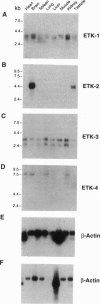
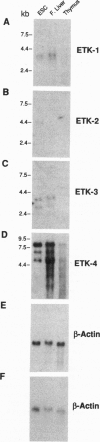
Abstract
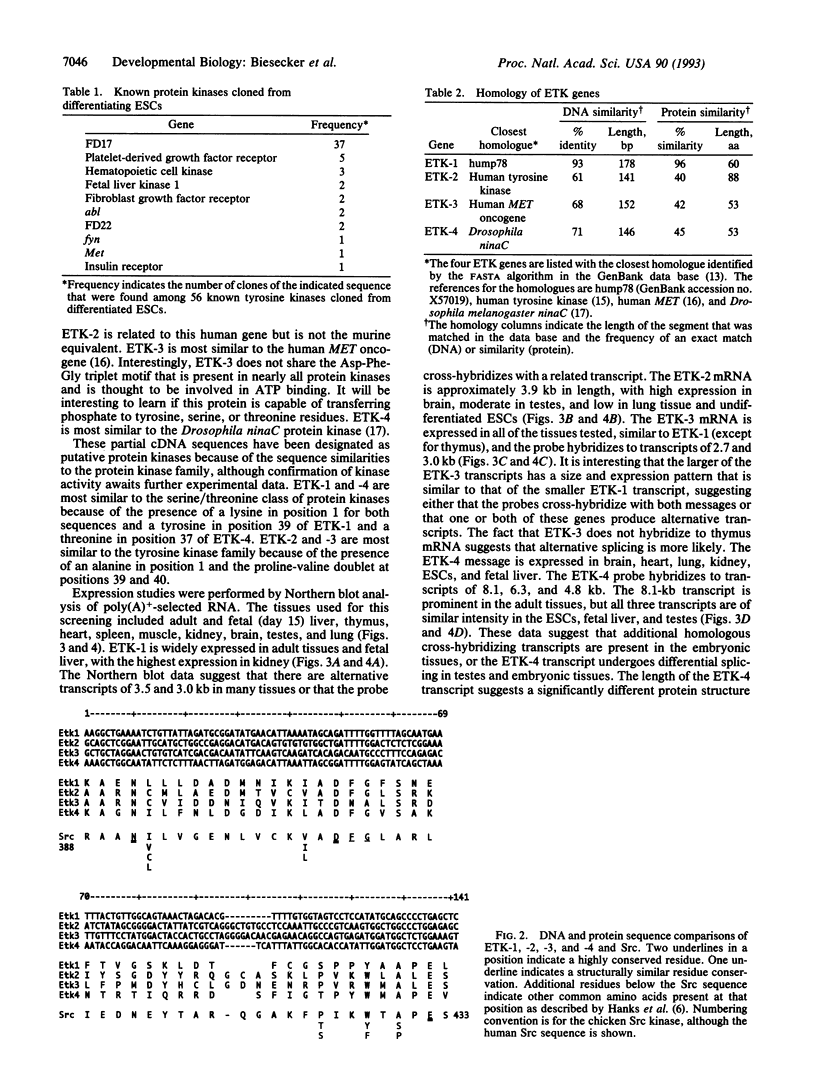
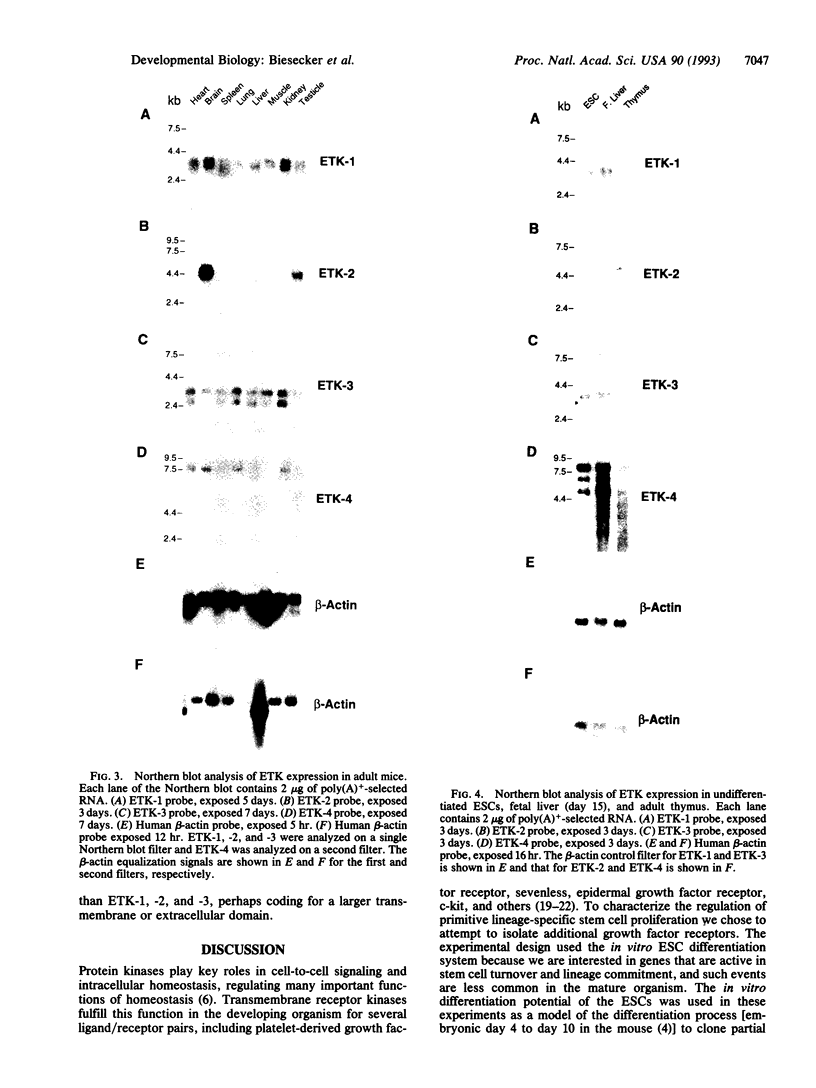
Protein kinases transduce signals from extracellular ligands in the hematopoietic and other systems through direct phosphorylation of tyrosine, serine, or threonine residues. Little is known about the ligands and receptors that are important in the earliest stages of development--i.e., stem cell self-renewal and lineage commitment. We have made use of the lineage differentiation potential of the murine embryonic stem cell system to clone partial cDNAs encoding four putative protein kinases. Three of the four genes contain the highly conserved residues Asp-Phe-Gly in domain VII of the protein kinase family. These genes are candidates for receptors or downstream effectors of cytokines that regulate self-renewal and lineage commitment in embryogenesis.
Full text
PDF
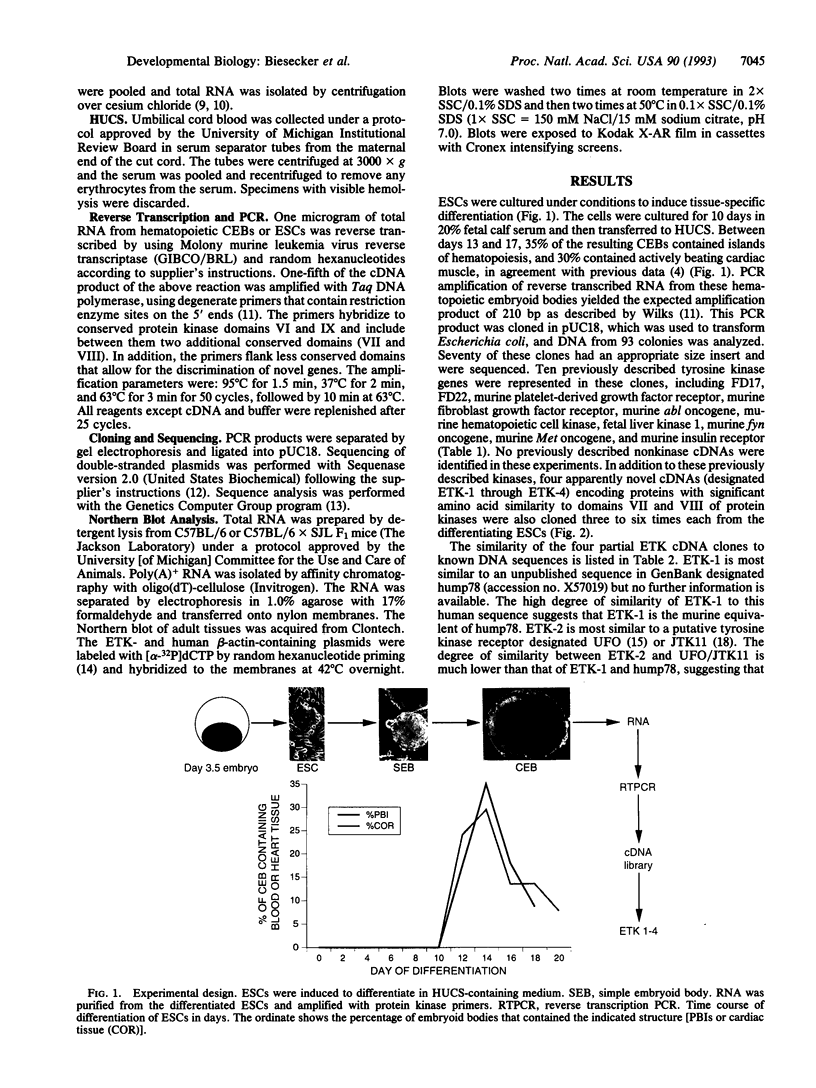

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doetschman T. C., Eistetter H., Katz M., Schmidt W., Kemler R. The in vitro development of blastocyst-derived embryonic stem cell lines: formation of visceral yolk sac, blood islands and myocardium. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Jun;87:27–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafen E., Basler K., Edstroem J. E., Rubin G. M. Sevenless, a cell-specific homeotic gene of Drosophila, encodes a putative transmembrane receptor with a tyrosine kinase domain. Science. 1987 Apr 3;236(4797):55–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2882603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen J. W., Schulz A. S., Steenvoorden A. C., Schmidberger M., Strehl S., Ambros P. F., Bartram C. R. A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor with oncogenic potential. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):2113–2120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C., Lemke G. An extended family of protein-tyrosine kinase genes differentially expressed in the vertebrate nervous system. Neuron. 