Abstract
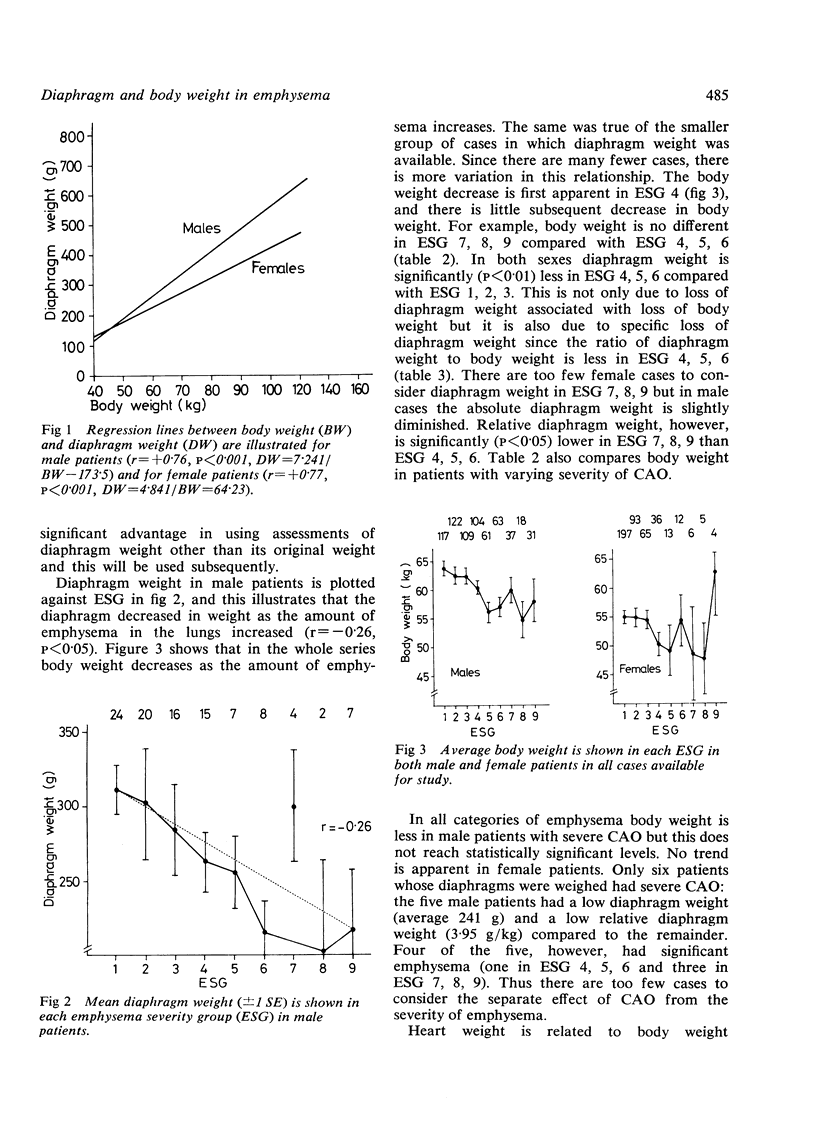
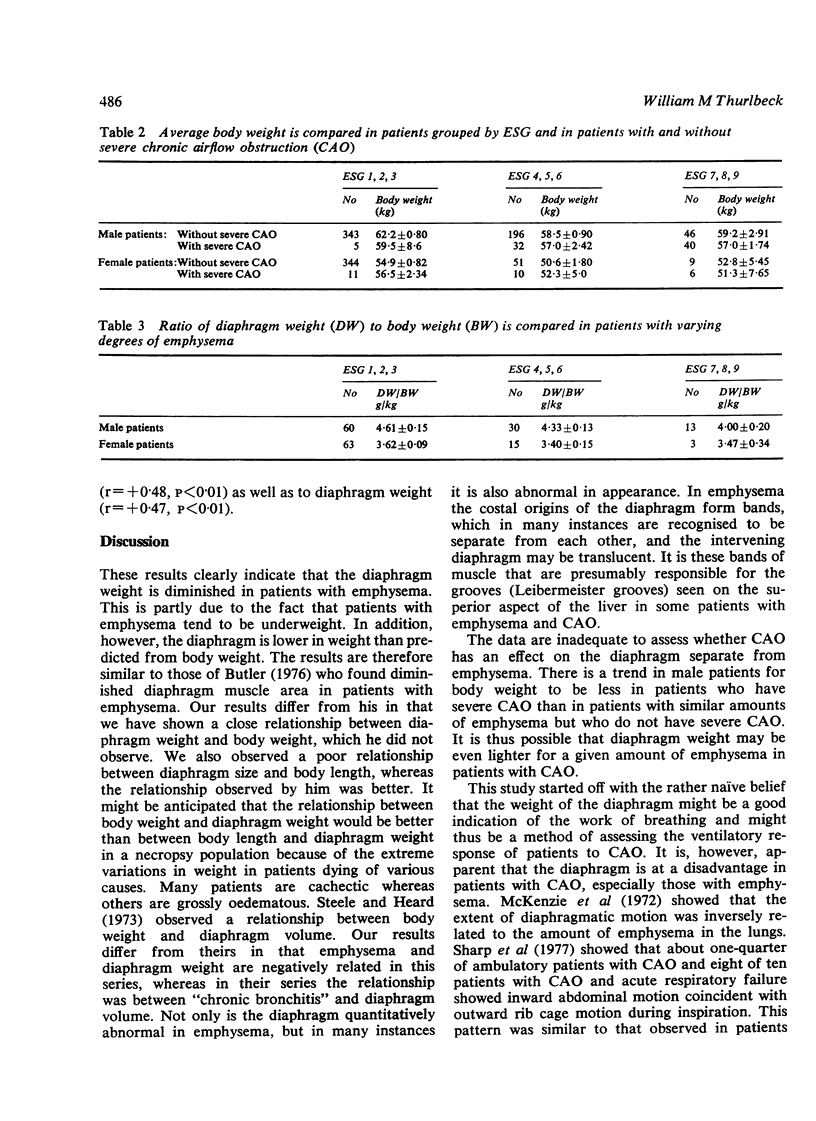
The weight of the diaphragm has been investigated in 103 male patients and 81 female patients, and the relationship between body weight and emphysema has been assessed in 662 male and 431 female patients. Diaphragm weight is related to body weight in both male (r = + 0.76) and female patients (r = +0.77) and is relatively larger in the former. Dissecting the diaphragm free of fat or freeze drying it does not appreciably improve the relationship between body weight and diaphragm weight. Diaphragm weight is better related to body weight than body length and is diminished in emphysema. Patients with emphysema weigh less. This is apparent with only moderate grades of emphysema, and there is no further loss of body weight as emphysema in the lung becomes more severe. The loss of diaphragm weight not only reflects the loss of body weight that occurs in emphysema, but the diaphragm is also less in weight than predicted from body weight. The diaphragm also appears abnormal on gross inspection in some patients with emphysema. Heart weight and diaphragm weight are related, probably because both are related to body weight.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashutosh K., Gilbert R., Auchincloss J. H., Jr, Peppi D. Asynchronous breathing movements in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Chest. 1975 May;67(5):553–557. doi: 10.1378/chest.67.5.553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler C. Diaphragmatic changes in emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Jul;114(1):155–159. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.114.1.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUGH J., WENTWORTH J. E. Thin sections of entire organs mounted on paper. Harvey Lect. 1957;53:182–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa S., Hayes J. A. Functional morphotometry of the diaphragm in patients with chronic obstructive lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1973 Jul;108(1):135–138. