Abstract
The Fe atom in the title ferrocene derivative, [Fe(C11H15O2)2], is situated on an inversion centre. As a result of the point-group symmetry -1 of the molecule, the ferrocene moiety adopts a staggered conformation. The average Fe—C(Cp) bond length (Cp is cyclopentadienyl) is 2.045 (4) Å, in agreement with that of other disubstituted ferrocenes. The Fe—C bond length involving the substituted C atom is slightly longer [2.0521 (17) Å] than the remaining Fe—C bond lengths caused by the inductive effect of the methylene group on the Cp ring. Apart from van der Waals forces, no significant intermolecular interactions are observed in the crystal packing.
Keywords: crystal structure, inversion symmetry, disubstituted ferrocene, ester
Related literature
The interest in disubstituted ferrocene compounds has increased due to their applications in the field of homogeneous catalysis, biology and medicine (Atkinson et al., 2004 ▸; Gao et al., 2009 ▸; Ferreira et al., 2006 ▸). The presence of ester groups on these compounds make them promising candidates for the construction of metal-containing polymers (Wilbert et al., 1995 ▸). Related structures have been described by Woodward et al. (1952 ▸); Cetina et al. (2003 ▸); Navarro et al. (2004 ▸); Pérez et al. (2015 ▸).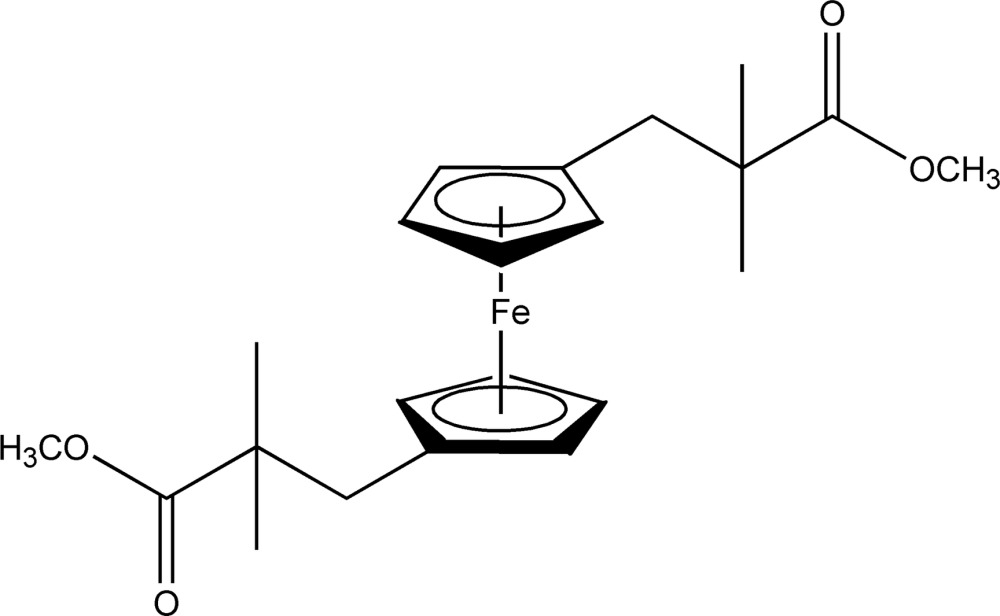
Experimental
Crystal data
[Fe(C11H15O2)2]
M r = 414.31
Triclinic,
a = 6.273 (3) Å
b = 8.313 (4) Å
c = 10.490 (5) Å
α = 83.833 (6)°
β = 74.405 (7)°
γ = 81.652 (8)°
V = 520.0 (4) Å3
Z = 1
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.75 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.15 × 0.12 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) T min = 0.896, T max = 0.916
2753 measured reflections
1793 independent reflections
1688 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.013
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.029
wR(F 2) = 0.074
S = 1.05
1793 reflections
124 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2012 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2012 ▸); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg & Berndt, 1999 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020642/wm5231sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020642/wm5231Isup2.hkl
x y z . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020642/wm5231fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title complex, showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. All H atoms have been omitted for clarity. Unlabelled atoms are related to labelled ones by the symmetry operation −x, −y + 1, −z + 1.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020642/wm5231fig2.tif
The packing of molecules in the crystal structure of the title compound.
CCDC reference: 1434467
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful for the financial support from the Open Project Program of Key Laboratory of Eco-textiles, Ministry of Education, Jiangnan University (No. KLET1303).
