SUMMARY
Fibro-osseous benign lesions rarely affect the sinonasal tract and are divided into 3 different entities, namely osteoma, fibrous dysplasia and ossifying fibroma. They share several clinical, radiological and histological similarities, but have different behaviours. Ossifying fibroma, and in particular the "juvenile" histological subtype, may have a locally aggressive evolution and a high risk for recurrence if removal is incomplete. The purpose of the present study is to compare the clinical behaviour of ossifying fibroma with the other benign fibro-osseous lesions; highlight different behaviour between the histological subtypes; compare the advantages, limitations and outcomes of an endoscopic endonasal approach with reports in the literature. We retrospectively reviewed 11 patients treated for sinonasal ossifying fibroma at a tertiary care centre. All patients underwent CT scan, and MRI was performed in cases of cranial base involvement or recurrence. Pre-operative biopsy was performed in cases where it was possible to use an endoscopic approach. One patient underwent pre-operative embolisation with ipsilateral visual loss after the procedure. Depending on its location, removal of the tumour was performed using an endoscopic (n = 7), or an external (n = 3) or combined (n = 1) approach. Histopathologically, 5 patients presented the conventional type, 5 the juvenile psammomatoid variant, which was associated in 1 case with an aneurismal bone cyst, and 1 case presented the trabecular juvenile variant. Three patients affected by the juvenile psammomatoid histological variant presented invasion of the skull base and underwent a subtotal removal that subsequently required, due to the regrowth of the remnant, a transbasal approach. Clinical, radiological and histological findings should all be considered to establish differential diagnosis among fibrous osseous lesions. More studies are necessary to conclude if the localisation and extension of the disease at the time of diagnosis is more important than the histological variant. An endoscopic approach is the first choice in most of cases even if an external open approach may be necessary in selected patients.
KEY WORDS: Ossifying fibroma, Endoscopic surgery, Fibrous dysplasia, Osteoma, Skull base
RIASSUNTO
Le lesioni fibro-ossee benigne raramente colpiscono i seni paranasali e sono suddivise in 3 entità: osteoma, displasia fibrosa e fibroma ossificante. Questi presentano simili caratteristiche cliniche, radiologiche e istologiche ma hanno un comportamento diverso. Il fibroma ossificante, in particolare la variante istologica giovanile, può presentare un comportamento aggressivo con un alto rischio di recidiva se rimosso in modo incompleto. Lo scopo dello studio è quello di paragonare il comportamento clinico del fibroma ossificante con quello delle altre lesioni fibro-ossee; di evidenziare un eventuale comportamento differente tra i vari sottotipi istologici; di descrivere i vantaggi, i limiti e i risultati della chirurgia endoscopica endonasale rispetto ai dati presenti in letteratura. Abbiamo analizzato retrospettivamente 11 pazienti affetti da fibroma ossificante naso-sinusale e trattati in un centro ospedaliero di terzo livello. Tutti i pazienti sono stati sottoposti a TC. La RM è stata eseguita in caso di coinvolgimento del basicranio o in caso di recidiva. Una biopsia pre-operatoria è stata effettuata nei casi in cui la massa era raggiungibile per via endoscopica. Un paziente è stato sottoposto a embolizzazione pre-operatoria ed ha riportato una cecità monolaterale al termine della procedure. In base alla localizzazione, l'exeresi del tumore è stata eseguita con un approccio endoscopico (7 pazienti), esterno (3), combinato (1). Istologicamente 5 pazienti hanno riportato un sottotipo convenzionale, 5 la variante giovanile psammomatoide associata in un caso a cisti aneurismatica ossea, e un paziente la variante giovanile trabecolare. Tre pazienti affetti dalla variante istologica giovanile psammomatoide hanno presentato un'invasione del basicranio e sono stati sottoposti ad exeresi subtotale per via endoscopica che ha richiesto in seguito, a causa di un aumento di volume del residuo, un secondo intervento per via transbasale. I reperti clinici, radiologici e istologici dovrebbero essere considerati insieme per una accurata diagnosi differenziale tra le lesioni fibro-ossee. Ulteriori studi sono necessari per concludere se la localizzazione e l'estensione del fibroma ossificante al momento della diagnosi sono più importanti della variante istologica. L'approccio endoscopico è la prima opzione nella maggior parte dei casi anche se in alcuni selezionati pazienti l'approccio esterno risulta ancora necessario.