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1973.108.1.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenzie H. I., Outhred K. G., Glick M. Postmortem evaluation of the use of diaphragmatic excursus in assessment of pulmonary emphysema in coal miners. Thorax. 1972 May;27(3):359–364. doi: 10.1136/thx.27.3.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott K. W., Hoy J. The cross sectional area of diaphragmatic muscle fibres in emphysema, measured by an automated image analysis system. J Pathol. 1976 Oct;120(2):121–128. doi: 10.1002/path.1711200208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp J. T., Goldberg N. B., Druz W. S., Fishman H. C., Danon J. Thoracoabdominal motion in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977 Jan;115(1):47–56. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1977.115.1.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele R. H., Heard B. E. Size of the diaphragm in chronic bronchitis. Thorax. 1973 Jan;28(1):55–60. doi: 10.1136/thx.28.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M., Dunnill M. S., Hartung W., Heard B. E., Heppleston A. G., Ryder R. C. A comparison of three methods of measuring emphysema. Hum Pathol. 1970 Jun;1(2):215–226. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M., Simon G. Radiographic appearance of the chest in emphysema. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978 Mar;130(3):429–440. doi: 10.2214/ajr.130.3.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON N. L., WILSON R. H., FARBER S. M. NUTRITION IN PULMONARY EMPHYSEMA. J Am Diet Assoc. 1964 Dec;45:530–536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYATT J. P., FISCHER V. W., SWEET H. C. THE PATHOMORPHOLOGY OF THE EMPHYSEMA COMPLEX. II. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1964 May;89:721–735. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1964.89.5.721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


