Abstract
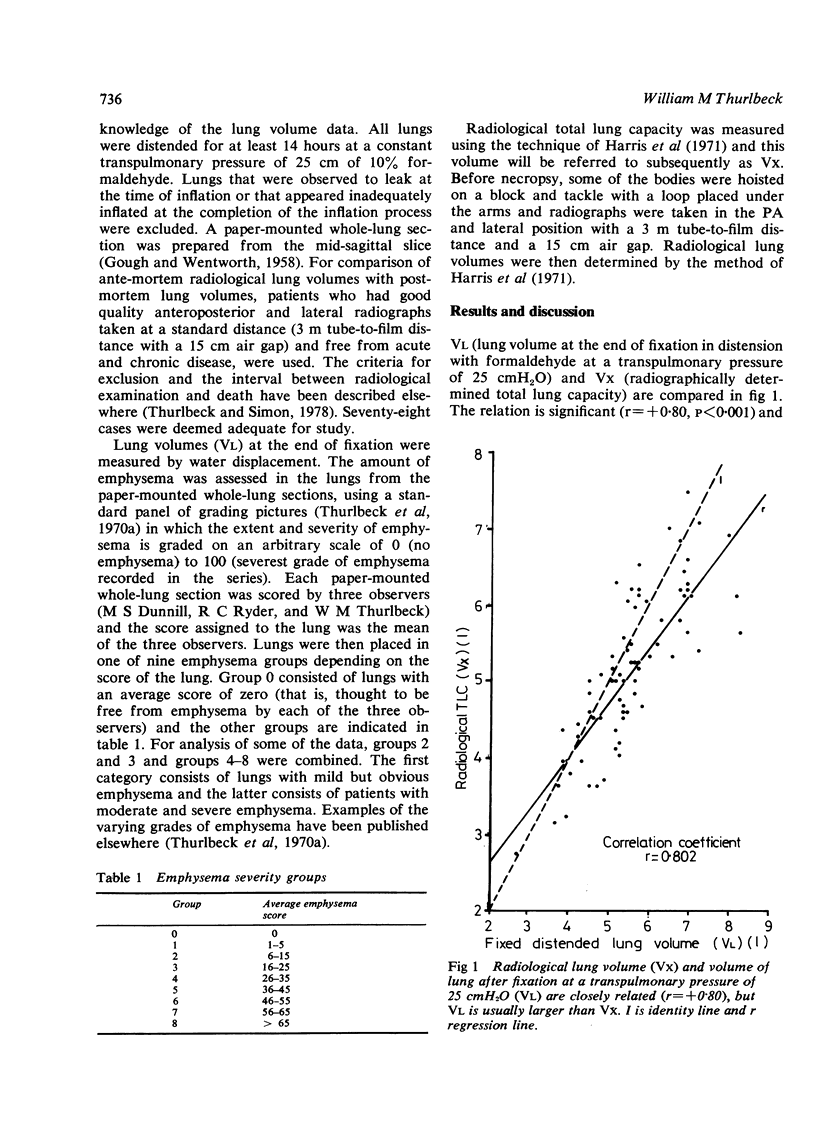
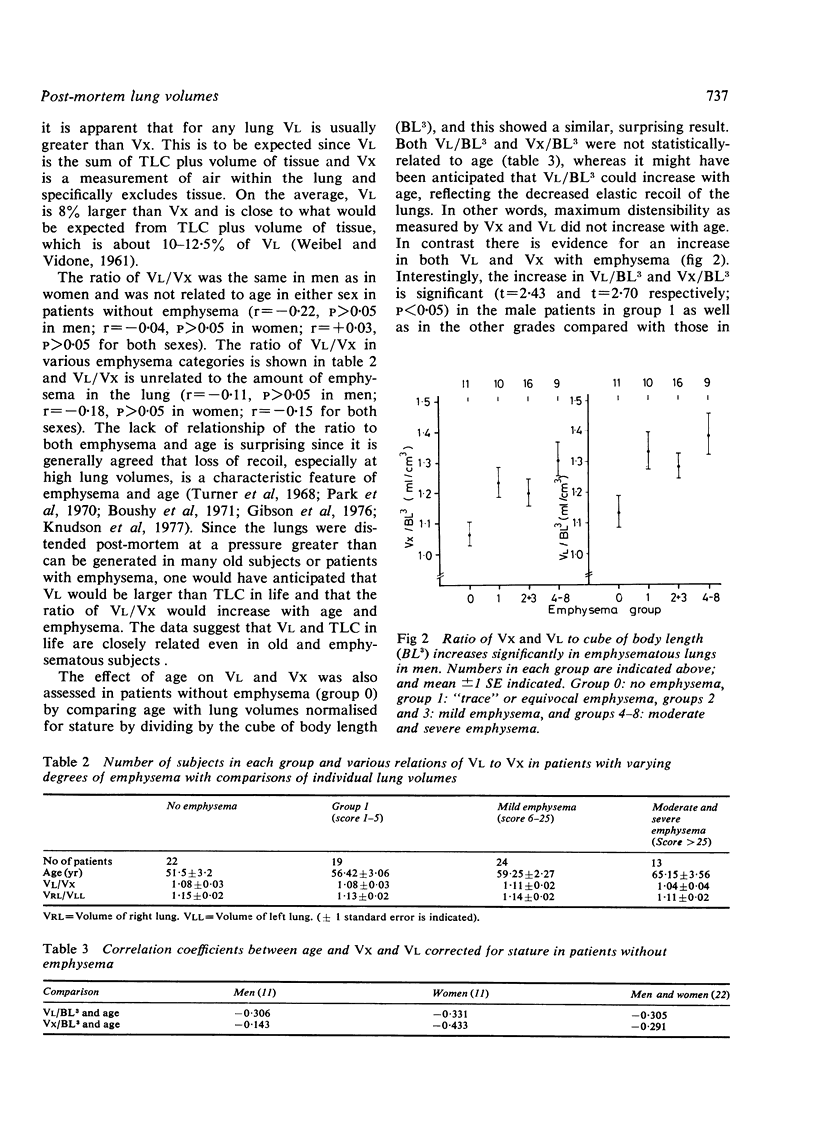
The volumes of 78 adult human lungs at necropsy after fixation with intrabronchial 10% formaldehyde at a transpulmonary pressure of 25 cm of water (VL) were similar to their total lung capacity (TLC) as assessed radiologically (VX). Corrected for stature, VL and VX did not increase with age in non-emphsematous lungs, nor did the radio of VL to VX (VL/VX) change with age. VL and VX relative to body length increased with emphysema, and the increase even occurred in lungs from men with trivial or equivocal amounts of emphysema. Thus alteration of the mechanical properties of the lung may precede the appearance of obvious emphysema. VL/VX was not affected by the presence or severity of emphysema. The right lung formed 53% of VL with a range of 49-58% in apparently normal lungs. The amount of air in 13 human lungs at necropsy averaged 61% of TLC with a wide variation, indicating that this is not a useful point at which to measure lung dimensions. It is concluded that the volume of lungs fixed with formaldehyde at a transpulmonary pressure of 25 cmH2O closely approximates to total lung capacity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boushy S. F., Aboumrad M. H., North L. B., Helgason A. H. Lung recoil pressure, airway resistance, and forced flows related to morphologic emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Oct;104(4):551–561. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.104.4.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukaya H., Martin C. J. Lung tissue shrinkage for histologic preparations. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Jun;99(6):946–948. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.6.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUGH J., WENTWORTH J. E. Thin sections of entire organs mounted on paper. Harvey Lect. 1957;53:182–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson G. J., Pride N. B., O'cain C., Quagliato R. Sex and age differences in pulmonary mechanics in normal nonsmoking subjects. J Appl Physiol. 1976 Jul;41(1):20–25. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1976.41.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEARD B. E. Pathology of pulmonary emphysema. Methods of study. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1960 Dec;82:792–799. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1960.82.6.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris T. R., Pratt P. C., Kilburn K. H. Total lung capacity measured by roentgenograms. Am J Med. 1971 Jun;50(6):756–763. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(71)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudson R. J., Clark D. F., Kennedy T. C., Knudson D. E. Effect of aging alone on mechanical properties of the normal adult human lung. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Dec;43(6):1054–1062. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.43.6.1054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEOPOLD J. G., GOUGH J. The centrilobular form of hypertrophic emphysema and its relation to chronic bronchitis. Thorax. 1957 Sep;12(3):219–235. doi: 10.1136/thx.12.3.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLEAN K. H. The macroscopic anatomy of pulmonary emphysema. Australas Ann Med. 1956 May;5(2):73–88. doi: 10.1111/imj.1956.5.2.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park S. S., Janis M., Shim C. S., Williams M. H., Jr Relationship of bronchitis and emphysema to altered pulmonary function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1970 Dec;102(6):927–936. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1970.102.6.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder R. C., Thurlbeck WM GOUGH J. A study of interobserver variation in the assessment of the amount of pulmonary emphysema in paper-mounted whole lung sections. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Mar;99(3):354–364. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.3.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M., Dunnill M. S., Hartung W., Heard B. E., Heppleston A. G., Ryder R. C. A comparison of three methods of measuring emphysema. Hum Pathol. 1970 Jun;1(2):215–226. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M., Horowitz I., Siemiatycki J., Dunnill M. S., Maisel J. C., Pratt P., Ryder R. Intra- and inter-observer variations in the assessment of emphysema. Arch Environ Health. 1969 Apr;18(4):646–659. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1969.10665467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M. Internal surface area and other measurements in emphysema. Thorax. 1967 Nov;22(6):483–496. doi: 10.1136/thx.22.6.483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thurlbeck W. M., Simon G. Radiographic appearance of the chest in emphysema. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1978 Mar;130(3):429–440. doi: 10.2214/ajr.130.3.429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner J. M., Mead J., Wohl M. E. Elasticity of human lungs in relation to age. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Dec;25(6):664–671. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.25.6.664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIBEL E. R., VIDONE R. A. Fixation of the lung by formalin steam in a controlled state of air inflation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 Dec;84:856–861. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.84.6.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT R. R. Elastic tissue of normal and emphysematous lungs. A tridimensional histologic study. Am J Pathol. 1961 Sep;39:355–367. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


