Abstract
In the title compound, Ph3Ge-SiMe2(t-Bu) or C24H30GeSi, the Si and Ge atoms both possess a tetrahedral coordination environment with C—E—C (E = Si, Ge) angles in the range 104.47 (5)–114.67 (5)°. The molecule adopts an eclipsed conformation, with three torsion angles less than 29.5°. In the crystal, neighbouring molecules are combined to dimers by six T-shaped C—H⋯π interactions, forming sixfold phenyl embraces (6PE).
Keywords: catenated compounds, silagermanes, C—H⋯π interactions, 6PE interactions, crystal structure
Related literature
For general background to the chemistry of Group 14 element catenated compounds, see: Marschner & Hlina (2013 ▸); Amadoruge & Weinert (2008 ▸); Párkányi et al. (1986 ▸); Leigh et al. (1997 ▸). As apart of our studies of the chemistry of oligogermanium compounds (Zaitsev et al. 2012 ▸, 2013 ▸, 2014a
▸,b
▸), the title compound was obtained and studied. For related crystal structures of silagermanes, see: Zaitsev et al. (2015 ▸). The 6PE interactions are intensively discussed in Scudder & Dance (2000 ▸); Steiner (2000 ▸); Churakov et al. (2005 ▸).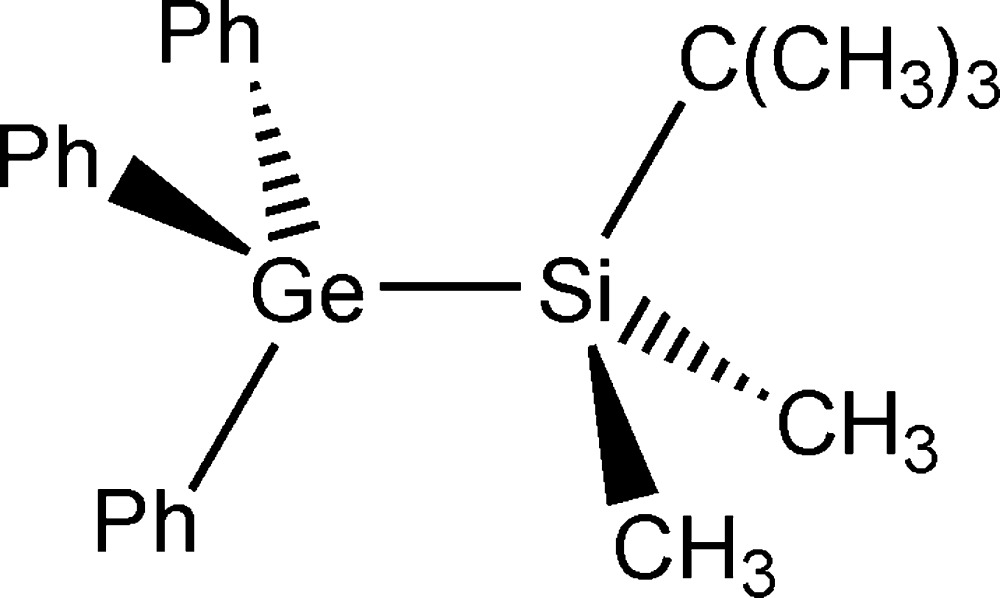
Experimental
Crystal data
C24H30GeSi
M r = 419.16
Monoclinic,

a = 13.5332 (6) Å
b = 14.9825 (7) Å
c = 22.7179 (13) Å
β = 106.2048 (10)°
V = 4423.3 (4) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.44 mm−1
T = 120 K
0.32 × 0.29 × 0.24 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013 ▸) T min = 0.720, T max = 0.862
32242 measured reflections
7990 independent reflections
6137 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.043
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.033
wR(F 2) = 0.071
S = 1.01
7990 reflections
240 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.37 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2013 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2013 ▸); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS2014 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸); molecular graphics: OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: OLEX2.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474Isup3.mol
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474Isup4.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474fig1.tif
Molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids shown at the 50% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474fig2.tif
Dimers formed by 6PE interactions between adjacent molecules.
