In the title compound, there is an intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond forming an S(9) ring motif. In the crystal, molecules are linked via C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds forming inversion dimers with an R 4 4(10) ring motif. The dimers are linked by C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming ribbons along [01-1].
Keywords: crystal structure, 8-quinolinol, bis(2-picolyl)amine, hydrogen bonding, π–π interactions
Abstract
In the title compound, C22H19ClN4O, the quinolinol moiety is almost planar [r.m.s. deviation = 0.012 Å]. There is an intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond involving the hydroxy group and a pyridine N atom forming an S(9) ring motif. The dihedral angles between the planes of the quinolinol moiety and the pyridine rings are 44.15 (9) and 36.85 (9)°. In the crystal, molecules are linked via C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds forming inversion dimers with an R 4 4(10) ring motif. The dimers are linked by C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming ribbons along [01-1]. The ribbons are linked by C—H⋯π and π–π interactions [inter-centroid distance = 3.7109 (11) Å], forming layers parallel to (01-1).
Chemical context
8-Quinolinol and its derivatives are well-known chelating reagents, forming fluorescent complexes with various metal ions, such as Al3+, Zn2+ and Cd2+ (Goon et al., 1953 ▸; Valeur & Leray, 2000 ▸; Pohl & Anzenbacher, 2003 ▸). Bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amine [di-(2-picolyl)amine (DPA)] is an excellent ligand showing high selectivity for Zn2+, which plays important roles in biological, pathological and environmental processes (Berg & Shi, 1996 ▸; Bush et al., 1994 ▸; Callender & Rice, 2000 ▸), and it is used to detect Zn2+ with low concentration in biological and environmental samples. Therefore, many