Significance
The magnetic-field tuned superconductor-to-insulator transition (H-SIT) is a paradigmatic quantum phase transition and, along with the quantum-Hall liquid-to-insulator transitions (QHIT), is among the best experimentally studied ones. However, in the transition and the proximate ground-state phases, it has consistently exhibited features that are seemingly at odds with the generally accepted theoretical “story.” The clear evidence we have found of particle–vortex duality at the H-SIT is one such example, as is the associated evidence that the proximate insulating phase is fundamentally distinct from a conventional “Anderson insulator” in that , rather than diverging, tends to a finite value as . That these features are analogous to behaviors previously documented near the QHIT supports the existence of the correspondence between the two problems implied by the composite boson theory.
Keywords: superconductor–insulator transition, quantum phase transition, self-duality, Hall insulator
Abstract
We combine measurements of the longitudinal () and Hall () resistivities of disordered 2D amorphous indium-oxide films to study the magnetic-field tuned superconductor-to-insulator transition (H-SIT) in the limit. At the critical field, , the full resistivity tensor is T independent with and within experimental uncertainty in all films (i.e., these appear to be “universal” values); this is strongly suggestive that there is a particle–vortex self-duality at . The transition separates the (presumably) superconducting state at from a “Hall-insulator” phase in which as whereas approaches a nonzero value smaller than its “classical value” ; i.e., . A still higher characteristic magnetic field, , at which the Hall resistance is T independent and roughly equal to its classical value, , marks an additional crossover to a high-field regime (probably to a Fermi insulator) in which and possibly diverges as . We also highlight a profound analogy between the H-SIT and quantum-Hall liquid-to-insulator transitions (QHIT).
Quantum phase transitions (QPTs) occur at zero temperature () as a quantum control parameter is varied. Where the transition is continuous, quantum critical phenomena are expected to give rise to universal physics that can be analyzed using a straightforward scaling theory. The magnetic-field tuned transition between superconducting and insulating ground states in 2D conductors is a particularly attractive exemplar of a QPT because the magnetic field can be continuously tuned, allowing a detailed scaling analysis of the QPTs and explorations of the ground-state phases proximate to criticality (1–9). However, the exact nature of the insulating and superconducting states above and below the magnetic-field tuned superconductor-to-insulator transition (H-SIT) and a satisfactory description of the transition between them are still lacking.
The conventional picture of phases of a 2D electron fluid in the presence of disorder is based on the assumption that the only stable phases are superconducting or insulating (or, in a magnetic field, quantum Hall liquid phases). In contrast, studies of films near the H-SIT have suggested the existence of several unexpected new ground-state phases in films that superconduct at zero field. In weakly disordered films (with normal state resistivity small compared with the quantum of resistance, ), the superconducting state gives way to an “anomalous metallic phase” with a resistivity that extrapolates to a nonzero value, (10–14). For highly disordered superconducting films with , a direct H-SIT seemingly occurs at a field , but as we will discuss, significant electron “pairing” persists in the insulating phase.
In a purely bosonic description (15–17) (where it is assumed that fermionic excitations are negligible), the insulating state is characterized as a condensate of delocalized vortices and localized Cooper pairs, whereas the superconducting state is a condensate of Cooper pairs with localized vortices. Quantum fluctuations of the phase of the superconducting order parameter control this QPT. A key feature of particle–vortex duality is that the (measured) conductivity tensor is equal to the vortex-resistivity tensor ,
| [1] |
An emergent self-duality in the neighborhood of would imply ( is the transpose) or in other words at criticality . If we further imagine that is continuous at , it would follow that because as in the insulating phase. [Analogous reasoning was used to infer the critical conductivity tensors at the quantum-Hall liquid-to-insulator transitions (QHIT); Supporting Information.] Together, these arguments imply
| [2] |
Previous studies have examined evidence for duality (18, 19) from resistivity measurements, but have not examined the full conductivity tensor across the transition.
In this paper we provide insights concerning the nature of the H-SIT in highly disordered films, using new measurements of the full resistivity tensor across the quantum transition. (Fig. 1.) We draw three key conclusions: (i) We identify the insulating state above as a “Hall insulator” (20) in which as , but , cementing a connection between the H-SIT and the QHIT; (ii) we observe self-duality consistent with Eq. 2 at the transition; and (iii) we present suggestive evidence that the superconducting state is a “vortex insulator” (dual to the Hall insulator) in which but approaches a finite value as .
Fig. 1.
Longitudinal () and Hall () resistances for two InOx samples. Solid lines mark the H-SIT field and critical resistivity , and dashed lines mark the Hall-crossing field and resistivity .
