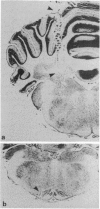
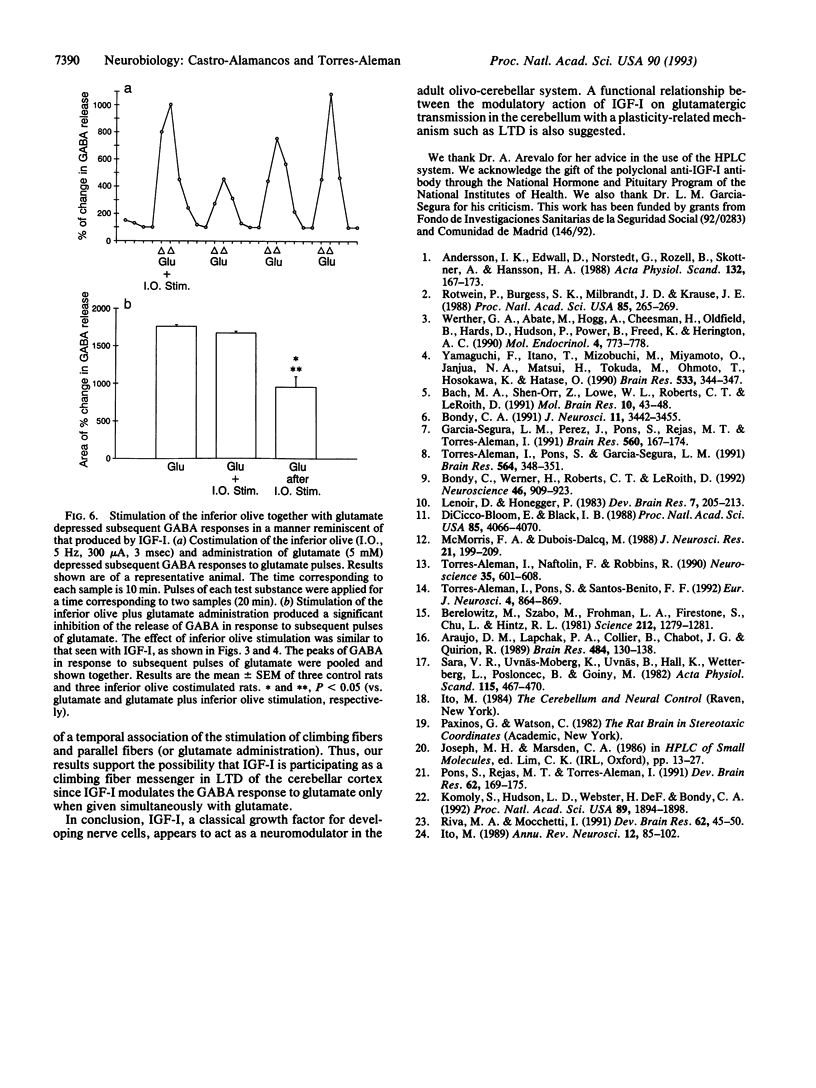
Abstract
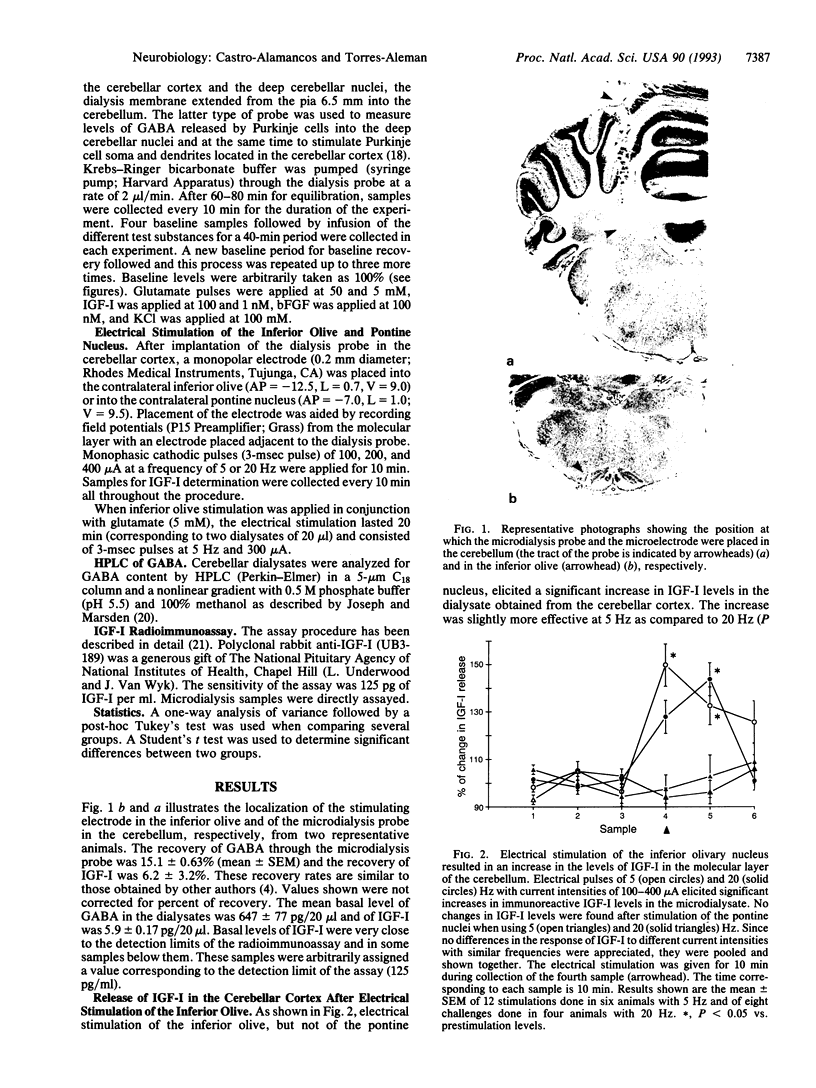
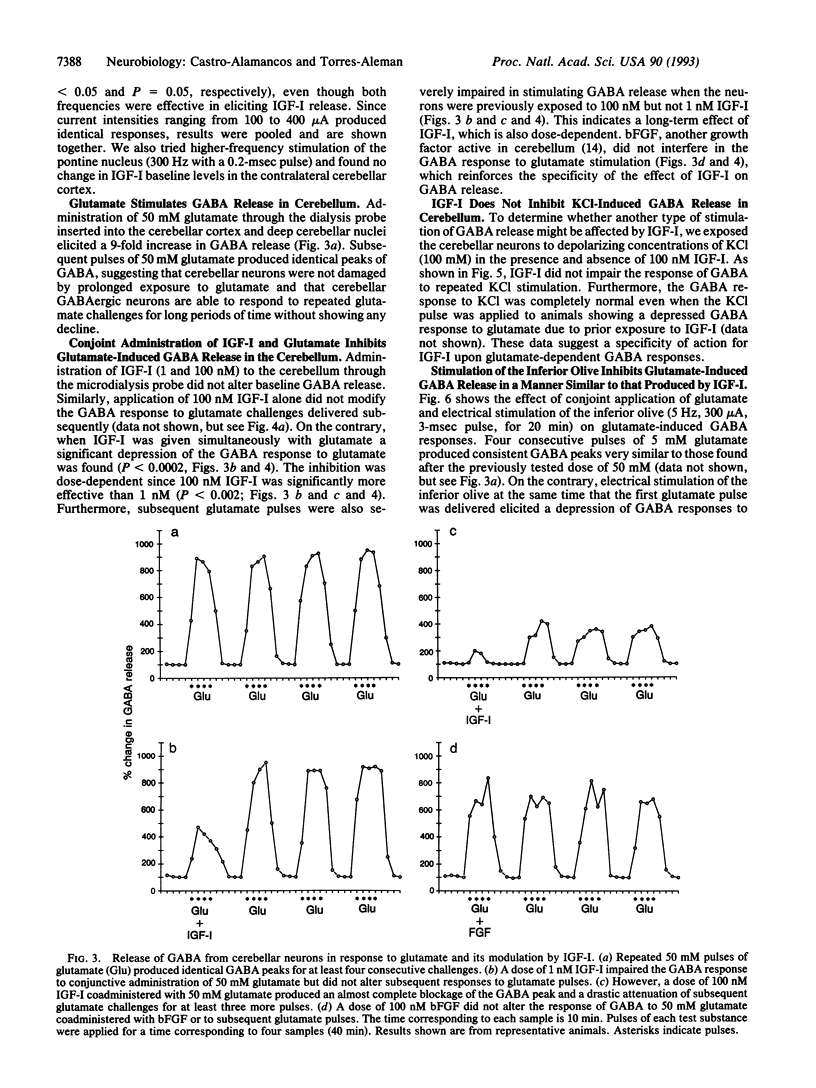
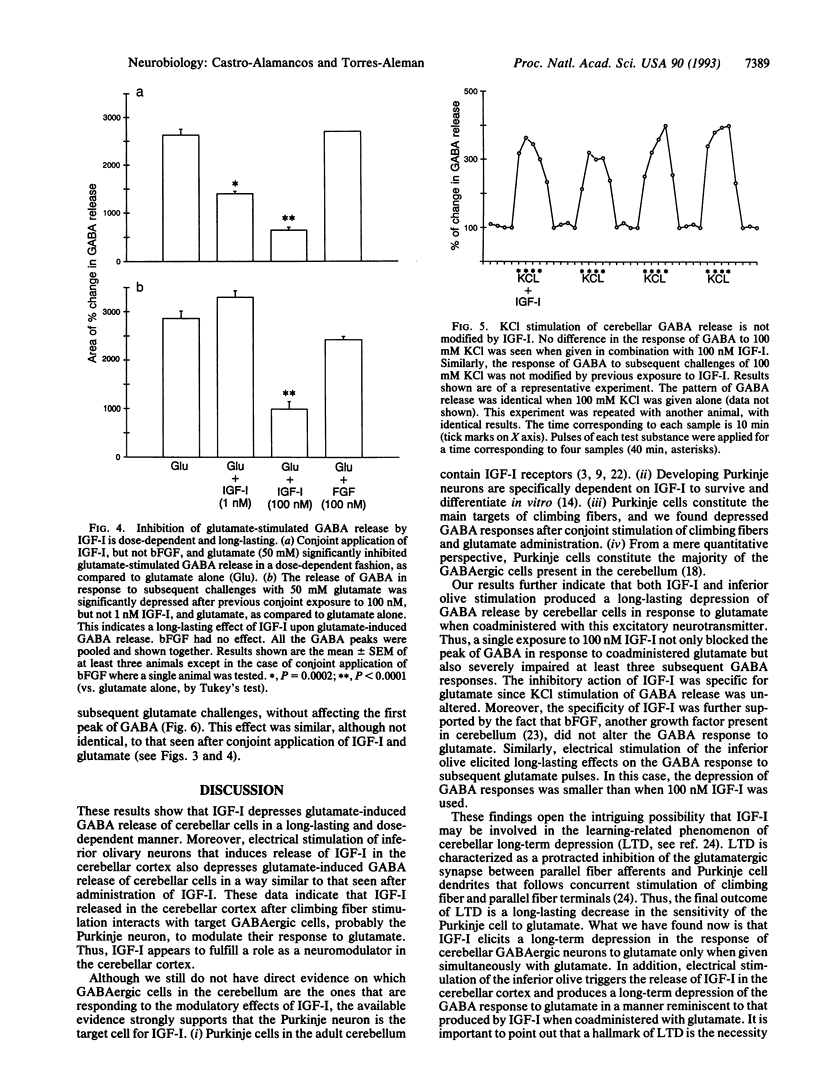
We tested the possibility that insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) acts as a neuromodulator in the adult cerebellar cortex since previous observations indicated that IGF-I is located in the olivo-cerebellar system encompassing the inferior olive and Purkinje cells. We found that conjoint administration of IGF-I and glutamate through a microdialysis probe stereotaxically implanted into the cerebellar cortex and deep cerebellar nuclei greatly depressed the release of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which normally follows a glutamate pulse. This inhibition was dose-dependent and long-lasting. Moreover, the effect was specific for glutamate since KCl-induced GABA release was not modified by IGF-I. Basic fibroblast growth factor, another growth-related peptide present in the cerebellum, did not alter the response of GABA to glutamate stimulation. In addition, electrical stimulation of the inferior olivary complex significantly raised IGF-I levels in the cerebellar cortex. Interestingly, when the inferior olive was stimulated in conjunction with glutamate administration, GABA release by cerebellar cells in response to subsequent glutamate pulses was depressed in a manner reminiscent of that seen after IGF-I. These findings indicate that IGF-I produces a long-lasting depression of GABA release by Purkinje cells in response to glutamate. IGF-I might be present in climbing fiber terminals and/or cells within the cerebellar cortex and thereby might affect Purkinje cell function. Whether this IGF-I-induced impairment of glutamate stimulation of Purkinje cells underlies functionally plastic processes such as long-term depression is open to question.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson I. K., Edwall D., Norstedt G., Rozell B., Skottner A., Hansson H. A. Differing expression of insulin-like growth factor I in the developing and in the adult rat cerebellum. Acta Physiol Scand. 