Introduction
Fibro-osseous lesions are benign tumours characterised by the replacement of normal bone by a fibrous cellular stroma containing various amounts of foci of mineralisation or ossification 1. These lesions rarely affect the sinonasal tract 2. They are usually divided into 3 different entities, namely osteoma, fibrous dysplasia (FD) and ossifying fibroma (OF) 3. Osteoma is the most frequent subtype, followed by FD and OF 4. The precise incidence of OF, however, remains unknown. These three entities share several clinical, radiological and histological similarities, but have different behaviours in the sinonasal tract 5 6. Osteoma is a slow-growing tumour, and FD usually stops growing spontaneously after puberty. In the absence of local complications, surgical intervention is not needed, and a "wait and see" attitude can be advocated 7-9. In contrast, OF, and in particular the "juvenile" histological subtype, may have a locally aggressive evolution and a high risk for recurrence if removal is incomplete 10 11. A proper initial diagnosis of the tumour is therefore mandatory to plan appropriate therapeutic management 3 5 12.
The aim of the present study is to describe the main characteristics that can help clinicians to differentiate OF from other fibro-osseous tumours; highlight different behaviour between histological subtypes; discuss the surgical management of OF, with special regard to the advantages and limitations of an endoscopic endonasal approach.
Materials and methods
Between 2006 and 2012, 11 patients were referred to our tertiary care centre for an OF of the sinonasal tract. Patient charts were retrospectively reviewed for demographics, clinical presentation, tumour extent based on nasal endoscopy and preoperative imaging, surgical approach and follow-up. This study was approved by the institutional review board of Lariboisière Hospital.
All cases were discussed at the head and neck meeting of the centre with a dedicated radiologist and pathologist, and all patients were operated on by the same surgeon. All patients were assessed preoperatively using CT scan with contrast medium administration. MRI was performed systematically in case of skull base/orbital involvement or recurrence.
Preoperative biopsy was performed in any case where the lesion was reachable through an endoscopic procedure. Follow- up was performed with endoscopic control after 3 and 6 months and then once a year. In case of subtotal removal, a CT scan eventually followed by MRI, was performed after 3 and 6 months to assess the size of the tumour remnant.
Results
From 2006 to 2012, 11 patients were surgically treated at our institution for an OF of the sinonasal tract. Demographic data, symptoms, tumour extension, surgical approach, surgical procedure and follow-up are summarised in Table I. The male to female ratio was 1.2:1, with a mean age at time of diagnosis of 34 years (range 12-61 years). The most frequent symptom at presentation was nasal obstruction, which was reported by 4 patients, associated in 2 cases with proptosis and in 1 case with facial pain. Other symptoms at presentation included isolated facial pain (n = 1), headache (n = 1) and facial deformation (n = 1). Of note, OF was an incidental finding in 3 asymptomatic patients. One patient had undergone previous surgical intervention at another institution, with preoperative embolisation followed by partial removal of the tumour through a lateral rhinotomy approach. He was referred for management of tumour recurrence.
Table I.
Paranasal ossifying fibromas: presenting signs, radiological findings, management and outcomes.