1991 May;6(5):691–704. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews W., Jordan C. T., Gavin M., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Lemischka I. R. A receptor tyrosine kinase cDNA isolated from a population of enriched primitive hematopoietic cells and exhibiting close genetic linkage to c-kit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9026–9030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercola M., Stiles C. D. Growth factor superfamilies and mammalian embryogenesis. Development. 1988 Mar;102(3):451–460. doi: 10.1242/dev.102.3.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Rubin G. M. The Drosophila ninaC locus encodes two photoreceptor cell specific proteins with domains homologous to protein kinases and the myosin heavy chain head. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):757–772. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90413-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicola N. A. Hemopoietic cell growth factors and their receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:45–77. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park M., Dean M., Kaul K., Braun M. J., Gonda M. A., Vande Woude G. Sequence of MET protooncogene cDNA has features characteristic of the tyrosine kinase family of growth-factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6379–6383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partanen J., Mäkelä T. P., Alitalo R., Lehväslaiho H., Alitalo K. Putative tyrosine kinases expressed in K-562 human leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8913–8917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulido D., Campuzano S., Koda T., Modolell J., Barbacid M. Dtrk, a Drosophila gene related to the trk family of neurotrophin receptors, encodes a novel class of neural cell adhesion molecule. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):391–404. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Shine J., Chirgwin J., Pictet R., Tischer E., Rutter W. J., Goodman H. M. Rat insulin genes: construction of plasmids containing the coding sequences. Science. 1977 Jun 17;196(4296):1313–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.325648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visser J. W., Van Bekkum D. W. Purification of pluripotent hemopoietic stem cells: past and present. Exp Hematol. 1990 Mar;18(3):248–256. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiles M. V., Keller G. Multiple hematopoietic lineages develop from embryonic stem (ES) cells in culture. Development. 1991 Feb;111(2):259–267. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilks A. F. Two putative protein-tyrosine kinases identified by application of the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1603–1607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. L., Hilton D. J., Pease S., Willson T. A., Stewart C. L., Gearing D. P., Wagner E. F., Metcalf D., Nicola N. A., Gough N. M. Myeloid leukaemia inhibitory factor maintains the developmental potential of embryonic stem cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):684–687. doi: 10.1038/336684a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Escobedo J. A., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T. L., Daniel T. O., Tremble P. M., Chen E. Y., Ando M. E., Harkins R. N., Francke U. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature. 1986 Sep 18;323(6085):226–232. doi: 10.1038/323226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T., Coussens L., Munemitsu S., Dull T. J., Chen E., Schlessinger J., Francke U., Ullrich A. Human proto-oncogene c-kit: a new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3341–3351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yue C. C. Novel putative protein kinase clones from a rat large granular lymphocyte tumor cell line. Mol Immunol. 1991 Apr-May;28(4-5):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(91)90153-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]