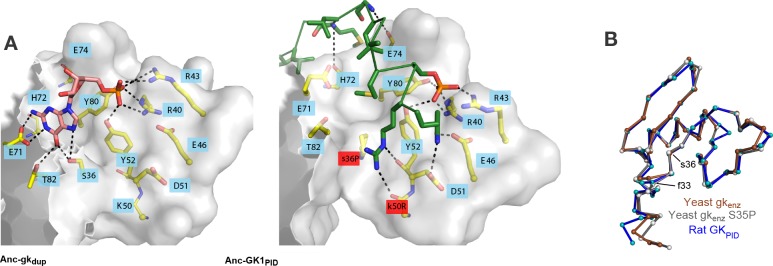
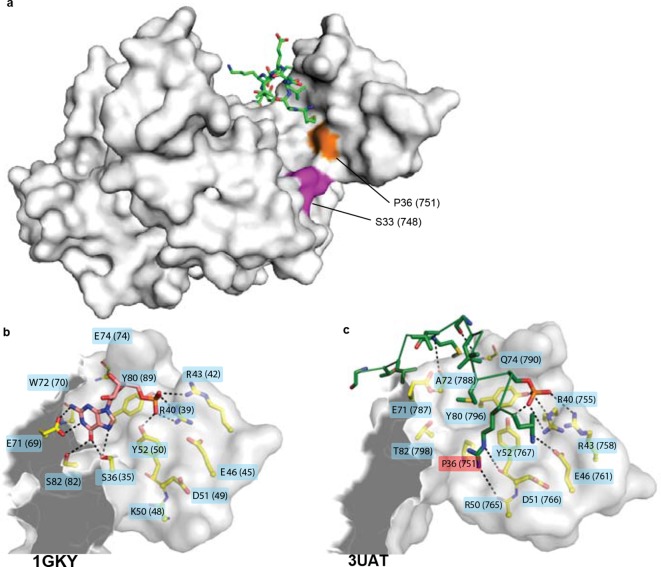
Figure 7. Evolution of GKPID’s new function by unveiling a latent protein-binding site.
(A) The binding surface for Pins in GKPIDs is derived from the GMP-binding surface of gk enzymes. Homology models of Anc-gkdup (left) and Anc-GK1PID (right) are shown as white surface, with all side chains that contact either GMP or Pins as yellow sticks. Pink sticks show GMP; green ribbon shows Pins backbone, with the side chains of all Pins residues that contact the GK protein shown as sticks. The phosphate group on GMP and on Pins residue 436 are shown as orange and red sticks. Black dotted lines, protein-ligand hydrogen bonds. In the AncGK1PID structure , substitutions at sites in the binding interface are shaded red, including key substitution s36P. The binding modes of extant gk enzymes and GKPIDs are similar and support the same conclusions (see Figure 7—figure supplement 1). (B) The structure of the hinge and GMP/Pins-binding lobes is conserved between the Pins-bound GKPID (blue, rat Dlg, 3UAT), the apo-gk enzyme (brown, S. cerevisiae guanylate kinase 1EX6), and the apo-gk-s36P mutant (gray, 4F4J), all in the open conformation.