1988 Feb;132(2):167–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08314.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo D. M., Lapchak P. A., Collier B., Chabot J. G., Quirion R. Insulin-like growth factor-1 (somatomedin-C) receptors in the rat brain: distribution and interaction with the hippocampal cholinergic system. Brain Res. 1989 Apr 10;484(1-2):130–138. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90355-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bach M. A., Shen-Orr Z., Lowe W. L., Jr, Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Insulin-like growth factor I mRNA levels are developmentally regulated in specific regions of the rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1991 Apr;10(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(91)90054-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berelowitz M., Szabo M., Frohman L. A., Firestone S., Chu L., Hintz R. L. Somatomedin-C mediates growth hormone negative feedback by effects on both the hypothalamus and the pituitary. Science. 1981 Jun 12;212(4500):1279–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.6262917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy C. A. Transient IGF-I gene expression during the maturation of functionally related central projection neurons. J Neurosci. 1991 Nov;11(11):3442–3455. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-11-03442.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bondy C., Werner H., Roberts C. T., Jr, LeRoith D. Cellular pattern of type-I insulin-like growth factor receptor gene expression during maturation of the rat brain: comparison with insulin-like growth factors I and II. Neuroscience. 1992;46(4):909–923. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(92)90193-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiCicco-Bloom E., Black I. B. Insulin growth factors regulate the mitotic cycle in cultured rat sympathetic neuroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):4066–4070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.4066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Segura