Abstract
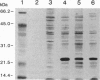
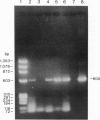
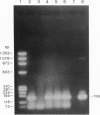
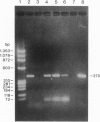
The isolation of the Lyme disease spirochete (Borrelia burgdorferi) from the southeastern United States is reported. Three isolates, two from cotton mice (Peromyscus gossypinus) and one from the black-legged tick (Ixodes scapularis), were recovered from Sapelo Island, Georgia, in July and September 1991. The spirochetes were characterized by indirect fluorescent antibody assay using a battery of five monoclonal antibodies, by sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS/PAGE) of whole cell lysates, and by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay using primers for three DNA target sequences found in B. burgdorferi reference strain B-31. Transmission experiments indicate that the three Georgia isolates can infect experimentally inoculated hamsters and mice. Tick transmission of one of the isolates has been attempted so far; I. scapularis transmitted isolate SI-1 from hamsters to mice, but the lone-star tick, Amblyomma americanum, did not.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G. Spirochetes in Ixodes dammini and mammals from Connecticut. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1983 Jul;32(4):818–824. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1983.32.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. F., Magnarelli L. A., McAninch J. B. New Borrelia burgdorferi antigenic variant isolated from Ixodes dammini from upstate New York. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Oct;26(10):2209–2212. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2209-2212.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G., Heiland R. A., Howe T. R. Heterogeneity of major proteins in Lyme disease borreliae: a molecular analysis of North American and European isolates. J Infect Dis. 1985 Sep;152(3):478–484. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.3.478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbour A. G. Immunochemical analysis of Lyme disease spirochetes. Yale J Biol Med. 1984 Jul-Aug;57(4):581–586. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Barbour A. G., Hayes S. F., Benach J. L., Grunwaldt E., Davis J. P. Lyme disease-a tick-borne spirochetosis? Science. 1982 Jun 18;216(4552):1317–1319. doi: 10.1126/science.7043737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgdorfer W., Gage K. L. Susceptibility of the black-legged tick, Ixodes scapularis, to the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):15–20. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80096-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson B. J., Happ C. M., Mayer L. W., Piesman J. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi in ticks by species-specific amplification of the flagellin gene. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Dec;47(6):730–741. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1992.47.730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Marek N., Kodner C. Infection of Syrian hamsters with Lyme disease spirochetes. J Clin Microbiol. 1984 Dec;20(6):1099–1101. doi: 10.1128/jcm.20.6.1099-1101.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow R. A. Current perspective on Lyme borreliosis. JAMA. 1992 Mar 11;267(10):1381–1383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurashige S., Bissett M., Oshiro L. Characterization of a tick isolate of Borrelia burgdorferi that possesses a major low-molecular-weight surface protein. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1362–1366. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1362-1366.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. S., Piesman J., Burgdorfer W. Lyme borreliosis: relation of its causative agent to its vectors and hosts in North America and Europe. Annu Rev Entomol. 1991;36:587–609. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.36.010191.003103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckhart S., Mullen G. R., Durden L. A., Wright J. C. Borrelia sp. in ticks recovered from white-tailed deer in Alabama. J Wildl Dis. 1992 Jul;28(3):449–452. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-28.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckhart S., Mullen G. R., Wright J. C. Etiologic agent of Lyme disease, Borrelia burgdorferi, detected in ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) collected at a focus in Alabama. J Med Entomol. 1991 Sep;28(5):652–657. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/28.5.652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F., Apperson C. S., Fish D., Johnson R. C., Chappell W. A. Spirochetes in ticks and antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in white-tailed deer from Connecticut, New York State, and North Carolina. J Wildl Dis. 1986 Apr;22(2):178–188. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-22.2.178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Anderson J. F. Ticks and biting insects infected with the etiologic agent of Lyme disease, Borrelia burgdorferi. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Aug;26(8):1482–1486. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.8.1482-1486.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Oliver J. H., Jr, Hutcheson H. J., Anderson J. F. Antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in deer and raccoons. J Wildl Dis. 1991 Oct;27(4):562–568. doi: 10.7589/0090-3558-27.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnarelli L. A., Oliver J. H., Jr, Hutcheson H. J., Boone J. L., Anderson J. F. Antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi in rodents in the eastern and southern United States. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jun;30(6):1449–1452. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.6.1449-1452.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver J. H., Jr, Owsley M. R., Hutcheson H. J., James A. M., Chen C., Irby W. S., Dotson E. M., McLain D. K. Conspecificity of the ticks Ixodes scapularis and I. dammini (Acari: Ixodidae). J Med Entomol. 1993 Jan;30(1):54–63. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/30.1.54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Telford S. R., 3rd, Spielman A., Barthold S. W. Detection of Borrelia burgdorferi infection in Ixodes dammini ticks with the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):566–572. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.566-572.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piesman J., Sinsky R. J. Ability to Ixodes scapularis, Dermacentor variabilis, and Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) to acquire, maintain, and transmit Lyme disease spirochetes (Borrelia burgdorferi). J Med Entomol. 1988 Sep;25(5):336–339. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/25.5.336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P. A., Schwan T. G. A specific and sensitive assay for the Lyme disease spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi using the polymerase chain reaction. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):1018–1029. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.1018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scrimenti R. J. Erythema chronicum migrans. Arch Dermatol. 1970 Jul;102(1):104–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinsky R. J., Piesman J. Ear punch biopsy method for detection and isolation of Borrelia burgdorferi from rodents. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Aug;27(8):1723–1727. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.8.1723-1727.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielman A., Wilson M. L., Levine J. F., Piesman J. Ecology of Ixodes dammini-borne human babesiosis and Lyme disease. Annu Rev Entomol. 1985;30:439–460. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.30.010185.002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C. Lyme disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Aug 31;321(9):586–596. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198908313210906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Hardin J. A., Ruddy S., Askenase W., Andiman W. A. Erythema chronicum migrans and Lyme arthritis. The enlarging clinical spectrum. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):685–698. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-685. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steere A. C., Malawista S. E., Snydman D. R., Shope R. E., Andiman W. A., Ross M. R., Steele F. M. Lyme arthritis: an epidemic of oligoarticular arthritis in children and adults in three connecticut communities. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jan-Feb;20(1):7–17. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Busch K. V. Immunochemical and immunological analysis of European Borrelia burgdorferi strains. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1986 Dec;263(1-2):92–102. doi: 10.1016/s0176-6724(86)80108-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilske B., Preac-Mursic V., Schierz G., Kühbeck R., Barbour A. G., Kramer M. Antigenic variability of Borrelia burgdorferi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:126–143. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31846.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]