fluorescence probes for Zn2+ bearing DPA as an ion-recognition site have been developed (Xue et al., 2008 ▸; Chen et al., 2011 ▸; Kwon et al., 2012 ▸). We have synthesized a new fluorescence chemosensor, based on 8-quinolinol containing DPA via a two-step reaction, and herein we report on its synthesis and crystal structure.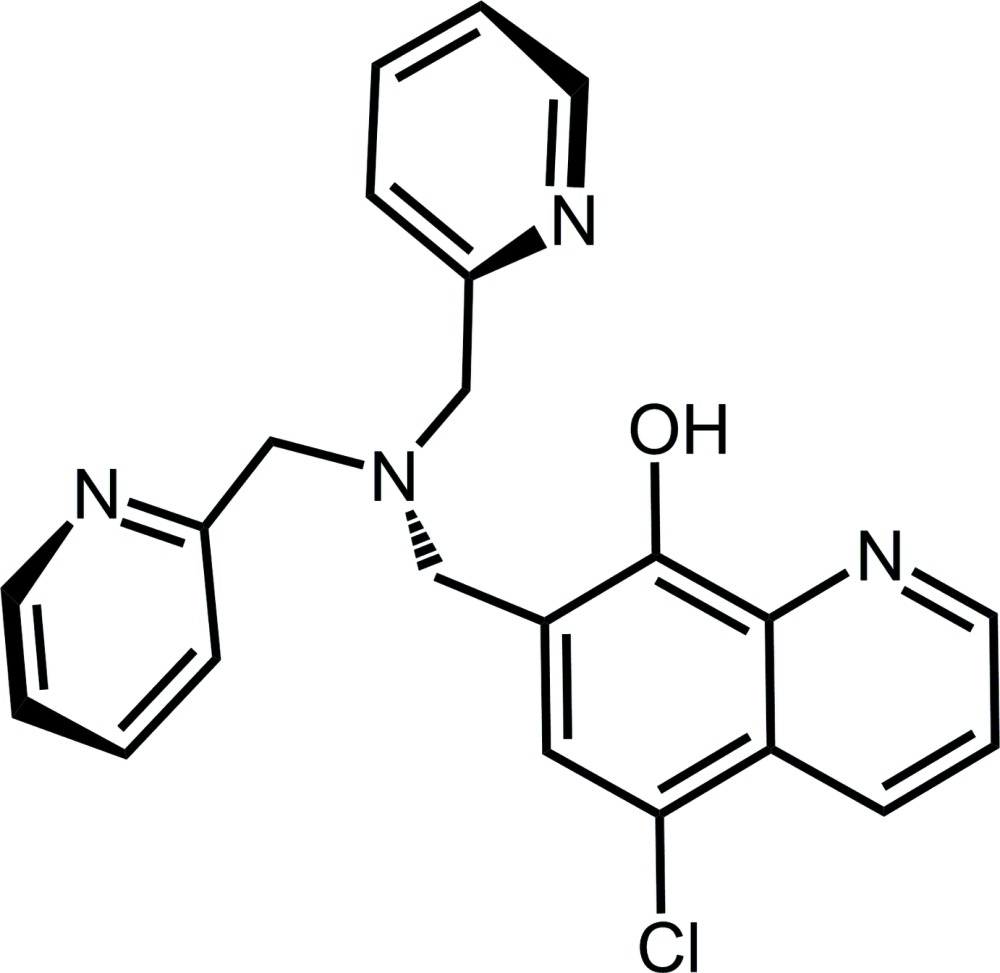
Structural commentary
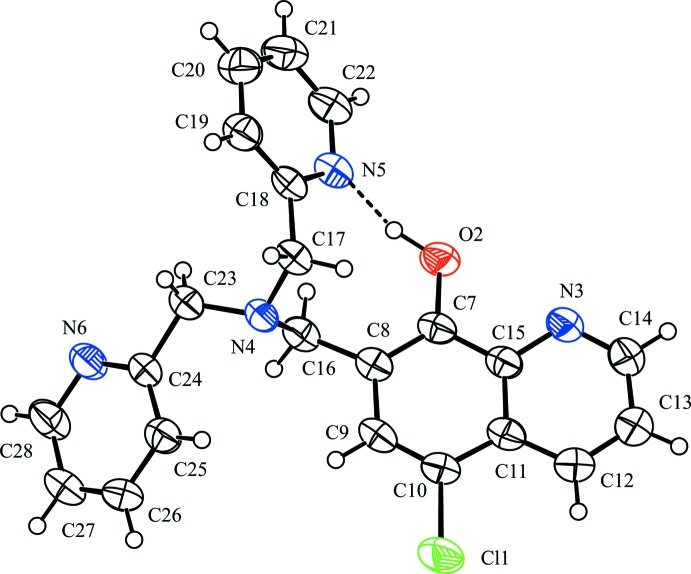
The molecular structure of the title compound, is shown in Fig. 1 ▸. There is an O—H⋯N intramolecular hydrogen bond involving the hydroxy group (O2—H2) and a pyridine N atom, N5, generating an S(9) ring motif (Fig. 1 ▸ and Table 1 ▸). The N(tertiaryamine)—C—C—N(pyridine) torsion angles, N4—C17—C18—N5 and N4—C23—C24—N6 are 75.0 (2) and 152.46 (19)°, respectively. The dihedral angle between the N5- and N6-containing pyridine rings pyridine rings is 80.97 (12)°, and they make dihedral angles of 44.15 (9) and 36.85 (9)°, respectively, with the quinolinol moiety.
Figure 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level. The intramolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bond is shown as a dashed line (see Table 1 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of rings N5/C18–C22 and N6/C24–C28, respectively.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2⋯N5 | 1.04 (3) | 1.66 (4) | 2.689 (3) | 168 (2) |
| C22—H22⋯O2i | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.348 (3) | 160 |
| C27—H27⋯N3ii | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.406 (3) | 153 |
| C17—H17b⋯Cg2iii | 0.97 | 2.79 | 3.599 (3) | 141 |
| C23—H23A⋯Cg3iv | 0.97 | 2.86 | 3.770 (3) | 156 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 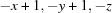 ; (ii)
; (ii) 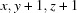 ; (iii)
; (iii) 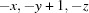 ; (iv)
; (iv) 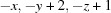 .
.
