Abstract
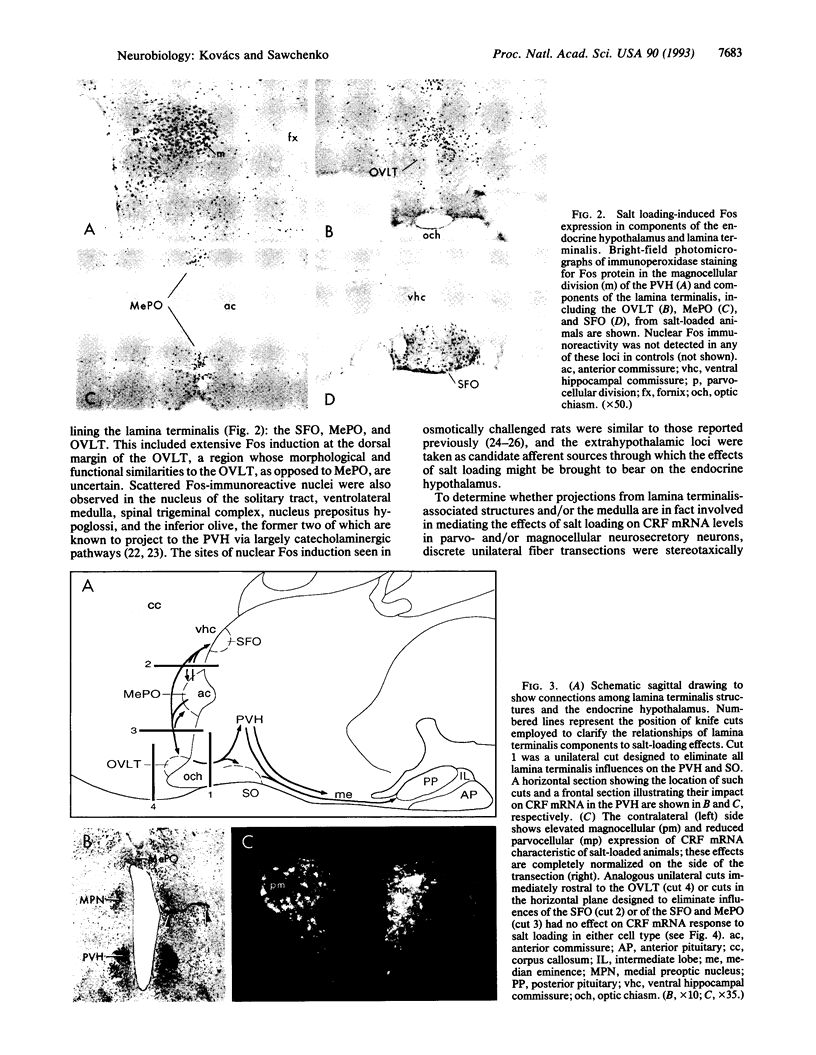
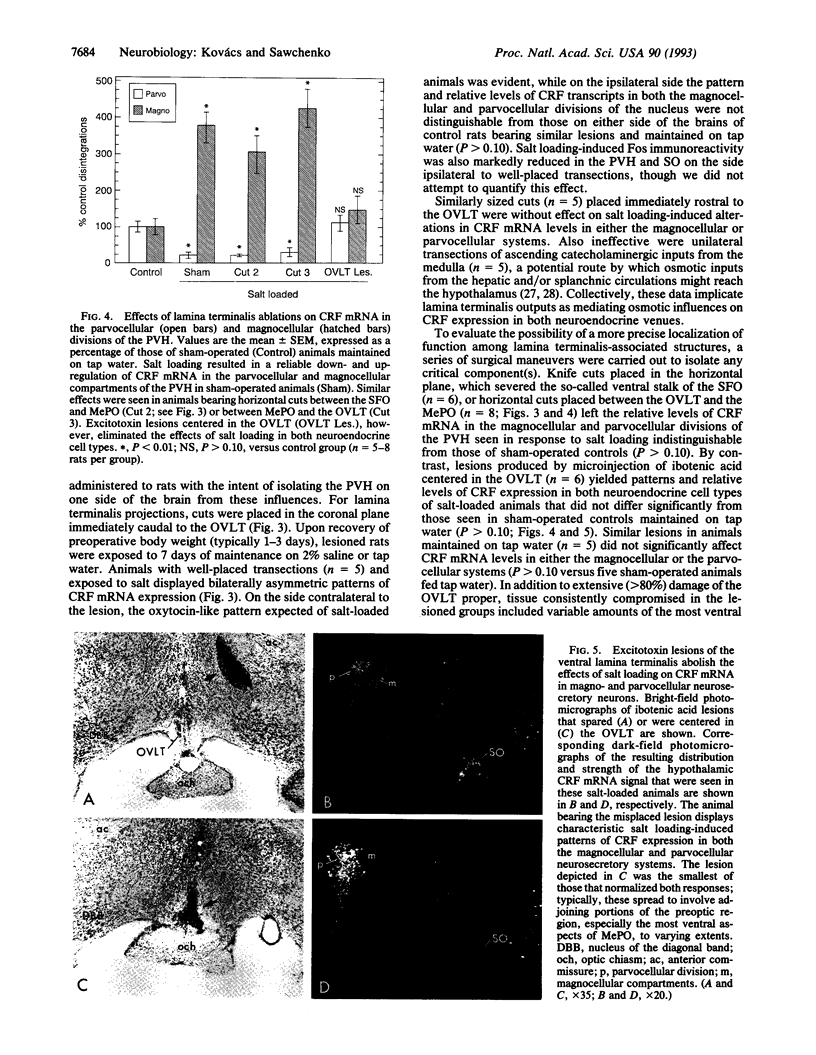
Chronic exposure to a hyperosmolar challenge invokes coordinate, differential, and ostensibly adaptive alterations in the expression of mRNA encoding corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in the endocrine hypothalamus. Rats maintained on 2% (wt/vol) saline for 7 days displayed the expected reduction in CRF mRNA levels in the parvocellular neurosecretory compartment of the paraventricular nucleus, as well as a concomitant increase in CRF transcripts in oxytocin-containing magnocellular neurosecretory neurons. Also detected in salt-loaded animals was a prominent induction of the immediate-early gene product Fos in magnocellular neurosecretory cell groups and in several brain regions that are known to provide major projections to the endocrine hypothalamus. These included a triad of cell groups making up the lamina terminalis of the third ventricle, and, to a lesser extent, catecholaminergic cell groups in the caudal brain stem. Discrete transections of descending projections from structures associated with the lamina terminals, as well as excitotoxin lesions centered in one lamina terminalis-associated structure, the organum vasculosum, abolished the effects of salt loading in both the magno- and parvocellular neurosecretory systems. Knife cuts in the lamina terminalis complex that spared only projections from the organum vasculosum region or cuts that disrupted ascending catecholaminergic projections failed to modify either effect of salt loading. The results suggest the existence of a simple circuit through which osmotic influences on gene expression in the magnocellular and parvocellular neurosecretory systems are effected.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cunningham E. T., Jr, Bohn M. C., Sawchenko P. E. Organization of adrenergic inputs to the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the hypothalamus in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Feb 22;292(4):651–667. doi: 10.1002/cne.902920413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham E. T., Jr, Sawchenko P. E. Anatomical specificity of noradrenergic inputs to the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the rat hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Aug 1;274(1):60–76. doi: 10.1002/cne.902740107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohanics J., Kovacs K. J., Makara G. B. Oxytocinergic neurons in rat hypothalamus. Dexamethasone-reversible increase in their corticotropin-releasing factor-41-like immunoreactivity in response to osmotic stimulation. Neuroendocrinology. 