Abstract
In the title compound, C21H16N2O2, the naphthalene fragment is twisted slightly, as indicated by the dihedral angle of 3.2 (2)° between the two six-membered rings. The pendant 4-methoxyphenyl ring makes a dihedral angle of 86.08 (6)° with the central six-membered ring of the 4H-benzo[g]chromene ring system. In the crystal, molecules are linked by pairs of N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, forming inversion dimers which are linked into chains propagating in the b-axis direction by N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Keywords: crystal structure, chromenes, benzopyrans, 2-amino-3-cyano-4H-chromene derivatives, 4H-chromene and fused 4H-chromene derivatives, hydrogen bonding
Related literature
For the chemical and pharmacological properties of 4H-chromene and fused 4H-chromene derivatives, see: Bonsignore et al. (1993 ▸); Martínez-Grau & Marco (1997 ▸); Abd-El-Aziz et al. (2007 ▸); Sabry et al. (2011 ▸). For the synthesis and biological activities of 2-amino-3-cyano-4H-chromene derivatives, see: Kemnitzer et al. (2005 ▸); Patil et al. (2012 ▸); Kumar et al. (2009 ▸).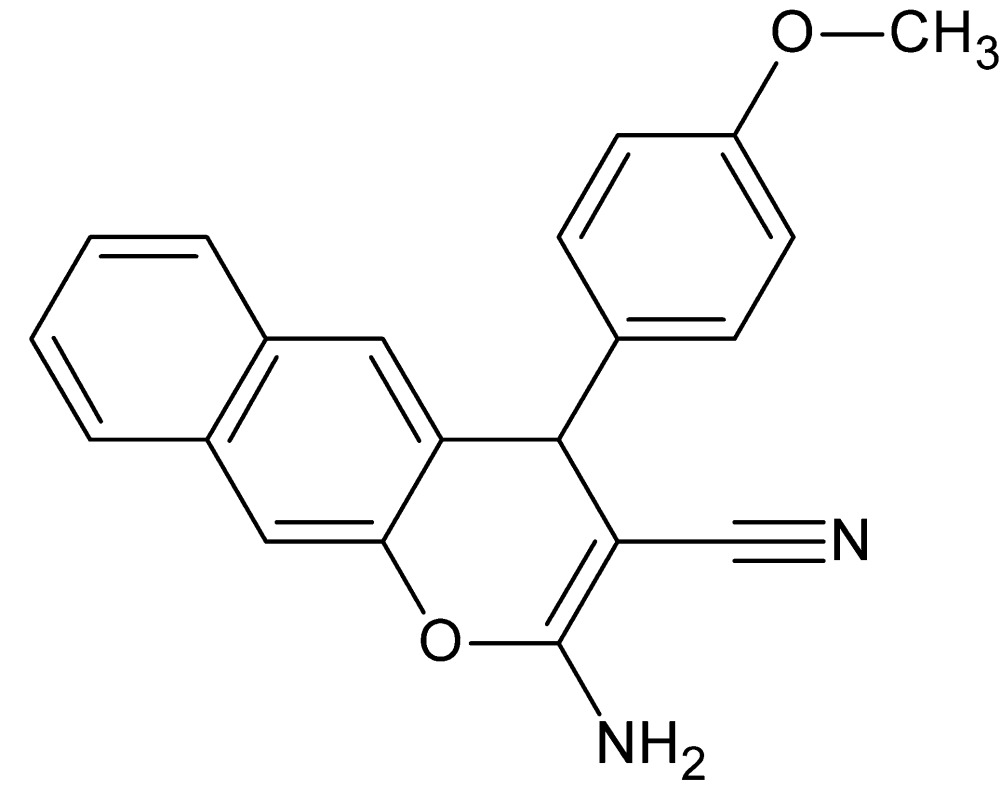
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H16N2O2
M r = 328.36
Triclinic,

a = 6.3833 (2) Å
b = 10.6009 (3) Å
c = 13.0915 (4) Å
α = 108.823 (2)°
β = 95.906 (2)°
γ = 97.467 (2)°
V = 821.44 (4) Å3
Z = 2
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 0.69 mm−1
T = 150 K
0.26 × 0.20 × 0.02 mm
Data collection
Bruker D8 VENTURE PHOTON 100 CMOS diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2015 ▸) T min = 0.78, T max = 0.99
6215 measured reflections
3039 independent reflections
2074 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.048
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.057
wR(F 2) = 0.151
S = 1.03
3039 reflections
235 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2015 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2015 ▸); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXT (Sheldrick, 2015a ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015b ▸); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg & Putz, 2012 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound with the labeling scheme and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
c . DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248fig2.tif
View along the c axis of one hydrogen-bonded layer. The N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (see Table 1) are shown as blue and purple dotted lines, respectively.