| Patient | Sex (M/F) |
Symptoms | Age at time of first surgery |
Tumour extension | Tumour dimension (mm) (Ax × Sag × Cor) |
Radiological diagnosis |
Surgical approach |
Surgical procedure | Pathological findings |
Follow-up (months) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | M | Headache | 32 | Ant. Ethmoid.; Post. Ethmoid. |
9 × 10 × 10 | OF | Endonasal | Ant. Ethmoidectomy; Post. Ethmoidectomy Sphenoidotomy |
Juvenile psammomatoid type |
48 |
| #2 | M | Asymptomatic | 35 | Frontal | 13 × 12 × 9 | OF | External approach to frontal sinus through Caim incision |
Frontal osteoplasty | Conventional type |
72 |
| #3 | M | Nasal obstruction + facial pain |
61 | Maxillar | 15 × 13 × 16 | OF | Endonasal + Caldwell-Luc |
Ant. Ethmoidectomy; Maxillectomy |
Conventional type |
60 |
| #4 | F | Facial deformity | 41 | Frontal | 21 × 21 × 15 | OF | External approach to frontal sinus through Caim incision |
Frontal osteoplasty | Conventional type |
20 |
| #5 | F | Follow-up after operation through lateral rhinotomy approach in another hospital |
13 | Ant. Ethmoid.; Post. Ethmoid.; Maxillar, Medial wall of orbit |
38 × 16 × 18 | OF | Endonasal | Ant. Ethmoidectomy; Post. Ethmoidectomy; medial Maxillectomy |
Juvenile trabecolar type |
12 |
| #6 | F | Asymptomatic | 46 | Post. Ethmoid.; Sphenoid, Middle cranial base; medial portion of optic nerve |
33 × 24 × 28 | OF or FD | Endonasal | Ant. Ethmoidectomy; Post. Ethmoidectomy; Sphenoidotomy; middle cranial base |
Juvenile psammomatoid type |
12 |
| #7 | F | Facial pain | 29 | Maxillar | 51 × 49 × 46 | OF | Degloving | Maxillectomy | Conventonal type | 50 |
| #8 | M | Asymptomatic | 53 | Maxillar | 25 × 21 × 18 | OF | Endonasal | Ant. Ethmoidectomy; Medial Maxillectomy |
Conventional type |
12 |
| #9 | M | Nasal obstruction + proptosis |
27 | Ant. Ethmoid.; Post. Ethmoid.; Medial wall of orbit; Sphenoid; Middle cranial base; Encasin optic nerve |
65 × 50 × 49 | ABC | Endonasal | Ant. Ethmoidectomy, Post. Ethmoidectomy; Medial Maxillectomy; Sphenoidotomy; Middle cranial base |
Juvenile psammomatoid type associated with aneurysmal bone cyst |
Recurrence after 6 months |
| #10 | F | Nasal obstruction + proptosis |
12 | Post. Ethmoid.; Sphenoid.; Middle cranial base; Encasing optic nerve |
43 × 24 × 44 | FD | Endonasal | Ant. Ethmoidectomy; Post. Ethmoidectomy; Sphenoidotomy; Middle cranial base |
Juvenile psammomatoid type |
Recurrence after 6 months |
| #11 | M | Nasal obstruction | 20 | Post. Ethmoid.; Sphenoid.; Middle cranial base; Encasing optic nerve |
72 × 58 × 60 | OF | Endonasal | Ant. Ethmoidectomy; Post. Ethmoidectomy; Sphenoidotomy; Middle cranial base |
Juvenile psammomatoid type |
Recurrence after 6 months |
Abbreviations: M: Male; F: Female; mm: millimetres; ax: axial; sag: sagittal; cor: coronal.
CT scan was performed pre-operatively in all patients (Fig. 1, case #11) and MRI only in the 5 patients with skull base or orbital involvement. Radiological findings were suggestive of OF in 8 cases (Fig. 2, case #8). In the 3 remaining patients, differential diagnoses were discussed, as the radiological aspect was more indicative of FD (2 cases) or primary aneurismal bone cyst (ABC) (Fig. 3, case #9). The mean maximum diameter was 35 mm (range 9-72 mm). OF was limited to the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses in 6 cases (54%). The cranial base and/ or the lamina papyracea were invaded in 5 cases (46%). Pre-operative biopsy was endoscopically performed in 9 cases, while 2 patients underwent surgery without biopsy because of the location of OF in the frontal sinus.
Fig. 1.
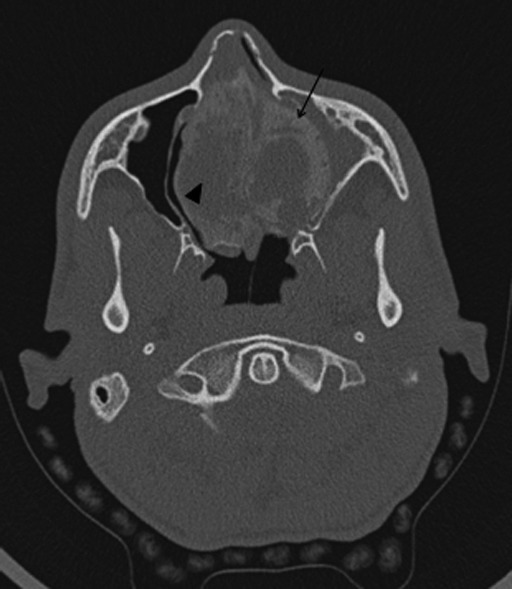
Axial CT: OF appears as a lesion with well-defined margins showing a hypodense signal corresponding to fibrous tissue (arrowhead) with intralesional foci of hyperdensity corresponding to areas of mineralisation (arrow).