L. M., Pérez J., Pons S., Rejas M. T., Torres-Alemán I. Localization of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I)-like immunoreactivity in the developing and adult rat brain. Brain Res. 1991 Sep 27;560(1-2):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91228-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M. Long-term depression. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1989;12:85–102. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.12.030189.000505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komoly S., Hudson L. D., Webster H. D., Bondy C. A. Insulin-like growth factor I gene expression is induced in astrocytes during experimental demyelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1894–1898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenoir D., Honegger P. Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF I) stimulates DNA synthesis in fetal rat brain cell cultures. Brain Res. 1983 Apr;283(2-3):205–213. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90177-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMorris F. A., Dubois-Dalcq M. Insulin-like growth factor I promotes cell proliferation and oligodendroglial commitment in rat glial progenitor cells developing in vitro. J Neurosci Res. 1988 Oct-Dec;21(2-4):199–209. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490210212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pons S., Rejas M. T., Torres-Aleman I. Ontogeny of insulin-like growth factor I, its receptor, and its binding proteins in the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1991 Oct 21;62(2):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(91)90164-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riva M. A., Mocchetti I. Developmental expression of the basic fibroblast growth factor gene in rat brain. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1991 Sep 19;62(1):45–50. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(91)90188-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotwein P., Burgess S. K., Milbrandt J. D., Krause J. E. Differential expression of insulin-like growth factor genes in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(1):265–269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.1.