Abstract
The title compound, C19H21N3O, comprises a central pyrazole ring which is N-connected to an aldehyde group and C-connected twice to substituted benzene rings. The pyrazole ring is twisted on the C—C single bond, and the least-squares plane through this ring forms dihedral angles of 82.44 (5) and 4.52 (5)° with the (dimethylamino)benzene and p-tolyl rings, respectively. In the crystal, weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link molecules into supramolecular tubes along the b axis.
Keywords: crystal structure, substituted pyrazole, pyrazole derivatives, pharmacological properties
Related literature
For pharmacological properties of pyrazole derivatives, see: Sarojini et al. (2010 ▸); Samshuddin et al. (2012 ▸). For their industrial applications, see: Wiley et al. (1958 ▸); Lu et al. (1999 ▸). For related structures, see Fun et al. (2010 ▸); Baktır et al. (2011 ▸).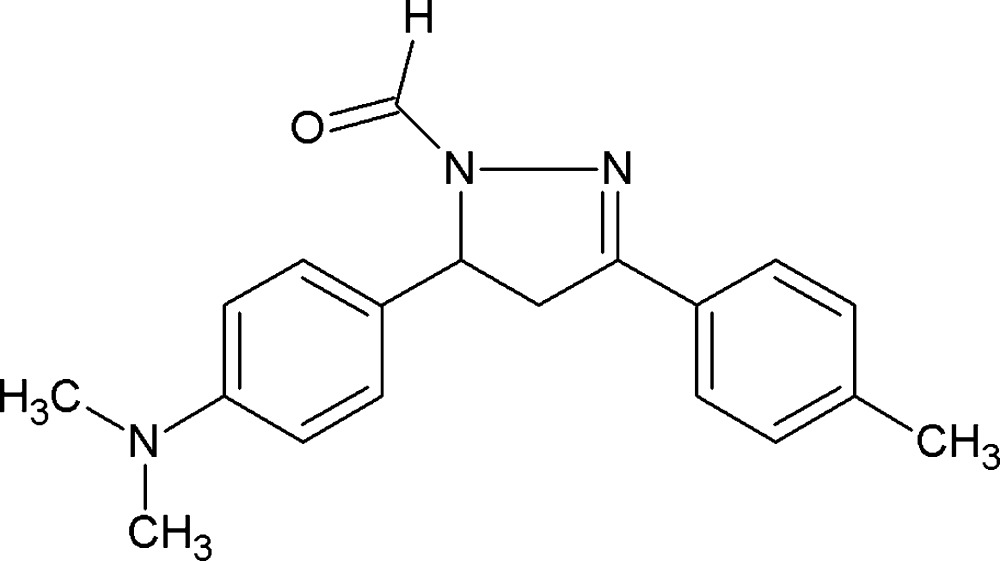
Experimental
Crystal data
C19H21N3O
M r = 307.39
Monoclinic,

a = 21.9524 (15) Å
b = 6.2511 (4) Å
c = 24.1521 (16) Å
β = 106.3069 (9)°
V = 3181.0 (4) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.45 × 0.26 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEX DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▸) T min = 0.921, T max = 0.962
27492 measured reflections
4750 independent reflections
4090 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.028
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.043
wR(F 2) = 0.122
S = 1.04
4750 reflections
211 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2014 ▸); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2014 ▸); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS2013 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL2014 (Sheldrick, 2015 ▸); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▸); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▸).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015023294/tk5413sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015023294/tk5413Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015023294/tk5413Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015023294/tk5413fig1.tif
The molecular structure of (I), showing the atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
b . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015023294/tk5413fig2.tif
The crystal packing of (I), viewed along the b axis.
CCDC reference: 1440601
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1A⋯O1i | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.4175 (12) | 158 |
| C19—H19A⋯O1ii | 0.98 | 2.45 | 3.3902 (15) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii) 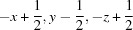 .
.
Acknowledgments
SS thanks Alva’s Education Foundation, Moodbidri, for providing research facilities. The authors would like to thank Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, SLAI, the Malaysian Ministry of Higher Education and the Universiti Sains Malaysia for RU research grants (Nos. PKIMIA/846017 and 1001/PKIMIA/811269), which partly supported this work.
supplementary crystallographic information
S1. Introduction
Pyrazolyl derivatives are well known for their versatile pharmacological activities (Sarojini et al., 2010; Samshuddin et al., 2012). In addition, many 1,3,5-triaryl-2-pyrazolyls have a variety of industrial applications such as functioning as scintillation solutes (Wiley et al., 1958) and fluorescent agents (Lu et al., 1999). The crystal structures of some pyrazolyls containing a N-alkyl chain viz., 3,5-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole-1-carbaldehyde (Baktır et al., 2011) and 1-[3,5-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-1-yl]ethanone (Fun et al., 2010) have been reported. In view of the importance of pyrazolines, the title compound (I) was prepared and its crystal structure reported.