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Experimental
1,1'-bis(1-methoxy-methyl)ferrocene was first prepared by refluxing 1,1'-bis(hydroxymethyl)ferrocene in methanol and acetic acid (12:1 v/v) for 16 h. Then a solution of 1,1,-bis(1-methoxy-methyl)ferrocene (3.481 g, 12.7 mmol), 1-methoxy-1-(trimethylsiloxy)-2-methyl-1-propene (10.5 ml, 50.8 mmol) and BF3—OEt2 (3.5 ml, 27.9 mmol) in CH2Cl2 (180 ml) was stirred at 195 K for 15 min. The reaction was quenched with a satured solution of NaHCO3 and extracted with CH2Cl2. The organic phases were combined and dried to give a viscous yellow oil, which was chromatographed over a column of silica gel using ethyl acetate/petroleum ether (1:4 v/v) as the eluent. Yellow crystals of the title compound were obtained by slow evaporation of a solution in dichloromethane/petroleum ether (333-363 K). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CDCl3) δ 3.97 (d, 8H, C5H4FeC5H4), 3.62 (s, 6H, OCH3), 2.57 (s, 4H, CH2), 1.08 (s, 12H, C(CH3)2). HRMS (ESI): C22H30FeO4 calcd for [M + H]+ 415.1572, found 415.1575.
S2. Refinement
H atoms were placed in calculated positions and thereafter treated as riding atoms, with C—H = 0.98 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) (Cp rings CH), 0.97 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) (methylene CH2) and 0.96 Å Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) (methyl CH3).
Figures
Fig. 1.
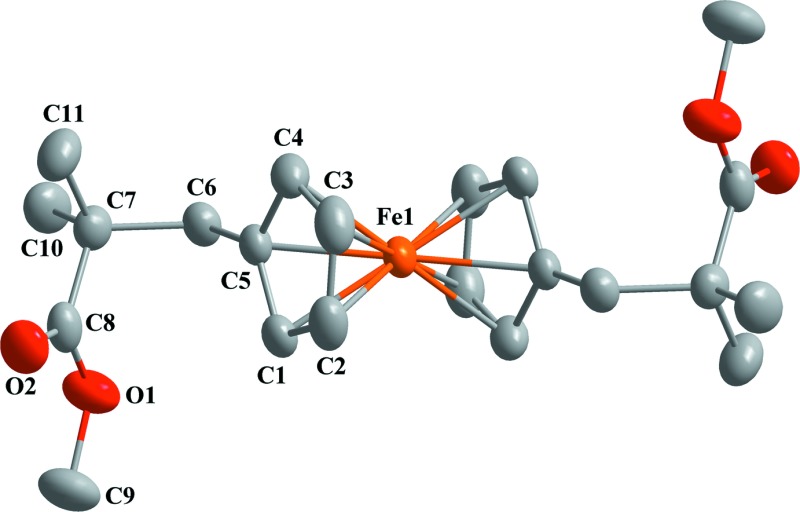
The molecular structure of the title complex, showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. All H atoms have been omitted for clarity. Unlabelled atoms are related to labelled ones by the symmetry operation -x, -y + 1, -z + 1.
Fig. 2.
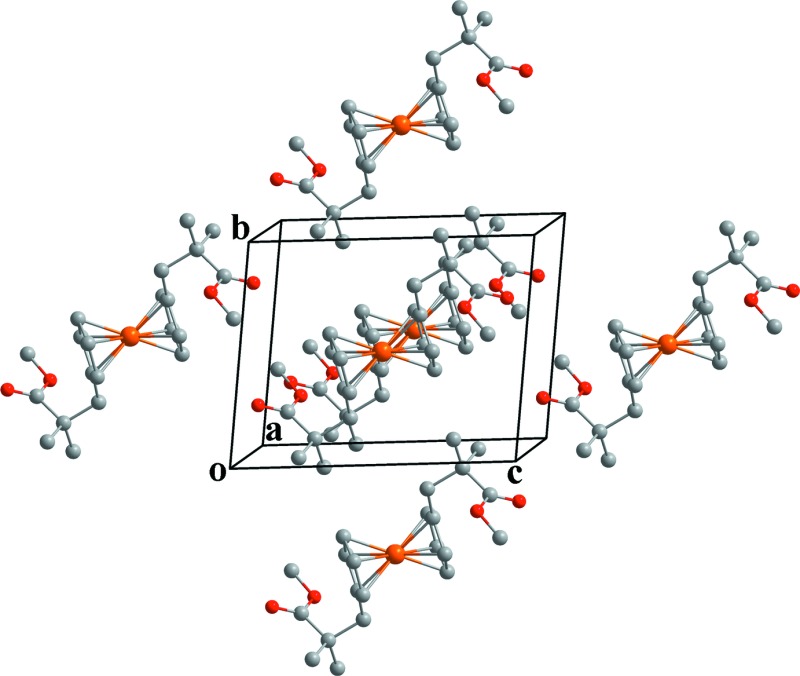
The packing of molecules in the crystal structure of the title compound.
