Abstract
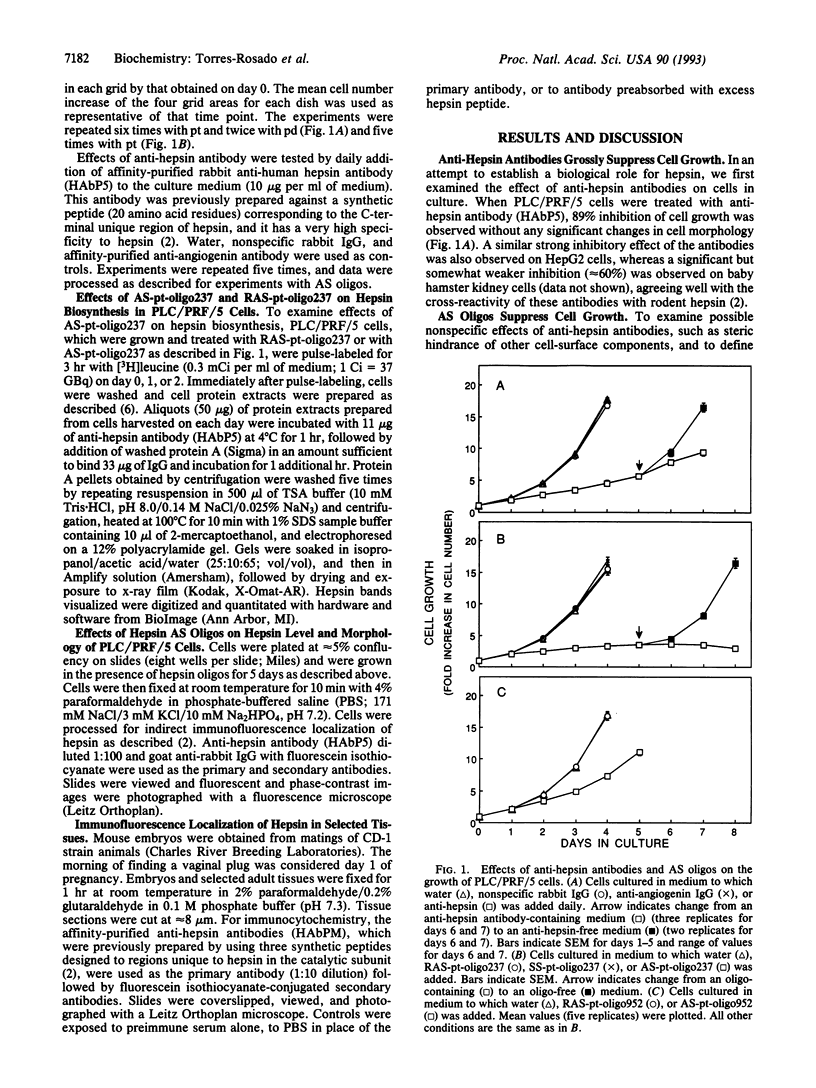
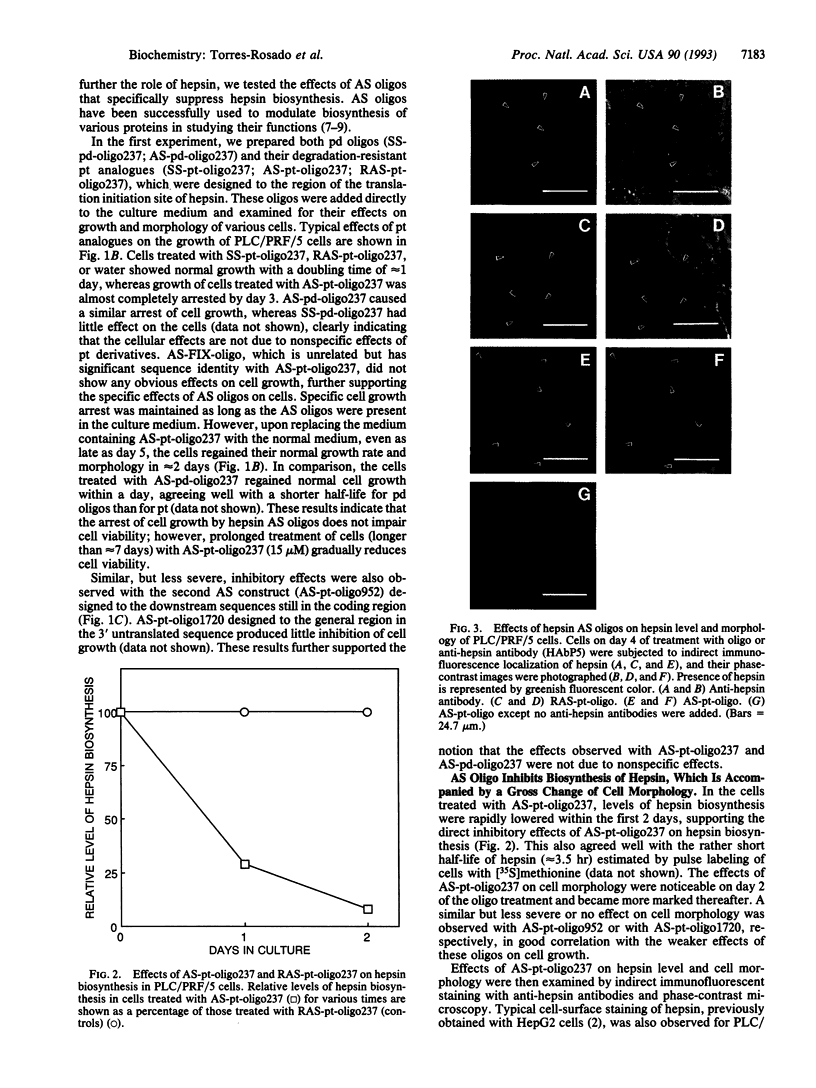
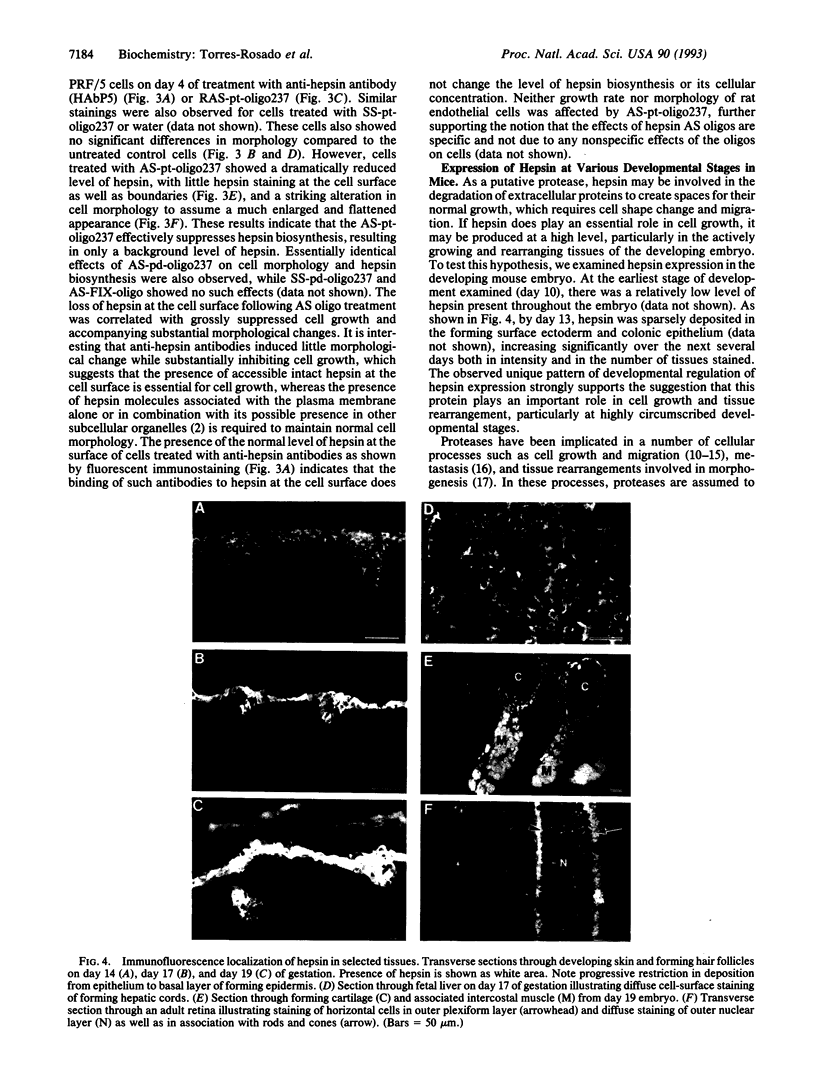
Hepsin was previously identified as a putative cell-surface serine protease. When hepatoma cells were treated with anti-hepsin antibodies, their growth was substantially arrested, suggesting the requirement of hepsin molecules present at the cell surface for normal cell growth. This was further supported by a gross inhibition of cell growth with hepsin-specific antisense oligonucleotides. Upon treatment of cells with antisense oligonucleotides, rapid reduction in cellular hepsin was observed. This reduction in cellular hepsin levels was accompanied by drastic morphological changes. Various tissues in the developing mouse embryo showed greatly elevated hepsin levels in regions of active proliferation. These results indicate that hepsin plays an essential role in cell growth and maintenance of cell morphology.
