Abstract
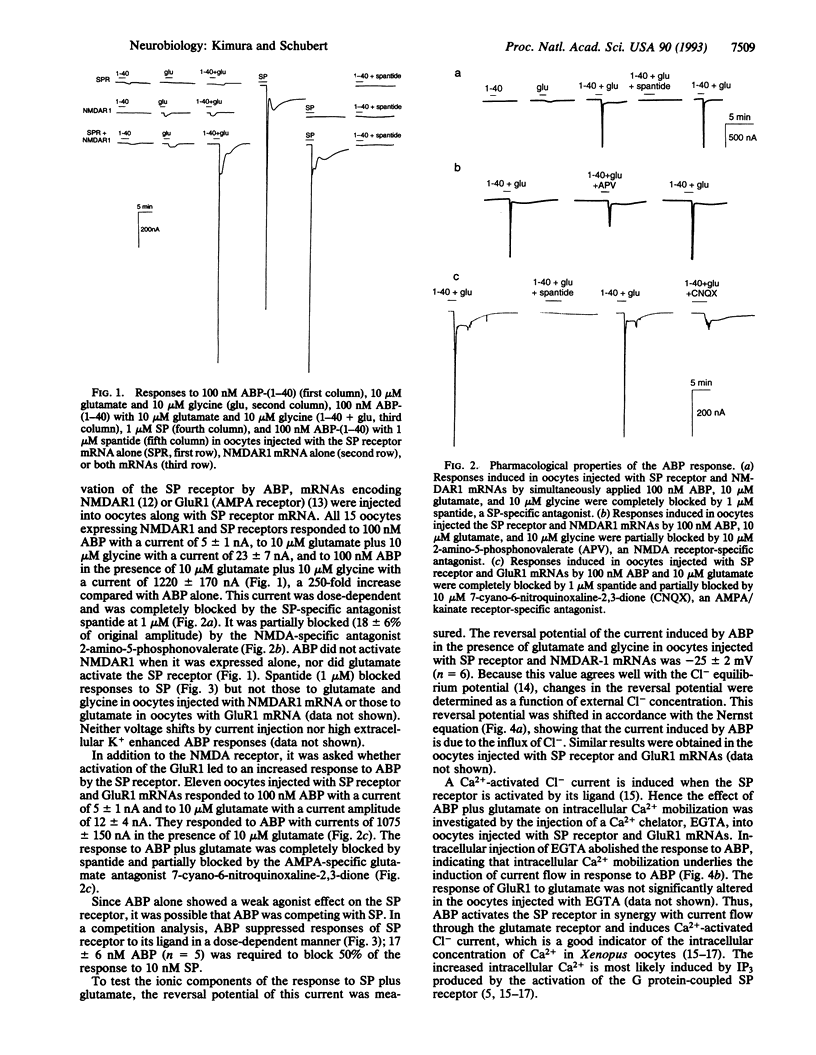
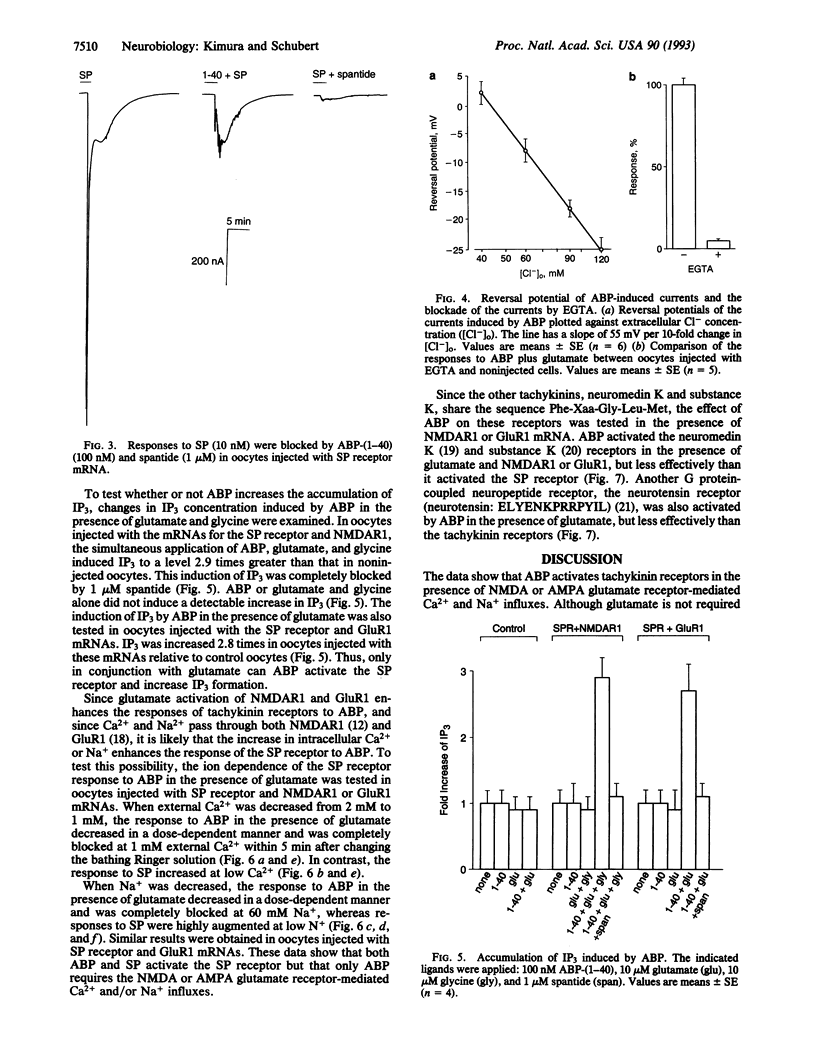
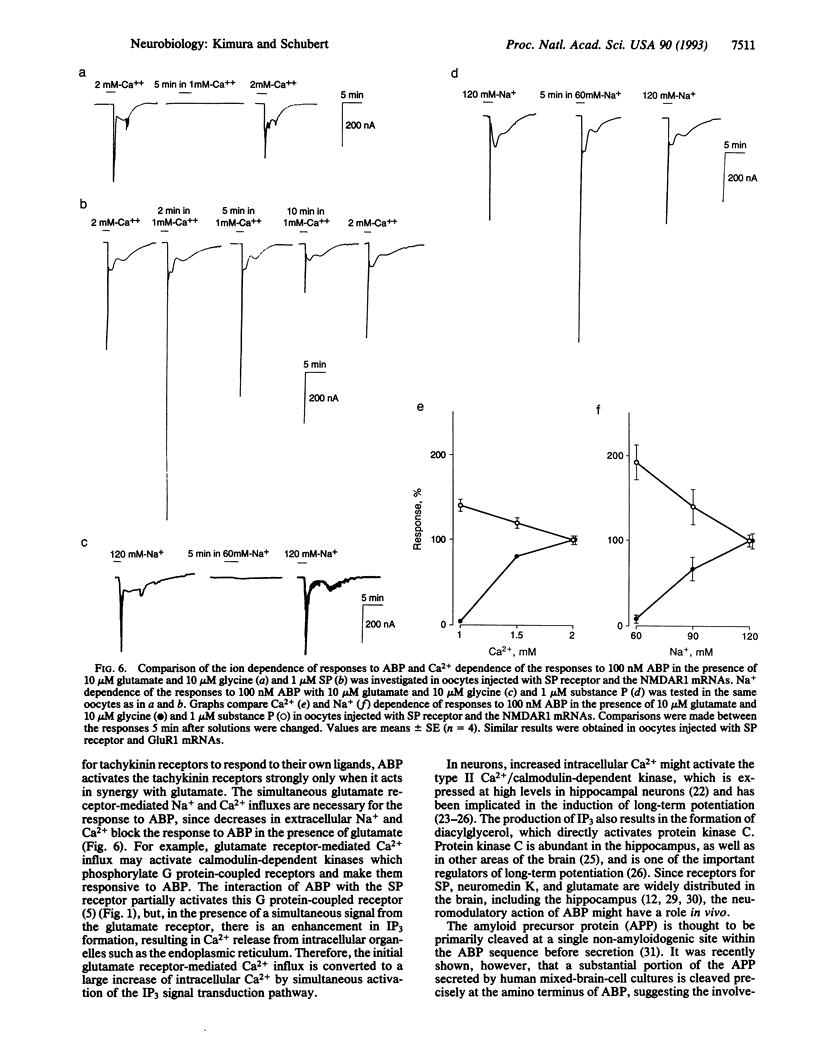
The biological function of the soluble form of the amyloid beta-protein (ABP) was examined by assaying its interaction with neuronal receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes. ABP weakly activated tachykinin receptors, but in the presence of N-methyl-D-aspartate and alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4- propionate-type glutamate receptors ABP-induced responses were greatly enhanced. Glutamate and ABP together also induced accumulation of inositol trisphosphate and increases in intracellular Ca2+. These observations suggest that in the presence of glutamate, ABP can activate tachykinin receptors and phosphatidylinositol turnover. ABP may therefore act as a neuromodulatory peptide.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cai X. D., Golde T. E., Younkin S. G. Release of excess amyloid beta protein from a mutant amyloid beta protein precursor. Science. 1993 Jan 22;259(5094):514–516. doi: 10.1126/science.8424174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartier-Harlin M. C., Crawford F., Houlden H., Warren A., Hughes D., Fidani L., Goate A., Rossor M., Roques P., Hardy J. Early-onset Alzheimer's disease caused by mutations at codon 717 of the beta-amyloid precursor protein gene. Nature. 1991 Oct 31;353(6347):844–846. doi: 10.1038/353844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erondu N. E., Kennedy M. B. Regional distribution of type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1985 Dec;5(12):3270–3277. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-12-03270.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Keim P. S., Beattie E. C., Blacher R. W., Culwell A. R., Oltersdorf T., McClure D., Ward P. J. Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.2111583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkers K., Håkanson R., Hörig J., Xu J. C., Leander S. Biological evaluation of substance P antagonists. Br J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct;83(2):449–456. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1984.tb16506.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goate A., Chartier-Harlin M. C., Mullan M., Brown J., Crawford F., Fidani L., Giuffra L., Haynes A., Irving N., James L. Segregation of a missense mutation in the amyloid precursor protein gene with familial Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1991 Feb 21;349(6311):704–706. doi: 10.1038/349704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haass C., Schlossmacher M. G., Hung A. Y., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Mellon A., Ostaszewski B. L., Lieberburg I., Koo E. H., Schenk D., Teplow D. B. Amyloid beta-peptide is produced by cultured cells during normal metabolism. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):322–325. doi: 10.1038/359322a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., Hartley M., Heinemann S. Ca2+ permeability of KA-AMPA--gated glutamate receptor channels depends on subunit composition. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):851–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1709304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Rogers S. W., Heinemann S. Cloning by functional expression of a member of the glutamate receptor family. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):643–648. doi: 10.1038/342643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph R., Han E. Amyloid beta-protein fragment 25-35 causes activation of cytoplasmic calcium in neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 May 15;184(3):1441–1447. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)80044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koh J. Y., Yang L. L., Cotman C. W. Beta-amyloid protein increases the vulnerability of cultured cortical neurons to excitotoxic damage. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 19;533(2):315–320. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91355-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusano K., Miledi R., Stinnakre J. Cholinergic and catecholaminergic receptors in the Xenopus oocyte membrane. J Physiol. 1982 Jul;328:143–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechleiter J., Girard S., Clapham D., Peralta E. Subcellular patterns of calcium release determined by G protein-specific residues of muscarinic receptors. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):505–508. doi: 10.1038/350505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malenka R. C., Kauer J. A., Perkel D. J., Mauk M. D., Kelly P. T., Nicoll R. A., Waxham M. N. An essential role for postsynaptic calmodulin and protein kinase activity in long-term potentiation. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):554–557. doi: 10.1038/340554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malinow R., Schulman H., Tsien R. W. Inhibition of postsynaptic PKC or CaMKII blocks induction but not expression of LTP. Science. 1989 Aug 25;245(4920):862–866. doi: 10.1126/science.2549638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masu Y., Nakayama K., Tamaki H., Harada Y., Kuno M., Nakanishi S. cDNA cloning of bovine substance-K receptor through oocyte expression system. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):836–838. doi: 10.1038/329836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson M. P., Cheng B., Davis D., Bryant K., Lieberburg I., Rydel R. E. beta-Amyloid peptides destabilize calcium homeostasis and render human cortical neurons vulnerable to excitotoxicity. J Neurosci. 1992 Feb;12(2):376–389. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.12-02-00376.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Parker I. Latencies of membrane currents evoked in Xenopus oocytes by receptor activation, inositol trisphosphate and calcium. J Physiol. 1989 Aug;415:189–210. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. G., Kennedy M. B. Regulation of brain type II Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase by autophosphorylation: a Ca2+-triggered molecular switch. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):861–870. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyoshi K., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Molecular cloning and characterization of the rat NMDA receptor. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):31–37. doi: 10.1038/354031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrell J., Farlow M., Ghetti B., Benson M. D. A mutation in the amyloid precursor protein associated with hereditary Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):97–99. doi: 10.1126/science.1925564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Sumikawa K., Miledi R. Neurotensin and substance P receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes by messenger RNA from rat brain. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1986 Nov 22;229(1255):151–159. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1986.0079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S. W., Hughes T. E., Hollmann M., Gasic G. P., Deneris E. S., Heinemann S. The characterization and localization of the glutamate receptor subunit GluR1 in the rat brain. J Neurosci. 1991 Sep;11(9):2713–2724. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-09-02713.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito N., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y., Tanaka C. Distribution of protein kinase C-like immunoreactive neurons in rat brain. J Neurosci. 1988 Feb;8(2):369–382. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-02-00369.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Oltersdorf T., Lee M. G., Barbour R., Blomquist C., Davis D. L., Bryant K., Fritz L. C., Galasko D., Thal L. J. Secretion of beta-amyloid precursor protein cleaved at the amino terminus of the beta-amyloid peptide. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):260–263. doi: 10.1038/361260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Vigo-Pelfrey C., Esch F., Lee M., Dovey H., Davis D., Sinha S., Schlossmacher M., Whaley J., Swindlehurst C. Isolation and quantification of soluble Alzheimer's beta-peptide from biological fluids. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):325–327. doi: 10.1038/359325a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shigemoto R., Yokota Y., Tsuchida K., Nakanishi S. Cloning and expression of a rat neuromedin K receptor cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoji M., Golde T. E., Ghiso J., Cheung T. T., Estus S., Shaffer L. M., Cai X. D., McKay D. M., Tintner R., Frangione B. Production of the Alzheimer amyloid beta protein by normal proteolytic processing. Science. 1992 Oct 2;258(5079):126–129. doi: 10.1126/science.1439760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A. J., Stevens C. F., Tonegawa S., Wang Y. Deficient hippocampal long-term potentiation in alpha-calcium-calmodulin kinase II mutant mice. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):201–206. doi: 10.1126/science.1378648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Masu M., Nakanishi S. Structure and functional expression of the cloned rat neurotensin receptor. Neuron. 1990 Jun;4(6):847–854. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90137-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Yokota Y., Nakanishi S. Tissue distribution and quantitation of the mRNAs for three rat tachykinin receptors. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):751–757. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19396.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yankner B. A., Duffy L. K., Kirschner D. A. Neurotrophic and neurotoxic effects of amyloid beta protein: reversal by tachykinin neuropeptides. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):279–282. doi: 10.1126/science.2218531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota Y., Akazawa C., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Delineation of structural domains involved in the subtype specificity of tachykinin receptors through chimeric formation of substance P/substance K receptors. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3585–3591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05442.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota Y., Sasai Y., Tanaka K., Fujiwara T., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Kakizuka A., Ohkubo H., Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA for rat substance P receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17649–17652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