S2. Supramolecular features
The asymmetric unit of (I) consists of a single crystallographic independent molecule as shown in Fig. 1. The pyrazoline ring (N1/N2/C7/C8/C9) is twisted about the C8—C7 bond [Q2 = 0.0964 (10) Å and φ2 = 133.5 (6)°] with maximum deviations of 0.057 (1) and −0.053 (1) Å from its mean plane for atoms C7 and C8, respectively. The methyl-substituted phenyl ring (C10–C15) and dimethylamino-substituted phenyl ring (C1–C6) make dihedral angles of 4.52 (5) and 82.44 (5)°, respectively, with the pyrazoline ring. In crystal, molecules are connected by weak C—H···O hydrogen bonds into one-dimensional spiral-like chains (Fig. 2), propagating along the crystallographic b-axis.
S3. Synthesis and crystallization
A mixture of (2E)-3-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]-1-(4-methylphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one (2.65 g, 0.01 mol) and hydrazine hydrate (1 ml) in 30 ml formic acid was refluxed for 6 h. The reaction mixture was cooled and poured into 250 ml ice-cold water. The precipitate formed was collected by filtration and purified by recrystallization from ethanol. Single crystals were grown from ethyl acetate by slow evaporation (m.p 473–476 K; yield: 68%).
S4. Refinement
The carbon-bound H-atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.95–1.00 Å) and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with Uiso(H) set to 1.2–1.5Uequiv(C) A rotating group model was applied to methyl groups.
Figures
Fig. 1.

The molecular structure of (I), showing the atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.

The crystal packing of (I), viewed along the b axis.
Crystal data
| C19H21N3O | F(000) = 1312 |
| Mr = 307.39 | Dx = 1.284 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 21.9524 (15) Å | Cell parameters from 9179 reflections |
| b = 6.2511 (4) Å | θ = 3.0–30.3° |
| c = 24.1521 (16) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| β = 106.3069 (9)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 3181.0 (4) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.45 × 0.26 × 0.15 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEX DUO CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4750 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4090 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.028 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 30.3°, θmin = 1.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −30→29 |
| Tmin = 0.921, Tmax = 0.962 | k = −8→8 |
| 27492 measured reflections | l = −34→34 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.043 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.122 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0683P)2 + 1.9935P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.04 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 4750 reflections | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 211 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.06265 (4) | 0.29904 (12) | 0.11364 (3) | 0.02109 (17) | |
| N1 | 0.01154 (4) | −0.01958 (13) | 0.10464 (3) | 0.01627 (17) | |
| N2 | −0.01890 (4) | −0.18157 (13) | 0.06779 (3) | 0.01565 (17) | |
| N3 | 0.25348 (4) | −0.20563 (14) | 0.32043 (4) | 0.01865 (18) | |
| C1 | 0.09931 (5) | −0.28895 (16) | 0.21033 (4) | 0.01817 (19) | |
| H1A | 0.0779 | −0.4002 | 0.1857 | 0.022* | |
| C2 | 0.15816 (5) | −0.33020 (16) | 0.24891 (4) | 0.01840 (19) | |
| H2A | 0.1757 | −0.4699 | 0.2508 | 0.022* | |
| C3 | 0.19237 (5) | −0.16856 (15) | 0.28528 (4) | 0.01578 (18) | |
| C4 | 0.16344 (5) | 0.03445 (15) | 0.28189 (4) | 0.01599 (18) | |
| H4A | 0.1847 | 0.1467 | 0.3062 | 0.019* | |
| C5 | 0.10411 (5) | 0.07238 (15) | 0.24333 (4) | 0.01551 (18) | |
| H5A | 0.0858 | 0.2108 | 0.2418 | 0.019* | |
| C6 | 0.07085 (5) | −0.08737 (15) | 0.20693 (4) | 0.01555 (18) | |
| C7 | 0.00689 (5) | −0.04206 (15) | 0.16474 (4) | 0.01606 (18) | |
| H7A | −0.0115 | 0.0911 | 0.1764 | 0.019* | |