A general issue in studies of ground-state phases and quantum critical phenomena is that experiments are carried out at nonzero T, so all results must be extrapolated to . There are numerous practical issues that define the lowest temperatures at which experiments can be carried out—in addition to issues of refrigeration, equilibration times (especially in disordered systems) tend to diverge rapidly with decreasing T and the range of current densities for which linear response theory applies decreases. In the present case, the fact that as ultimately limits our ability to reliably measure , although using the distinct symmetries of and with respect to helps greatly in this regard. Here, we report results at high enough temperatures that we avoid measurement ambiguities and yet reach temperatures that are low compared with “microscopic” scales (for instance, low compared with the zero field ) so that we are well within the quantum critical fan that describes the basin of influence of the quantum critical point such that it is reasonable to extrapolate the results to . We note that although this argument is compelling at criticality, there is always an emergent energy scale that vanishes upon approach to criticality, so inferring the asymptotic properties of the stable phases near criticality is intrinsically subtle (21).
Near the H-SIT, it is reasonable to expect that the singular parts of various physical quantities, most especially the diagonal resistivity, are well described by a universal scaling function with appropriate universal critical exponents. Thus, in common with earlier studies of the H-SIT in highly disordered films, we perform a scaling analysis of the T and H dependence of in a narrow neighborhood of the critical resistivity (shown in Fig. 2):
| [3] |
This yields the combination of critical exponents (Fig. 2) and a value of that is universal (within experimental uncertainty) and equal to the “Cooper-pair quantum of resistance,” k. [Uncertainty of order (or larger) is typical when determining the geometrical aspect ratio needed to calculate the 2D resistivity of disordered films.] Moreover, from an additional scaling ansatz (5) for the nonlinear field dependence of the differential resistivity at criticality [the lowest temperature is more than five times the effective temperature associated with the electric field , where is the electron–phonon relaxation length, ensuring that heating is not present (22)],
| [4] |
one can extract another combination of critical exponents, . Together, these results imply that the correlation length exponent and the dynamical exponent .
Fig. 2.
Scaling of isotherms (Left) and constant electric field curves (Right) near the H-SIT for sample 1. Temperature and applied bias voltages are indicated. Insets show the raw resistivity isotherm and constant electric field data, with the same vertical scale as in the main panels.
Analogous behavior has been observed (23, 24) at various QHITs in two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) systems. In fact, a formal mapping between the two problems yields an analogy between the H-SIT and the QHIT (20). As has been emphasized previously (20), it is striking that a scaling collapse of data from both the integer (filling factor 2) and the fractional (filling factor 1/3) QHIT produce scaling curves that look extremely similar to those from the H-SIT in highly disordered films with the same value of , with a different (but analogous) universal critical resistance (25). Significantly, the insulating phase proximate to the QHIT transition is an unconventional Hall insulator in the sense that whereas as , approaches a finite field-dependent value (26, 27).
Experimental Results
The amorphous InOx films used in the present study were synthesized and measured as described previously (4, 9) and are further discussed in Supporting Information. Fig. 1 depicts the basic structure of and for two representative InOx samples (samples 1 and 2). (Comparable results were found on six additional samples measured during this study and are similar to data previously published in ref. 18.) In comparison with some other strongly disordered films (e.g., refs. 3, 4, 28, 29) the magnetoresistance peaks exhibited at accessible temperatures by the present films are only moderately large, which allows for accurate measurements of . (All data are field antisymmetric.) Strongly disordered samples with , which includes the two presented here, all show critical resistance at the H-SIT within 10 of the quantum of resistance, [uncertainty of order (or larger) is typical when determining the geometrical aspect ratio needed to calculate the 2D resistivity of disordered films] and exhibit good scaling of the form of Eqs. 3 and 4.
There are several important features in the data of Fig. 1. First, in addition to the hallmark crossing point of at (,) marking the SIT, we observe at higher fields a crossing point of at (). roughly coincides with the field at which the longitudinal magnetoresistance peaks, suggesting that it is associated with a crossover from Bose-dominated to Fermi-dominated behavior. Although for decreases with decreasing T, this dependence weakens as , suggesting that approaches a finite value.
Results Extrapolated to .
To obtain a more explicit understanding of the nature of the different regimes above and below the H-SIT, and what can be inferred about the limit, we analyzed the full set of data that determine the resistivity tensor.
In Fig. 3 we present the T dependence of the resistivity tensor of sample 1 at various fixed values of H. Note that, having measured both and , we can calculate the off-diagonal term of the conductivity tensor: . Fig. 3 shows , , and of sample 1 for various fixed fields as a function of T, as well as sketching ways in which we infer values by extrapolation. We now distinguish several field regimes describing the different behavior of and as the magnetic field is increasing from low fields to much above . Fig. 4 summarizes the ground-state Hall response as a function of H based on a linear extrapolation of the data to (i.e., according to the dashed lines in Fig. 3). Error bars reflect statistical uncertainty in the extrapolation procedure. On the high-field side of the H-SIT (), where presumably and , approaches a finite limit that is greater than 0 and less than its classical value , whereas —these are the defining features of a Hall-insulator phase (20). [The value of the Hall resistance is taken from measurements at ; for sample 1, , i.e., for .] At the low-field edge of the Hall-insulating regime, as , and it grows monotonically with increasing H, approaching roughly its classical value at the high-field boundary of the regime.