Crystal data
| [Fe(C11H15O2)2] | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 414.31 | F(000) = 220 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.323 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.273 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 1589 reflections |
| b = 8.313 (4) Å | θ = 3.3–28.2° |
| c = 10.490 (5) Å | µ = 0.75 mm−1 |
| α = 83.833 (6)° | T = 296 K |
| β = 74.405 (7)° | Block, yellow |
| γ = 81.652 (8)° | 0.15 × 0.12 × 0.12 mm |
| V = 520.0 (4) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 1793 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1688 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.013 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | h = −7→5 |
| Tmin = 0.896, Tmax = 0.916 | k = −9→9 |
| 2753 measured reflections | l = −12→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.029 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.074 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.038P)2 + 0.1517P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1793 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 124 parameters | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Fe1 | 0.0000 | 0.5000 | 0.5000 | 0.03254 (14) | |
| O1 | 0.6653 (2) | 0.24987 (19) | 0.15534 (14) | 0.0536 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.4288 (3) | 0.2353 (2) | 0.03404 (15) | 0.0646 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.4892 (3) | 0.1969 (2) | 0.13268 (18) | 0.0397 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.1330 (3) | 0.3282 (2) | 0.36443 (16) | 0.0335 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.1796 (3) | 0.4864 (2) | 0.30665 (17) | 0.0387 (4) | |
| H1A | 0.3282 | 0.5203 | 0.2685 | 0.046* | |
| C6 | 0.2998 (3) | 0.1817 (2) | 0.37491 (17) | 0.0377 (4) | |
| H6A | 0.2343 | 0.1094 | 0.4496 | 0.045* | |
| H6B | 0.4288 | 0.2169 | 0.3931 | 0.045* | |
| C4 | −0.1038 (3) | 0.3335 (2) | 0.40734 (18) | 0.0410 (4) | |
| H4A | −0.1861 | 0.2426 | 0.4513 | 0.049* | |
| C7 | 0.3785 (3) | 0.0848 (2) | 0.24845 (18) | 0.0372 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.1817 (4) | 0.0227 (3) | 0.2186 (2) | 0.0547 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.2329 | −0.0363 | 0.1400 | 0.082* | |
| H11B | 0.0746 | 0.1134 | 0.2049 | 0.082* | |
| H11C | 0.1134 | −0.0482 | 0.2920 | 0.082* | |
| C10 | 0.5508 (4) | −0.0594 (3) | 0.2709 (2) | 0.0519 (5) | |
| H10A | 0.6012 | −0.1197 | 0.1930 | 0.078* | |
| H10B | 0.4836 | −0.1293 | 0.3452 | 0.078* | |
| H10C | 0.6753 | −0.0192 | 0.2884 | 0.078* | |
| C2 | −0.0263 (4) | 0.5867 (3) | 0.31440 (18) | 0.0467 (5) | |
| H2A | −0.0442 | 0.7018 | 0.2825 | 0.056* | |
| C9 | 0.7892 (5) | 0.3576 (3) | 0.0540 (3) | 0.0721 (7) | |
| H9A | 0.9106 | 0.3869 | 0.0826 | 0.108* | |
| H9B | 0.6925 | 0.4542 | 0.0387 | 0.108* | |
| H9C | 0.8468 | 0.3033 | −0.0267 | 0.108* | |
| C3 | −0.1995 (4) | 0.4931 (3) | 0.3759 (2) | 0.0488 (5) | |
| H3A | −0.3593 | 0.5316 | 0.3944 | 0.059* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Fe1 | 0.0326 (2) | 0.0351 (2) | 0.0286 (2) | −0.00167 (15) | −0.00463 (15) | −0.00833 (14) |
| O1 | 0.0475 (8) | 0.0685 (10) | 0.0448 (8) | −0.0180 (7) | −0.0123 (7) | 0.0122 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0833 (12) | 0.0734 (11) | 0.0426 (8) | −0.0069 (9) | −0.0298 (8) | 0.0029 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0437 (11) | 0.0398 (10) | 0.0332 (10) | 0.0076 (8) | −0.0094 (8) | −0.0109 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0359 (9) | 0.0366 (9) | 0.0269 (8) | −0.0039 (7) | −0.0040 (7) | −0.0089 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0447 (11) | 0.0408 (10) | 0.0270 (9) | −0.0049 (8) | −0.0019 (8) | −0.0060 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0409 (10) | 0.0396 (10) | 0.0306 (9) | −0.0009 (8) | −0.0075 (8) | −0.0034 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0371 (10) | 0.0479 (11) | 0.0395 (10) | −0.0079 (8) | −0.0069 (8) | −0.0138 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0375 (10) | 0.0338 (9) | 0.0394 (10) | 0.0018 (8) | −0.0098 (8) | −0.0073 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0513 (12) | 0.0519 (13) | 0.0651 (14) | −0.0067 (10) | −0.0150 (11) | −0.0224 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0533 (13) | 0.0396 (11) | 0.0557 (12) | 0.0082 (9) | −0.0100 (10) | −0.0017 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0610 (13) | 0.0430 (11) | 0.0338 (10) | 0.0073 (10) | −0.0139 (9) | −0.0068 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0694 (16) | 0.0802 (18) | 0.0595 (15) | −0.0259 (14) | −0.0050 (13) | 0.0195 (13) |
| C3 | 0.0414 (11) | 0.0622 (13) | 0.0449 (11) | 0.0074 (10) | −0.0155 (9) | −0.0199 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Fe1—C2i | 2.043 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.554 (3) |
| Fe1—C2 | 2.043 (2) | C6—H6A | 0.9700 |
| Fe1—C4i | 2.044 (2) | C6—H6B | 0.9700 |
| Fe1—C4 | 2.044 (2) | C4—C3 | 1.418 (3) |
| Fe1—C3i | 2.044 (2) | C4—H4A | 0.9800 |
| Fe1—C3 | 2.044 (2) | C7—C11 | 1.522 (3) |
| Fe1—C1i | 2.0445 (19) | C7—C10 | 1.536 (3) |
| Fe1—C1 | 2.0445 (19) | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| Fe1—C5i | 2.0521 (17) | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| Fe1—C5 | 2.0521 (17) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| O1—C8 | 1.333 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| O1—C9 | 1.446 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| O2—C8 | 1.192 (2) | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C8—C7 | 1.522 (3) | C2—C3 | 1.400 (3) |
| C5—C1 | 1.424 (3) | C2—H2A | 0.9800 |
| C5—C4 | 1.428 (3) | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.501 (3) | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.420 (3) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9800 | C3—H3A | 0.9800 |
| C2i—Fe1—C2 | 180.0 | C2—C1—C5 | 108.24 (18) |
| C2i—Fe1—C4i | 67.98 (9) | C2—C1—Fe1 | 69.61 (10) |
| C2—Fe1—C4i | 112.02 (9) | C5—C1—Fe1 | 69.95 (10) |
| C2i—Fe1—C4 | 112.02 (9) | C2—C1—H1A | 125.9 |
| C2—Fe1—C4 | 67.98 (9) | C5—C1—H1A | 125.9 |
| C4i—Fe1—C4 | 180.0 | Fe1—C1—H1A | 125.9 |
| C2i—Fe1—C3i | 40.08 (9) | C5—C6—C7 | 113.97 (15) |
| C2—Fe1—C3i | 139.92 (9) | C5—C6—H6A | 108.8 |
| C4i—Fe1—C3i | 40.61 (8) | C7—C6—H6A | 108.8 |
| C4—Fe1—C3i | 139.39 (8) | C5—C6—H6B | 108.8 |
| C2i—Fe1—C3 | 139.92 (9) | C7—C6—H6B | 108.8 |
| C2—Fe1—C3 | 40.08 (9) | H6A—C6—H6B | 107.7 |
| C4i—Fe1—C3 | 139.39 (8) | C3—C4—C5 | 108.21 (18) |
| C4—Fe1—C3 | 40.61 (8) | C3—C4—Fe1 | 69.70 (12) |
| C3i—Fe1—C3 | 180.0 | C5—C4—Fe1 | 69.92 (10) |
| C2i—Fe1—C1i | 40.65 (8) | C3—C4—H4A | 125.9 |
| C2—Fe1—C1i | 139.35 (8) | C5—C4—H4A | 125.9 |
| C4i—Fe1—C1i | 68.18 (8) | Fe1—C4—H4A | 125.9 |
| C4—Fe1—C1i | 111.82 (8) | C11—C7—C8 | 110.12 (17) |
| C3i—Fe1—C1i | 68.00 (9) | C11—C7—C10 | 109.95 (17) |
| C3—Fe1—C1i | 112.00 (9) | C8—C7—C10 | 108.85 (16) |
| C2i—Fe1—C1 | 139.35 (8) | C11—C7—C6 | 110.52 (16) |
| C2—Fe1—C1 | 40.65 (8) | C8—C7—C6 | 108.53 (15) |
| C4i—Fe1—C1 | 111.82 (8) | C10—C7—C6 | 108.84 (16) |
| C4—Fe1—C1 | 68.18 (8) | C7—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C3i—Fe1—C1 | 112.00 (9) | C7—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C3—Fe1—C1 | 68.00 (9) | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C1i—Fe1—C1 | 180.0 | C7—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C2i—Fe1—C5i | 68.48 (8) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C2—Fe1—C5i | 111.52 (8) | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C4i—Fe1—C5i | 40.80 (8) | C7—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C4—Fe1—C5i | 139.20 (8) | C7—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C3i—Fe1—C5i | 68.51 (8) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C3—Fe1—C5i | 111.49 (8) | C7—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C1i—Fe1—C5i | 40.67 (7) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C1—Fe1—C5i | 139.33 (7) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C2i—Fe1—C5 | 111.52 (8) | C3—C2—C1 | 108.31 (18) |