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sara V. R., Uvnäs-Moberg K., Uvnäs B., Hall K., Wetterberg L., Posloncec B., Goiny M. The distribution of somatomedins in the nervous system of the cat and their release following neural stimulation. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Aug;115(4):467–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07105.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Aleman I., Naftolin F., Robbins R. J. Trophic effects of insulin-like growth factor-I on fetal rat hypothalamic cells in culture. Neuroscience. 1990;35(3):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Aleman I., Pons S., Santos-Benito F. F. Survival of Purkinje Cells in Cerebellar Cultures is Increased by Insulin-like Growth Factor I. Eur J Neurosci. 1992;4(9):864–869. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Alemán I., Pons S., García-Segura L. M. Climbing fiber deafferentation reduces insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) content in cerebellum. Brain Res. 1991 Nov 15;564(2):348–351. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91476-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werther G. A., Abate M., Hogg A., Cheesman H., Oldfield B., Hards D., Hudson P., Power B., Freed K., Herington A. C. Localization of insulin-like growth factor-I mRNA in rat brain by in situ hybridization--relationship to IGF-I receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 May;4(5):773–778. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-5-773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi F., Itano T., Mizobuchi M., Miyamoto O., Janjua N. A., Matsui H., Tokuda M., Ohmoto T., Hosokawa K., Hatase O. Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) distribution in the tissue and extracellular compartment in different regions of rat brain. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 19;533(2):344–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91361-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]