Fig. 2.
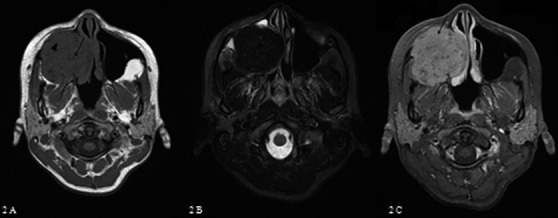
Axial MRI: on T1-weighted sequences (A) OF appears as a lesion with intermediate signal intensity, fibrous tissue (arrowhead) with small areas of hypointensity osseus areas (arrow). On T2-weighted sequences (B), ossified areas appear with low signal (arrow), while fibrous tissue exhibits an isointense signal (arrowhead). Contrast enhancement (C) is heterogeneous and is related to fibrous areas (arrow).
Fig. 3.
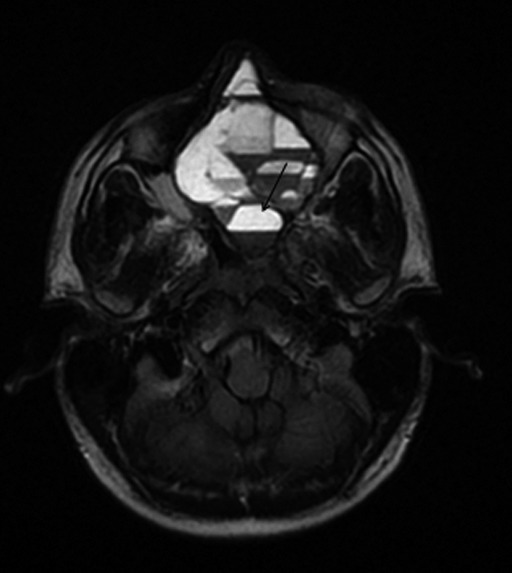
On T2-weighted sequences, a multicystic lesion with "fluid-fluid" levels (arrow) suggestive for ABC is present within OF .
One patient underwent pre-operative embolisation. He was referred to our institution for a cystic mass of the sphenoid bone evocative of ABC. A pre-operative biopsy was performed and resulted in massive bleeding: pre-operative embolisation was therefore advocated for this patient. Selective angiography revealed a major feeder from the left middle meningeal artery that was embolised with microspheres (100-300 microns). Immediately after the procedure, the patient presented complete left visual loss. Fundoscopy exam revealed a pale papilla, while fluorescein angiography showed papillar hypoperfusion in each phase of the examination and late choroidal and retinal circulation. Atrophic bands on the periphery without areas of ischaemia were also present. These findings were consistent with central retinal occlusion.
Surgical removal of the tumour was performed through a purely endoscopic approach in 7 cases (64%) (Fig. 4, case #10), through a combined approach in 1 case (endoscopic/ Caldwell-Luc) and through a midfacial degloving or a coronal approach in 1 and 2 cases, respectively. When the tumour developed on the lamina papyracea (case #5), aberrant tumour vessels feeding the neoplasm across the periorbit were observed during surgery.
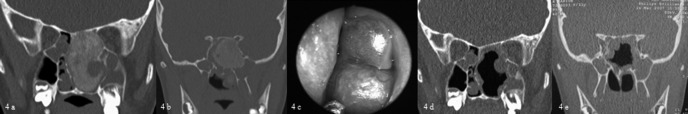
Fig. 4.
(A) Pre-operative coronal CT scan showing the tumour at the level of the left ethmoid sinus and (B) at the level of the sphenoid. (C) Endoscopic view of the OF appearing as a submucosal mass. (D) Post-operative coronal CT scan at the level of the ethmoid sinus and sphenoid sinus.
Intra-operative complications occurred in 2 cases, consisting in CSF-leak after endoscopic drilling of the cribriform plate or dissection of the sheath of the optic nerve. Preoperative intratechal fluorescein was not used in any case. However, the CSF-leak was immediately evident and treated successfully at the end of the surgical procedure in both cases with application of Tachosil®. Lumbar drains were never used.
