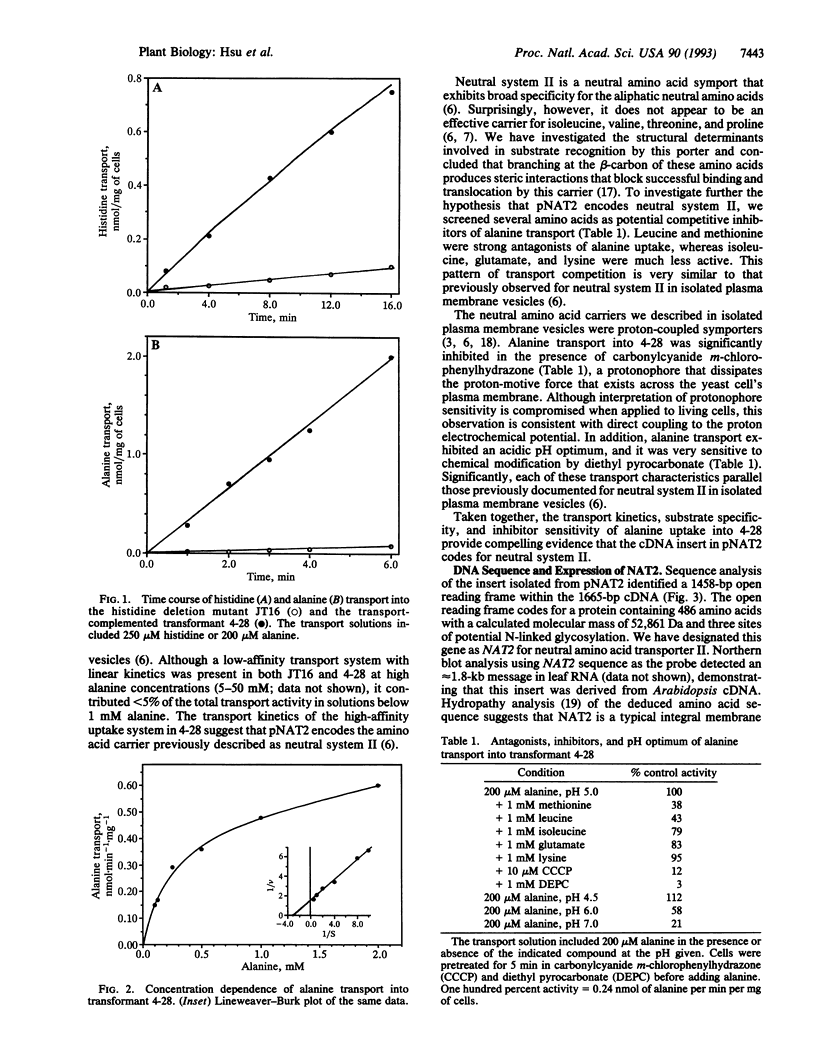
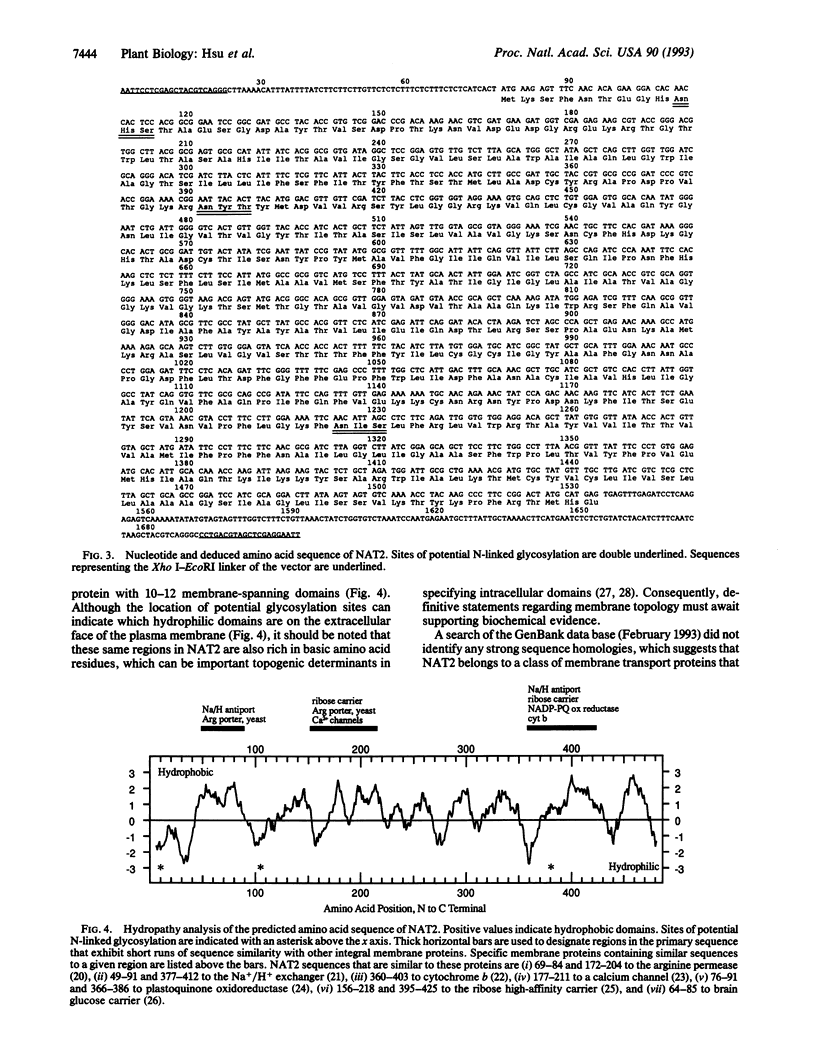
Abstract
Amino acids are transported across the plasma membrane of plant cells by proton-amino acid symports. We report here the successful cloning of a neutral amino acid carrier by functional complementation. A histidine transport deletion mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae was transformed with an Arabidopsis thaliana cDNA library constructed in a yeast expression vector. Forty transformants, out of 10(5), allowed growth on a histidine-limiting medium. The acquired ability to grow on low histidine was shown to be strictly dependent on the protein encoded by the expression plasmid. Histidine and alanine transport activity were 10- to 20-fold greater in the transformants. The transport kinetics, inhibitor sensitivity, and substrate specificity match those of neutral system II, a neutral amino acid carrier we previously described in plasma membrane vesicles isolated from leaf tissue. The cDNA insert is 1.7 kb with an open reading frame that codes for a protein containing 486 amino acids with a calculated molecular mass of 52.9 kDa and three sites of potential N-linked glycosylation. Hydropathy analysis of the deduced amino acid sequence suggests this is an integral membrane protein with 10-12 membrane-spanning alpha-helices. Overall, the sequence of this amino acid carrier is not closely related to any other protein sequences in the GenBank data base. Interestingly, however, there are small regions of sequence that exhibit significant levels of similarity with at least seven other integral membrane proteins.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad M., Bussey H. Yeast arginine permease: nucleotide sequence of the CAN1 gene. Curr Genet. 1986;10(8):587–592. doi: 10.1007/BF00418125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. A., Huprikar S. S., Kochian L. V., Lucas W. J., Gaber R. F. Functional expression of a probable Arabidopsis thaliana potassium channel in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3736–3740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker D. M., Guarente L. High-efficiency transformation of yeast by electroporation. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:182–187. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94015-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell A. W., Buckel S. D., Groarke J. M., Hope J. N., Kingsley D. H., Hermodson M. A. The nucleotide sequences of the rbsD, rbsA, and rbsC genes of Escherichia coli K12. