Abstract
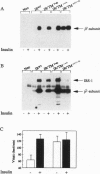
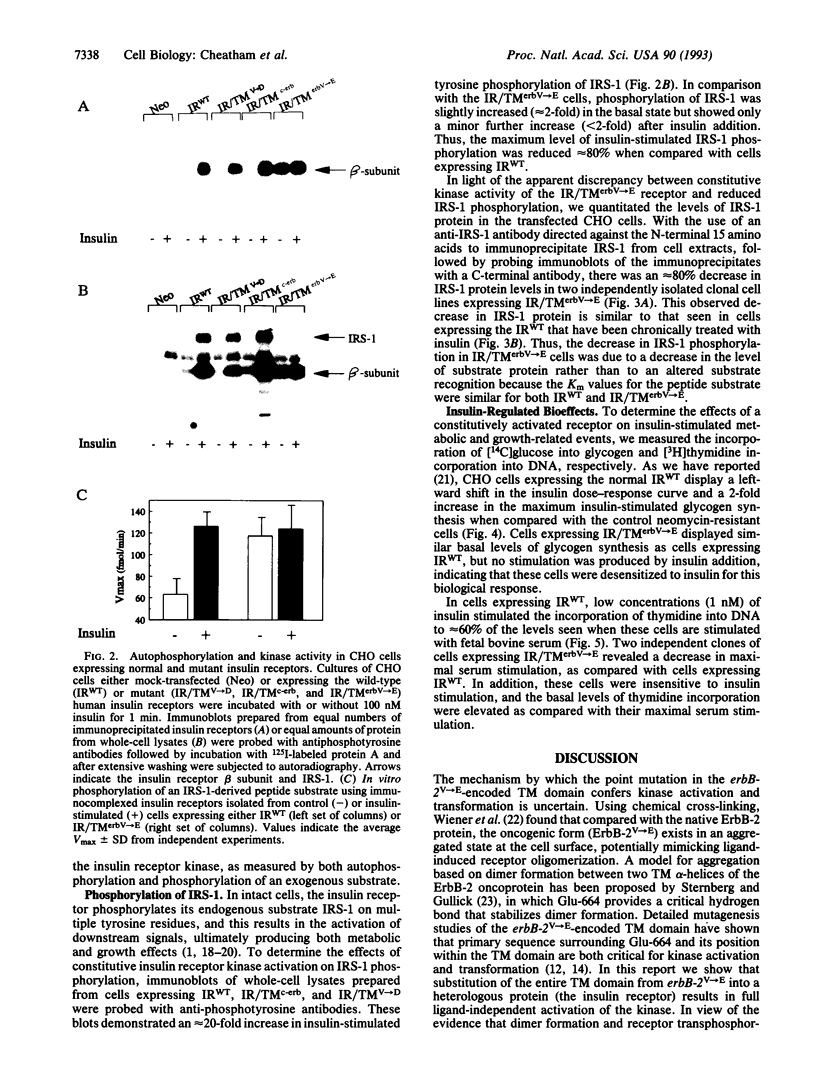
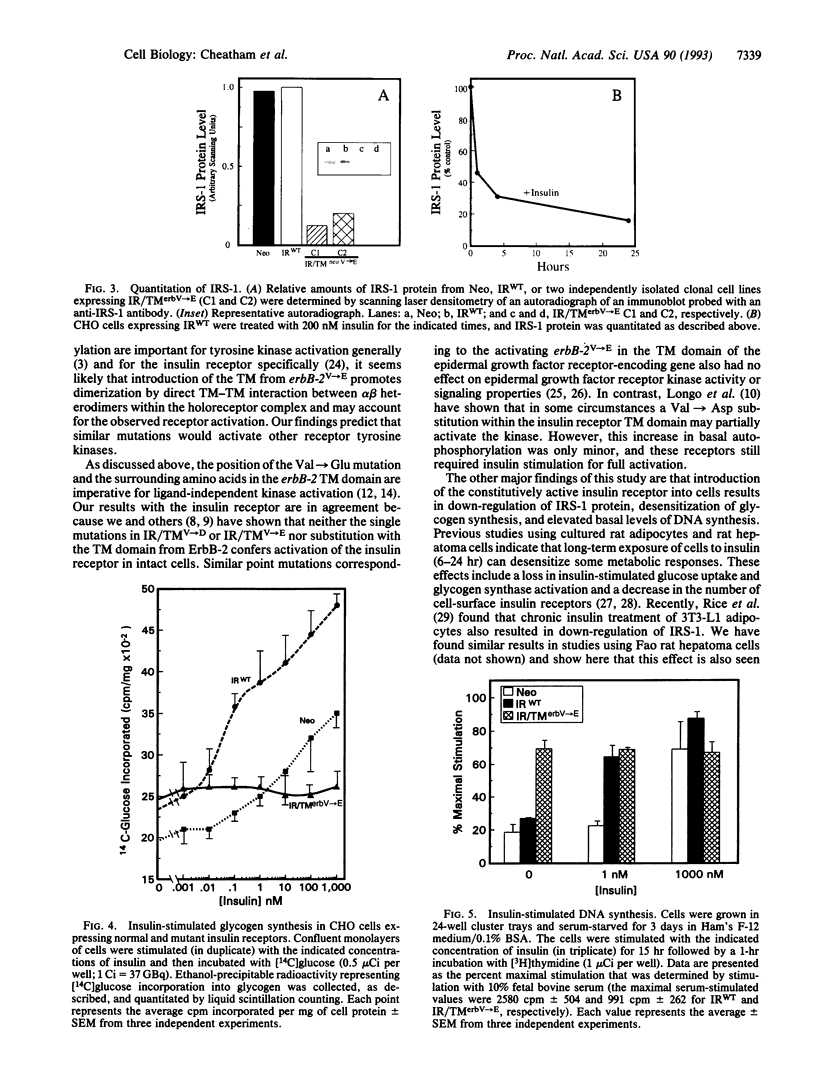
The mechanism through which insulin binding to the extracellular domain of the insulin receptor activates the intrinsic tyrosine kinase in the intracellular domain of the protein is unknown. For the c-neu/erbB-2 (c-erbB-2) protooncogene, a single point mutation within the transmembrane (TM) domain converting Val-664 to Glu (erbB-2V-->E) results in elevated levels of tyrosine kinase activity and cellular transformation. We report the construction of a chimeric insulin receptor in which the TM domain of the receptor has been substituted with that encoded by erbB-2V-->E. When expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells this chimeric receptor displays maximal levels of autophosphorylation and kinase activity in the absence of insulin. This activity results in an increase in the level of insulin-receptor substrate 1 phosphorylation but a down-regulation in insulin-receptor substrate 1 protein and desensitization to insulin stimulation of glycogen synthesis. By contrast, basal levels of DNA synthesis are elevated to levels approximately 60% of those observed in serum-stimulated cells. Over-expression of chimeric insulin receptors containing the c-erbB-2 TM domain or a single point mutation in the insulin receptor TM domain of Val-938-->Asp, on the other hand, shows none of these alterations. Thus, the TM domain encoded by erbB-2V-->E contains structural features that can confer ligand-independent activation in a heterologous protein. Constitutive activation of the insulin receptor results in a relative increase in basal levels of DNA synthesis, but an apparent resistance to the metabolic effects of insulin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Matsuda S., Namba Y., Saito T., Toyoshima K., Yamamoto T. The transforming potential of the c-erbB-2 protein is regulated by its autophosphorylation at the carboxyl-terminal domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):833–842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backer J. M., Myers M. G., Jr, Shoelson S. E., Chin D. J., Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Hu P., Margolis B., Skolnik E. Y., Schlessinger J. Phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase is activated by association with IRS-1 during insulin stimulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3469–3479. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Hung M. C., Weinberg R. A. Multiple independent activations of the neu oncogene by a point mutation altering the transmembrane domain of p185. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90779-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A. Oncogenic activation of the neu-encoded receptor protein by point mutation and deletion. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2043–2052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03044.