Supramolecular features
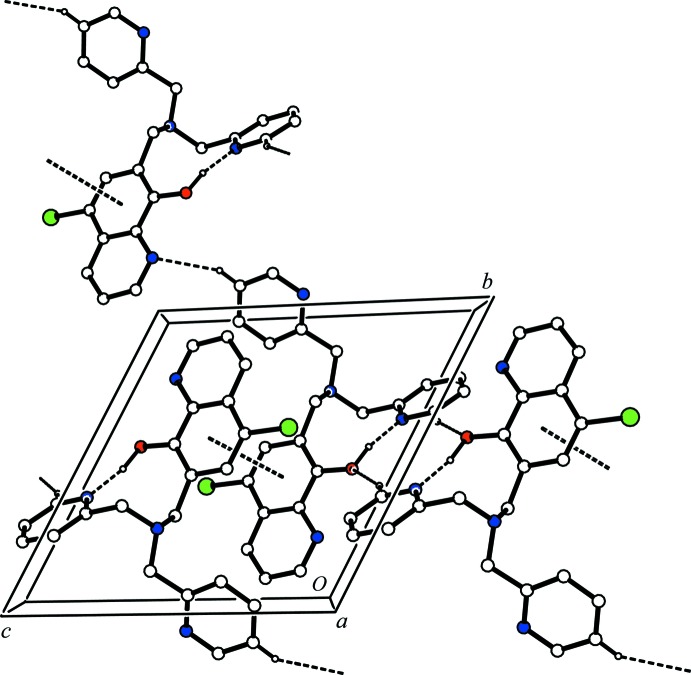
In the crystal, molecules are linked via C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming inversion dimers with an 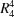 (10) ring motif (Fig. 2 ▸ and Table 1 ▸). The dimers are linked by C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming ribbons along [01
(10) ring motif (Fig. 2 ▸ and Table 1 ▸). The dimers are linked by C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming ribbons along [01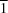 ]. The ribbons are linked by C—H⋯π (Table 1 ▸) and slipped parallel π–π interactions [Cg1⋯Cg1i, = 3.7109 (11) Å; Cg1 is the centroid of ring C7–C11/C15; inter-planar distance = 3.5518 (8) Å; slippage = 1.075 Å; symmetry code: (i) −x, −y + 1, −z], forming layers parallel to (01
]. The ribbons are linked by C—H⋯π (Table 1 ▸) and slipped parallel π–π interactions [Cg1⋯Cg1i, = 3.7109 (11) Å; Cg1 is the centroid of ring C7–C11/C15; inter-planar distance = 3.5518 (8) Å; slippage = 1.075 Å; symmetry code: (i) −x, −y + 1, −z], forming layers parallel to (01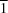 ) .
) .
Figure 2.
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. The hydrogen bonds (see Table 1 ▸) and π–π interactions are shown as dashed lines. H atoms not involved in these interactions have been omitted for clarity.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.36; Groom & Allen, 2014 ▸) for 8-quinolinols gave 387 hits, and for DPA, bis(pyridine-2-ylmethyl)amine gave 4535 hits. A search for the fragment 2-[bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl-amino)-methyl]phenol gave 56 hits of which none contained 8-quinolinol. In the compounds that resemble the title compound, namely 2,6-bis[bis(pyridine-2-ylmethyl)aminomethyl]-4-tert-butylphenol (I) (Bjernemose & McKenzie, 2003 ▸), and 3-{[bis(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino]methyl}-2-hydroxy-5-methylbenzaldehyde (II) (Wang et al., 2012 ▸), an intramolecular bifurcated hydrogen bond is formed. The N—C—C—N torsion angles in the related compounds are −46.9 (2) and 152.7 (2)° in (I) and 48.35 (18) and −116.99 (15)° in (II), compared to 75.0 (2) and 152.46 (19)° in the title compound. The crystal structures of other compounds containing a fluorescent core and bis(pyridine-2-ylmethyl)amine have been reported; for example one containing a fluorescein core (Wong et al., 2009 ▸), and another a coumarin core (Kobayashi et al., 2014 ▸).
Synthesis and crystallization
A suspension of paraformaldehyde (0.41 g, 14 mmol) and bis(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (1.99 g, 10 mmol) in 100 ml of MeOH was stirred for 18 h at room temperature. The solvent was removed under vacuum. To the product obtained was added 100 ml of toluene and 5-chloro-8-quinolinol (1.80 g, 10 mmol), and the mixture was heated for 24 h at 353 K. The solvent was removed under vacuum to give an oily product, which was crystallized from hexane–dichloromethane. The crude solid was recrystallized from acetonitrile to obtain yellow crystals of the title compound (yield 55%; m.p. 380.4–382.6 K). HRMS (m/z): [M + 1]+ calculated, 391.1326; found, 391.1271. Analysis calculated for C22H19ClN4O: C 67.60, H 4.90, N 14.33%; found: C 67.50, H 5.01, N 14.37%.
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The hydroxy H atom was located in a difference Fourier map and freely refined. The C-bound H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model: C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C).