CCDC reference: 1439529
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
This work was supported financially by the Russian President Grant for Young Russian Scientists (MK-1790.2014.3)
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Structural commentary
In the title compound, Ph3Ge-SiMe2(t-Bu), both Si and Ge atoms possess tetrahedral coordination environments with C—E—C angles ranging within 104.47 (5)- 114.67 (5) °. The Ge—Si bond length (2.4026 (4) Å) is slightly longer than in the closely related compound Ph3Ge-SiMe3 (2.384 (1) Å (Párkányi et al., 1986). The molecule adopts an eclipsed conformation with three torsion angles less than 29.5°.
In the crystal, neighbouring molecules are combined to dimers by six T-shaped C—H···π interactions forming sixfold phenyl embraces (6PE, Steiner, 2000; Churakov et al., 2005). As expected for 6PE-bonded molecules, the Cax—Ge···Ge angle is almost linear − 175.9° (Fig. 2; Scudder & Dance, 2000).
The title compound is isostructural with the corresponding silicon complex Ph3Si-SiMe2(t-Bu) (Leigh et al., 1997).
S2. Synthesis and crystallization
The synthetic procedure leading to the title compound was reported by us earlier (Zaitsev et al., 2014b) to give a white crystalline material in good yield (86%) by the reaction of Ph3GeLi (generated in situ from equimolar amounts of Ph3GeH and n-BuLi at room temperature in Et2O) with t-BuMe2SiCl in diethyl ether. Solvent-free crystals of the title compound suitable for X-Ray analysis were obtained after recrystallization from n-hexane at room temperature.
S3. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 1. A l l non-hydrogen atoms were refined with anisotropic thermal parameters.
All hydrogen atoms were placed in calculated positions and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C) for aromatic H atoms or 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms. A rotating model was applied to the methyl groups.
Figures
Fig. 1.

Molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids shown at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.

Dimers formed by 6PE interactions between adjacent molecules.
Crystal data
| C24H30GeSi | F(000) = 1760 |
| Mr = 419.16 | Dx = 1.259 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 13.5332 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 8565 reflections |
| b = 14.9825 (7) Å | θ = 2.5–31.7° |
| c = 22.7179 (13) Å | µ = 1.44 mm−1 |
| β = 106.2048 (10)° | T = 120 K |
| V = 4423.3 (4) Å3 | Irregular, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.32 × 0.29 × 0.24 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 7990 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | 6137 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.043 |
| Detector resolution: 8 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 32.6°, θmin = 1.9° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −19→20 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2013) | k = −22→22 |
| Tmin = 0.720, Tmax = 0.862 | l = −33→34 |
| 32242 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.033 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.071 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0303P)2 + 1.8636P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 7990 reflections | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 240 parameters | Δρmin = −0.37 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. Absorption correctgion: SADABS2008/1 (Bruker,2008) was used for absorption correction. wR2(int) was 0.0820 before and 0.0431 after correction. The Ratio of minimum to maximum transmission is 0.8344. The λ/2 correction factor is 0.0015. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ge1 | 0.36354 (2) | 0.03558 (2) | 0.37248 (2) | 0.01369 (4) | |
