Abstract
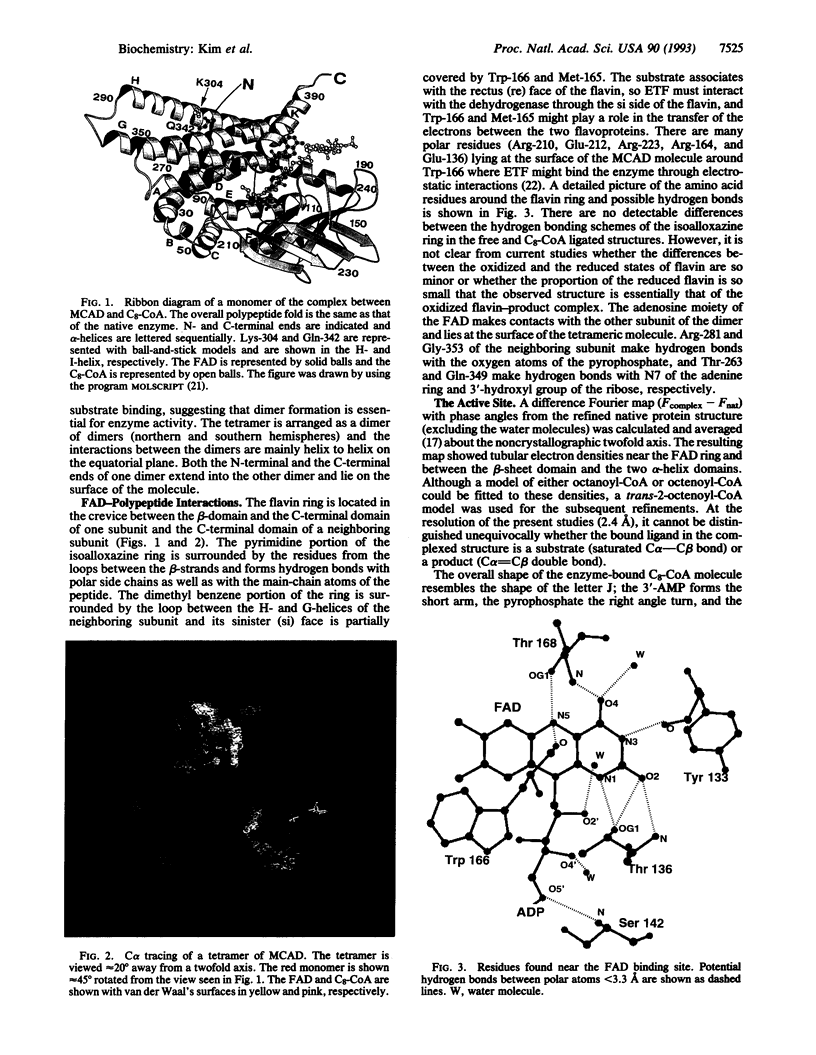
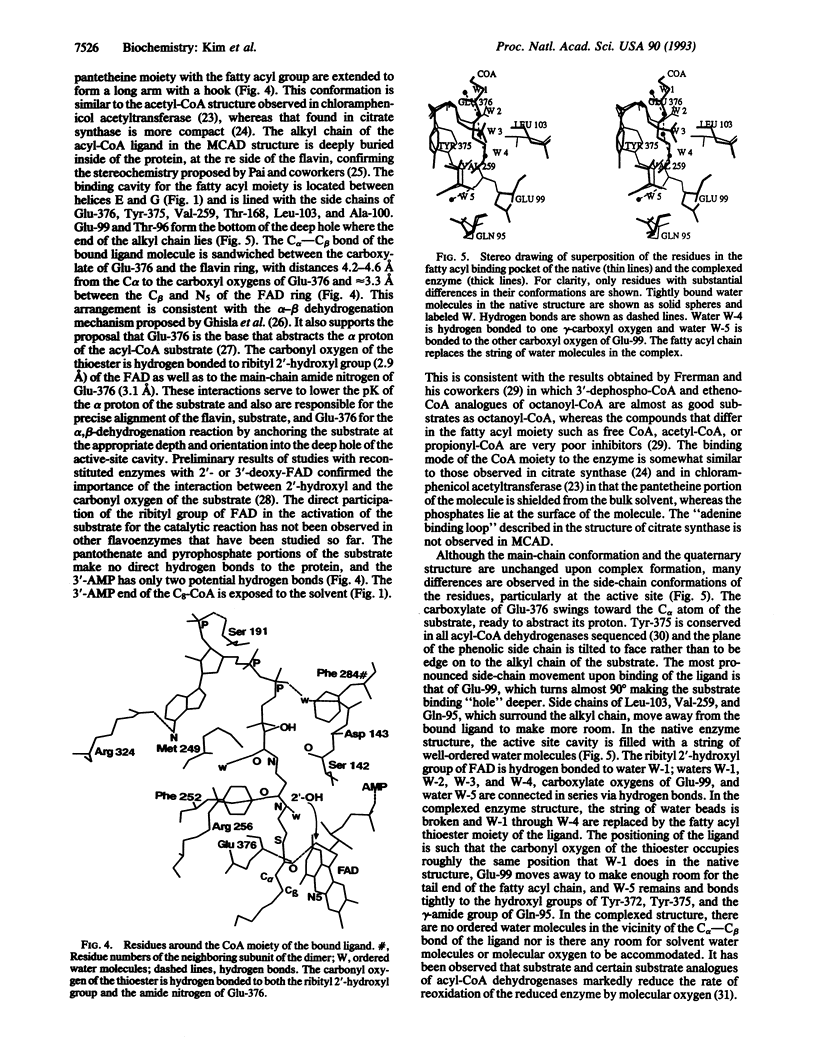
The three-dimensional structure of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase from pig mitochondria in the native form and that of a complex of the enzyme and a substrate (product) have been solved and refined by x-ray crystallographic methods at 2.4-A resolution to R factors of 0.172 and 0.173, respectively. The overall polypeptide folding and the quaternary structure of the tetramer are essentially unchanged upon binding of the ligand, octanoyl (octenoyl)-CoA. The ligand binds to the enzyme at the rectus (re) face of the FAD in the crevice between the two alpha-helix domains and the beta-sheet domain of the enzyme. The fatty acyl chain of the thioester substrate is buried inside of the polypeptide and the 3'-AMP moiety is close to the surface of the tetrameric enzyme molecule. The alkyl chain displaces the tightly bound water molecules found in the native enzyme and the carbonyl oxygen of the thioester interacts with the ribityl 2'-hydroxyl group of the FAD and the main-chain carbonyl oxygen of Glu-376. The C alpha--C beta of the fatty acyl moiety lies between the flavin and the gamma-carboxylate of Glu-376, supporting the role of Glu-376 as the base that abstracts the alpha proton in the alpha--beta dehydrogenation reaction catalyzed by the enzyme. Trp-166 and Met-165 are located at the sinister (si) side of the flavin ring at the surface of the enzyme, suggesting that they might be involved in the interactions with electron transferring flavoprotein. Lys-304, the prevalent mutation site found in patients with medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency, is located approximately 20 A away from the active site of the enzyme.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEINERT H., PAGE E. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. V. Oxidation-reductions of the flavoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1957 Mar;225(1):479–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann J. D., Frerman F. E. The effects of pH, ionic strength, and chemical modifications on the reaction of electron transfer flavoprotein with an acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7563–7569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE F. L., BEINERT H. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. II. The electron-transferring flavoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):717–731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRANE F. L., MII S., HAUGE J. G., GREEN D. E., BEINERT H. On the mechanism of dehydrogenation of fatty acyl derivatives of coenzyme A. I. The general fatty acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):701–706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frerman F. E., Miziorko H. M., Beckmann J. D. Enzyme-activated inhibitors, alternate substrates, and a dead end inhibitor of the general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 10;255(23):11192–11198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Engst S., Moll M., Bross P., Strauss A. W., Kim J. J. Alpha, beta-dehydrogenation by acyl-CoA dehydrogenases: role of functional groups at the active center. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1992;375:127–142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghisla S., Thorpe C., Massey V. Mechanistic studies with general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase and butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase: evidence for the transfer of the beta-hydrogen to the flavin N(5)-position as a hydride. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3154–3161. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Tanaka K. Purification and characterization of 2-methyl-branched chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase, an enzyme involved in the isoleucine and valine metabolism, from rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9477–9487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda Y., Tanaka K. Purification and characterization of isovaleryl coenzyme A dehydrogenase from rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1077–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izai K., Uchida Y., Orii T., Yamamoto S., Hashimoto T. Novel fatty acid beta-oxidation enzymes in rat liver mitochondria. I. Purification and properties of very-long-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 15;267(2):1027–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. P., Kim J. J., Billadello J. J., Hainline B. E., Chu T. W., Strauss A. W. Nucleotide sequence of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase mRNA and its expression in enzyme-deficient human tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4068–4072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly D. P., Whelan A. J., Ogden M. L., Alpers R., Zhang Z. F., Bellus G., Gregersen N., Dorland L., Strauss A. W. Molecular characterization of inherited medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9236–9240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. J., Wu J. Structure of the medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase from pig liver mitochondria at 3-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6677–6681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau S. M., Powell P., Buettner H., Ghisla S., Thorpe C. Medium-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase from pig kidney has intrinsic enoyl coenzyme A hydratase activity. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4184–4189. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenich A. C., Goodman S. I. The purification and characterization of glutaryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase from porcine and human liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4090–4096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie A. G., Moody P. C., Shaw W. V. Structure of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase at 1.75-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4133–4137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manstein D. J., Pai E. F., Schopfer L. M., Massey V. Absolute stereochemistry of flavins in enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6807–6816. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara Y., Indo Y., Naito E., Ozasa H., Glassberg R., Vockley J., Ikeda Y., Kraus J., Tanaka K. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNAs encoding the precursors of rat long chain acyl-coenzyme A, short chain acyl-coenzyme A, and isovaleryl-coenzyme A dehydrogenases. Sequence homology of four enzymes of the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16321–16331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara Y., Narisawa K., Miyabayashi S., Tada K., Coates P. M. Molecular lesion in patients with medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency. Lancet. 1990 Jun 30;335(8705):1589–1589. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)91413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizzer J. P., Thorpe C. Stabilization of the red semiquinone form of pig kidney general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase by acyl coenzyme A derivatives. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 18;20(17):4965–4970. doi: 10.1021/bi00520a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell P. J., Thorpe C. 2-octynoyl coenzyme A is a mechanism-based inhibitor of pig kidney medium-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase: isolation of the target peptide. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 18;27(21):8022–8028. doi: 10.1021/bi00421a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington S., Wiegand G., Huber R. Crystallographic refinement and atomic models of two different forms of citrate synthase at 2.7 and 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 15;158(1):111–152. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90452-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzicka F. J., Beinert H. A new iron-sulfur flavoprotein of the respiratory chain. A component of the fatty acid beta oxidation pathway. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8440–8445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer L. M., Massey V., Ghisla S., Thorpe C. Oxidation-reduction of general acyl-CoA dehydrogenase by the butyryl-CoA/crotonyl-CoA couple. A new investigation of the rapid reaction kinetics. Biochemistry. 1988 Aug 23;27(17):6599–6611. doi: 10.1021/bi00417a059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Thorpe C. Reactivity of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase toward molecular oxygen. Biochemistry. 1991 Aug 13;30(32):7895–7901. doi: 10.1021/bi00246a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota I., Indo Y., Coates P. M., Tanaka K. Molecular basis of medium chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency. An A to G transition at position 985 that causes a lysine-304 to glutamate substitution in the mature protein is the single prevalent mutation. J Clin Invest. 1990 Sep;86(3):1000–1003. doi: 10.1172/JCI114761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]