Histopathological examination confirmed a diagnosis of OF in all cases. Five patients presented the conventional type and 1 case presented the trabecular juvenile variant, while 5 patients presented the juvenile psammomatoid variant which was associated in 1 case with an ABC.
In 3 of the 7 patients first operated through an endoscopic approach, removal was incomplete since the tumour extended at the skull base beyond the optic nerve. Postoperative follow-up evidenced a rapid growth of the remnant (about 1 mm per month) (Fig. 5). A transbasal approach was performed and allowed complete removal. All these 3 patients presented a juvenile psammomatoid histological variant.
Fig. 5.
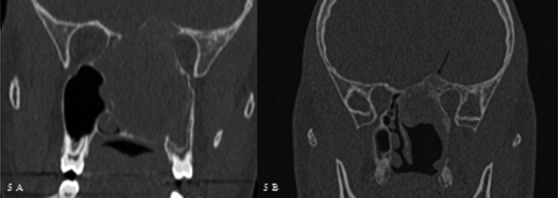
(A) Pre-operative coronal CT of case #10 who underwent a subtotal removal of the lesion with an endoscopic approach. (B) Coronal CT scan performed 6 months after surgery showing rapid regrowth of the remnant (arrow). An external approach was subsequently performed.
To date, all patients are free of disease after a mean follow- up of 27 months (range 6-72 months). Long term complications included 1 case of stenosis of the lacrimal duct after endoscopic medial maxillectomy, successfully treated by endoscopic dacryocystorhinostomy, and 1 case of multiple mucoceles of the maxillary sinus after a midfacial degloving procedure, which was treated by endoscopic marsupialisation.
Discussion
In this report, we have added our experience to the limited amount of data available in the literature reviewing 11 clinical cases of OF operated on at a tertiary centre.
In our series, there were no specific symptoms of OF: as for other benign fibrous osseous lesions, it can be incidentally discovered when imaging is performed for another indication, or may become symptomatic in relation to a mass effect of the tumour on adjacent structures. When the lesion protrudes in the nasal fossa, it can be visualised on endoscopy as a submucosal smooth rounded mass 13 (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6.
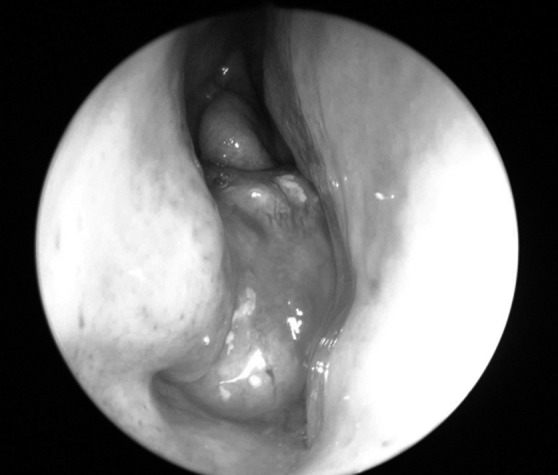
Endoscopic view of OF at the level of the right nasal fossa presenting with its typical aspect: a submucosal smooth rounded mass.
The imaging work-up relies mainly on CT scan, but in selected cases MRI should also be performed. Radiological findings can be very suggestive of OF, but, as shown in the present report, differential diagnosis with other bony lesions can be difficult. CT has distinct advantages over MRI, as it allows better bony assessment. OF presents like a tumour, with contour deformity and loss of anatomical shape, while FD consists mainly in bone hypertrophy which keeps the global shape of the bone intact 14. In contrast to FD, OF does not exhibit a ground glass appearance, but rather a mixture of bone density and soft tissues with thick bony walls. The sharply defined outside margins of OF are the most important radiological sign for differential diagnosis with FD and malignant tumours such as sarcoma or chondrosarcoma, which present with ill-defined margins 15. Contrast CT scan may show subtle enhancement corresponding to the soft tissues of OF, while osteomas are not enhanced. In our case series, CT scan was useful in pre-surgical planning to assess the precise extension of the tumour. However, while delineation of OF with soft tissues seemed sharp, dissection revealed adherence of the tumour to soft tissues, i.e. periorbit and dura mater, in contrast to osteomas.