| Si1 | 0.26294 (3) | 0.07258 (3) | 0.27044 (2) | 0.01566 (8) | |
| C1 | 0.19468 (11) | −0.02626 (9) | 0.22333 (7) | 0.0193 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.14760 (13) | −0.08808 (11) | 0.26222 (8) | 0.0280 (3) | |
| H2A | 0.2015 | −0.1135 | 0.2947 | 0.042* | |
| H2B | 0.1099 | −0.1350 | 0.2369 | 0.042* | |
| H2C | 0.1020 | −0.0544 | 0.2794 | 0.042* | |
| C3 | 0.10842 (13) | 0.00982 (12) | 0.16951 (8) | 0.0286 (4) | |
| H3A | 0.0582 | 0.0399 | 0.1849 | 0.043* | |
| H3B | 0.0763 | −0.0388 | 0.1437 | 0.043* | |
| H3C | 0.1368 | 0.0509 | 0.1462 | 0.043* | |
| C4 | 0.26903 (13) | −0.08070 (11) | 0.19725 (8) | 0.0293 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.2967 | −0.0432 | 0.1715 | 0.044* | |
| H4B | 0.2327 | −0.1298 | 0.1737 | 0.044* | |
| H4C | 0.3241 | −0.1032 | 0.2303 | 0.044* | |
| C5 | 0.16501 (12) | 0.15374 (11) | 0.28177 (8) | 0.0288 (4) | |
| H5A | 0.1152 | 0.1229 | 0.2971 | 0.043* | |
| H5B | 0.1311 | 0.1814 | 0.2433 | 0.043* | |
| H5C | 0.1984 | 0.1986 | 0.3107 | 0.043* | |
| C6 | 0.34687 (14) | 0.13018 (13) | 0.22957 (8) | 0.0340 (4) | |
| H6A | 0.3806 | 0.1798 | 0.2536 | 0.051* | |
| H6B | 0.3056 | 0.1512 | 0.1905 | 0.051* | |
| H6C | 0.3976 | 0.0891 | 0.2235 | 0.051* | |
| C7 | 0.48101 (10) | 0.11767 (9) | 0.39511 (6) | 0.0160 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.46614 (12) | 0.20997 (10) | 0.38666 (7) | 0.0244 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.3997 | 0.2322 | 0.3713 | 0.029* | |
| C9 | 0.54855 (13) | 0.26859 (11) | 0.40074 (8) | 0.0287 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.5371 | 0.3295 | 0.3948 | 0.034* | |
| C10 | 0.64792 (12) | 0.23684 (11) | 0.42370 (7) | 0.0258 (3) | |
| H10 | 0.7032 | 0.2763 | 0.4332 | 0.031* | |
| C11 | 0.66436 (11) | 0.14632 (11) | 0.43231 (7) | 0.0223 (3) | |
| H11 | 0.7310 | 0.1247 | 0.4475 | 0.027* | |
| C12 | 0.58171 (11) | 0.08718 (10) | 0.41835 (6) | 0.0185 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.5939 | 0.0264 | 0.4246 | 0.022* | |
| C13 | 0.28202 (11) | 0.05273 (9) | 0.43088 (6) | 0.0159 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.19262 (11) | 0.00334 (10) | 0.42642 (7) | 0.0210 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.1719 | −0.0391 | 0.3956 | 0.025* | |
| C15 | 0.13399 (12) | 0.01638 (11) | 0.46710 (7) | 0.0254 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.0750 | −0.0174 | 0.4635 | 0.031* | |
| C16 | 0.16361 (12) | 0.07993 (11) | 0.51311 (7) | 0.0252 (3) | |
| H16 | 0.1242 | 0.0891 | 0.5402 | 0.030* | |
| C17 | 0.25164 (12) | 0.12936 (11) | 0.51847 (7) | 0.0251 (3) | |
| H17 | 0.2717 | 0.1719 | 0.5494 | 0.030* | |
| C18 | 0.31062 (11) | 0.11602 (10) | 0.47793 (7) | 0.0203 (3) | |
| H18 | 0.3700 | 0.1497 | 0.4821 | 0.024* | |
| C19 | 0.41975 (10) | −0.08517 (9) | 0.38053 (6) | 0.0151 (3) | |
| C20 | 0.47948 (11) | −0.11181 (10) | 0.34217 (7) | 0.0192 (3) | |
| H20 | 0.4907 | −0.0719 | 0.3134 | 0.023* | |
| C21 | 0.52196 (12) | −0.19630 (10) | 0.34629 (7) | 0.0238 (3) | |
| H21 | 0.5611 | −0.2128 | 0.3203 | 0.029* | |
| C22 | 0.50633 (12) | −0.25642 (10) | 0.38912 (7) | 0.0250 (3) | |
| H22 | 0.5351 | −0.3132 | 0.3921 | 0.030* | |
| C23 | 0.44760 (12) | −0.23154 (10) | 0.42747 (7) | 0.0247 (3) | |
| H23 | 0.4366 | −0.2718 | 0.4561 | 0.030* | |
| C24 | 0.40487 (11) | −0.14636 (10) | 0.42328 (7) | 0.0194 (3) | |
| H24 | 0.3659 | −0.1302 | 0.4494 | 0.023* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ge1 | 0.01210 (7) | 0.01250 (7) | 0.01693 (7) | −0.00005 (6) | 0.00481 (5) | −0.00168 (6) |
| Si1 | 0.01585 (18) | 0.01453 (18) | 0.01666 (18) | 0.00156 (14) | 0.00463 (14) | −0.00171 (14) |