Full text
PDF

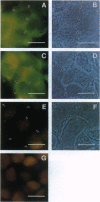
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aoyama A., Chen W. T. A 170-kDa membrane-bound protease is associated with the expression of invasiveness by human malignant melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8296–8300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond J. S. Plasma membrane proteases: introductory remarks. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1991;50(4-6):775–780. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. M., Chen W. T. Fibronectin-degrading proteases from the membranes of transformed cells. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):193–203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90423-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delmas B., Gelfi J., L'Haridon R., Vogel L. K., Sjöström H., Norén O., Laude H. Aminopeptidase N is a major receptor for the entero-pathogenic coronavirus TGEV. Nature. 1992 Jun 4;357(6377):417–420. doi: 10.1038/357417a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido H., Fukutomi A., Katunuma N. A novel membrane-bound serine esterase in human T4(+)-lymphocytes is a binding protein of envelope glycoprotein gp120 of HIV-1. Biomed Biochim Acta. 1991;50(4-6):781–789. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leytus S. P., Loeb K. R., Hagen F. S., Kurachi K., Davie E. W. A novel trypsin-like serine protease (hepsin) with a putative transmembrane domain expressed by human liver and hepatoma cells. Biochemistry. 1988 Feb 9;27(3):1067–1074. doi: 10.1021/bi00403a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacNab G. M., Alexander J. J., Lecatsas G., Bey E. M., Urbanowicz J. M. Hepatitis B surface antigen produced by a human hepatoma cell line. Br J Cancer. 1976 Nov;34(5):509–515. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Stein C., Subasinghe C., Haldar S., Croce C. M., Yum S., Cohen J. Antisense-mediated inhibition of BCL2 protooncogene expression and leukemic cell growth and survival: comparisons of phosphodiester and phosphorothioate oligodeoxynucleotides. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 15;50(20):6565–6570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh M., Yokosawa H., Ishii S. Membrane-bound trypsin-like enzyme functioning in degradation of dynorphin in neuroblastoma cells. Purification and characterization. J Biochem. 1988 Mar;103(3):493–498. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott G. K., Seow H. F. Further evidence for a cell surface proteinase essential to the growth of cultured fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1985 May;158(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90429-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott G. K., Seow H. F., Tse C. A. Investigations into the nature of growth-related proteolysis in human fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Feb 9;1010(2):160–165. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(89)90156-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein C. A., Cohen J. S. Oligodeoxynucleotides as inhibitors of gene expression: a review. Cancer Res. 1988 May 15;48(10):2659–2668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven F. S., Griffin M. M. Inhibitors of guanidinobenzoatase and their possible role in cell migration. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1988 May;369 (Suppl):137–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Nakamura T., Ichihara A. A unique trypsin-like protease associated with plasma membranes of rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2610–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji A., Torres-Rosado A., Arai T., Le Beau M. M., Lemons R. S., Chou S. H., Kurachi K. Hepsin, a cell membrane-associated protease. Characterization, tissue distribution, and gene localization. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16948–16953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valinsky J. E., Le Douarin N. M. Production of plasminogen activator by migrating cephalic neural crest cells. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1403–1406. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03793.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeager C. L., Ashmun R. A., Williams R. K., Cardellichio C. B., Shapiro L. H., Look A. T., Holmes K. V. Human aminopeptidase N is a receptor for human coronavirus 229E. Nature. 1992 Jun 4;357(6377):420–422. doi: 10.1038/357420a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitake S., Schach B. G., Foster D. C., Davie E. W., Kurachi K. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human factor IX (antihemophilic factor B). Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3736–3750. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]