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C22H19ClN4O |
| M r | 390.86 |
| Crystal system, space group | Triclinic, P
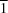
|
| Temperature (K) | 296 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 8.3170 (5), 11.5993 (7), 11.6135 (6) |
| α, β, γ (°) | 116.8473 (13), 105.2809 (13), 92.0110 (17) |
| V (Å3) | 948.68 (10) |
| Z | 2 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.22 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.10 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi, 1995 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.769, 0.978 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [F 2 > 2.0σ(F 2)] reflections | 9412, 4293, 2329 |
| R int | 0.023 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.648 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.036, 0.123, 1.09 |
| No. of reflections | 4293 |
| No. of parameters | 257 |
| H-atom treatment | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.26, −0.24 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022410/su5241sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022410/su5241Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022410/su5241Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1438483
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This study was supported financially in part by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research (No. 15 K05539) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C22H19ClN4O | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 390.86 | F(000) = 408.00 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.368 Mg m−3 |
| a = 8.3170 (5) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71075 Å |
| b = 11.5993 (7) Å | Cell parameters from 5840 reflections |
| c = 11.6135 (6) Å | θ = 3.1–27.4° |
| α = 116.8473 (13)° | µ = 0.22 mm−1 |
| β = 105.2809 (13)° | T = 296 K |
| γ = 92.0110 (17)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 948.68 (10) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.20 × 0.10 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID diffractometer | 2329 reflections with F2 > 2.0σ(F2) |
| Detector resolution: 10.000 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.023 |
| ω scans | θmax = 27.4°, θmin = 3.1° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi, 1995) | h = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.769, Tmax = 0.978 | k = −15→15 |
| 9412 measured reflections | l = −14→15 |
| 4293 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.036 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.123 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0488P)2 + 0.1777P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4293 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 257 parameters | Δρmax = 0.26 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
Special details
| Geometry. Refinement was performed using all reflections. The weighted R-factor (wR) and goodness of fit (S) are based on F2. R-factor (gt) are based on F. The threshold expression of F2 > 2.0 sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factor (gt). |
| Refinement. Refinement was performed using all reflections. The weighted R-factor (wR) and goodness of fit (S) are based on F2. R-factor (gt) are based on F. The threshold expression of F2 > 2.0 σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factor (gt). |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.20020 (9) | 0.40251 (6) | 0.58501 (6) | 0.0724 (2) | |
| O2 | 0.3787 (2) | 0.45209 (15) | 0.14798 (14) | 0.0563 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.3767 (2) | 0.22221 (18) | 0.14868 (17) | 0.0560 (5) | |