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248fig3.tif
Crystal packing viewed along the c axis, with the N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (see Table 1) shown as blue and purple dotted lines, respectively.
CCDC reference: 1439459
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2A⋯N1i | 0.96 (3) | 2.03 (3) | 2.995 (3) | 178 (3) |
| N2—H2B⋯O2ii | 0.95 (3) | 2.10 (3) | 3.028 (3) | 166 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The support of NSF–MRI Grant No. 1228232 for the purchase of the diffractometer and Tulane University for support of the Tulane Crystallography Laboratory are gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Structural commentary
Fused benzo-4H-pyran, namely, 4H-chromene moiety, is the key building block of many oxygen-containing heterocyclic natural products whose pharmacological and biological activity such as anti-tumor, anti-oxidant, anti-bacterial, anti-viral, anti-fungal, hypotensive, anti-coagulant, anti-leishmanial, diuretic, and anti-allergenic activities (Bonsignore et al., 1993; Martínez-Grau & Marco, 1997; Abd-El-Aziz et al., 2007; Sabry et al., 2011). Moreover, 2-amino-3-cyano-4H-chromene derivatives have been also used as anti-cancers, inhibitors of insulin-regulated aminopeptidase (IRAP) for enhancing memory and learning functions and anti-bacterial agents (Kemnitzer et al., 2005; Patil et al., 2012; Kumar et al., 2009). In continuation of our interest in the chemical and pharmacological properties of 4H-chromene and fused 4H-chromene derivatives, we herein report on the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound.
In the title compound, Fig. 1, the naphthalene fragment is slightly twisted as indicated by the dihedral angle of 3.2 (2)° between the two 6-membered rings. The pendant 4-methoxyphenyl ring makes a dihedral angle of 86.08 (6)° with the (C4—C7/C12/C13) ring. The heterocyclic ring (O1/C1—C4/C13) can best be described as having an envelope conformation, with atom C3 as the flap, and with pucking parameters of Q = 0.099 (2) Å, θ = 109.8 (12)° and φ = 6.5 (14)°.
In the crystal, pairwise N2—H2A···N1i hydrogen bonds form inversion dimers which are linked into chains running along the b axis direction (Fig. 2 and Table 1). The overall packing of these units in the crystal is illustrated in Fig. 3.
S2. Synthesis and crystallization
To a solution of 4-methoxybenzylidene-malononitrile (1 mmol, 180 mg) in 10 ml of ethanol was added 4- 1-naphthol (1 mmol, 144 mg) in the presence of few catalytic drops of piperedine and the temperature was adjusted at 353 K for 1 h. A solid product was obtained on cooling, collected by filtration and recrystallized from ethanol to afford colorless plate-like crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis.
S3. Refinement
The NH2 H-atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and freely refined. The C-bound H atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95 − 1.00 Å) and included as riding contributions with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C-methyl) and 1.2Ueq(C) for other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.

The molecular structure of the title compound with the labeling scheme and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.

View along the c axis of one hydrogen-bonded layer. The N—H···N and N—H···O hydrogen bonds (see Table 1) are shown as blue and purple dotted lines, respectively.
Fig. 3.

Crystal packing viewed along the c axis, with the N—H···N and N—H···O hydrogen bonds (see Table 1) shown as blue and purple dotted lines, respectively.