Fig. 3.
(A–C) T dependence of the resistivity tensor ( in A and in B) and (C) of sample 1 in units of the superconducting quanta for various values of H. For this sample, T, T, K, and .
Fig. 4.
The extrapolated values of and for sample 1.The vertical solid lines mark the SIT, and dashed lines show the Hall crossing field. Right panel highlights the SIT region (marked in Left panel); lines through the data are guides to the eye, showing the symmetry between and .
Conversely, in the low-field phase (), , whereas approaches a finite limit that tends to 0 as . If we accept the identification of this phase as superconducting (although this is not entirely established in the accessible range of T), then we expect that and as , i.e., that the conductivity tensor on the low-field side of the H-SIT behaves analogously to the resistivity tensor on the high-field side (30, 31).
There also appears to be a second critical (or crossover) field at which a transition to a “Fermionic insulator” occurs. For , (as well as ) grows with decreasing T. Although the T dependence of clearly suggests that it diverges as , the much weaker T dependence of and our limited temperature range make it less clear whether for it diverges. In any case, the upward curvature of suggests that the value shown in Fig. 4, obtained from linear extrapolation to , underestimates the true value.
We now look with more detail at the T dependence of the resistivity tensor of sample 1 in the various distinct field ranges, particularly those aspects that affect the extrapolation :
. Here is a decreasing function of decreasing T. However, the T dependence of is sufficiently weak that a linear extrapolation to would imply a nonzero magnitude of , which would be inconsistent with our identification of this as a superconducting phase. This issue appears to plague all measurements of strongly disordered films (3, 4, 32), although it has not been commented on previously. (We return to this point in the discussion, below.) in this range of H is always very much smaller than its classical value () and clearly tends to zero as . Inverting the resistivity tensor to obtain amplifies the error bars. Of course, because , is negative; it is also small and approximately a linear function of T, but a linear extrapolation of to (dashed lines in Fig. 3) suggests that approaches nonzero negative values, as shown in Fig. 4.
. At this magnetic field is essentially T independent and ∼10% less than . As mentioned above, the sign and magnitude of vary from sample to sample, but are rarely larger than this. Although the resistance can be measured with much better than 10% accuracy, extracting the resistivity requires precise knowledge of the geometry of the current pathways. In the present experiments, this geometric uncertainty is at least equal to the apparent deviations from universality. Both and are vanishingly small within experimental accuracy; i.e., and .
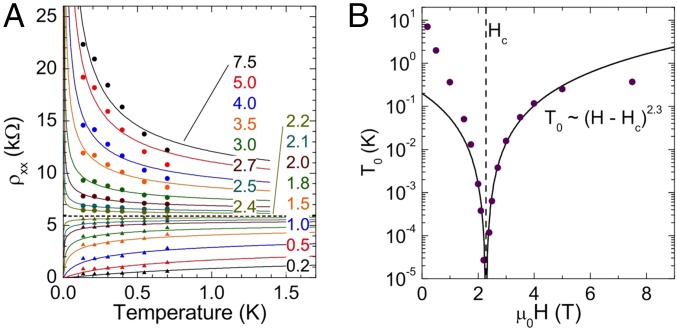
. In this regime is a strongly increasing function of decreasing T, with pronounced upward curvature and low T magnitudes that are large compared with the quantum of resistance. This behavior identifies this as an insulating state, with a T dependence that is consistent with activated behavior or various forms of variable-range hopping, with , 1/2, or 1/3 (4). However, the data are not consistent with any reasonable power law and we do not find the super-Arrhenius behavior that has been reported in some systems (33, 34), suggesting that we are indeed probing an equilibrium phase. as a function of H grows continuously from at to a maximal value at around . If we adopt , appropriate for Mott variable-range hopping in 2D, we find for sample 1 that K, comparable to the zero-field transition temperature, . This is highly suggestive that superconducting pairing remains significant even in the Hall-insulating regime. is a weakly decreasing function of decreasing T, with a magnitude that is always less than its classical value, . Indeed, is, within experimental uncertainty, a linear function of T, which extrapolates to the finite zero temperature value, , shown in Fig. 4, which grows monotonically with H from 0 at to its classical value at . By contrast, extrapolates roughly linearly to values indistinguishable from 0 as .
. This is the field at which is approximately T independent, reflecting the crossover from a low-field regime where decreases with decreasing T to a high-field regime where it increases. It is also roughly the value of H at which achieves its largest value for fixed T. This large magnitude ensures that as .