| C8 | −0.04155 (5) | −0.22678 (17) | 0.15670 (4) | 0.01855 (19) | |
| H8A | −0.0255 | −0.3427 | 0.1850 | 0.022* | |
| H8B | −0.0828 | −0.1755 | 0.1607 | 0.022* | |
| C9 | −0.04769 (4) | −0.30150 (15) | 0.09584 (4) | 0.01509 (18) | |
| C10 | −0.08377 (4) | −0.48998 (15) | 0.06946 (4) | 0.01530 (18) | |
| C11 | −0.08705 (5) | −0.55364 (16) | 0.01292 (4) | 0.01714 (19) | |
| H11A | −0.0660 | −0.4718 | −0.0093 | 0.021* | |
| C12 | −0.12078 (5) | −0.73494 (16) | −0.01069 (4) | 0.01826 (19) | |
| H12A | −0.1226 | −0.7754 | −0.0490 | 0.022* | |
| C13 | −0.15214 (5) | −0.85946 (16) | 0.02091 (4) | 0.0189 (2) | |
| C14 | −0.14841 (5) | −0.79645 (18) | 0.07700 (5) | 0.0228 (2) | |
| H14A | −0.1690 | −0.8797 | 0.0993 | 0.027* | |
| C15 | −0.11508 (5) | −0.61392 (17) | 0.10118 (4) | 0.0203 (2) | |
| H15A | −0.1136 | −0.5733 | 0.1394 | 0.024* | |
| C16 | 0.03751 (4) | 0.14662 (16) | 0.08404 (4) | 0.01661 (18) | |
| H16A | 0.0363 | 0.1457 | 0.0444 | 0.020* | |
| C17 | −0.18897 (6) | −1.05622 (18) | −0.00455 (5) | 0.0265 (2) | |
| H17A | −0.1673 | −1.1291 | −0.0295 | 0.040* | |
| H17B | −0.2317 | −1.0148 | −0.0273 | 0.040* | |
| H17C | −0.1919 | −1.1528 | 0.0266 | 0.040* | |
| C18 | 0.27313 (5) | −0.42547 (17) | 0.33548 (5) | 0.0208 (2) | |
| H18A | 0.3182 | −0.4282 | 0.3570 | 0.031* | |
| H18B | 0.2665 | −0.5105 | 0.3002 | 0.031* | |
| H18C | 0.2479 | −0.4857 | 0.3594 | 0.031* | |
| C19 | 0.28414 (5) | −0.04748 (17) | 0.36345 (5) | 0.0205 (2) | |
| H19A | 0.3290 | −0.0845 | 0.3794 | 0.031* | |
| H19B | 0.2634 | −0.0456 | 0.3945 | 0.031* | |
| H19C | 0.2806 | 0.0941 | 0.3454 | 0.031* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0212 (3) | 0.0179 (3) | 0.0216 (4) | −0.0049 (3) | 0.0017 (3) | −0.0014 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0194 (4) | 0.0166 (4) | 0.0116 (3) | −0.0050 (3) | 0.0023 (3) | −0.0016 (3) |
| N2 | 0.0171 (4) | 0.0146 (4) | 0.0137 (4) | −0.0027 (3) | 0.0017 (3) | −0.0016 (3) |
| N3 | 0.0183 (4) | 0.0157 (4) | 0.0204 (4) | 0.0010 (3) | 0.0028 (3) | 0.0008 (3) |
| C1 | 0.0234 (5) | 0.0151 (4) | 0.0158 (4) | −0.0033 (3) | 0.0051 (3) | −0.0029 (3) |
| C2 | 0.0233 (5) | 0.0137 (4) | 0.0184 (4) | 0.0003 (3) | 0.0063 (4) | −0.0006 (3) |
| C3 | 0.0185 (4) | 0.0156 (4) | 0.0141 (4) | −0.0009 (3) | 0.0059 (3) | 0.0007 (3) |
| C4 | 0.0194 (4) | 0.0144 (4) | 0.0138 (4) | −0.0018 (3) | 0.0041 (3) | −0.0013 (3) |
| C5 | 0.0194 (4) | 0.0135 (4) | 0.0135 (4) | −0.0005 (3) | 0.0044 (3) | −0.0003 (3) |
| C6 | 0.0187 (4) | 0.0157 (4) | 0.0121 (4) | −0.0021 (3) | 0.0041 (3) | −0.0007 (3) |
| C7 | 0.0182 (4) | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0121 (4) | −0.0028 (3) | 0.0037 (3) | −0.0018 (3) |
| C8 | 0.0199 (4) | 0.0220 (5) | 0.0145 (4) | −0.0060 (4) | 0.0060 (3) | −0.0034 (3) |
| C9 | 0.0143 (4) | 0.0165 (4) | 0.0138 (4) | −0.0010 (3) | 0.0030 (3) | −0.0012 (3) |
| C10 | 0.0143 (4) | 0.0157 (4) | 0.0150 (4) | −0.0014 (3) | 0.0026 (3) | −0.0002 (3) |
| C11 | 0.0198 (4) | 0.0162 (4) | 0.0154 (4) | −0.0026 (3) | 0.0051 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| C12 | 0.0212 (4) | 0.0175 (4) | 0.0148 (4) | −0.0018 (3) | 0.0029 (3) | −0.0011 (3) |
| C13 | 0.0182 (4) | 0.0171 (4) | 0.0187 (4) | −0.0039 (3) | 0.0007 (3) | 0.0004 (3) |
| C14 | 0.0236 (5) | 0.0257 (5) | 0.0194 (5) | −0.0110 (4) | 0.0063 (4) | 0.0002 (4) |
| C15 | 0.0214 (5) | 0.0238 (5) | 0.0160 (4) | −0.0073 (4) | 0.0057 (4) | −0.0021 (4) |
| C16 | 0.0160 (4) | 0.0167 (4) | 0.0158 (4) | −0.0017 (3) | 0.0024 (3) | 0.0018 (3) |
| C17 | 0.0296 (5) | 0.0218 (5) | 0.0240 (5) | −0.0107 (4) | 0.0010 (4) | −0.0018 (4) |
| C18 | 0.0230 (5) | 0.0185 (5) | 0.0214 (5) | 0.0047 (4) | 0.0069 (4) | 0.0027 (4) |
| C19 | 0.0177 (4) | 0.0208 (5) | 0.0213 (5) | 0.0008 (4) | 0.0026 (4) | −0.0018 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C16 | 1.2256 (12) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| N1—C16 | 1.3459 (12) | C9—C10 | 1.4622 (13) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3892 (11) | C10—C15 | 1.3982 (13) |
