2):321–328. doi: 10.1017/s0033291700020420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearlson G. D., Rabins P. V., Kim W. S., Speedie L. J., Moberg P. J., Burns A., Bascom M. J. Structural brain CT changes and cognitive deficits in elderly depressives with and without reversible dementia ('pseudodementia'). Psychol Med. 1989 Aug;19(3):573–584. doi: 10.1017/s003329170002417x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peppard R. F., Martin W. R., Carr G. D., Grochowski E., Schulzer M., Guttman M., McGeer P. L., Phillips A. G., Tsui J. K., Calne D. B. Cerebral glucose metabolism in Parkinson's disease with and without dementia. Arch Neurol. 1992 Dec;49(12):1262–1268. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1992.00530360060019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. M., DeLisi L. E., Holcomb H. H., Uhde T. W., Cohen R., Buchsbaum M. S. Glucose utilization in the temporal cortex of affectively ill patients: positron emission tomography. Biol Psychiatry. 1987 May;22(5):545–553. doi: 10.1016/0006-3223(87)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prohovnik I., Mayeux R., Sackeim H. A., Smith G., Stern Y., Alderson P. O. Cerebral perfusion as a diagnostic marker of early Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1988 Jun;38(6):931–937. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.6.931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabins P. V., Pearlson G. D., Aylward E., Kumar A. J., Dowell K. Cortical magnetic resonance imaging changes in elderly inpatients with major depression. Am J Psychiatry. 1991 May;148(5):617–620. doi: 10.1176/ajp.148.5.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reivich M., Alavi A., Wolf A., Fowler J., Russell J., Arnett C., MacGregor R. R., Shiue C. Y., Atkins H., Anand A. Glucose metabolic rate kinetic model parameter determination in humans: the lumped constants and rate constants for [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose and [11C]deoxyglucose. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1985 Jun;5(2):179–192. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1985.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reivich M., Kuhl D., Wolf A., Greenberg J., Phelps M., Ido T., Casella V., Fowler J., Hoffman E., Alavi A. The [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization in man. Circ Res. 1979 Jan;44(1):127–137. doi: 10.1161/01.res.44.1.127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson R. G., Kubos K. L., Starr L. B., Rao K., Price T. R. Mood disorders in stroke patients. Importance of location of lesion. Brain. 1984 Mar;107(Pt 1):81–93. doi: 10.1093/brain/107.1.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruegg R. G., Zisook S., Swerdlow N. R. Depression in the aged. An overview. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1988 Mar;11(1):83–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackeim H. A., Prohovnik I., Moeller J. R., Brown R. P., Apter S., Prudic J., Devanand D. P., Mukherjee S. Regional cerebral blood flow in mood disorders. I. Comparison of major depressives and normal controls at rest. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1990 Jan;47(1):60–70. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1990.01810130062009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L., Reivich M., Kennedy C., Des Rosiers M. H., Patlak C. S., Pettigrew K. D., Sakurada O., Shinohara M. The [14C]deoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization: theory, procedure, and normal values in the conscious and anesthetized albino rat. J Neurochem. 1977 May;28(5):897–916. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1977.tb10649.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sokoloff L. Relationships among local functional activity, energy metabolism, and blood flow in the central nervous system. Fed Proc. 1981 Jun;40(8):2311–2316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uytdenhoef P., Portelange P., Jacquy J., Charles G., Linkowski P., Mendlewicz J. Regional cerebral blood flow and lateralized hemispheric dysfunction in depression. Br J Psychiatry. 1983 Aug;143:128–132. doi: 10.1192/bjp.143.2.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]