Crystal data
| C21H16N2O2 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 328.36 | F(000) = 344 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.328 Mg m−3 |
| a = 6.3833 (2) Å | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54178 Å |
| b = 10.6009 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 3044 reflections |
| c = 13.0915 (4) Å | θ = 3.6–72.4° |
| α = 108.823 (2)° | µ = 0.69 mm−1 |
| β = 95.906 (2)° | T = 150 K |
| γ = 97.467 (2)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 821.44 (4) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.20 × 0.02 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker D8 VENTURE PHOTON 100 CMOS diffractometer | 3039 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: INCOATEC IµS micro–focus source | 2074 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Mirror monochromator | Rint = 0.048 |
| Detector resolution: 10.4167 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 72.4°, θmin = 3.6° |
| ω scans | h = −7→6 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2015) | k = −12→13 |
| Tmin = 0.78, Tmax = 0.99 | l = −16→16 |
| 6215 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.057 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.151 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0739P)2 + 0.065P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3039 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 235 parameters | Δρmax = 0.18 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. H-atoms attached to carbon were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95 − 1.00 Å). All were included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters 1.2 − 1.5 times those of the attached atoms. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.3785 (2) | 0.96970 (14) | 0.76705 (13) | 0.0403 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.3737 (3) | 0.29798 (15) | 0.88255 (14) | 0.0498 (5) | |
| N1 | 1.0346 (3) | 0.8671 (2) | 0.90170 (17) | 0.0471 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.6393 (3) | 1.08806 (19) | 0.90280 (19) | 0.0475 (6) | |
| H2A | 0.741 (5) | 1.101 (3) | 0.966 (2) | 0.060 (8)* | |
| H2B | 0.559 (5) | 1.159 (3) | 0.909 (2) | 0.064 (8)* | |
| C1 | 0.5666 (3) | 0.9677 (2) | 0.82491 (19) | 0.0368 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.6619 (3) | 0.8565 (2) | 0.80085 (18) | 0.0357 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.5665 (3) | 0.7233 (2) | 0.71189 (18) | 0.0369 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.6756 | 0.6971 | 0.6629 | 0.044* | |
| C4 | 0.3733 (3) | 0.7425 (2) | 0.64460 (18) | 0.0369 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.2723 (4) | 0.6386 (2) | 0.5477 (2) | 0.0438 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.3325 | 0.5587 | 0.5229 | 0.053* | |
| C6 | 0.0909 (4) | 0.6488 (2) | 0.4883 (2) | 0.0451 (6) | |
| H6 | 0.0290 | 0.5778 | 0.4223 | 0.054* | |
| C7 | −0.0054 (4) | 0.7651 (2) | 0.52499 (19) | 0.0395 (5) | |
| C8 | −0.2030 (4) | 0.7755 (3) | 0.4698 (2) | 0.0483 (6) | |
| H8 | −0.2732 | 0.7031 | 0.4063 | 0.058* | |
| C9 | −0.2917 (4) | 0.8878 (3) | 0.5073 (2) | 0.0527 (7) | |
| H9 | −0.4237 | 0.8935 | 0.4697 | 0.063* | |
| C10 | −0.1911 (4) | 0.9956 (3) | 0.6005 (2) | 0.0512 (6) | |
| H10 | −0.2559 | 1.0735 | 0.6256 | 0.061* | |
| C11 | −0.0004 (4) | 0.9904 (2) | 0.6562 (2) | 0.0437 (6) | |
| H11 | 0.0674 | 1.0646 | 0.7189 | 0.052* | |
| C12 | 0.0955 (3) | 0.8731 (2) | 0.61949 (19) | 0.0372 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.2878 (3) | 0.8580 (2) | 0.67621 (18) | 0.0356 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.8674 (4) | 0.8653 (2) | 0.85785 (19) | 0.0387 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.5109 (3) | 0.6109 (2) | 0.75824 (18) | 0.0353 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.3363 (4) | 0.6046 (2) | 0.8117 (2) | 0.0414 (6) | |
| H16 | 0.2487 | 0.6720 | 0.8190 | 0.050* | |
| C17 | 0.2843 (4) | 0.5033 (2) | 0.8551 (2) | 0.0438 (6) | |
| H17 | 0.1631 | 0.5017 | 0.8914 | 0.053* | |
| C18 | 0.4117 (4) | 0.4042 (2) | 0.84493 (19) | 0.0395 (5) | |
| C19 | 0.5888 (4) | 0.4095 (2) | 0.79246 (19) | 0.0417 (6) | |