| N4 | 0.1525 (2) | 0.72637 (15) | 0.33905 (15) | 0.0432 (4) | |
| N5 | 0.2432 (2) | 0.61932 (17) | 0.06500 (16) | 0.0500 (4) | |
| N6 | 0.2990 (2) | 1.07071 (18) | 0.58796 (17) | 0.0562 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.3408 (2) | 0.4468 (2) | 0.25274 (18) | 0.0444 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.3075 (2) | 0.5531 (2) | 0.35655 (19) | 0.0440 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.2637 (3) | 0.5344 (2) | 0.45812 (19) | 0.0488 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.2564 (3) | 0.4177 (2) | 0.45746 (19) | 0.0474 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.2949 (2) | 0.3074 (2) | 0.35528 (18) | 0.0451 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.2940 (3) | 0.1827 (2) | 0.3486 (2) | 0.0546 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.3335 (3) | 0.0841 (2) | 0.2454 (2) | 0.0642 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.3733 (3) | 0.1088 (2) | 0.1483 (2) | 0.0645 (6) | |
| C15 | 0.3387 (2) | 0.3236 (2) | 0.25179 (18) | 0.0439 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.3190 (3) | 0.6889 (2) | 0.3710 (2) | 0.0469 (5) | |
| C17 | 0.0484 (3) | 0.6472 (2) | 0.19651 (18) | 0.0453 (5) | |
| C18 | 0.1068 (3) | 0.67040 (19) | 0.09391 (18) | 0.0440 (5) | |
| C19 | 0.0266 (3) | 0.7400 (2) | 0.0336 (2) | 0.0542 (5) | |
| C20 | 0.0860 (3) | 0.7593 (3) | −0.0582 (2) | 0.0646 (6) | |
| C21 | 0.2264 (3) | 0.7087 (3) | −0.0865 (2) | 0.0637 (6) | |
| C22 | 0.2999 (3) | 0.6399 (2) | −0.0238 (2) | 0.0577 (6) | |
| C23 | 0.1681 (3) | 0.8665 (2) | 0.3842 (2) | 0.0549 (6) | |
| C24 | 0.2147 (3) | 0.9495 (2) | 0.53687 (19) | 0.0463 (5) | |
| C25 | 0.1679 (3) | 0.9048 (2) | 0.6174 (2) | 0.0563 (6) | |
| C26 | 0.2149 (3) | 0.9865 (2) | 0.7564 (2) | 0.0600 (6) | |
| C27 | 0.3044 (3) | 1.1103 (2) | 0.8101 (2) | 0.0570 (6) | |
| C28 | 0.3404 (3) | 1.1481 (2) | 0.7224 (2) | 0.0614 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.329 (3) | 0.526 (3) | 0.129 (3) | 0.098 (9)* | |
| H9 | 0.23914 | 0.60515 | 0.52745 | 0.0585* | |
| H12 | 0.26668 | 0.16817 | 0.41415 | 0.0655* | |
| H13 | 0.33386 | 0.00152 | 0.23959 | 0.0771* | |
| H14 | 0.39931 | 0.0399 | 0.07819 | 0.0774* | |
| H16A | 0.38532 | 0.7515 | 0.46354 | 0.0563* | |
| H16B | 0.37804 | 0.69349 | 0.31109 | 0.0563* | |
| H17A | −0.06633 | 0.66426 | 0.18846 | 0.0544* | |
| H17B | 0.04458 | 0.55522 | 0.17233 | 0.0544* | |
| H19 | −0.06765 | 0.77418 | 0.05442 | 0.0651* | |
| H20 | 0.03192 | 0.80564 | −0.10001 | 0.0776* | |
| H21 | 0.27022 | 0.72111 | −0.14678 | 0.0764* | |
| H22 | 0.39441 | 0.60539 | −0.04348 | 0.0692* | |
| H23A | 0.06141 | 0.88388 | 0.34197 | 0.0659* | |
| H23B | 0.25394 | 0.89247 | 0.35362 | 0.0659* | |
| H25 | 0.10548 | 0.82092 | 0.57873 | 0.0676* | |
| H26 | 0.18619 | 0.95777 | 0.81246 | 0.0720* | |
| H27 | 0.33951 | 1.16686 | 0.90321 | 0.0684* | |
| H28 | 0.39751 | 1.2333 | 0.75867 | 0.0737* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0990 (5) | 0.0762 (4) | 0.0553 (4) | 0.0150 (4) | 0.0451 (3) | 0.0312 (3) |
| O2 | 0.0698 (10) | 0.0665 (10) | 0.0499 (8) | 0.0272 (8) | 0.0355 (8) | 0.0321 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0734 (13) | 0.0579 (12) | 0.0446 (10) | 0.0263 (10) | 0.0282 (9) | 0.0247 (9) |
| N4 | 0.0515 (10) | 0.0396 (9) | 0.0336 (8) | 0.0077 (8) | 0.0159 (7) | 0.0123 (8) |
| N5 | 0.0525 (11) | 0.0546 (11) | 0.0389 (9) | 0.0099 (9) | 0.0180 (8) | 0.0169 (9) |