| N1—C7 | 1.4901 (12) | C10—C11 | 1.4049 (13) |
| N2—C9 | 1.2889 (12) | C11—C12 | 1.3858 (13) |
| N3—C3 | 1.3908 (12) | C11—H11A | 0.9500 |
| N3—C19 | 1.4550 (13) | C12—C13 | 1.3991 (14) |
| N3—C18 | 1.4556 (13) | C12—H12A | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.3884 (14) | C13—C14 | 1.3910 (15) |
| C1—C6 | 1.3986 (14) | C13—C17 | 1.5051 (14) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9500 | C14—C15 | 1.3922 (14) |
| C2—C3 | 1.4094 (13) | C14—H14A | 0.9500 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9500 | C15—H15A | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.4112 (13) | C16—H16A | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3923 (13) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9500 | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.3938 (13) | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9500 | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| C6—C7 | 1.5121 (13) | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.5446 (14) | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7A | 1.0000 | C19—H19A | 0.9800 |
| C8—C9 | 1.5118 (13) | C19—H19B | 0.9800 |
| C8—H8A | 0.9900 | C19—H19C | 0.9800 |
| C16—N1—N2 | 120.22 (8) | C15—C10—C11 | 118.47 (9) |
| C16—N1—C7 | 125.80 (8) | C15—C10—C9 | 119.82 (9) |
| N2—N1—C7 | 113.78 (7) | C11—C10—C9 | 121.70 (8) |
| C9—N2—N1 | 107.81 (8) | C12—C11—C10 | 120.48 (9) |
| C3—N3—C19 | 119.75 (8) | C12—C11—H11A | 119.8 |
| C3—N3—C18 | 118.50 (8) | C10—C11—H11A | 119.8 |
| C19—N3—C18 | 114.70 (8) | C11—C12—C13 | 121.23 (9) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.52 (9) | C11—C12—H12A | 119.4 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 119.2 | C13—C12—H12A | 119.4 |
| C6—C1—H1A | 119.2 | C14—C13—C12 | 118.05 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 121.18 (9) | C14—C13—C17 | 120.48 (9) |
| C1—C2—H2A | 119.4 | C12—C13—C17 | 121.47 (9) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 119.4 | C13—C14—C15 | 121.39 (9) |
| N3—C3—C2 | 120.99 (9) | C13—C14—H14A | 119.3 |
| N3—C3—C4 | 121.77 (9) | C15—C14—H14A | 119.3 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 117.14 (9) | C14—C15—C10 | 120.38 (9) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.88 (9) | C14—C15—H15A | 119.8 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.6 | C10—C15—H15A | 119.8 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.6 | O1—C16—N1 | 123.54 (9) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.73 (9) | O1—C16—H16A | 118.2 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.1 | N1—C16—H16A | 118.2 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.1 | C13—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 117.53 (9) | C13—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.91 (8) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 121.55 (8) | C13—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C6 | 111.69 (8) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C8 | 100.43 (7) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 114.89 (8) | N3—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—H7A | 109.8 | N3—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7A | 109.8 | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 109.8 | N3—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 102.92 (8) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8A | 111.2 | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8A | 111.2 | N3—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8B | 111.2 | N3—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8B | 111.2 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| H8A—C8—H8B | 109.1 | N3—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—C10 | 121.69 (9) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—C8 | 114.10 (8) | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 124.20 (8) | ||
