Abstract
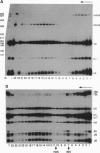
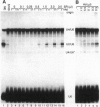
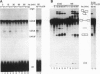
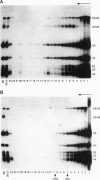
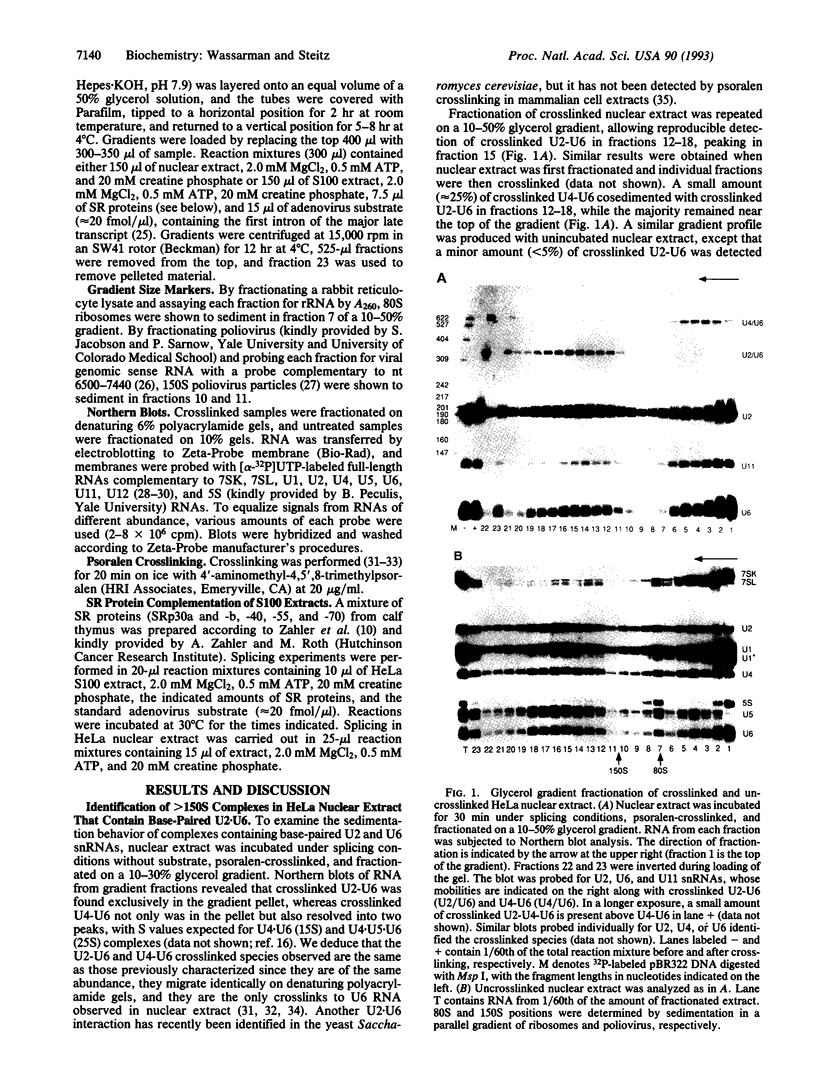
In mammalian cells, base pairing between the U2 and U6 small nuclear RNAs is required during pre-RNA splicing. We show by psoralen crosslinking of HeLa nuclear extract that U2.U6 base pairing occurs within abundant ribonucleoprotein complexes that sediment at > 150 S in glycerol gradients. All of the spliceosomal RNAs (U1, U2, U4, U5, and U6) cosediment with these large complexes, suggesting that they may be related to small nuclear RNA-containing structures called speckles/coiled bodies or snurposomes, which have been visualized in mammalian or amphibian nuclei, respectively. In contrast to nuclear extract, S100 extract, which is splicing-defective and lacks the > 150S complexes, does not contain base-paired U2.U6. However, U2.U6 base pairs form in S100 extract that has been made splicing-competent by supplementation with Ser/Arg-rich (SR) proteins, ATP, and an adenovirus splicing substrate. During splicing in supplemented S100 extract, U2.U6 base pairing precedes the appearance of splicing intermediates and occurs initially in an approximately 60S spliceosome complex but also in progressively larger (100-300 S) complexes. Possible functional relationships between the 60S spliceosome and the > 150S complexes are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black D. L., Pinto A. L. U5 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein: RNA structure analysis and ATP-dependent interaction with U4/U6. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3350–3359. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brasch K., Ochs R. L. Nuclear bodies (NBs): a newly "rediscovered" organelle. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Oct;202(2):211–223. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90068-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brow D. A., Guthrie C. Spliceosomal RNA U6 is remarkably conserved from yeast to mammals. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):213–218. doi: 10.1038/334213a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Pepperkok R., Carvalho M. T., Lamond A. I. Transcription-dependent colocalization of the U1, U2, U4/U6, and U5 snRNPs in coiled bodies. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta B., Weiner A. M. Genetic evidence for base pairing between U2 and U6 snRNA in mammalian mRNA splicing. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):821–824. doi: 10.1038/352821a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabrizio P., Abelson J. Two domains of yeast U6 small nuclear RNA required for both steps of nuclear precursor messenger RNA splicing. Science. 1990 Oct 19;250(4979):404–409. doi: 10.1126/science.2145630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Maniatis T. Isolation of a complementary DNA that encodes the mammalian splicing factor SC35. Science. 1992 Apr 24;256(5056):535–538. doi: 10.1126/science.1373910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Zuo P., Manley J. L. Primary structure of the human splicing factor ASF reveals similarities with Drosophila regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):373–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90626-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabowski P. J., Seiler S. R., Sharp P. A. A multicomponent complex is involved in the splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):345–353. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80130-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Biochemical mechanisms of constitutive and regulated pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:559–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guthrie C. Messenger RNA splicing in yeast: clues to why the spliceosome is a ribonucleoprotein. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):157–163. doi: 10.1126/science.1853200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausner T. P., Giglio L. M., Weiner A. M. Evidence for base-pairing between mammalian U2 and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2146–2156. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Sharp P. A. Association of U2, U4, U5, and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins in a spliceosome-type complex in absence of precursor RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5459–5462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Conway G. C., Kozak D. Purification and characterization of pre-mRNA splicing factor SF2 from HeLa cells. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1158–1171. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Mayeda A., Kozak D., Binns G. Functional expression of cloned human splicing factor SF2: homology to RNA-binding proteins, U1 70K, and Drosophila splicing regulators. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):383–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90627-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Konarska M. M., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A. Spliceosome assembly involves the binding and release of U4 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):411–415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Bordonné R., Guthrie C. Multiple roles for U6 snRNA in the splicing pathway. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12B):2264–2277. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12b.2264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madhani H. D., Guthrie C. A novel base-pairing interaction between U2 and U6 snRNAs suggests a mechanism for the catalytic activation of the spliceosome. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):803–817. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90556-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayeda A., Zahler A. M., Krainer A. R., Roth M. B. Two members of a conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins are involved in pre-mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1301–1304. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Appel B., Digweed M., Lührmann R. Localization of a base-paired interaction between small nuclear RNAs U4 and U6 in intact U4/U6 ribonucleoprotein particles by psoralen cross-linking. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 20;185(4):721–731. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson B. L., Cote G. J., Berget S. M. Exon definition may facilitate splice site selection in RNAs with multiple exons. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):84–94. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. B., Zahler A. M., Stolk J. A. A conserved family of nuclear phosphoproteins localized to sites of polymerase II transcription. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(3):587–596. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.3.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D. Trans splicing of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):157–164. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spann P., Feinerman M., Sperling J., Sperling R. Isolation and visualization of large compact ribonucleoprotein particles of specific nuclear RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):466–470. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperling R., Spann P., Offen D., Sperling J. U1, U2, and U6 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) are associated with large nuclear RNP particles containing transcripts of an amplified gene in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6721–6725. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vankan P., McGuigan C., Mattaj I. W. Roles of U4 and U6 snRNAs in the assembly of splicing complexes. EMBO J. 1992 Jan;11(1):335–343. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagatsuma M., Obinata M., Moroi Y., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. Detection of beta-globin mRNA precursor in heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein associated with U1-RNP by using anti-RNP antibody. J Biochem. 1985 Jun;97(6):1727–1735. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A. Psoralen crosslinking of small RNAs in vitro. Mol Biol Rep. 1993 Feb;17(2):143–151. doi: 10.1007/BF00996222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A., Steitz J. A. Interactions of small nuclear RNA's with precursor messenger RNA during in vitro splicing. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1918–1925. doi: 10.1126/science.1411506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman D. A., Steitz J. A. Structural analyses of the 7SK ribonucleoprotein (RNP), the most abundant human small RNP of unknown function. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3432–3445. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassarman K. M., Steitz J. A. The low-abundance U11 and U12 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs) interact to form a two-snRNP complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1276–1285. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J. A., Manley J. L. Base pairing between U2 and U6 snRNAs is necessary for splicing of a mammalian pre-mRNA. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):818–821. doi: 10.1038/352818a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Manley J. L. Multiple functional domains of human U2 small nuclear RNA: strengthening conserved stem I can block splicing. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5464–5473. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z. A., Murphy C., Callan H. G., Gall J. G. Small nuclear ribonucleoproteins and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins in the amphibian germinal vesicle: loops, spheres, and snurposomes. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):465–483. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yean S. L., Lin R. J. U4 small nuclear RNA dissociates from a yeast spliceosome and does not participate in the subsequent splicing reaction. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5571–5577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Lane W. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):837–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]