| N6 | 0.0747 (13) | 0.0454 (11) | 0.0413 (10) | 0.0005 (9) | 0.0243 (9) | 0.0122 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0422 (11) | 0.0567 (13) | 0.0350 (10) | 0.0116 (10) | 0.0153 (9) | 0.0206 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0415 (11) | 0.0493 (12) | 0.0364 (10) | 0.0063 (9) | 0.0121 (8) | 0.0167 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0504 (12) | 0.0543 (13) | 0.0336 (10) | 0.0101 (10) | 0.0165 (9) | 0.0125 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0511 (12) | 0.0551 (14) | 0.0363 (10) | 0.0075 (10) | 0.0161 (9) | 0.0208 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0416 (11) | 0.0543 (13) | 0.0347 (10) | 0.0079 (10) | 0.0108 (8) | 0.0181 (10) |
| C12 | 0.0622 (14) | 0.0598 (15) | 0.0463 (12) | 0.0117 (11) | 0.0188 (11) | 0.0281 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0846 (18) | 0.0573 (15) | 0.0593 (14) | 0.0216 (13) | 0.0287 (13) | 0.0308 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0896 (18) | 0.0579 (15) | 0.0530 (13) | 0.0316 (13) | 0.0333 (13) | 0.0250 (12) |
| C15 | 0.0437 (11) | 0.0522 (13) | 0.0352 (10) | 0.0132 (10) | 0.0143 (9) | 0.0192 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0478 (12) | 0.0478 (12) | 0.0364 (10) | 0.0022 (10) | 0.0140 (9) | 0.0129 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0450 (11) | 0.0461 (12) | 0.0361 (10) | 0.0051 (9) | 0.0135 (9) | 0.0122 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0441 (11) | 0.0431 (11) | 0.0305 (9) | 0.0027 (9) | 0.0095 (8) | 0.0075 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0544 (13) | 0.0585 (14) | 0.0441 (11) | 0.0130 (11) | 0.0146 (10) | 0.0201 (11) |
| C20 | 0.0732 (17) | 0.0701 (16) | 0.0520 (13) | 0.0108 (13) | 0.0155 (12) | 0.0326 (13) |
| C21 | 0.0717 (16) | 0.0737 (17) | 0.0466 (12) | 0.0020 (13) | 0.0214 (12) | 0.0288 (13) |
| C22 | 0.0566 (14) | 0.0681 (15) | 0.0446 (12) | 0.0090 (12) | 0.0230 (10) | 0.0203 (12) |
| C23 | 0.0801 (16) | 0.0432 (13) | 0.0376 (11) | 0.0105 (11) | 0.0217 (11) | 0.0144 (10) |
| C24 | 0.0585 (13) | 0.0413 (12) | 0.0363 (10) | 0.0111 (10) | 0.0191 (9) | 0.0137 (9) |
| C25 | 0.0781 (16) | 0.0463 (13) | 0.0465 (12) | 0.0078 (11) | 0.0280 (11) | 0.0193 (11) |
| C26 | 0.0820 (17) | 0.0648 (16) | 0.0449 (12) | 0.0187 (13) | 0.0331 (12) | 0.0283 (12) |
| C27 | 0.0613 (14) | 0.0620 (15) | 0.0355 (11) | 0.0108 (12) | 0.0189 (10) | 0.0113 (11) |
| C28 | 0.0685 (16) | 0.0535 (14) | 0.0442 (12) | −0.0039 (12) | 0.0215 (11) | 0.0076 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Cl1—C10 | 1.743 (3) | C21—C22 | 1.366 (4) |
| O2—C7 | 1.361 (3) | C23—C24 | 1.514 (3) |
| N3—C14 | 1.313 (4) | C24—C25 | 1.382 (4) |
| N3—C15 | 1.368 (3) | C25—C26 | 1.384 (3) |
| N4—C16 | 1.470 (3) | C26—C27 | 1.369 (4) |
| N4—C17 | 1.466 (2) | C27—C28 | 1.370 (4) |
| N4—C23 | 1.454 (3) | O2—H2 | 1.04 (3) |
| N5—C18 | 1.349 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.930 |
| N5—C22 | 1.347 (4) | C12—H12 | 0.930 |
| N6—C24 | 1.334 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.930 |
| N6—C28 | 1.338 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.930 |
| C7—C8 | 1.381 (3) | C16—H16A | 0.970 |
| C7—C15 | 1.424 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.970 |
| C8—C9 | 1.422 (4) | C17—H17A | 0.970 |
| C8—C16 | 1.504 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.970 |
| C9—C10 | 1.349 (4) | C19—H19 | 0.930 |
| C10—C11 | 1.416 (3) | C20—H20 | 0.930 |
| C11—C12 | 1.412 (4) | C21—H21 | 0.930 |
| C11—C15 | 1.429 (4) | C22—H22 | 0.930 |
| C12—C13 | 1.359 (3) | C23—H23A | 0.970 |
| C13—C14 | 1.394 (5) | C23—H23B | 0.970 |
| C17—C18 | 1.521 (4) | C25—H25 | 0.930 |
| C18—C19 | 1.375 (4) | C26—H26 | 0.930 |
| C19—C20 | 1.384 (4) | C27—H27 | 0.930 |
| C20—C21 | 1.376 (4) | C28—H28 | 0.930 |
| C14—N3—C15 | 117.7 (2) | N6—C28—C27 | 124.4 (2) |
| C16—N4—C17 | 113.69 (15) | C7—O2—H2 | 112.4 (18) |