| C1 | 0.0175 (6) | 0.0189 (7) | 0.0196 (7) | 0.0025 (5) | 0.0021 (5) | −0.0043 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0260 (8) | 0.0266 (8) | 0.0293 (8) | −0.0083 (7) | 0.0042 (7) | −0.0038 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0249 (8) | 0.0306 (9) | 0.0245 (8) | 0.0037 (7) | −0.0025 (6) | −0.0045 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0281 (8) | 0.0279 (8) | 0.0297 (9) | 0.0060 (7) | 0.0044 (7) | −0.0127 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0269 (8) | 0.0245 (8) | 0.0309 (9) | 0.0112 (7) | 0.0013 (7) | −0.0060 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0410 (10) | 0.0391 (10) | 0.0243 (8) | −0.0134 (8) | 0.0132 (7) | −0.0001 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0152 (6) | 0.0170 (6) | 0.0161 (6) | −0.0019 (5) | 0.0050 (5) | −0.0015 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0198 (7) | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0322 (8) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0024 (6) | −0.0008 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0291 (8) | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0356 (9) | −0.0064 (6) | 0.0039 (7) | −0.0003 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0231 (7) | 0.0305 (8) | 0.0225 (7) | −0.0123 (6) | 0.0040 (6) | −0.0018 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0148 (6) | 0.0328 (8) | 0.0178 (7) | −0.0026 (6) | 0.0021 (5) | 0.0009 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0176 (7) | 0.0208 (7) | 0.0168 (6) | −0.0004 (5) | 0.0044 (5) | 0.0014 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0151 (6) | 0.0158 (6) | 0.0167 (6) | 0.0016 (5) | 0.0044 (5) | −0.0001 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0220 (7) | 0.0226 (7) | 0.0199 (7) | −0.0051 (6) | 0.0082 (6) | −0.0044 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0220 (7) | 0.0318 (9) | 0.0251 (8) | −0.0066 (6) | 0.0108 (6) | −0.0023 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0249 (8) | 0.0334 (9) | 0.0206 (7) | 0.0041 (7) | 0.0117 (6) | −0.0005 (6) |
| C17 | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0277 (8) | 0.0200 (7) | 0.0009 (6) | 0.0069 (6) | −0.0073 (6) |
| C18 | 0.0189 (7) | 0.0209 (7) | 0.0209 (7) | −0.0017 (6) | 0.0051 (6) | −0.0037 (6) |
| C19 | 0.0135 (6) | 0.0123 (6) | 0.0189 (6) | −0.0003 (5) | 0.0034 (5) | −0.0023 (5) |
| C20 | 0.0184 (7) | 0.0187 (7) | 0.0215 (7) | 0.0019 (5) | 0.0073 (5) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C21 | 0.0216 (7) | 0.0216 (7) | 0.0290 (8) | 0.0051 (6) | 0.0083 (6) | −0.0045 (6) |
| C22 | 0.0256 (8) | 0.0124 (6) | 0.0327 (8) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0010 (6) | −0.0025 (6) |
| C23 | 0.0306 (8) | 0.0173 (7) | 0.0239 (8) | −0.0016 (6) | 0.0038 (6) | 0.0047 (6) |
| C24 | 0.0201 (7) | 0.0183 (7) | 0.0201 (7) | −0.0017 (6) | 0.0060 (5) | −0.0009 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Ge1—Si1 | 2.4026 (4) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| Ge1—C7 | 1.9618 (14) | C9—C10 | 1.384 (2) |
| Ge1—C13 | 1.9648 (14) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| Ge1—C19 | 1.9512 (13) | C10—C11 | 1.379 (2) |
| Si1—C1 | 1.9078 (15) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| Si1—C5 | 1.8687 (15) | C11—C12 | 1.393 (2) |
| Si1—C6 | 1.8670 (17) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.536 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.398 (2) |
| C1—C3 | 1.534 (2) | C13—C18 | 1.400 (2) |
| C1—C4 | 1.537 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9600 | C14—C15 | 1.389 (2) |
| C2—H2B | 0.9600 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2C | 0.9600 | C15—C16 | 1.388 (2) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9600 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3B | 0.9600 | C16—C17 | 1.379 (2) |
| C3—H3C | 0.9600 | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9600 | C17—C18 | 1.391 (2) |