| H19 | 0.6772 | 0.3426 | 0.7858 | 0.050* | |
| C20 | 0.6375 (4) | 0.5111 (2) | 0.74989 (19) | 0.0400 (5) | |
| H20 | 0.7595 | 0.5132 | 0.7142 | 0.048* | |
| C21 | 0.1919 (5) | 0.2878 (3) | 0.9351 (2) | 0.0562 (7) | |
| H21A | 0.2068 | 0.3672 | 1.0013 | 0.084* | |
| H21B | 0.1803 | 0.2057 | 0.9547 | 0.084* | |
| H21C | 0.0631 | 0.2833 | 0.8855 | 0.084* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0357 (8) | 0.0340 (8) | 0.0500 (10) | 0.0045 (6) | −0.0064 (7) | 0.0171 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0608 (11) | 0.0361 (8) | 0.0593 (11) | 0.0072 (7) | 0.0046 (9) | 0.0271 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0425 (12) | 0.0469 (11) | 0.0494 (13) | 0.0127 (9) | −0.0028 (10) | 0.0141 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0478 (13) | 0.0318 (10) | 0.0568 (14) | 0.0053 (8) | −0.0132 (10) | 0.0138 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0327 (12) | 0.0353 (11) | 0.0452 (13) | 0.0006 (8) | −0.0021 (10) | 0.0221 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0317 (12) | 0.0361 (11) | 0.0414 (13) | 0.0037 (8) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0183 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0355 (12) | 0.0365 (11) | 0.0411 (13) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0043 (10) | 0.0169 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0357 (12) | 0.0369 (11) | 0.0407 (13) | 0.0021 (9) | 0.0034 (9) | 0.0190 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0462 (14) | 0.0405 (12) | 0.0448 (14) | 0.0063 (10) | 0.0045 (11) | 0.0159 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0452 (14) | 0.0477 (13) | 0.0397 (13) | −0.0015 (10) | −0.0010 (11) | 0.0173 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0363 (12) | 0.0440 (12) | 0.0425 (13) | −0.0015 (9) | 0.0013 (10) | 0.0252 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0405 (14) | 0.0583 (15) | 0.0473 (15) | −0.0045 (11) | −0.0047 (11) | 0.0282 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0385 (14) | 0.0650 (16) | 0.0605 (17) | 0.0047 (11) | −0.0042 (12) | 0.0349 (14) |
| C10 | 0.0418 (14) | 0.0567 (15) | 0.0630 (17) | 0.0120 (11) | 0.0006 (12) | 0.0320 (14) |
| C11 | 0.0429 (13) | 0.0421 (12) | 0.0507 (14) | 0.0055 (10) | 0.0009 (11) | 0.0246 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0340 (12) | 0.0415 (12) | 0.0420 (13) | 0.0010 (9) | 0.0025 (10) | 0.0254 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0344 (12) | 0.0351 (11) | 0.0389 (12) | −0.0012 (8) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0191 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0416 (14) | 0.0333 (11) | 0.0424 (13) | 0.0069 (9) | 0.0037 (10) | 0.0152 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0386 (12) | 0.0305 (10) | 0.0372 (12) | 0.0071 (8) | 0.0010 (9) | 0.0130 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0448 (14) | 0.0347 (11) | 0.0521 (15) | 0.0147 (9) | 0.0132 (11) | 0.0199 (11) |
| C17 | 0.0476 (14) | 0.0364 (12) | 0.0522 (15) | 0.0098 (10) | 0.0119 (11) | 0.0195 (11) |
| C18 | 0.0495 (14) | 0.0282 (10) | 0.0398 (13) | 0.0029 (9) | −0.0034 (10) | 0.0148 (10) |
| C19 | 0.0495 (14) | 0.0322 (11) | 0.0450 (14) | 0.0134 (9) | 0.0011 (11) | 0.0147 (10) |
| C20 | 0.0381 (13) | 0.0388 (12) | 0.0429 (13) | 0.0090 (9) | 0.0045 (10) | 0.0131 (10) |
| C21 | 0.0716 (18) | 0.0427 (13) | 0.0585 (17) | 0.0007 (12) | 0.0089 (14) | 0.0269 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C1 | 1.359 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.355 (4) |
| O1—C13 | 1.387 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C18 | 1.372 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.399 (4) |
| O2—C21 | 1.418 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C14 | 1.154 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.370 (3) |
| N2—C1 | 1.339 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| N2—H2A | 0.96 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.423 (3) |
| N2—H2B | 0.95 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.359 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.422 (3) |
