Abstract
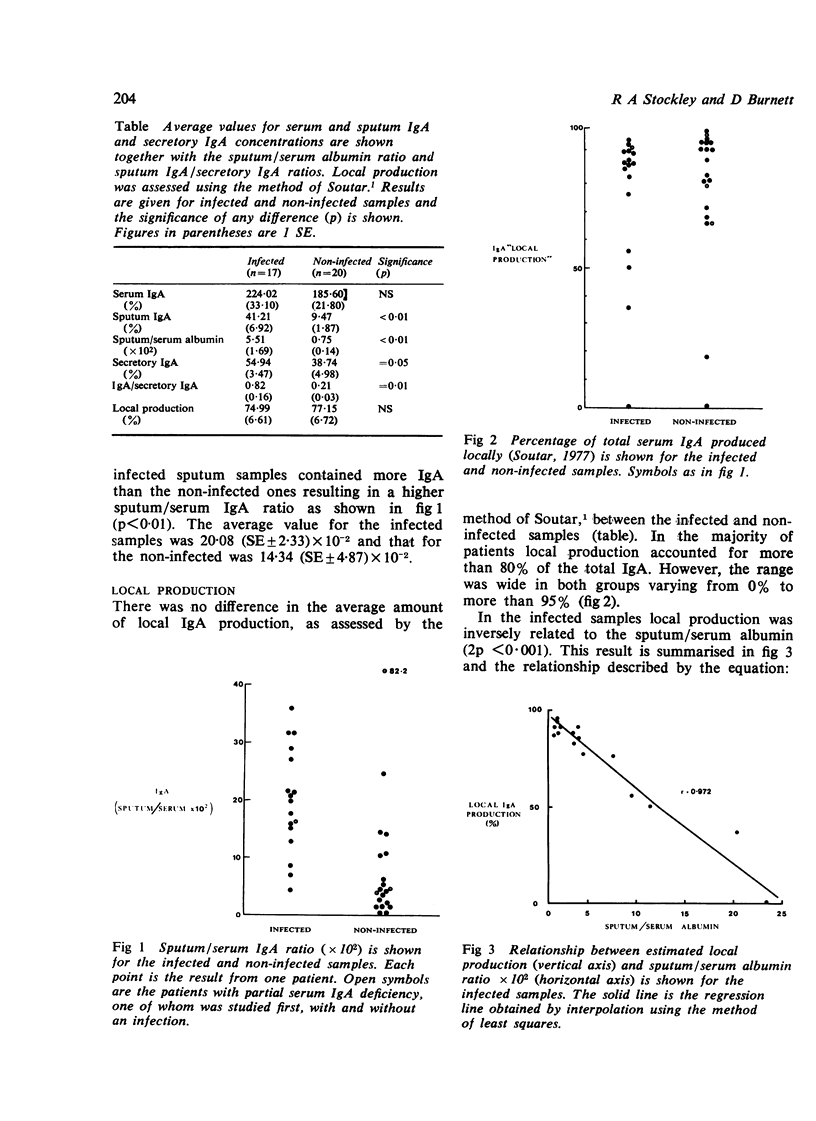
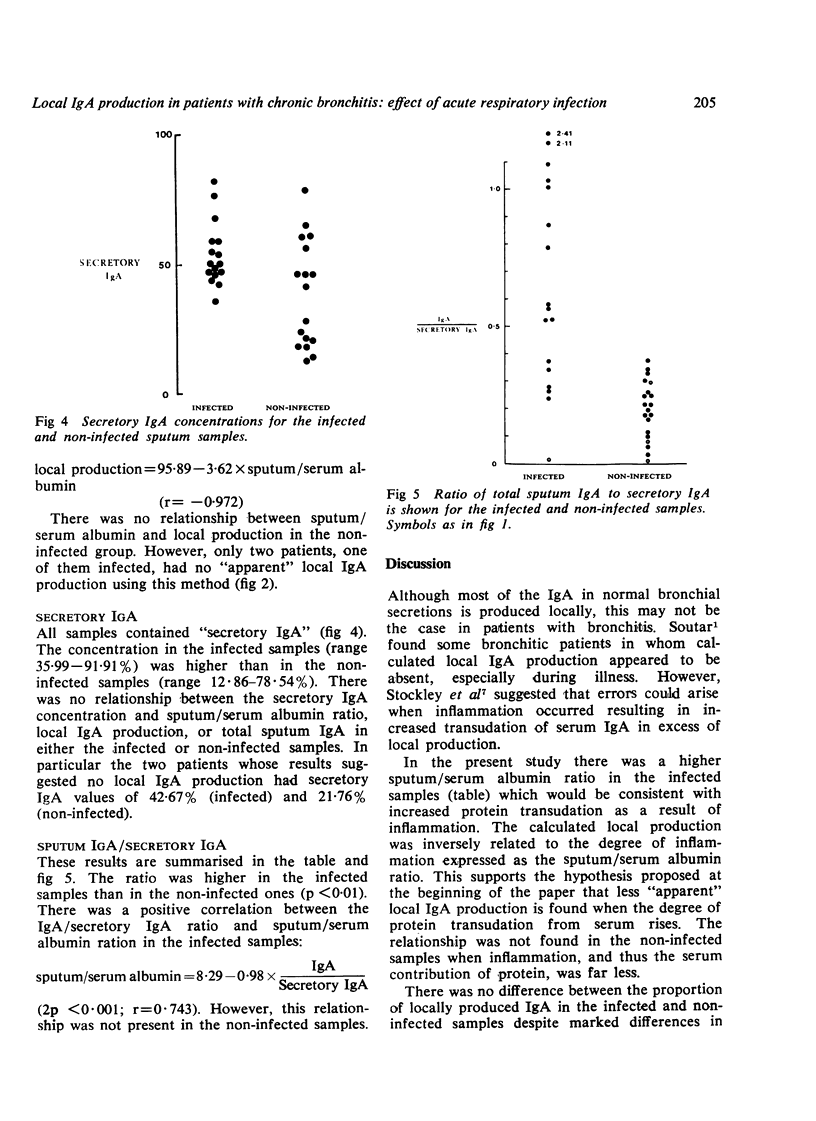
The immunoglobulin A and secretory IgA concentrations were studied in the serum and sputum of patients with chronic bronchitis to determine the effect of active chest infection and inflammation upon the estimation of local IgA production. The sputum/serum albumin ratio was higher during chest infection (5.51; SE+/-1.60x10(-2)) than in the non-infected samples (0.75; SE+/-0.14x10(-2);p less than 0.01) suggesting increased transudation as a result of inflammation. There was a similar increase in sputum/serum IgA during infection from 9.47 (SE+/-1.87)x10(-2) to 41.21 (SE+/-6.92)x10(-2)(p less than 0.01). However, the proportion of IgA locally produced when assessed by conventional techniques was unchanged. There was a significant inverse relationship between the estimated local IgA production of the infected samples and the degree of inflammation (r= -0.972;2p less than 0.001) indicating that inflammation was a major determinant of local IgA production. However, the secretory IgA concentrations of the samples were independent of the degree of inflammation. Furthermore, secretory IgA was found in samples that appeared to have failure of local IgA production using the method of Soutar. Clearer information about local IgA production can be obtained by measuring protein components unique to the bronchial secretions rather than applying correction factors to estimate the contribution of serum components, particularly in the presence of inflammation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradwell A. R., Burnett D., Ramsden D. B., Burr W. A., Prince H. P., Hoffenberg R. Preparation of a monospecific antiserum to thyroxine binding globulin for its quantitation by rocket immunoelectrophoresis. Clin Chim Acta. 1976 Sep 20;71(3):501–510. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(76)90102-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipps B. E., Talamo R. C., Winkelstein J. A. IgA deficiency, recurrent pneumonias, and bronchiectasis. Chest. 1978 Apr;73(4):519–526. doi: 10.1378/chest.73.4.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke C. W. Aspects of serum and sputum antibody in chronic airways obstruction. Thorax. 1976 Dec;31(6):702–707. doi: 10.1136/thx.31.6.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschl H., Johansson S. G. Immunoglobulins in tracheo-bronchial secretion with special reference to IgE. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Mar;16(3):401–412. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltreider H. B. Expression of immune mechanisms in the lung. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1976 Mar;113(3):347–379. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1976.113.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medici T. C., Buergi H. The role of immunoglobulin A in endogenous bronchial defense mechanisms in chronic bronchitis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1971 Jun;103(6):784–791. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1971.103.6.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds H. Y., Newball H. H. Analysis of proteins and respiratory cells obtained from human lungs by bronchial lavage. J Lab Clin Med. 1974 Oct;84(4):559–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soutar C. A. Distribution of plasma cells and other cells containing immunoglobulin in the respiratory tract in chronic bronchitis. Thorax. 1977 Aug;32(4):387–396. doi: 10.1136/thx.32.4.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockley R. A., Mistry M., Bradwell A. R., Burnett D. A study of plasma proteins in the sol phase of sputum from patients with chronic bronchitis. Thorax. 1979 Dec;34(6):777–782. doi: 10.1136/thx.34.6.777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