| C2—Fe1—C5 | 68.48 (8) | C3—C2—Fe1 | 69.99 (12) |
| C4i—Fe1—C5 | 139.20 (8) | C1—C2—Fe1 | 69.73 (11) |
| C4—Fe1—C5 | 40.80 (8) | C3—C2—H2A | 125.8 |
| C3i—Fe1—C5 | 111.49 (8) | C1—C2—H2A | 125.8 |
| C3—Fe1—C5 | 68.51 (8) | Fe1—C2—H2A | 125.8 |
| C1i—Fe1—C5 | 139.33 (7) | O1—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C1—Fe1—C5 | 40.67 (7) | O1—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C5i—Fe1—C5 | 180.00 (7) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C8—O1—C9 | 117.84 (18) | O1—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O2—C8—O1 | 123.17 (19) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O2—C8—C7 | 125.6 (2) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| O1—C8—C7 | 111.19 (16) | C2—C3—C4 | 108.28 (18) |
| C1—C5—C4 | 106.96 (17) | C2—C3—Fe1 | 69.92 (12) |
| C1—C5—C6 | 126.84 (17) | C4—C3—Fe1 | 69.69 (11) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 126.17 (17) | C2—C3—H3A | 125.9 |
| C1—C5—Fe1 | 69.38 (10) | C4—C3—H3A | 125.9 |
| C4—C5—Fe1 | 69.28 (10) | Fe1—C3—H3A | 125.9 |
| C6—C5—Fe1 | 127.75 (13) |
Symmetry code: (i) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: WM5231).
References
- Atkinson, R. C. J., Gibson, V. C. & Long, N. J. (2004). Chem. Soc. Rev. 33, 313–328. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, K. & Berndt, M. (1999). DIAMOND. University of Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2012). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cetina, M., Jukić, M., Rapić, V. & Golobič, A. (2003). Acta Cryst. C59, m212–m214. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C. L., Ewart, C. B., Barta, C. A., Little, S., Yardley, V., Martins, C., Polishchuk, E., Smith, P. J., Moss, J. R., Merkel, M., Adam, M. J. & Orvig, C. (2006). Inorg. Chem. 45, 8414–8422. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Gao, L. M., Hernández, R., Matta, J. & Meléndez, E. (2009). Metal-based Drugs, Article ID 420784, 10.1155/2009/420784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Navarro, A.-E., Spinelli, N., Moustrou, C., Chaix, C., Mandrand, B. & Brisset, H. (2004). Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 5310–5319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Pérez, W. I., Rheingold, A. L. & Meléndez, E. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, 536–539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Wilbert, G., Wiesemann, A. & Zentel, R. (1995). Macromol. Chem. Phys. 196, 3771–3788.
- Woodward, R. B., Rosenblum, M. & Whiting, M. C. (1952). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 74, 3458–3459.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020642/wm5231sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020642/wm5231Isup2.hkl
x y z . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020642/wm5231fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title complex, showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. All H atoms have been omitted for clarity. Unlabelled atoms are related to labelled ones by the symmetry operation −x, −y + 1, −z + 1.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015020642/wm5231fig2.tif
The packing of molecules in the crystal structure of the title compound.
CCDC reference: 1434467
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


