Abstract
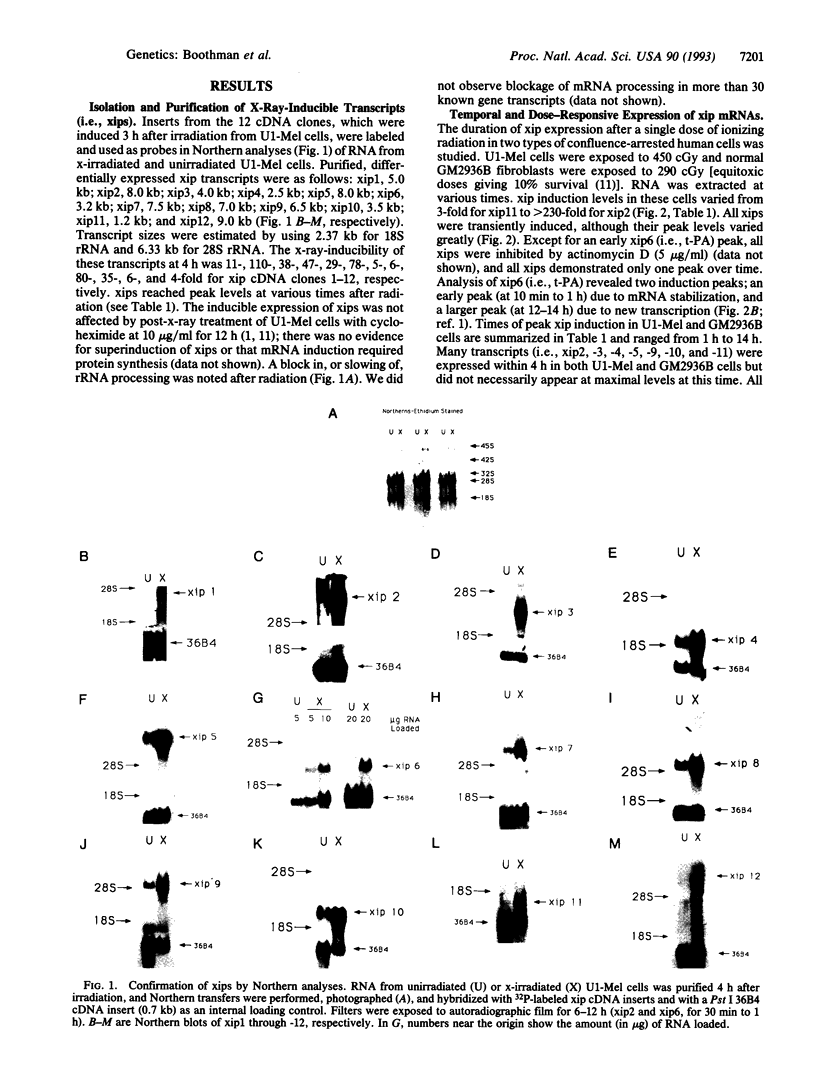
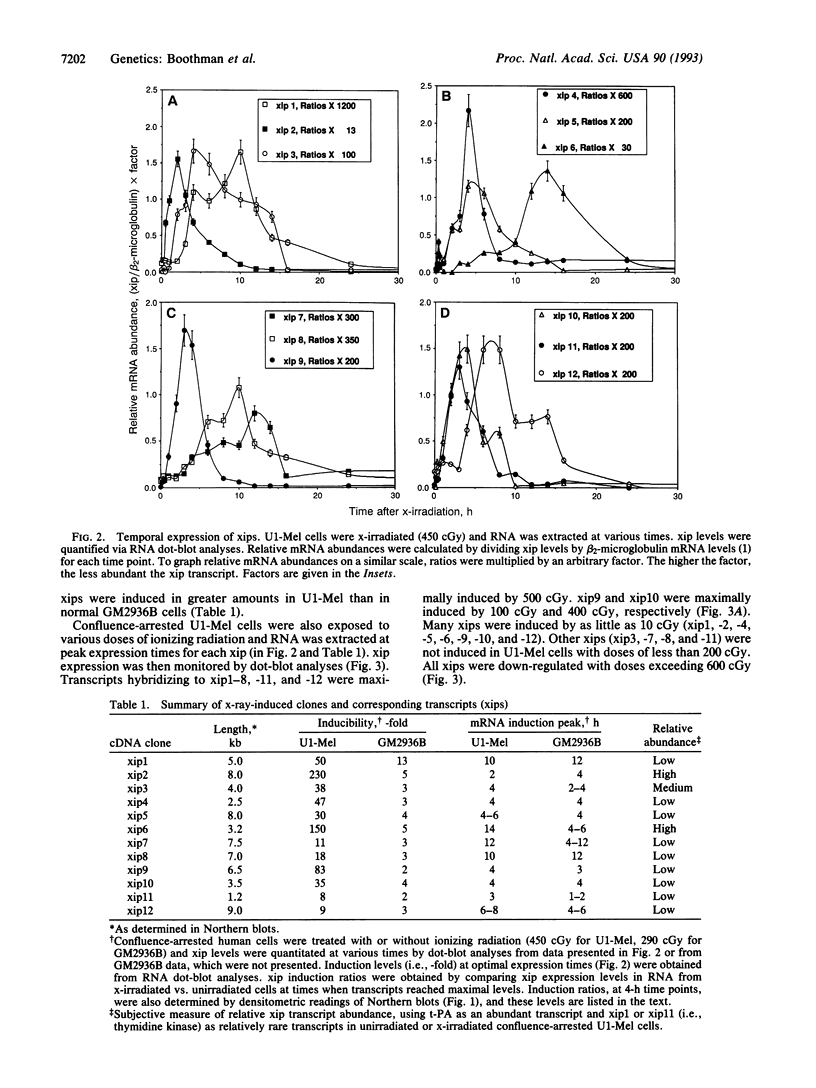
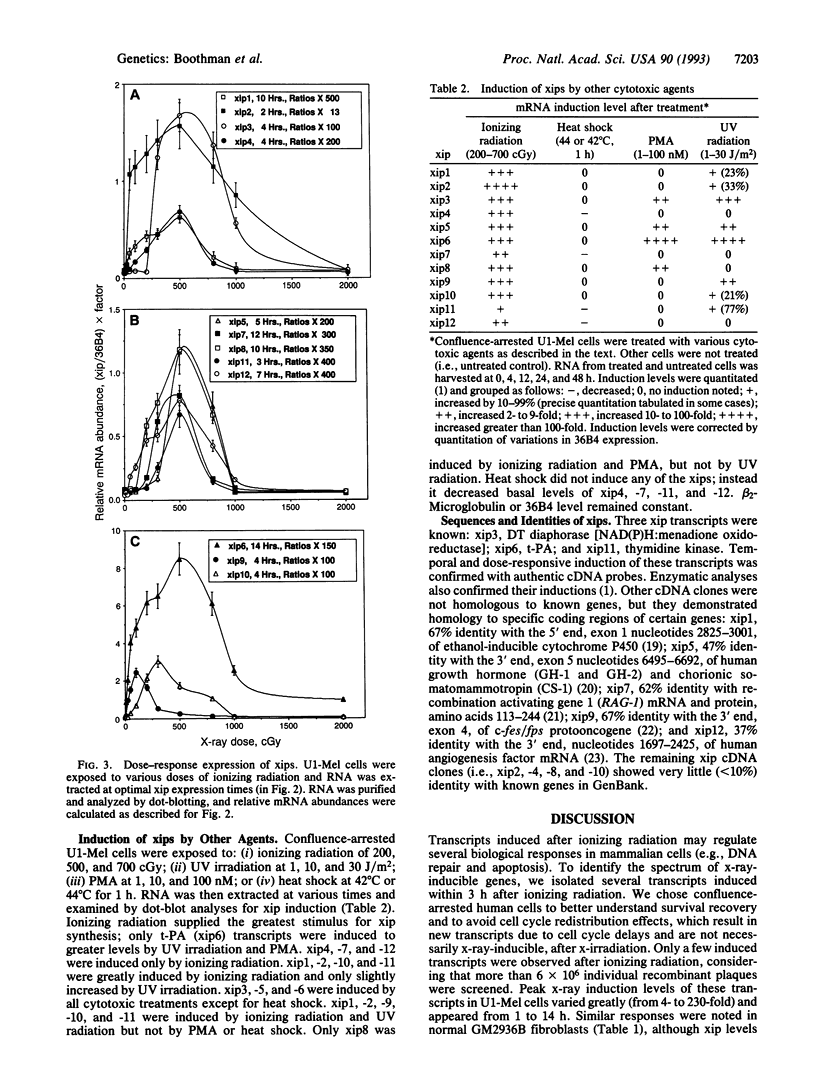
Twelve x-ray-induced transcripts (xips), differentially expressed 8- to 230-fold in x-irradiated versus unirradiated radioresistant human melanoma (U1-Mel) cells, were isolated as cDNA clones (xip1 through xip12) after four rounds of differential hybridization. Northern analyses revealed rare, medium, and abundant xips, ranging in size from 1.2 to 10 kb. All transcripts were transiently expressed and induced by low, but not by high (> 600 cGy), doses of radiation. Three transcripts (xip4, -7, and -12) were induced only by ionizing radiation, and many (i.e., xip1, -2, -3, -5, -6, -8, -9, -10, and -11) were also induced by UV irradiation or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. Heat shock did not induce any of the xips, but it decreased basal levels of xip4, -7, -11, and -12. Three xip cDNA clones were identified as encoding thymidine kinase, DT diaphorase, and tissue-type plasminogen activator. The remaining nine cDNA clones showed little homology to known genes. Three clones contained regions homologous to c-fes/fps protooncogene, recombination activating gene 1, or the human angiogenesis factor gene. X-ray-inducible genes may function in damaged cells to regulate DNA repair, apoptosis, mutagenesis, and carcinogenesis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bicher H. I., Hetzel F. W., Sandhu T. S. Results of a phase I/II clinical trial of fractionated hyperthermia in combination with low dose ionizing radiation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1982;157:87–97. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4388-2_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedermann K. A., Sun J. R., Giaccia A. J., Tosto L. M., Brown J. M. scid mutation in mice confers hypersensitivity to ionizing radiation and a deficiency in DNA double-strand break repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1394–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothman D. A., Bouvard I., Hughes E. N. Identification and characterization of X-ray-induced proteins in human cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jun 1;49(11):2871–2878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothman D. A., Wang M., Lee S. W. Induction of tissue-type plasminogen activator by ionizing radiation in human malignant melanoma cells. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 15;51(20):5587–5595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Liao Y. C., Smith D. H., Barrera-Saldaña H. A., Gelinas R. E., Seeburg P. H. The human growth hormone locus: nucleotide sequence, biology, and evolution. Genomics. 1989 May;4(4):479–497. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90271-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Mitchell J. B. Induction of B2 RNA polymerase III transcription by heat shock: enrichment for heat shock induced sequences in rodent cells by hybridization subtraction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5793–5811. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaga N., Burrows H. L., Meyers M., Schea R. A., Boothman D. A. Enhanced induction of tissue-type plasminogen activator in normal human cells compared to cancer-prone cells following ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1992;24(5):949–957. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(92)90479-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimovitz-Friedman A., Vlodavsky I., Chaudhuri A., Witte L., Fuks Z. Autocrine effects of fibroblast growth factor in repair of radiation damage in endothelial cells. Cancer Res. 1991 May 15;51(10):2552–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallahan D. E., Sukhatme V. P., Sherman M. L., Virudachalam S., Kufe D., Weichselbaum R. R. Protein kinase C mediates x-ray inducibility of nuclear signal transducers EGR1 and JUN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2156–2160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollander M. C., Fornace A. J., Jr Estimation of relative mRNA content by filter hybridization to a polythymidylate probe. Biotechniques. 1990 Aug;9(2):174–179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W., Strydom D. J., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Sequence of the cDNA and gene for angiogenin, a human angiogenesis factor. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5494–5499. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert M., Borek C. X-ray-induced changes in gene expression in normal and oncogene-transformed rat cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Nov 16;80(18):1492–1497. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.18.1492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. W., Tomasetto C., Sager R. Positive selection of candidate tumor-suppressor genes by subtractive hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2825–2829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masiakowski P., Breathnach R., Bloch J., Gannon F., Krust A., Chambon P. Cloning of cDNA sequences of hormone-regulated genes from the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):7895–7903. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.7895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel R. J., Zhang H. B., Iliakis G., McKenna W. G. Cyclin B expression in HeLa cells during the G2 block induced by ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 1;51(19):5113–5117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oettinger M. A., Schatz D. G., Gorka C., Baltimore D. RAG-1 and RAG-2, adjacent genes that synergistically activate V(D)J recombination. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1517–1523. doi: 10.1126/science.2360047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebroek A. J., Schalken J. A., Verbeek J. S., Van den Ouweland A. M., Onnekink C., Bloemers H. P., Van de Ven W. J. The structure of the human c-fes/fps proto-oncogene. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2897–2903. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04020.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shadley J. D., Afzal V., Wolff S. Characterization of the adaptive response to ionizing radiation induced by low doses of X rays to human lymphocytes. Radiat Res. 1987 Sep;111(3):511–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman M. L., Datta R., Hallahan D. E., Weichselbaum R. R., Kufe D. W. Ionizing radiation regulates expression of the c-jun protooncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5663–5666. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umeno M., McBride O. W., Yang C. S., Gelboin H. V., Gonzalez F. J. Human ethanol-inducible P450IIE1: complete gene sequence, promoter characterization, chromosome mapping, and cDNA-directed expression. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 13;27(25):9006–9013. doi: 10.1021/bi00425a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woloschak G. E., Chang-Liu C. M., Jones P. S., Jones C. A. Modulation of gene expression in Syrian hamster embryo cells following ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 1990 Jan 15;50(2):339–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