| C2—C14 | 1.417 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.381 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.513 (3) | C15—C20 | 1.396 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.516 (3) | C16—C17 | 1.387 (3) |
| C3—C15 | 1.522 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 1.0000 | C17—C18 | 1.391 (3) |
| C4—C13 | 1.365 (3) | C17—H17 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.409 (3) | C18—C19 | 1.386 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.363 (3) | C19—C20 | 1.380 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C19—H19 | 0.9500 |
| C6—C7 | 1.415 (3) | C20—H20 | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C21—H21A | 0.9800 |
| C7—C12 | 1.409 (3) | C21—H21B | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.423 (3) | C21—H21C | 0.9800 |
| C1—O1—C13 | 119.06 (17) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C18—O2—C21 | 117.97 (18) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.6 |
| C1—N2—H2A | 123.6 (16) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.6 (2) |
| C1—N2—H2B | 119.0 (17) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| H2A—N2—H2B | 115 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.2 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 127.4 (2) | C7—C12—C13 | 118.0 (2) |
| N2—C1—O1 | 110.53 (18) | C7—C12—C11 | 119.3 (2) |
| C2—C1—O1 | 122.1 (2) | C13—C12—C11 | 122.6 (2) |
| C1—C2—C14 | 119.1 (2) | C4—C13—O1 | 123.04 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 123.89 (19) | C4—C13—C12 | 122.7 (2) |
| C14—C2—C3 | 116.96 (18) | O1—C13—C12 | 114.30 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 109.13 (17) | N1—C14—C2 | 177.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—C15 | 111.84 (18) | C16—C15—C20 | 117.4 (2) |
| C4—C3—C15 | 111.76 (18) | C16—C15—C3 | 121.60 (18) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 108.0 | C20—C15—C3 | 121.0 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 108.0 | C15—C16—C17 | 122.3 (2) |
| C15—C3—H3 | 108.0 | C15—C16—H16 | 118.8 |
| C13—C4—C5 | 117.7 (2) | C17—C16—H16 | 118.8 |
| C13—C4—C3 | 121.9 (2) | C16—C17—C18 | 119.3 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.39 (19) | C16—C17—H17 | 120.4 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 122.1 (2) | C18—C17—H17 | 120.4 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 118.9 | O2—C18—C19 | 116.25 (19) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.9 | O2—C18—C17 | 124.5 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.1 (2) | C19—C18—C17 | 119.3 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C20—C19—C18 | 120.5 (2) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C20—C19—H19 | 119.8 |
| C12—C7—C6 | 119.2 (2) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.8 |
| C12—C7—C8 | 118.9 (2) | C19—C20—C15 | 121.3 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 121.8 (2) | C19—C20—H20 | 119.4 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.4 (2) | C15—C20—H20 | 119.4 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.8 | O2—C21—H21A | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.8 | O2—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 120.8 (2) | H21A—C21—H21B | 109.5 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.6 | O2—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.6 | H21A—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.9 (2) | H21B—C21—H21C | 109.5 |
| C13—O1—C1—N2 | 174.13 (19) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | 1.2 (3) |
| C13—O1—C1—C2 | −4.3 (3) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −176.9 (2) |
| N2—C1—C2—C14 | −4.0 (4) | C5—C4—C13—O1 | −176.9 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2—C14 | 174.2 (2) | C3—C4—C13—O1 | 4.8 (3) |
| N2—C1—C2—C3 | 179.2 (2) | C5—C4—C13—C12 | 4.2 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −2.6 (3) | C3—C4—C13—C12 | −174.2 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 9.3 (3) | C1—O1—C13—C4 | 3.3 (3) |
| C14—C2—C3—C4 | −167.6 (2) | C1—O1—C13—C12 | −177.71 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C15 | −114.9 (2) | C7—C12—C13—C4 | −2.0 (3) |