At MRI, OF usually harbour low to intermediate signal intensity on T1 weighted imaging: the signal in fibrous areas is intermediate, while that in osseous areas is hypointense. Contrast enhancement is heterogeneous and may be related to fibrous areas 16. On T2, ossified areas appear with low signal, while fibrous tissue exhibits a hypointense signal. Fluid-fluid levels have been reported, but as shown herein they seem to be associated with a secondary ABC 17. While MRI, combined with CT scan, helps to make a correct diagnosis, it also allows assessment of at risk structures in the case of intracranial or intraorbital extension, and at last during follow-up to discriminate scar tissue from mucocele as in the case of the patient treated with midfacial degloving.
In consideration of the overlapping radiological and clinical features among fibro-osseous lesions, even if the imaging may be evocative for OF, we suggest pre-operative biopsy when the lesion is endoscopically accessed. In our opinion, is important to exclude malignant tumours such as sarcomas that radiologically may present with a range of findings such as intact margins, bone sclerosis, bone erosion and gross bone destruction, as well as varying degrees of internal calcified or ossified matrix that may complicate differential diagnosis 18. Preoperative biopsy may also help to differentiate other benign fibro-osseous lesions, in particular FD which may require alternative management. In our series, before biopsy three cases were presumed to be affected by FD and ABC rather than OF. However, we did not perform a preoperative biopsy in 2 patients because of the frontal sinus localisation of the tumour.
Histological classification of OF is somewhat confusing: multiple, sometimes overlapping terms are used, including ossifying fibroma, cementifying fibroma, cemento-ossifying fibroma, desmo-osteoblastoma, psammo-osteoid fibroma, psammomatoid ossifying fibroma, juvenile ossifying fibroma, juvenile aggressive ossifying fibroma, or juvenile active ossifying fibroma 5. These terms partially refer to a more or less well-defined subtypes of OF but some might also be used synonymously. Herein, we used the most recent guidelines of WHO 19 for odontogenic tumours: conventional type OF (COF) includes a juvenile histological variant that is further subdivided in trabecular (TJOF) and psammomatoid (PJOF) types.
COF is composed of both fibrous and mineralised tissue, and exhibits a sharp delimitation from surrounding healthy tissue, in contrast to FD, and the pattern of mineralisation varies from area to area, while it is homogeneous in FD. The trabecular juvenile variant is composed of densely cellular fibrous tissue with little collagen, containing thin strand-like trabeculae of osteoid and woven bone. The psammomatoid juvenile variant is also densely cellular, but the calcifications are spherical or lamellated like typical psammomatoid bodies 19. Manens et al. 13 in their review on 137 cases reported a similar clinical behaviour between the subtypes of OF, while Wang et al. 20 in their case series on 31 patients reported a higher rate of recurrence in the juvenile type. In our series, the 5 patients presenting with extensive disease at the time of diagnosis, including massive involvement of the paranasal sinus and skull base or medial orbital wall, invasion and destruction of surrounding tissue and bony erosion had the juvenile variant. Three of these patients presented extensive sphenoid involvement with an extension beyond the optic nerve and, even if an external approach would have lead to a more radical surgery, in consideration of the benign nature of the pathology, we decided to primarily perform an endoscopic approach with a subtotal resection at the level of the clinoid. A wait and see policy was then adopted that showed rapid regrowth requiring a subsequent subfrontal approach. Thus, from our case series, we had the impression that the juvenile type presented a more aggressive behaviour. To avoid recurrence, when preoperative biopsy highlights the juvenile type, we suggest total removal of the lesion.
However, due to the small series and the limited data in the literature, it is not possible to conclude if a higher percentage of recurrences is related to active behaviour due to an unknown intrinsic biologic factor associated with the juvenile variant, or to features unrelated to the histological subtypes such as the extension into adjacent structures (orbit, optic canal, cranial fossa) at the time of diagnosis and the incomplete surgical resection performed to avoid the risk of iatrogenic lesions and excessive bone resection causing facial deformity. Thus, larger case series on this topic are needed.