. Here is an increasing function of decreasing temperature, with a magnitude that is larger than its classical value. Over the accessible range of T, it can be roughly fit to a linear function, which results in the extrapolated values shown in Fig. 4. However, the clear upward curvature likely indicates that this represents an underestimate, and it is even plausible that in this entire range, as . is also an increasing function of decreasing T, but at fixed T it is a decreasing function of increasing H; i.e., the film is increasingly metallic at higher fields. A linear extrapolation of to would imply a nonzero value, as shown in Fig. 4. At present, it is not clear what to conclude about the nature of the ground-state behavior in this regime.
Indeed, in Fig. 1 data are presented on sample 2 up to 32 T, i.e., to fields much higher than any estimate of a mean-field . Here, one can see that takes on values that are significantly smaller than the electron resistivity quantum, k, yet much larger than the normal state value, k. Nonetheless, shows an “insulating-like” T dependence. Moreover, although is a linearly increasing function of H with an almost T-independent slope (plausibly giving a measure of ), it has a peculiar extrapolated offset that grows with decreasing T. It is not at all clear what the nature of the state is that gives rise to these behaviors.
Global Consistency Check.
The success of the scaling analysis near criticality supports the assertion that the accessible range of T is sufficiently low to penetrate well into the quantum critical regime. However, the relatively weak T dependence of in the putative “superconducting” regime () or similarly weak T dependence of on the insulating side of the transition () may suggest that the temperatures probed are not yet sufficiently low to fully sense the character of the respective ground states. Thus, we introduce a simple ansatz for the T and H dependence of , which presupposes the existence of a H-SIT with particle–vortex duality to test the self-consistently of this assumption.
Starting on the insulating side of the transition, we consider it most likely that the resistance is dominated by variable-range hopping of Cooper pairs,
| [5] |
with , and we assume that
| [6] |
(which of course implies that as ). We can already see from Fig. 3 that this ansatz gives a good account of the H and T dependence of in this range of fields, and indeed from Fig. 4 it is clear that near the H-SIT, . In Fig. 5A we exhibit the quality of the fit obtained setting and treating as a fitting parameter. Although there are differences between the results based on this ansatz and the data. especially at higher T, given that variable-range hopping is a low T asymptotic and the (excessive) simplicity of the ansatz involved, the fit is quite acceptable. Note in Fig. 5B the dependence of on H is consistent with scaling close to ; i.e., with . This confirms that the data are at least consistent with the existence of an insulating phase as for .
Fig. 5.
(A) Fits of the low-temperature scaling of curves using Eqs. 5 and 7. (B) The characteristic temperatures extracted from the fits to Eqs. 5 and 7 as a function of magnetic field, showing a critical behavior at consistent with the critical exponent found in Fig. 2.
Moving to the superconducting side of the transition, we invoke duality to describe the resistivity tensor in terms of variable-range hopping of vortices. In other words, we introduce the ansatz
| [7] |
again with , and we assume that
| [8] |
and by implication, as . The consistency of this ansatz with the Hall data can again be read from Figs. 3 and 4, and the comparison for is shown in Fig. 5. The apparent good quality of the fit reinforces the assumption that the low-field phase is superconducting. Note that away from criticality, the accessible temperatures extend well below ; the experimentally observed weak T dependence stems from the small exponent, , rather than from being at a larger T than characterizes the superconducting state.
Discussion
Quantum fluctuations of the superconducting order parameter ultimately drive the transition from the superconducting state; the long-distance properties of these fluctuations are described by a complex (bosonic) scalar field that, loosely speaking, represents the Cooper pairs. A dual description of the same degrees of freedom can be given in terms of vortex variables (16, 17, 30). In the superconducting phase, the vortices are localized and the Cooper pairs are condensed, whereas in an insulating phase, the vortices are condensed and the Cooper pairs are localized (15). A similar situation pertains to the QHIT in the context of the composite boson formulation of the problem: Here, the quantized Hall plateau phase in which and with (or , etc.) corresponds to the condensed phase of the appropriate form of composite bosons. Deep in this phase, isolated vortices are identified as (possibly fractionally charged) localized quasiholes. Thus, the QHIT is equivalent to a SIT transition of composite bosons, albeit with the difference that the composite bosons are coupled to an emergent Chern–Simons gauge field. The observation that the conductivity–resistivity duality relation is satisfied within remarkably tight error bars wherever a direct SIT is observed (as demonstrated in Fig. 4) and that the analogous relations are satisfied at the transition points in a number of quantum Hall experiments is strong evidence that the critical theory is self-dual.