| C14—C2—C3—C15 | 68.2 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C4 | 176.1 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C13 | −10.2 (3) | C7—C12—C13—O1 | 178.94 (18) |
| C15—C3—C4—C13 | 114.1 (2) | C11—C12—C13—O1 | −2.9 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 171.5 (2) | C2—C3—C15—C16 | 74.0 (3) |
| C15—C3—C4—C5 | −64.3 (3) | C4—C3—C15—C16 | −48.7 (3) |
| C13—C4—C5—C6 | −2.3 (3) | C2—C3—C15—C20 | −104.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 176.1 (2) | C4—C3—C15—C20 | 132.4 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −1.7 (4) | C20—C15—C16—C17 | −0.6 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C12 | 3.9 (3) | C3—C15—C16—C17 | −179.5 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −175.3 (2) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | 0.0 (4) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | 0.4 (3) | C21—O2—C18—C19 | −178.9 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 179.6 (2) | C21—O2—C18—C17 | 0.3 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.1 (4) | C16—C17—C18—O2 | −178.6 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.1 (4) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 0.6 (3) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.8 (4) | O2—C18—C19—C20 | 178.7 (2) |
| C6—C7—C12—C13 | −2.1 (3) | C17—C18—C19—C20 | −0.6 (3) |
| C8—C7—C12—C13 | 177.1 (2) | C18—C19—C20—C15 | 0.0 (3) |
| C6—C7—C12—C11 | 179.7 (2) | C16—C15—C20—C19 | 0.6 (3) |
| C8—C7—C12—C11 | −1.1 (3) | C3—C15—C20—C19 | 179.5 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2A···N1i | 0.96 (3) | 2.03 (3) | 2.995 (3) | 178 (3) |
| N2—H2B···O2ii | 0.95 (3) | 2.10 (3) | 3.028 (3) | 166 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+2, −z+2; (ii) x, y+1, z.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: SU5248).
References
- Abd-El-Aziz, A. S., Mohamed, H. M., Mohammed, S., Zahid, S., Ata, A., Bedair, A. H., El-Agrody, A. M. & Harvey, P. D. (2007). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 44, 1287–1301.
- Bonsignore, L., Loy, G., Secci, D. & Calignano, A. (1993). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 28, 517–520.
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2012). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2015). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Kemnitzer, W., Kasibhatla, S., Jiang, S., Zhang, H., Zhao, J., Jia, S., Xu, L., Crogan-Grundy, C., Denis, R. A., Barriault, N., Vaillancourt, L., Charron, S., Dodd, J., Attardo, G., Labrecque, D., Lamothe, S., Gourdeau, H., Tseng, B., Drewe, J. & Cai, S. X. (2005). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 15, 4745–4751. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D., Reddy, V. B., Sharad, S., Dube, U. & Kapur, S. (2009). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44, 3805–3809. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Grau, A. & Marco, J. (1997). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 7, 3165–3170.
- Patil, S. A., Wang, J., Li, X. S., Chen, J., Jones, T. S., Hosni-Ahmed, A., Patil, R., Seibel, W. L., Li, W. & Miller, D. D. (2012). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 22, 4458–4461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sabry, N. M., Mohamed, H. M., Khattab, E. S. A. E. H., Motlaq, S. S. & El-Agrody, A. M. (2011). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 46, 765–772. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248fig1.tif
The molecular structure of the title compound with the labeling scheme and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
c . DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248fig2.tif
View along the c axis of one hydrogen-bonded layer. The N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (see Table 1) are shown as blue and purple dotted lines, respectively.
. DOI: 10.1107/S205698901502280X/su5248fig3.tif
Crystal packing viewed along the c axis, with the N—H⋯N and N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (see Table 1) shown as blue and purple dotted lines, respectively.
CCDC reference: 1439459
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