| C4—H4B | 0.9600 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4C | 0.9600 | C19—C20 | 1.4019 (19) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9600 | C19—C24 | 1.390 (2) |
| C5—H5B | 0.9600 | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5C | 0.9600 | C20—C21 | 1.383 (2) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9600 | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C6—H6B | 0.9600 | C21—C22 | 1.385 (2) |
| C6—H6C | 0.9600 | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.403 (2) | C22—C23 | 1.384 (2) |
| C7—C12 | 1.3939 (19) | C23—H23 | 0.9300 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C23—C24 | 1.393 (2) |
| C8—C9 | 1.385 (2) | C24—H24 | 0.9300 |
| C7—Ge1—Si1 | 107.93 (4) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.4 |
| C7—Ge1—C13 | 107.92 (6) | C9—C8—C7 | 121.19 (15) |
| C13—Ge1—Si1 | 110.34 (4) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.4 |
| C19—Ge1—Si1 | 113.92 (4) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.9 |
| C19—Ge1—C7 | 106.89 (6) | C10—C9—C8 | 120.28 (15) |
| C19—Ge1—C13 | 109.61 (6) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.9 |
| C1—Si1—Ge1 | 114.67 (5) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| C5—Si1—Ge1 | 104.47 (5) | C11—C10—C9 | 119.52 (14) |
| C5—Si1—C1 | 109.35 (7) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.2 |
| C6—Si1—Ge1 | 109.08 (6) | C10—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| C6—Si1—C1 | 110.26 (7) | C10—C11—C12 | 120.39 (14) |
| C6—Si1—C5 | 108.72 (9) | C12—C11—H11 | 119.8 |
| C2—C1—Si1 | 111.05 (10) | C7—C12—H12 | 119.5 |
| C2—C1—C4 | 108.84 (13) | C11—C12—C7 | 121.06 (14) |
| C3—C1—Si1 | 108.38 (10) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.5 |
| C3—C1—C2 | 109.00 (13) | C14—C13—Ge1 | 121.31 (10) |
| C3—C1—C4 | 108.31 (13) | C14—C13—C18 | 117.60 (13) |
| C4—C1—Si1 | 111.20 (10) | C18—C13—Ge1 | 121.09 (11) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 109.5 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.3 |
| C1—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C15—C14—C13 | 121.38 (14) |
| C1—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.3 |
| H2A—C2—H2B | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| H2A—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C16—C15—C14 | 119.93 (15) |
| H2B—C2—H2C | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| C1—C3—H3A | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C1—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C17—C16—C15 | 119.72 (14) |
| C1—C3—H3C | 109.5 | C17—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 109.5 | C16—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| H3A—C3—H3C | 109.5 | C16—C17—C18 | 120.36 (14) |
| H3B—C3—H3C | 109.5 | C18—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| C1—C4—H4A | 109.5 | C13—C18—H18 | 119.5 |
| C1—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C17—C18—C13 | 121.01 (14) |
| C1—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.5 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 109.5 | C20—C19—Ge1 | 118.88 (10) |
| H4A—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C24—C19—Ge1 | 123.24 (10) |
| H4B—C4—H4C | 109.5 | C24—C19—C20 | 117.87 (13) |
| Si1—C5—H5A | 109.5 | C19—C20—H20 | 119.3 |
| Si1—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C21—C20—C19 | 121.30 (14) |
| Si1—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C21—C20—H20 | 119.3 |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C20—C21—H21 | 120.0 |
| H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C20—C21—C22 | 120.06 (14) |
| H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C22—C21—H21 | 120.0 |
| Si1—C6—H6A | 109.5 | C21—C22—H22 | 120.2 |
| Si1—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C23—C22—C21 | 119.62 (14) |