We have interpreted our results as reflecting primarily collective order parameter (Cooper pair) fluctuations, neglecting the role of gapless quasiparticles. This interpretation is plausible, given that (for all of the samples used in this study), is much smaller than the estimated mean-field critical field, (3, 4). The strong positive magnetoresistance of the insulating phase close to is also highly suggestive that substantial pairing persists for a wide range of fields on either side of . Thus, it is plausible that gapless quasiparticle degrees of freedom do not play a significant role in the quantum dynamics in the neighborhood of the SIT. By contrast, such quasiparticles are thought to play a key role in the anomalous metallic phase in weakly disordered films (11, 35–37). Applying the analysis of ref. 20 for the QHIT, we note that if the quantum critical point is self-dual and both and are continuous functions of the magnetic field, then the insulating phase proximate to the SIT will exhibit a finite that rises continuously as a function of increasing H for , whereas the superconducting phase will exhibit a finite that increases continuously with decreasing H for .
There have been several attempts to derive the properties of the Hall insulator directly. It was shown (38) for an Anderson insulator that in the noncanonical order of limits, first and then , that . However, in experiments, the resistivity is measured in the zero-frequency limit at finite T and then the results are extrapolated to the limit. It has been shown that for the conventional theory of variable-range hopping as , although this divergence is much slower than the divergence of (39). This suggests the possibility that the “break” in the Hall resistance at marks the transition from a bosonic Hall insulator to a more conventional Anderson insulator. Conversely, an analysis of vortex dynamics in a weakly superconducting state by Vinokur et al. (40) led to the conclusion that it gives rise to a nonvanishing value of as ; as these authors already pointed out, duality maps this behavior for to Hall-insulating behavior for .
Phase Diagram
The most straightforward scenario is depicted in Fig. 6A; here superconductivity is lost at due to phase fluctuations, but the amplitude fluctuates slowly enough that we can consider Cooper pairs as still maintaining their identity, similar to a Kosterlitz–Thouless transition (15). In this case, a Hall-insulating phase appears near the SIT, but it crosses over to a true insulating phase, below a low crossover temperature (dashed line in Fig. 6A), below which would begin to grow, making this phase ultimately no different from the fermionic-insulating phase expected at higher fields.
Fig. 6.
Possible (T,H) phase diagrams for the SIT based on the trends of and . (A) A scenario where superconductivity is lost at due to phase fluctuations. A Hall-insulating phase appears near the SIT, but it crosses over to a true insulating phase at high fields. (B) A true Hall-insulating phase exists in the field range . Here we show the possibility of a standard Hall-insulator phase in B, i and a quantized Hall-insulating phase in B, ii.
A different scenario is depicted in Fig. 6B in which the Hall insulator for is taken to be a distinct phase, characterized by a finite zero T value of . In this case we distinguish a “standard” Hall-insulator phase (20) (solid line, labeled “i” in Fig. 6B) and a “quantized Hall-insulator” phase (dashed line, labeled “ii” in Fig. 6B). Because there is always uncertainty in extrapolation , it is still possible that for , in which case this phase could be classified as “quantized” (41, 42) with . For , both and increase (likely diverging) as as expected for a fermion-dominated insulator.
Conclusions
We have shown that when the Hall effect can be measured near the H-SIT, (i) the resistivity tensor at criticality approaches the universal value expected at a point of vortex–particle self-duality, (ii) the critical exponents and z appear to be the same as those observed at both the integer and fractional QHIT, and (iii) the insulating phase proximate to the SIT appears to be a Hall insulator in which and is finite as , approaching with increasing field.
Finally, we observe that our data are consistent with the existence of a second quantum phase transition at . This would give a natural explanation for the sharp change in behavior of and imply that the Hall insulator should be taken to be a distinct quantum phase of matter. However, we cannot rule out the possibility that is the point of a crossover at which unpaired electrons reassert their significance. (Although a dangerously irrelevant operator could account for an additional temperature scale, smaller than the one governing , below which would diverge, it cannot account for the sharp change in the 𝑇 dependence of that is seen at .)
SI Materials and Methods
Films were prepared by electron beam evaporation of sintered InOx onto acid-cleaned silicon–nitride substrates. Control of the amount of disorder (hence, the “strength” of the SIT) is achieved by adding oxygen during growth and then subsequent careful, low-temperature annealing of the samples. An argon ion etch was used to pattern the films into a Hall bar pattern. Throughout the preparation we were careful to keep the temperature below 60 °C to avoid recrystallization of the indium oxide. After evaporating Ti-Au contact pads, the films were annealed in a 10 mtorr vacuum at about 55 °C for 3 wk, during which time the room temperature sheet resistance decreased by about 10%; a higher temperature anneal would have sped up the process but might have changed the microstructure of the film. Further details on the growth process are given in ref. 4.
