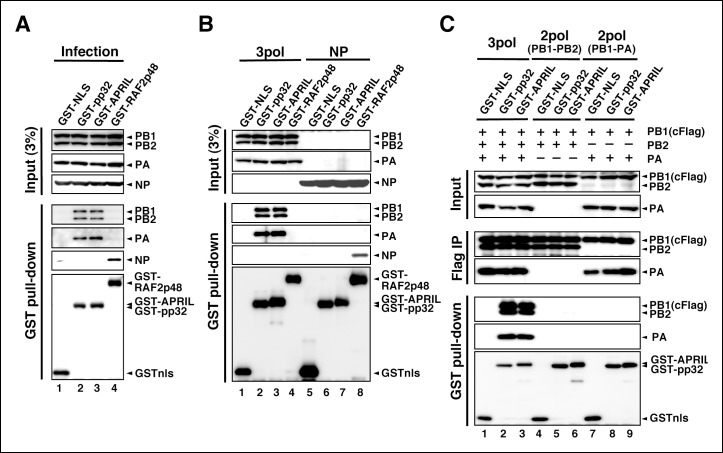
Figure 4. Interaction of influenza virus replication factor-2 (IREF-2) proteins with free forms of viral polymerase trimeric complexes.
(A) Interaction between IREF-2 and viral proteins in infected cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with 10 μg of plasmids expressing GSTnls (lane 1), GST-pp32 (lane 2), GST-APRIL (lane 3), and GST-RAF2p48 (lane 4). At 48 hr post transfection, influenza virus was infected at an multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 3. At 6 hr post infection, the transfected and infected cells were collected, lysed, and subjected to GST pull-down assays, as described in 'Materials and methods'. The pulled-down materials and 3% equivalent of the input samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by western blot analysis with anti-PB1, -PB2, -PA, -NP, and -GST (only the pull-down sample) antibodies. (B) Interaction between IREF-2 and viral proteins in the transfected cells. HEK293T cells were transfected with 5 μg of plasmids expressing GSTnls (lanes 1 and 5), GST-pp32 (lanes 2 and 6), GST-APRIL (lanes 3 and 7), and GST-RAF2p48 (lanes 4 and 8) and also co-transfected with the plasmids for the viral polymerase subunits (5 μg of pCAGGS-PB1, 12.5 μg of pCAGGS-PB2, and 2.5 μg of pCAGGS-PA [lanes 1–4] or 10 μg of pCAGGS-NP for NP expression [lanes 5–8]). Forty-eight hours post transfection, the cotransfected cells were collected, lysed, and subjected to GST pull-down assays. The input samples (3%) and pulled-down materials were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by western blot analysis. (C) Interaction between IREF-2 and trimeric or binary complexes of vRdRP. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with 5 μg of plasmids expressing GSTnls (lanes 1, 4, and 7), GST-pp32 (lanes 2, 5, and 6), GST-APRIL (lanes 3, 6, and 9), 5 μg of pCAGGS-PB1cFlag (lanes 1–9), 12.5 μg of pCAGGS-PB2 (lanes 1–6), and 2.5 μg of pCAGGS-PA (lanes 1–3 and 7–9). Forty-eight hours post transfection, the lysates from the cotransfected cells were subjected to GST pull-down assays or immunoprecipitation assays with anti-Flag antibody. The precipitated materials were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by western blot analysis.
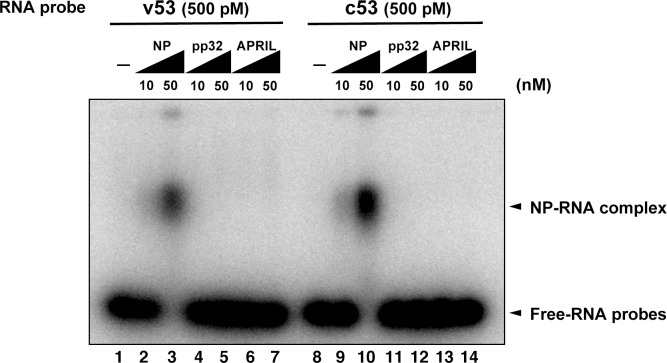
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Electrophoresis mobility shift assay for influenza virus replication factor-2 (IREF-2) and viral RNA.
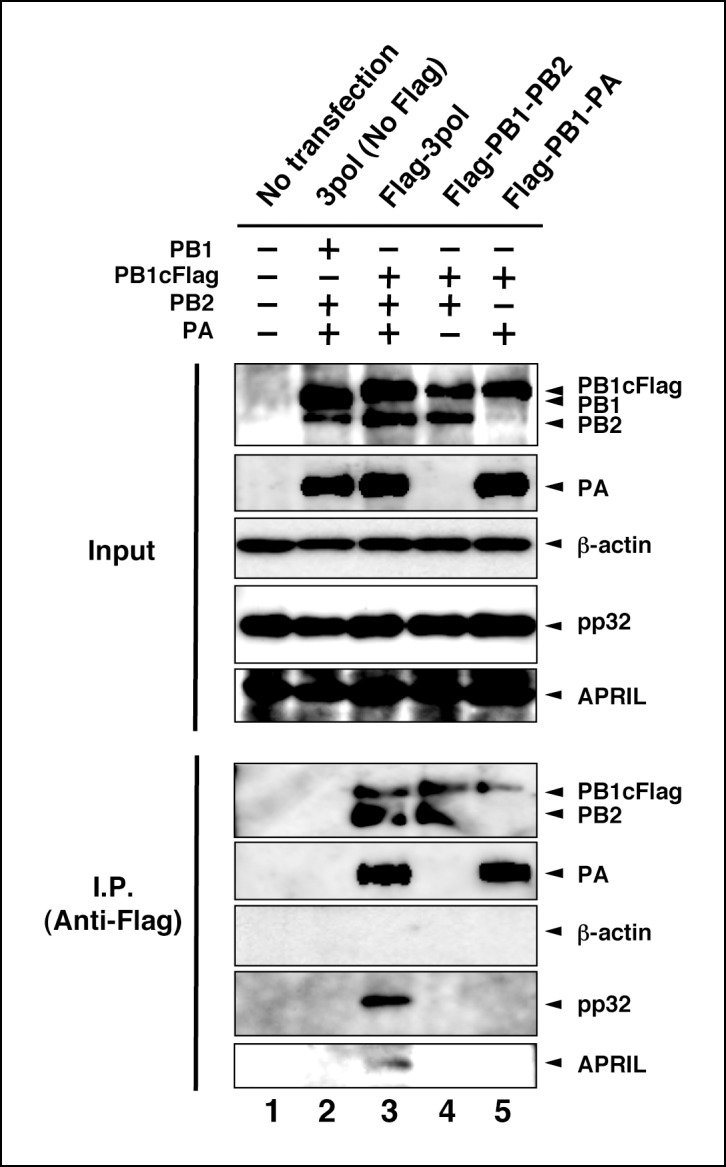
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. Interaction between viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (vRdRP) complexes and endogenous influenza virus replication factor-2 (IREF-2).