| Si1—C6—H6C | 109.5 | C23—C22—H22 | 120.2 |
| H6A—C6—H6B | 109.5 | C22—C23—H23 | 119.9 |
| H6A—C6—H6C | 109.5 | C22—C23—C24 | 120.25 (14) |
| H6B—C6—H6C | 109.5 | C24—C23—H23 | 119.9 |
| C8—C7—Ge1 | 120.48 (11) | C19—C24—C23 | 120.90 (14) |
| C12—C7—Ge1 | 121.93 (11) | C19—C24—H24 | 119.6 |
| C12—C7—C8 | 117.57 (13) | C23—C24—H24 | 119.6 |
| Ge1—C7—C8—C9 | −178.11 (13) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.4 (2) |
| Ge1—C7—C12—C11 | 177.92 (11) | C14—C13—C18—C17 | −0.3 (2) |
| Ge1—C13—C14—C15 | −178.96 (12) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −0.5 (3) |
| Ge1—C13—C18—C17 | 178.66 (12) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.2 (2) |
| Ge1—C19—C20—C21 | 179.40 (11) | C16—C17—C18—C13 | 0.2 (2) |
| Ge1—C19—C24—C23 | −179.38 (11) | C18—C13—C14—C15 | 0.0 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.1 (3) | C19—C20—C21—C22 | −0.3 (2) |
| C8—C7—C12—C11 | −0.3 (2) | C20—C19—C24—C23 | −0.4 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.2 (2) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | 0.3 (2) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.3 (2) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | −0.3 (2) |
| C10—C11—C12—C7 | 0.4 (2) | C22—C23—C24—C19 | 0.4 (2) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | 0.2 (2) | C24—C19—C20—C21 | 0.3 (2) |
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: IM2474).
References
- Amadoruge, M. L. & Weinert, C. S. (2008). Chem. Rev. 108, 4253–4294. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2013). APEX2, SADABS and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Churakov, A. V., Prikhodchenko, P. V. & Howard, J. A. K. (2005). CrystEngComm, 7, 664–669.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Leigh, W. J., Kroll, E. C., Toltl, N. P. & Britten, J. F. (1997). Acta Cryst. C53, IUC9700006.
- Marschner, C. & Hlina, J. (2013). Comprehensive Inorganic Chemistry II, 2nd ed., edited by J. Reedijk & K. Poeppelmeier, pp. 83–117. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
- Párkányi, L., Hernandez, C. & Pannell, K. H. (1986). J. Organomet. Chem. 301, 145–151.
- Scudder, M. & Dance, I. (2000). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 2909–2915.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Steiner, T. (2000). New J. Chem. 24, 137–142.
- Zaitsev, K. V., Churakov, A. V., Poleshchuk, O. K., Oprunenko, Yu. F., Zaitseva, G. S. & Karlov, S. S. (2014a). Dalton Trans. 43, 6605–6609. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Zaitsev, K. V., Kapranov, A. A., Churakov, A. V., Poleshchuk, O. K., Oprunenko, Yu. F., Tarasevich, B. N., Zaitseva, G. S. & Karlov, S. S. (2013). Organometallics, 32, 6500–6510.
- Zaitsev, K. V., Kapranov, A. A., Oprunenko, Y. F., Churakov, A. V., Howard, J. A. K., Tarasevich, B. N., Karlov, S. S. & Zaitseva, G. S. (2012). J. Organomet. Chem. 700, 207–213.
- Zaitsev, K. V., Lermontova, E. K., Churakov, A. V., Tafeenko, V. A., Tarasevich, B. N., Poleshchuk, O. K., Kharcheva, A. V., Magdesieva, T. V., Nikitin, O. M., Zaitseva, G. S. & Karlov, S. S. (2015). Organometallics, 34, 2765–2774.
- Zaitsev, K. V., Oprunenko, Y. F., Churakov, A. V., Zaitseva, G. S. & Karlov, S. S. (2014b). Main Group Met. Chem. 37, 67–74.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474Isup3.mol
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474Isup4.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474fig1.tif
Molecular structure of the title compound, with displacement ellipsoids shown at the 50% probability level.
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015022872/im2474fig2.tif
Dimers formed by 6PE interactions between adjacent molecules.
CCDC reference: 1439529
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


