Abstract
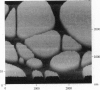
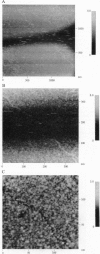
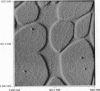
To date, no microscopic methods are available to confirm scanning tunneling microscope (STM) images of DNA. The difficulties encountered in repeating these images may be attributed to inadequate distribution of molecules on the substrate, poor adhesion to the substrate, or the low conductivity of the molecules. However, these factors are difficult to assess in an STM experiment where they may act simultaneously. A method to isolate these factors involves partly masking the deposited molecules before coating them with a conductive film to produce adjacent segments of coated and bare DNA after the mask is removed. The coated DNA segments are conductive and mechanically stable to allow easy identification of DNA by the STM. Furthermore, the path of a molecule can be traced from a coated to an uncoated region to test STM imaging of bare DNA. Masked preparations of DNA deposited on platinum/carbon-coated mica and highly oriented pyrolytic graphite were examined with a tunneling current 1000 times lower than the usual nanoamps. The tip apparently displaces molecules adsorbed to graphite to preclude imaging whereas more stably bound DNA on platinum/carbon-coated mica appears in reversed contrast.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison D. P., Bottomley L. A., Thundat T., Brown G. M., Woychik R. P., Schrick J. J., Jacobson K. B., Warmack R. J. Immobilization of DNA for scanning probe microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10129–10133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arscott P. G., Lee G., Bloomfield V. A., Evans D. F. Helical period of Z-DNA. Nature. 1990 Aug 23;346(6286):706–706. doi: 10.1038/346706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beebe T. P., Jr, Wilson T. E., Ogletree D. F., Katz J. E., Balhorn R., Salmeron M. B., Siekhaus W. J. Direct observation of native DNA structures with the scanning tunneling microscope. Science. 1989 Jan 20;243(4889):370–372. doi: 10.1126/science.2911747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemmer C. R., Beebe T. P., Jr Graphite: a mimic for DNA and other biomolecules in scanning tunneling microscope studies. Science. 1991 Feb 8;251(4994):640–642. doi: 10.1126/science.1992517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coratger R., Chahboun A., Ajustron F., Beauvillain J., Erard M., Amalric F. Scanning tunneling microscopy of a liquid crystalline phase of poly((dA-dT).(dA-dT)) induced by a histone H1 peptide. Ultramicroscopy. 1990 Dec;34(3):141–147. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(90)90068-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cricenti A., Selci S., Felici A. C., Generosi R., Gori E., Djaczenko W., Chiarotti G. Molecular structure of DNA by scanning tunneling microscopy. Science. 1989 Sep 15;245(4923):1226–1227. doi: 10.1126/science.2781279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll R. J., Youngquist M. G., Baldeschwieler J. D. Atomic-scale imaging of DNA using scanning tunnelling microscopy. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):294–296. doi: 10.1038/346294a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap D. D., Bustamante C. Images of single-stranded nucleic acids by scanning tunnelling microscopy. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):204–206. doi: 10.1038/342204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García R., Yuqiu J., Schabtach E., Bustamante C. Deposition and imaging of metal-coated biomolecules with the STM. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1250–1254. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90431-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller D., Bustamante C., Keller R. W. Imaging of single uncoated DNA molecules by scanning tunneling microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5356–5360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Lieber C. M. Scanning tunneling microscopy imaging of synthetic oligonucleotides and oligonucleotide-metal complexes. Scanning Microsc. 1991 Jun;5(2):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsay S. M., Tao N. J., DeRose J. A., Oden P. I., Lyubchenko YuL, Harrington R. E., Shlyakhtenko L. Potentiostatic deposition of DNA for scanning probe microscopy. Biophys J. 1992 Jun;61(6):1570–1584. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81961-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu J. D., Li M. Q., Xiu L. Z., Zhu J. Q., Hu J., Gu M. M., Xu Y. L., Zhang L. P., Huang Z. Q., Chernov B. K. Parallel stranded DNA under the scanning tunnelling microscope. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Jan 23;1115(3):239–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]