| C16—N4—C23 | 111.51 (16) | C8—C9—H9 | 118.825 |
| C17—N4—C23 | 112.33 (18) | C10—C9—H9 | 118.839 |
| C18—N5—C22 | 117.9 (2) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.293 |
| C24—N6—C28 | 117.2 (2) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.294 |
| O2—C7—C8 | 123.5 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.515 |
| O2—C7—C15 | 116.17 (17) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.514 |
| C8—C7—C15 | 120.4 (2) | N3—C14—H14 | 117.649 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 118.4 (2) | C13—C14—H14 | 117.655 |
| C7—C8—C16 | 124.0 (2) | N4—C16—H16A | 108.956 |
| C9—C8—C16 | 117.66 (18) | N4—C16—H16B | 108.959 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 122.34 (19) | C8—C16—H16A | 108.959 |
| Cl1—C10—C9 | 119.55 (16) | C8—C16—H16B | 108.962 |
| Cl1—C10—C11 | 119.4 (2) | H16A—C16—H16B | 107.759 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 121.1 (2) | N4—C17—H17A | 108.296 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 124.8 (2) | N4—C17—H17B | 108.295 |
| C10—C11—C15 | 117.6 (2) | C18—C17—H17A | 108.301 |
| C12—C11—C15 | 117.59 (18) | C18—C17—H17B | 108.301 |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.4 (3) | H17A—C17—H17B | 107.402 |
| C12—C13—C14 | 119.0 (3) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.991 |
| N3—C14—C13 | 124.7 (2) | C20—C19—H19 | 119.983 |
| N3—C15—C7 | 118.2 (2) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.561 |
| N3—C15—C11 | 121.6 (2) | C21—C20—H20 | 120.563 |
| C7—C15—C11 | 120.18 (18) | C20—C21—H21 | 120.849 |
| N4—C16—C8 | 113.11 (17) | C22—C21—H21 | 120.854 |
| N4—C17—C18 | 115.94 (17) | N5—C22—H22 | 118.151 |
| N5—C18—C17 | 116.4 (2) | C21—C22—H22 | 118.151 |
| N5—C18—C19 | 121.2 (2) | N4—C23—H23A | 108.897 |
| C17—C18—C19 | 122.4 (2) | N4—C23—H23B | 108.899 |
| C18—C19—C20 | 120.0 (2) | C24—C23—H23A | 108.892 |
| C19—C20—C21 | 118.9 (3) | C24—C23—H23B | 108.896 |
| C20—C21—C22 | 118.3 (3) | H23A—C23—H23B | 107.725 |
| N5—C22—C21 | 123.7 (2) | C24—C25—H25 | 120.400 |
| N4—C23—C24 | 113.4 (2) | C26—C25—H25 | 120.399 |
| N6—C24—C23 | 115.3 (2) | C25—C26—H26 | 120.492 |
| N6—C24—C25 | 122.17 (18) | C27—C26—H26 | 120.490 |
| C23—C24—C25 | 122.53 (19) | C26—C27—H27 | 121.022 |
| C24—C25—C26 | 119.2 (2) | C28—C27—H27 | 121.032 |
| C25—C26—C27 | 119.0 (3) | N6—C28—H28 | 117.816 |
| C26—C27—C28 | 117.95 (19) | C27—C28—H28 | 117.809 |
| C14—N3—C15—C7 | −179.57 (17) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.9 (3) |
| C14—N3—C15—C11 | −0.6 (3) | Cl1—C10—C11—C12 | −1.0 (2) |
| C15—N3—C14—C13 | 0.1 (3) | Cl1—C10—C11—C15 | 179.37 (11) |
| C16—N4—C17—C18 | −70.7 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 178.57 (16) |
| C17—N4—C16—C8 | −65.3 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C15 | −1.1 (3) |
| C16—N4—C23—C24 | −72.8 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −179.91 (16) |
| C23—N4—C16—C8 | 166.49 (16) | C10—C11—C15—N3 | −179.63 (15) |
| C17—N4—C23—C24 | 158.23 (17) | C10—C11—C15—C7 | −0.7 (2) |
| C23—N4—C17—C18 | 57.1 (2) | C12—C11—C15—N3 | 0.7 (2) |
| C18—N5—C22—C21 | −0.4 (2) | C12—C11—C15—C7 | 179.66 (15) |
| C22—N5—C18—C17 | −178.93 (13) | C15—C11—C12—C13 | −0.3 (3) |
| C22—N5—C18—C19 | 0.8 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.2 (3) |
| C24—N6—C28—C27 | 1.1 (3) | C12—C13—C14—N3 | 0.4 (4) |
| C28—N6—C24—C23 | 178.99 (18) | N4—C17—C18—N5 | 75.0 (2) |
| C28—N6—C24—C25 | 1.3 (3) | N4—C17—C18—C19 | −104.73 (19) |
| O2—C7—C8—C9 | 177.87 (14) | N5—C18—C19—C20 | −0.3 (2) |
| O2—C7—C8—C16 | −3.8 (3) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | 179.38 (13) |
| O2—C7—C15—N3 | 1.0 (2) | C18—C19—C20—C21 | −0.5 (3) |