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao H., Bangalore L., Bormann B. J., Stern D. F. A subdomain in the transmembrane domain is necessary for p185neu* activation. EMBO J. 1992 Mar;11(3):923–932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. D., Ingraham H. A., Cochet C., Walton G. M., Lazar C. S., Sowadski J. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Gill G. N. Structural analysis of the transmembrane domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5750–5755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheatham B., Kahn C. R. Cysteine 647 in the insulin receptor is required for normal covalent interaction between alpha- and beta-subunits and signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7108–7115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Kashles O., Chambaz E. M., Borrello I., King C. R., Schlessinger J. Demonstration of epidermal growth factor-induced receptor dimerization in living cells using a chemical covalent cross-linking agent. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3290–3295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Insulin receptor regulation and desensitization in rat hepatoma cells. Concomitant changes in receptor number and in binding affinity. Diabetes. 1984 May;33(5):477–485. doi: 10.2337/diab.33.5.477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frattali A. L., Treadway J. L., Pessin J. E. Evidence supporting a passive role for the insulin receptor transmembrane domain in insulin-dependent signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9829–9834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frattali A. L., Treadway J. L., Pessin J. E. Transmembrane signaling by the human insulin receptor kinase. Relationship between intramolecular beta subunit trans- and cis-autophosphorylation and substrate kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19521–19528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Olefsky J. M., Marshall S. Insulin induces progressive insulin resistance in cultured rat adipocytes. Sequential effects at receptor and multiple postreceptor sites. Diabetes. 1986 Mar;35(3):258–267. doi: 10.2337/diab.35.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammacher A., Mellström K., Heldin C. H., Westermark B. Isoform-specific induction of actin reorganization by platelet-derived growth factor suggests that the functionally active receptor is a dimer. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2489–2495. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., White M. F. The insulin receptor and the molecular mechanism of insulin action. J Clin Invest. 1988 Oct;82(4):1151–1156. doi: 10.1172/JCI113711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashles O., Szapary D., Bellot F., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Schmidt A. Ligand-induced stimulation of epidermal growth factor receptor mutants with altered transmembrane regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9567–9571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longo N., Shuster R. C., Griffin L. D., Langley S. D., Elsas L. J. Activation of insulin receptor signaling by a single amino acid substitution in the transmembrane domain. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12416–12419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice K. M., Lienhard G. E., Garner C. W. Regulation of the expression of pp160, a putative insulin receptor signal protein, by insulin, dexamethasone, and 1-methyl-3-isobutylxanthine in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10163–10167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M. After insulin binds. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1452–1458. doi: 10.1126/science.2442814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg P. L., Lane W. S., Karasik A., Backer J., White M., Kahn C. R. Purification and partial sequence analysis of pp185, the major cellular substrate of the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8302–8311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifert R. A., Hart C. E., Phillips P. E., Forstrom J. W., Ross R., Murray M. J., Bowen-Pope D. F. Two different subunits associate to create isoform-specific platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8771–8778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson S. E., Chatterjee S., Chaudhuri M., White M. F. YMXM motifs of IRS-1 define substrate specificity of the insulin receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2027–2031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg M. J., Gullick W. J. Neu receptor dimerization. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):587–587. doi: 10.1038/339587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Miralpeix M., Myers M. G., Jr, Glasheen E. M., Backer J. M., Kahn C. R., White M. F. Expression and function of IRS-1 in insulin signal transmission. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22662–22672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. J., Rothenberg P., Kahn C. R., Backer J. M., Araki E., Wilden P. A., Cahill D. A., Goldstein B. J., White M. F. Structure of the insulin receptor substrate IRS-1 defines a unique signal transduction protein. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):73–77. doi: 10.1038/352073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner D. B., Liu J., Cohen J. A., Williams W. V., Greene M. I. A point mutation in the neu oncogene mimics ligand induction of receptor aggregation. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):230–231. doi: 10.1038/339230a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden P. A., Backer J. M., Kahn C. R., Cahill D. A., Schroeder G. J., White M. F. The insulin receptor with phenylalanine replacing tyrosine-1146 provides evidence for separate signals regulating cellular metabolism and growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3358–3362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Goncalves E., Kahn C. R., Shoelson S. E. Substitution of the insulin receptor transmembrane domain with the c-neu/erbB2 transmembrane domain constitutively activates the insulin receptor kinase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jun 25;267(18):12452–12461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1443–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]