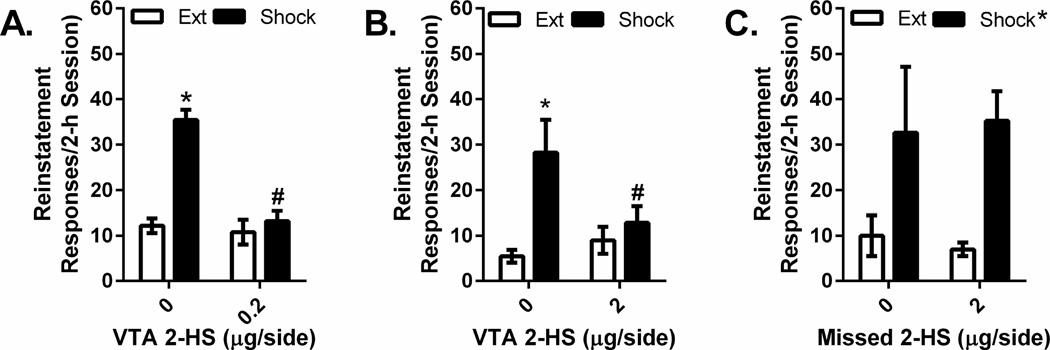
Figure 5. Effects of intra-VTA 2-hydroxysaclofen injections on shock-induced reinstatement.
Data represent responding (lever presses/2-h session ±S.E.) recorded during reinstatement testing following electric footshock (0.5 mA, 0.5” shocks delivered an average of every 40 sec over a 15-min period) in rats pretreated with intra-VTA injections of vehicle or 0.2 µg/side (Figure 5A) or 2 µg/side (Figure 5B) of the GABAB receptor antagonist, 2-hydroxysaclofen (2-HS) and responding during the previous extinction (Ext) session. Shock reinstated cocaine seeking following vehicle (0 µg/side) pretreatment (*P<0.05 vs. Ext) but not following injections of 0.2 or 2 µg/side 2-hydroxysaclofen into the VTA. Moreover, lever pressing during the reinstatement session following shock delivery was significantly lower in rats that received intra-VTA injections of 0.2 or 2 µg/side 2-hydroxysaclofen relative to rats pretreated with vehicle (#P<0.05 vs. 0 µg/side). By contrast, in rats with misplaced cannula that received 2-hydroxysaclofen injections into brain regions adjacent to the VTA, 2-hydroxysaclofen (2 µg/side) failed to affects shock-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking (Figure 5C).