| O2—C7—C15—C11 | −177.99 (13) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | 0.9 (3) |
| C8—C7—C15—N3 | −178.35 (15) | C20—C21—C22—N5 | −0.4 (3) |
| C8—C7—C15—C11 | 2.7 (2) | N4—C23—C24—N6 | 152.46 (19) |
| C15—C7—C8—C9 | −2.8 (2) | N4—C23—C24—C25 | −29.9 (3) |
| C15—C7—C8—C16 | 175.54 (14) | N6—C24—C25—C26 | −2.4 (4) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 1.1 (3) | C23—C24—C25—C26 | −179.9 (2) |
| C7—C8—C16—N4 | 107.8 (2) | C24—C25—C26—C27 | 1.0 (4) |
| C9—C8—C16—N4 | −73.8 (2) | C25—C26—C27—C28 | 1.2 (4) |
| C16—C8—C9—C10 | −177.37 (15) | C26—C27—C28—N6 | −2.3 (4) |
| C8—C9—C10—Cl1 | −179.55 (14) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of rings N5/C18–C22 and N6/C24–C28, respectively.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2···N5 | 1.04 (3) | 1.66 (4) | 2.689 (3) | 168 (2) |
| C22—H22···O2i | 0.93 | 2.46 | 3.348 (3) | 160 |
| C27—H27···N3ii | 0.93 | 2.55 | 3.406 (3) | 153 |
| C17—H17b···Cg2iii | 0.97 | 2.79 | 3.599 (3) | 141 |
| C23—H23A···Cg3iv | 0.97 | 2.86 | 3.770 (3) | 156 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z; (ii) x, y+1, z+1; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z; (iv) −x, −y+2, −z+1.
References
- Altomare, A., Cascarano, G., Giacovazzo, C. & Guagliardi, A. (1993). J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 343–350.
- Berg, J. M. & Shi, Y. (1996). Science, 271, 1081–1085. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bjernemose, J. K. & McKenzie, C. J. (2003). Acta Cryst. E59, o1275–o1276.
- Bush, A. I., Pettingell, W. H., Multhaup, G., d Paradis, M., Vonsattel, J.-P., Gusella, J. F., Beyreuther, K., Masters, C. L. & Tanzi, R. E. (1994). Science, 265, 1464–1467. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Callender, E. & Rice, K. C. (2000). Environ. Sci. Technol. 34, 232–238.
- Chen, W.-H., Xing, Y. & Pang, Y. (2011). Org. Lett. 13, 1362–1365. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Goon, E., Petley, J. E., McMullen, W. H. & Wiberley, S. E. (1953). Anal. Chem. 25, 608–610.
- Groom, C. R. & Allen, F. H. (2014). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 662–671. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T. (1995). ABSCOR. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Kobayashi, H., Katano, K., Hashimoto, T. & Hayashita, T. (2014). Anal. Sci. 30, 1045–1050. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kwon, J. E., Lee, S., You, Y., Baek, K.-H., Ohkubo, K., Cho, J., Fukuzumi, S., Shin, I., Park, S. Y. & Nam, W. (2012). Inorg. Chem. 51, 8760–8774. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Pohl, R. & Anzenbacher, P. Jr (2003). Org. Lett. 5, 2769–2772. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku (2006). RAPID-AUTO. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2014). CrystalStructure. Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Valeur, B. & Leray, I. (2000). Coord. Chem. Rev. 205, 3–40.
- Wang, R.-X., Gao, D.-Z., Ye, F., Wu, Y.-F. & Zhu, D.-R. (2012). Acta Cryst. E68, o1672–o1673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wong, B. A., Friedle, S. & Lippard, S. J. (2009). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 131, 7142–7152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Xue, L., Wang, H.-H., Wang, X. J. & Jiang, H. (2008). Inorg. Chem. 47, 4310–4318. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022410/su5241sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022410/su5241Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022410/su5241Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1438483
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report