1990 May;51(5):515–522. doi: 10.1159/000125385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannelli L., Shiromani P. J., Jirikowski G. F., Bloom F. E. Oxytocin neurons in the rat hypothalamus exhibit c-fos immunoreactivity upon osmotic stress. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 29;531(1-2):299–303. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90789-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P. M., Weindl A. Peering through the windows of the brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 1987 Dec;7(6):663–672. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.1987.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamamura M., Nunez D. J., Leng G., Emson P. C., Kiyama H. c-fos may code for a common transcription factor within the hypothalamic neural circuits involved in osmoregulation. Brain Res. 1992 Feb 14;572(1-2):42–51. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90448-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman J. P., Schäfer K. H., Sladek C. D., Day R., Young E. A., Akil H., Watson S. J. Chronic electroconvulsive shock treatment elicits up-regulation of CRF and AVP mRNA in select populations of neuroendocrine neurons. Brain Res. 1989 Nov 6;501(2):235–246. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90641-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imaki T., Vale W., Sawchenko P. E. Regulation of corticotropin-releasing factor mRNA in neuroendocrine and autonomic neurons by osmotic stimulation and volume loading. Neuroendocrinology. 1992 Nov;56(5):633–640. doi: 10.1159/000126286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessop D. S., Eckland D. J., Todd K., Lightman S. L. Osmotic regulation of hypothalamo-neurointermediate lobe corticotrophin-releasing factor-41 in the rat. J Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;120(1):119–124. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1200119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lightman S. L., Young W. S., 3rd Vasopressin, oxytocin, dynorphin, enkephalin and corticotrophin-releasing factor mRNA stimulation in the rat. J Physiol. 1987 Dec;394:23–39. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miselis R. R., Shapiro R. E., Hand P. J. Subfornical organ efferents to neural systems for control of body water. Science. 1979 Sep 7;205(4410):1022–1025. doi: 10.1126/science.472723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr E., Fehr S., Richter D. Axonal transport of neuropeptide encoding mRNAs within the hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract of rats. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2419–2424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07781.