| C16—N1—N2—C9 | −170.18 (9) | C1—C6—C7—C8 | 38.39 (12) |
| C7—N1—N2—C9 | 4.90 (11) | N1—C7—C8—C9 | 9.05 (9) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.62 (15) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −110.93 (9) |
| C19—N3—C3—C2 | −171.16 (9) | N1—N2—C9—C10 | −179.08 (8) |
| C18—N3—C3—C2 | −22.08 (13) | N1—N2—C9—C8 | 2.03 (11) |
| C19—N3—C3—C4 | 12.60 (14) | C7—C8—C9—N2 | −7.57 (11) |
| C18—N3—C3—C4 | 161.68 (9) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 173.57 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3—N3 | −174.66 (9) | N2—C9—C10—C15 | −179.05 (9) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.75 (14) | C8—C9—C10—C15 | −0.28 (14) |
| N3—C3—C4—C5 | 175.25 (9) | N2—C9—C10—C11 | 2.17 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.13 (14) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −179.05 (9) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.36 (14) | C15—C10—C11—C12 | 0.19 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.14 (14) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 178.98 (9) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −179.11 (8) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.23 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.77 (14) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.17 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 179.72 (9) | C11—C12—C13—C17 | 179.86 (9) |
| C16—N1—C7—C6 | −72.07 (12) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.62 (16) |
| N2—N1—C7—C6 | 113.18 (9) | C17—C13—C14—C15 | −179.41 (10) |
| C16—N1—C7—C8 | 165.67 (9) | C13—C14—C15—C10 | −0.67 (17) |
| N2—N1—C7—C8 | −9.08 (10) | C11—C10—C15—C14 | 0.25 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7—N1 | 103.78 (10) | C9—C10—C15—C14 | −178.56 (9) |
| C1—C6—C7—N1 | −75.15 (11) | N2—N1—C16—O1 | 176.82 (9) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −142.69 (9) | C7—N1—C16—O1 | 2.38 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1A···O1i | 0.95 | 2.52 | 3.4175 (12) | 158 |
| C19—H19A···O1ii | 0.98 | 2.45 | 3.3902 (15) | 161 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y−1, z; (ii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supporting information for this paper is available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: TK5413).
References
- Baktır, Z., Akkurt, M., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2011). Acta Cryst. E67, o1292–o1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2014). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Fun, H.-K., Hemamalini, M., Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2010). Acta Cryst. E66, o582–o583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z. Y., Zhu, W. G., Jiang, Q. & Xie, M. G. (1999). Chin. Chem. Lett. 10, 679–682.
- Samshuddin, S., Narayana, B., Sarojini, B. K., Khan, M. T. H., Yathirajan, H. S., Raj, C. G. D. & Raghavendra, R. (2012). Med. Chem. Res. 21, 2012–2022.
- Sarojini, B. K., Vidyagayatri, M., Darshanraj, C. G., Bharath, B. R. & Manjunatha, H. (2010). Lett. Drug. Des. Discov. 7, 214–224.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wiley, R. H., Jarboe, C. H., Hayes, F. N., Hansbury, E., Nielsen, J. T., Callahan, P. X. & Sellars, M. (1958). J. Org. Chem. 23, 732–738.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, New_Global_Publ_Block. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015023294/tk5413sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015023294/tk5413Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015023294/tk5413Isup3.cml
. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015023294/tk5413fig1.tif
The molecular structure of (I), showing the atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
b . DOI: 10.1107/S2056989015023294/tk5413fig2.tif
The crystal packing of (I), viewed along the b axis.
CCDC reference: 1440601
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report