Although InOx has been known as an amorphous low-carrier-density superconductor ( carriers/cm3) and was used in many studies of SIT, different preparation methods result in different microstructure and hence a different amount of “disorder.” The reason disorder is put here in quotation marks is because of the complexity to quantify it when applied to the SIT. When films are granular, it is obvious that their SIT is dominated by Josephson tunneling among grains and hence by phase fluctuations. However, even if films are inherently homogeneous, small and hardly detectable perturbations in the microstructure may lead to large variations in the local strength of the superconducting order parameter and hence to effective granularity. This effect is strongly magnified in the presence of a magnetic field (relevant to the H-SIT) that destroys weak links and thus enhances granularity. Pertaining to the InOx films used for the present study, we followed the process first described by by Kowal and Ovadyahu (43), who showed that InOx can be made nongranular by using a very low-temperature annealing technique. In their studies of similar films transmission electron micrographs were shown to be completely amorphous, and comparison with electron diffraction patterns from pure indium films ruled out the presence of In crystallites as small as that were observed in films prepared by other methods. Nevertheless, the insulating side of the SIT was found to behave as a granular system.
SI Theoretical
Duality and Self-Duality.
Consider a 2D superconductor connected to a current source. Forcing a current density through the superconductor means that a vortex will feel a Magnus (Lorentz) force
| [S1] |
where with . In the absence of vortices the applied current transforms inside the superconductor into supercurrent of Cooper pairs (with charge 2e) with no dissipation. However, in the presence of vortices the phase changes by each time a vortex crosses any imaginary line in the sample (e.g., the sample edge), resulting in a voltage determined by the Josephson relation
| [S2] |
where is the rate of chance of the phase, depending on the sense of the magnetic field (i.e., the sign of the vorticity), and are, respectively, the vortex density and mean velocity, and L is the size of the sample in the direction of the current. In other words,
| [S3] |
where is the vortex current density. The minus sign in the equation reflects the fact that if the current is in the direction, then according to Eq. S1 the force on the vortex is in the direction. In the same way, dividing Eq. S1 by the charge of a vortex and by the size of the sample in the direction of vortex propagation, we obtain a “vortex electric field”
| [S4] |
Using the relations between current density and electric field
| [S5] |
we arrive at the duality relation
| [S6] |
where with is the Levi–Cevita tensor. In the case of an isotropic medium, this is equivalent to the duality relation given in Eq. 1 of the main text.
It is easy to see that if we invert the vortex resistivity tensor, the Cooper-pair and vortex conductivities are related through
| [S7] |
where is the transpose of the vortex conductivity tensor. Now, the statement of self-duality is that (in our units) the magnitudes of the current density of Cooper pairs and vortices are equal; that is, . Using Eqs. S3–S5, we can verify that self-duality implies
| [S8] |
and therefore
| [S9] |
We note that these relations do not fully determine and independently. However, we can obtain an independent constraint from the following argument. The H-SIT is controlled at zero temperature by the magnetic field that is tuned through the critical point at . Assuming that the conductivity tensor at the critical point is universal, it cannot depend on . This implies that the Hall angle is zero; that is, , and therefore . The consequences of this assertion are therefore that at criticality , , and as stated in the main text.
Limiting Behavior of and .
Starting from the insulating side, because as , it implies that as . Therefore, in that regime,
| [S10] |
where the last equality used the fact that . For a finite we obtain the general relation that on the insulating side . This relation is identical to the condition , found in ref. 20 for the Hall-insulator phase for which the longitudinal resistivity diverges, whereas the Hall resistivity approaches a constant as .
Although the term Hall insulator was first coined for the insulating phase above the QHIT (20), for the present case of SIT it may be more revealing to analyze the superconducting side of the transition. The Cooper-pairs conductivity diverges “” and vortices become pinned, hence contributing a diverging vortex resistivity as . This implies that the vortex Hall conductivity is
| [S11] |
Using the fact that , which we observed to be finite on the superconducting side, we find that the dual condition for the Hall insulator for is . This is equivalent to , a relation that was previously obtained by Vinokur et al. (40) for the quenching of vortex motion in disordered superconductors. On lowering the temperature pinning becomes relevant, and displays thermally activated behavior, causing the measured to decrease exponentially with temperature. In this regime the temperature dependence of the measured is dominated by that of the measured , yielding Eq. S11.
Composite Bosons and SIT.
Composite bosons in the quantum Hall effect are composed of an electron bound to an odd integer, k, of quanta of “statistical” flux, a construction that has a precise meaning in terms of a Cherns–Simon field theory (44). The composite bosons are minimally coupled to an effective gauge field that is the sum of the electromagnetic gauge field, A, and the statistical gauge fields, a, where a is a fluctuating (quantum dynamical) field. However, to the extent that the fluctuations of a about its mean-field (saddle-point) value can be treated as “small,” the response of the composite bosons can be treated in linear response. In this case, the physical conductivity tensor (in units in which ) can be expressed (20) in terms of the composite boson conductivity tensor, , according to the relations
| [S12] |
| [S13] |
The implications of this for the QHIT can be illustrated by evaluating it in important limiting conditions:
The superconducting phase of the composite bosons in which corresponds to the quantum Hall phase with and .