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. I., Curran T. Stimulus-transcription coupling in the nervous system: involvement of the inducible proto-oncogenes fos and jun. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:421–451. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.14.030191.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield B. J., Bicknell R. J., McAllen R. M., Weisinger R. S., McKinley M. J. Intravenous hypertonic saline induces Fos immunoreactivity in neurons throughout the lamina terminalis. Brain Res. 1991 Oct 4;561(1):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90760-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff H. Glucocorticoid inhibition of neurohypophysial vasopressin secretion. Am J Physiol. 1987 Apr;252(4 Pt 2):R635–R644. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1987.252.4.R635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier C., Rivier J., Vale W. Inhibition of adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion in the rat by immunoneutralization of corticotropin-releasing factor. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):377–379. doi: 10.1126/science.6289439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawchenko P. E., Swanson L. W. The organization of forebrain afferents to the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1983 Aug 1;218(2):121–144. doi: 10.1002/cne.902180202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawchenko P. E., Swanson L. W., Vale W. W. Corticotropin-releasing factor: co-expression within distinct subsets of oxytocin-, vasopressin-, and neurotensin-immunoreactive neurons in the hypothalamus of the male rat. J Neurosci. 1984 Apr;4(4):1118–1129. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-04-01118.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman T. G., Civelli O., Douglass J., Herbert E., Watson S. J. Coordinate expression of hypothalamic pro-dynorphin and pro-vasopressin mRNAs with osmotic stimulation. Neuroendocrinology. 1986;44(2):222–228. doi: 10.1159/000124649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson L. W., Sawchenko P. E., Rivier J., Vale W. W. Organization of ovine corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactive cells and fibers in the rat brain: an immunohistochemical study. Neuroendocrinology. 1983;36(3):165–186. doi: 10.1159/000123454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Tol H. H., Voorhuis D. T., Burbach J. P. Oxytocin gene expression in discrete hypothalamic magnocellular cell groups is stimulated by prolonged salt loading. Endocrinology. 1987 Jan;120(1):71–76. doi: 10.1210/endo-120-1-71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]