Abstract
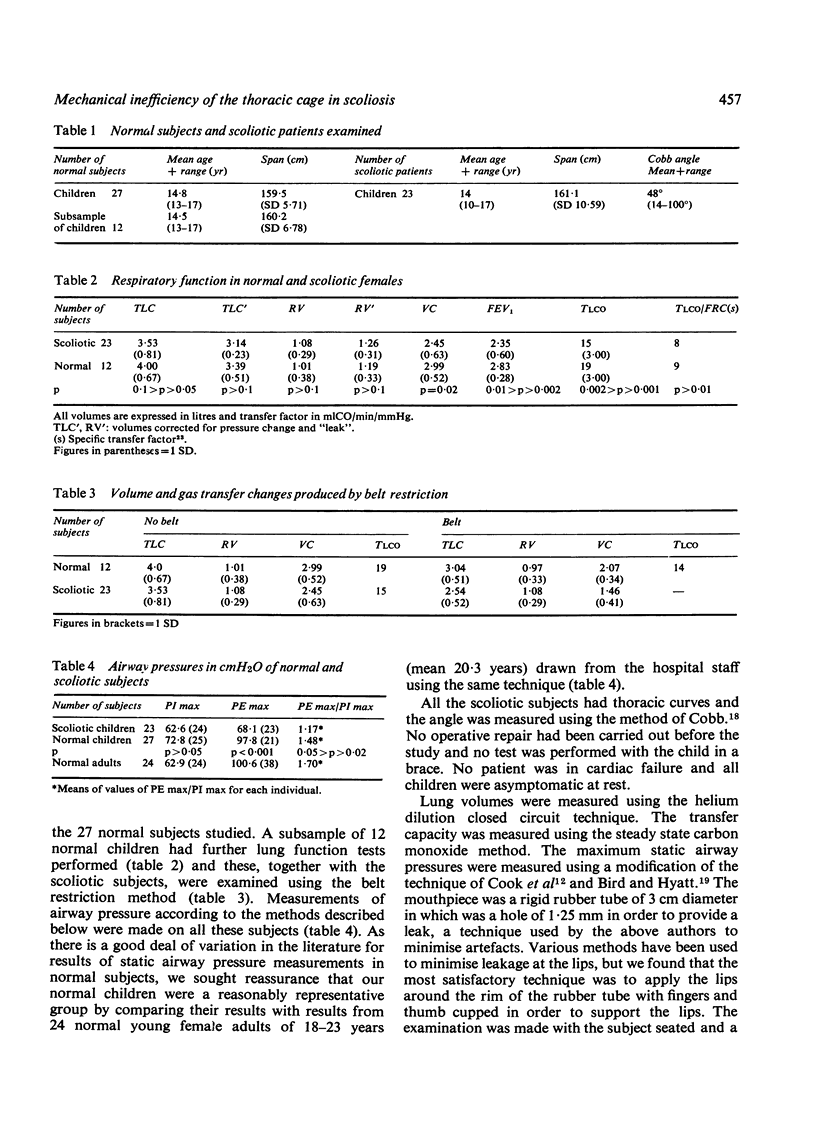
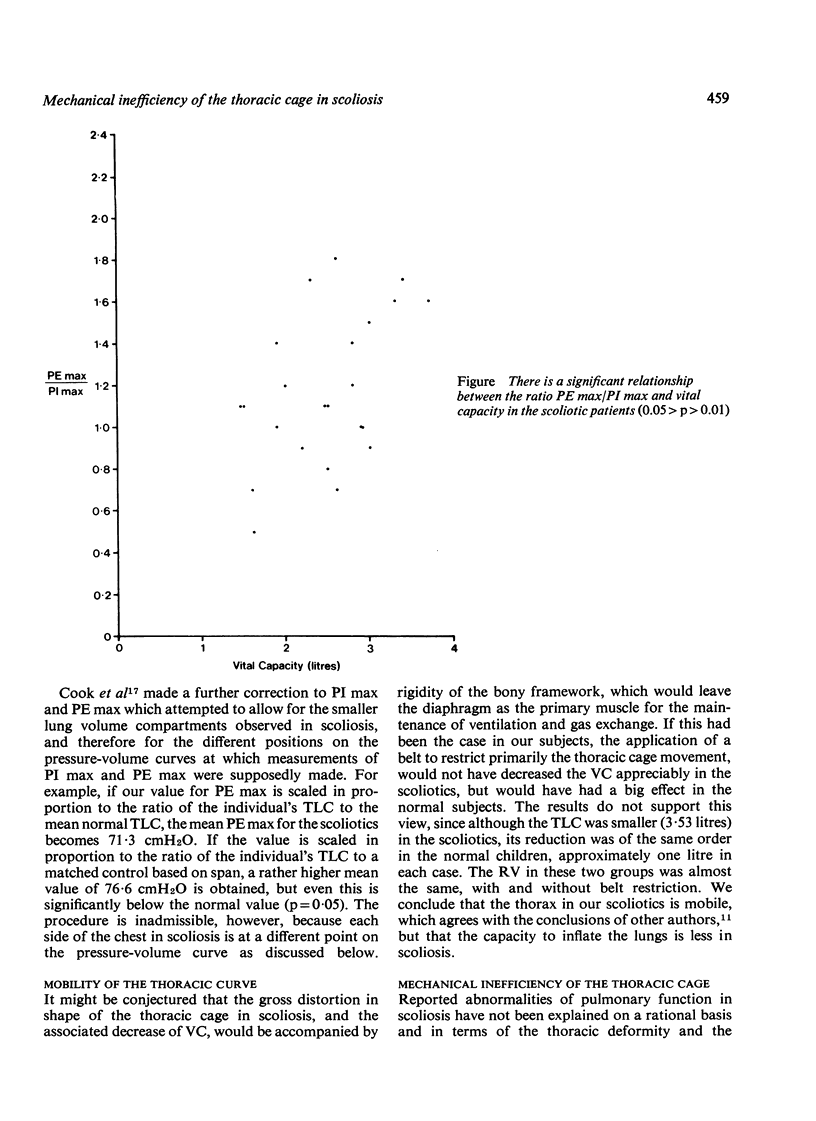
The mechanism of impairment of ventilatory function in idiopathic scoliosis has been studied in 23 children, all girls, and compared with 27 normal children and 24 normal young adult females. The vital capacity, FEV 1, gas transfer factor, and the maximum static expiratory airway pressure were all significantly reduced. total lung capacity and the maximum inspiratory pressure were lower than in the normal subjects, but the difference was not significant. Restriction of thoracic cage movement by a belt showed that the thorax in the children with scoliosis was as mobile as in the normal subjects. The results are explained in terms of the characteristic deformity in scoliosis which causes one hemi-thorax to become relatively smaller than the other. It is concluded that this causes an inherent mechanical inefficiency of ventilation which is likely to contribute to respiratory failure in these subjects.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERGOFSKY E. H., TURINO G. M., FISHMAN A. P. Cardiorespiratory failure in kyphoscoliosis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1959 Sep;38:263–317. doi: 10.1097/00005792-195909000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black L. F., Hyatt R. E. Maximal respiratory pressures: normal values and relationship to age and sex. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 May;99(5):696–702. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.5.696. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrd R. B., Hyatt R. E. Maximal respiratory pressures in chronic obstructive lung disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1968 Nov;98(5):848–856. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1968.98.5.848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARO C. G., DUBOIS A. B. Pulmonary function in kyphoscoliosis. Thorax. 1961 Sep;16:282–290. doi: 10.1136/thx.16.3.282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK C. D., BARRIE H., DEFOREST S. A., HELLIESEN P. J. Pulmonary physiology in children. III. Lungvolumes, mechanics of respiration and respiratory muscle strength in scoliosis. Pediatrics. 1960 May;25:766–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK C. D., MEAD J., ORZALESI M. M. STATIC VOLUME-PRESSURE CHARACTERISTICS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DURING MAXIMAL EFFORTS. J Appl Physiol. 1964 Sep;19:1016–1022. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1964.19.5.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOLLERY C. T., GILLAM P. M., HUGH-JONEP, ZORAB P. A. REGIONAL LUNG FUNCTION IN KYPHOSCOLIOSIS. Thorax. 1965 Mar;20:175–181. doi: 10.1136/thx.20.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey S. Respiratory and cardiovascular consequences of scoliosis. Respiration. 1970;27(Suppl):67–70. doi: 10.1159/000192722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ITICOVICI H. N., LYONS H. A. Ventilatory and lung volume determinations in patients with chest deformities. Am J Med Sci. 1956 Sep;232(3):265–passim. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195609000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindh M., Bjure J. Lung volumes in scoliosis before and after correction by the Harrington instrumentation method. Acta Orthop Scand. 1975 Dec;46(6):934–948. doi: 10.3109/17453677508989282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littler W. A., Brown I. K., Roaf R. Regional lung function in scoliosis. Thorax. 1972 Jul;27(4):420–428. doi: 10.1136/thx.27.4.420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochester D. F., Braun N. M., Arora N. S. Respiratory muscle strength in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1979 Feb;119(2 Pt 2):151–154. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1979.119.2P2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shannon D. C., Riseborough E. J., Valenca L. M., Kazemi H. The distribution of abnormal lung function in kyphoscoliosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970 Jan;52(1):131–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber B., Smith J. P., Briscoe W. A., Friedman S. A., King T. K. Pulmonary function in asymptomatic adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1975 Apr;111(4):389–397. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1975.111.4.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weng T. R., Levison H. Standards of pulmonary function in children. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Jun;99(6):879–894. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.99.6.879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Troyer A., Yernault J. C. Inspiratory muscle force in normal subjects and patients with interstitial lung disease. Thorax. 1980 Feb;35(2):92–100. doi: 10.1136/thx.35.2.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