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7652–7658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd D., Beckwith J. Positively charged amino acid residues can act as topogenic determinants in membrane proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9446–9450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush D. R., Langston-Unkefer P. J. Amino Acid transport into membrane vesicles isolated from zucchini : evidence of a proton-amino Acid symport in the plasmalemma. Plant Physiol. 1988 Oct;88(2):487–490. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.2.487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Mulligan J. T., Ramer S. W., Spottswood M., Davis R. W. Lambda YES: a multifunctional cDNA expression vector for the isolation of genes by complementation of yeast and Escherichia coli mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1731–1735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frommer W. B., Hummel S., Riesmeier J. W. Expression cloning in yeast of a cDNA encoding a broad specificity amino acid permease from Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):5944–5948. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.5944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gifford R. M., Thorne J. H., Hitz W. D., Giaquinta R. T. Crop productivity and photoassimilate partitioning. Science. 1984 Aug 24;225(4664):801–808. doi: 10.1126/science.225.4664.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall T. C., Ma Y., Buchbinder B. U., Pyne J. W., Sun S. M., Bliss F. A. Messenger RNA for G1 protein of French bean seeds: Cell-free translation and product characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3196–3200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heijne G. The distribution of positively charged residues in bacterial inner membrane proteins correlates with the trans-membrane topology. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):3021–3027. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herdenberger F., Weil J. H., Steinmetz A. Organization and nucleotide sequence of the broad bean chloroplast genes trnL-UAG, ndhF and two unidentified open reading frames. Curr Genet. 1988 Dec;14(6):609–615. doi: 10.1007/BF00434087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. C., Bush D. R. DeltapH-Dependent Amino Acid Transport into Plasma Membrane Vesicles Isolated from Sugar Beet (Beta vulgaris L.) Leaves: II. Evidence for Multiple Aliphatic, Neutral Amino Acid Symports. Plant Physiol. 1991 Aug;96(4):1338–1344. doi: 10.1104/pp.96.4.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. C., Bush D. R. DeltapH-Dependent Amino Acid Transport into Plasma Membrane Vesicles Isolated from Sugar Beet Leaves: I. Evidence for Carrier-Mediated, Electrogenic Flux through Multiple Transport Systems. Plant Physiol. 1990 Sep;94(1):268–277. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.1.268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. C., Bush D. R. Structural determinants in substrate recognition by proton-amino acid symports in plasma membrane vesicles isolated from sugar beet leaves. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 May 1;294(2):519–526. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90719-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riesmeier J. W., Willmitzer L., Frommer W. B. Isolation and characterization of a sucrose carrier cDNA from spinach by functional expression in yeast. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):4705–4713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05575.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac H., Bonneaud N., Minet M., Lacroute F., Salmon J. M., Gaymard F., Grignon C. Cloning and expression in yeast of a plant potassium ion transport system. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):663–665. doi: 10.1126/science.1585180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snutch T. P., Leonard J. P., Gilbert M. M., Lester H. A., Davidson N. Rat brain expresses a heterogeneous family of calcium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(9):3391–3395. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.9.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka J., Fink G. R. The histidine permease gene (HIP1) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90219-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse C. M., Brant S. R., Walker M. S., Pouyssegur J., Donowitz M. Cloning and sequencing of a rabbit cDNA encoding an intestinal and kidney-specific Na+/H+ exchanger isoform (NHE-3). J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9340–9346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandenbol M., Jauniaux J. C., Grenson M. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae NPR1 gene required for the activity of ammonia-sensitive amino acid permeases encodes a protein kinase homologue. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jul;222(2-3):393–399. doi: 10.1007/BF00633845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahleithner J. A., Wolstenholme D. R. Ribosomal protein S14 genes in broad bean mitochondrial DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14B):6897–6913. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiler-Güttler H., Zinke H., Möckel B., Frey A., Gassen H. G. cDNA cloning and sequence analysis of the glucose transporter from porcine blood-brain barrier. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1989 May;370(5):467–473. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1989.370.1.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


