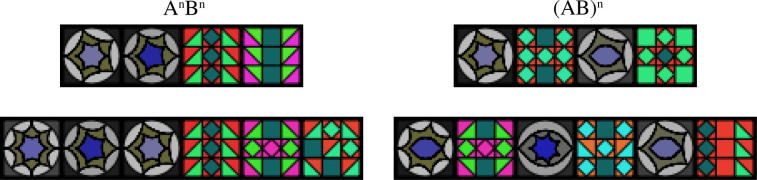
Fig. 1.
Example of training patterns. Top: an AABB (equivalent to A2B2, left) and ABAB (equivalent to (AB)2, right) pattern; bottom: same patterns for n = 3. During the training, birds were simultaneously presented with an AnBn and an (AB)n stimulus (with n = 2 or 3) and were rewarded for pecking on one of them, depending on the experimental group to which they were randomly assigned.