The insulating phase of the composite bosons in which and corresponds to the insulating phase of the electrons in which and .
Assuming the by now familiar universal values for the composite boson conductivity tensor at criticality, and [which was conjectured to hold at the QHIT (20)], one finds and and correspondingly and . Note that this last equality implies that the Hall resistance at criticality is equal to its value in the quantum Hall liquid phase—this is highly suggestive that even in the limit , the Hall resistance remains a continuous function of H across the transition and into the proximate insulating phase, implying that it must be a Hall insulator.
As in the case of the SIT, a more careful analysis of the way in which the vanishes as is necessary to determine the character of the resistivity tensor in the insulating phase proximate to the QHIT. Specifically, exploiting the appropriate particle–vortex duality for the quantum Hall context, it was argued in ref. 20 that , as , in which case but , where .
Although much of this discussion appears in Kivelson et al. (20), a more pedagogic review of these expressions, including generalizations to transitions involving more complex quantum Hall liquid phases, is contained in ref. 45.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge important discussions with Boris Spivak, Yigal Meir, and Dan Shaha; especially important input from Mike Mulligan; and experimental assistance from Alexey Suslov at the NHMFL DC Field facility. Initial work was supported by the NSF. This work was supported by the Department of Energy Grant DE-AC02-76SF00515. A portion of this work was performed at the National High Magnetic Field Laboratory, which is supported by the National Science Foundation Cooperative Agreement DMR-1157490, the State of Florida, and the US Department of Energy.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1522435113/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Hebard AF, Paalanen MA. Magnetic-field-tuned superconductor-insulator transition in two-dimensional films. Phys Rev Lett. 1990;65(7):927–930. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.65.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gantmakher VF, Golubkov MV, Dolgopolov VT, Tsydynzhapov GE, Shashkin AA. Destruction of localized electron pairs above the magnetic-field-driven superconductor-insulator transition in amorphous In-O films. JETP Lett. 1998;68:363–369. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sambandamurthy G, Engel LW, Johansson A, Shahar D. Superconductivity-related insulating behavior. Phys Rev Lett. 2004;92(10):107005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.92.107005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Steiner MA, Kapitulnik A. Superconductivity in the insulating phase above the field-tuned superconductor-insulator transition in disordered indium oxide films. Physica C. 2005;422:16–26. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yazdani A, Kapitulnik A. Superconducting-insulating transition in two-dimensional a-MoGe thin films. Phys Rev Lett. 1995;74(15):3037–3040. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.74.3037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Marković N, Christiansen C, Goldman AM. Thickness–magnetic field phase diagram at the superconductor-insulator transition in 2D. Phys Rev Lett. 1998;81:5217–5220. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bielejec E, Wu W. Field-tuned superconductor-insulator transition with and without current bias. Phys Rev Lett. 2002;88(20):206802–206805. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.88.206802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Baturina TI, et al. Superconductivity on the localization threshold and magnetic-field-tuned superconductor-insulator transition in TiN films. JETP Lett. 2004;79:337–341. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Steiner MA, Breznay NP, Kapitulnik A. Approach to a superconductor to Bose-insulator transition in disordered films. Phys Rev B. 2008;77:212501. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ephron D, Yazdani A, Kapitulnik A, Beasley MR. Observation of quantum dissipation in the vortex state of a highly disordered superconducting thin film. Phys Rev Lett. 1996;76(9):1529–1532. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.76.1529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mason N, Kapitulnik A. Dissipation effects on the superconductor-insulator transition in 2-D superconductors. Phys Rev Lett. 1999;82:5341–5344. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Eley S, Gopalakrishnan SG, Goldbart PM, Mason N. Approaching zero-temperature metallic states in mesoscopic superconductor–normal–superconductor arrays. Nat Phys. 2012;8:59–62. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Liu W, et al. Microwave spectroscopy evidence of superconducting pairing in the magnetic-field-induced metallic state of InO(x) films at zero temperature. Phys Rev Lett. 2013;111(6):067003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.067003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Han Z, et al. Collapse of superconductivity in a hybrid tin-graphene Josephson junction array. Nat Phys. 2014;10:380–386. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Fisher MPA. Quantum phase transitions in disordered two-dimensional superconductors. Phys Rev Lett. 1990;65(7):923–926. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.65.923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee D-H, Fisher MPA. Anyon superconductivity and the fractional quantum Hall effect. Phys Rev Lett. 1989;63(8):903–906. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.63.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wen X-G, Zee A. Universal conductance at superconductor-insulator transition. Int J Mod Phys B. 1990;4:437–445. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Paalanen MA, Hebard AF, Ruel RR. Low-temperature insulating phases of uniformly disordered two-dimensional superconductors. Phys Rev Lett. 1992;69(10):1604–1607. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.69.1604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ovadia M, Kalok D, Sacépé B, Shahar D. Duality symmetry and its breakdown in the vicinity of the superconductor-insulator transition. Nat Phys. 2013;9:415–418. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kivelson S, Lee D-H, Zhang S-C. Global phase diagram in the quantum Hall effect. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1992;46(4):2223–2238. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.46.2223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sachdev S. Quantum Phase Transitions. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ Press; 2011. 2nd Ed. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ovadyahu Z, Moehlecke S, Imry Y. Weak localization in indium oxide films. Surf Sci. 1982;113:544–549. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wong LW, Jiang H-W, Trivedi N, Palm E. Disorder-tuned transition between a quantum Hall liquid and Hall insulator. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1995;51(24):18033–18036. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.51.18033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sondhi SL, Girvin SM, Carini JP, Shahar D. Continuous quantum phase transitions. Rev Mod Phys. 1997;69:315–333. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Dubi Y, Meir Y, Avishai Y. Nature of the superconductor-insulator transition in disordered superconductors. Nature. 2007;449(7164):876–880. doi: 10.1038/nature06180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Johnson CE, Jiang H-W. Observation of a nondivergent Hall coefficient for a localized two-dimensional electron gas. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1993;48(4):2823–2826. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.48.2823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shahar D, et al. On the nature of the Hall insulator. Solid State Commun. 1997;102:817–821. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Baturina TI, Mironov AY, Vinokur VM, Baklanov MR, Strunk C. Localized superconductivity in the quantum-critical region of the disorder-driven superconductor-insulator transition in TiN thin films. Phys Rev Lett. 2007;99(25):257003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.257003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ovadia M, et al. Evidence for a finite-temperature insulator. Sci Rep. 2015;5:13503. doi: 10.1038/srep13503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Fisher MPA, Grinstein G, Girvin SM. Presence of quantum diffusion in two dimensions: Universal resistance at the superconductor-insulator transition. Phys Rev Lett. 1990;64(5):587–590. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.64.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schakel AMJ. Self-duality in superconductor-insulator quantum phase transitions. Phys Rev Lett. 2000;85(18):3934–3937. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.3934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Baturina TI, Strunk C, Baklanov MR, Satta A. Quantum metallicity on the high-field side of the superconductor-insulator transition. Phys Rev Lett. 2007;98(12):127003. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.98.127003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Vinokur VM, et al. Superinsulator and quantum synchronization. Nature. 2008;452(7187):613–615. doi: 10.1038/nature06837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Baturina TI, Vinokur VM. Superinsulator – superconductor duality in two dimensions. Ann Phys. 2013;331:236–257. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kapitulnik A, Mason N, Kivelson SA, Chakravarty S. Effects of dissipation on quantum phase transitions. Phys Rev B. 2001;63:125322. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tewari S, Toner J, Chakravarty S. Floating phase in a dissipative Josephson junction array. Phys Rev B. 2006;72:060505(1)–060505(4). [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tewari S, Toner J, Chakravarty S. Nature and boundary of the floating phase in a dissipative Josephson junction array. Phys Rev B. 2005;73:064503. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhang S-C, Kivelson S, Lee D-H. Zero-temperature Hall coefficient of an insulator. Phys Rev Lett. 1992;69(8):1252–1255. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.69.1252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Entin-Wohlman O, Aronov AG, Levinson Y, Imry Y. Hall resistance in the Hopping regime: A “Hall insulator”? Phys Rev Lett. 1995;75(22):4094–4097. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.4094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vinokur VM, Geshkenbein VB, Feigel’man MV, Blatter G. Scaling of the Hall resistivity in high-Tc superconductors. Phys Rev Lett. 1993;71(8):1242–1245. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.71.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Shimshoni E, Auerbach A. Quantized Hall insulator: Transverse and longitudinal transport. Phys Rev B. 1997;55:9817–9823. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hilke M, et al. Experimental evidence for a two-dimensional quantized Hall insulator. Nature. 1998;395:675–677. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Kowal D, Ovadyahu Z. Disorder induced granularity in an amorphous superconductor. Solid State Commun. 1994;90:783–786. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zhang S-C, Hansson TH, Kivelson S. Effective-field-theory model for the fractional quantum Hall effect. Phys Rev Lett. 1989;62(1):82–85. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.62.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Karlhede A, Kivelson SA, Sondhi SL. Quantum Hall effect: The article. In: Emery VJ, editor. Correlated Electron Systems. World Scientific; Singapore: 1993. [Google Scholar]