Surgical removal of OF is difficult compared with osteoma: total resection is mandatory to avoid recurrences, but OF are characterised by high vascularisation and frequent adherence to the dura and periorbit 4 5 12. Thus, complete removal of this benign lesion has always been challenging. As reported by Wang et al. 20, to avoid recurrences, we found necessary to remove the outer lamella of the tumour and drill out pathological bone with a diamond burr until reaching smooth healthy bone that presents a less friable consistence. Traditionally, extranasal or microscopical techniques have been described to achieve complete resection. However, recent studies have reported on the endoscopic removal of OF 6 10, with improved endoscopes and instruments, increased surgical experience, refinements of techniques (e.g. "four-hand-technique") and the routine use of navigation systems.
In our series, four cases were not addressed through a purely endoscopic approach. One was operated on in 2006 using a Caldwell-Luc approach that would nowadays be amenable to an endoscopic approach. The other three cases illustrate the limitations and contraindications of an endoscopic approach: tumour extension to the anterior wall of the frontal sinus and supraorbital recess 21 22, extension beyond the optic nerve and extension to the anterior wall of maxillary sinus, which should be addressed using a Cairn approach or midfacial degloving or Caldwell-Luc approaches, respectively.
In the last 20 years, pre-operative embolisation of feeding vessels has been increasingly used preoperatively for vascular head and neck tumours, such as paragangliomas and JNAs 23. The most important risk when embolising the orbital region is the occlusion of the central retinal artery, which is a terminal vessel and results in blindness of the patient. Anastomotic connections between the ophthalmic artery and the external carotid artery are vestiges of embryonic configurations that may occasionally persist into adulthood as anatomic variants. In particular, the middle meningeal artery, which was embolised in the patient treated in our institute and affected by ABC secondary to OF, may present a small anastomosis, the recurrent meningeal artery, with the lacrimal branch of the ophthalmic artery 24 that may explain the sudden post-operative ipsilateral visual loss that occurred in our patient.
Complications of endovascular treatment are rare and well-known and may be due to reflux of embolic agent or migration through undetected external/internal carotid artery collaterals. While such complications are supposedly rare, the present work highlights that OFs with or without associated ABC are highly vascularised, and in close connection with the ophthalmic arterial network. Therefore, based on this experience, and with the availability of new haemostatic agents, we would not recommend preoperative embolisation for these tumours.
Conclusions
OF of the sinonasal tract is a rare benign fibro-osseous tumour. Clinical, radiological and histological findings should all be considered to better establish a differential diagnosis with other fibro-osseous tumours, either benign or malignant, and a pre-operative biopsy should always be performed when possible.
In the present case series, patients affected by the histological juvenile variant presented extensive localisation and rapid regrowth when subtotally removed. However, due to the small number of cases in the literature and in the present series, no conclusions can be drawn if the biological behaviour of the different histological subtypes of OF is more important than the extension of the tumour at the time of diagnosis, and larger cases series may be necessary to clarify this point.
Complete surgical removal is the only curative treatment for OF, and should be performed through an endoscopic approach as a first choice option. An external approach is still needed in cases of OF affecting the anterior wall of the frontal sinus or supraorbital recess, encasing the optic nerve or invading the skull base laterally to the optic nerve. In these tumours, even if highly vascularised, when proximal to the orbit embolisation should be avoided due to the close connection with the ophthalmic arterial network.
References
- 1.Speight PM, Carlos R. Maxillofacial fibro-osseous lesions. Curr Diagn Pathol. 2006;12:1–10. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Commins DJ, Tolley NS, Milford CA. Fibrous dysplasia and ossifying fibroma of the paranasal sinuses. J Laryngol Otol. 1998;112:964–968. doi: 10.1017/s0022215100142203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Eller R, Sillers M. Common fibro-osseous lesions of the paranasal sinuses. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2006;39:585–600. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2006.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lund VJ, Stammberger H, Nicolai P, et al. European position paper on endoscopic management of tumours of the nose, paranasal sinuses and skull base. Rhinol Suppl. 2010;22:1–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ledderose GJ, Stelter K, Becker S, et al. Paranasal ossifying fibroma: endoscopic resection or wait and scan? Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;268:999–1004. doi: 10.1007/s00405-011-1503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Post G, Kountakis SE. Endoscopic resection of large sinonasal ossifying fibroma. Am J Otolaryngol. 2005;26:54–56. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2004.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Turri-Zanoni M, Dallan I, Terranova P, et al. Frontoethmoidal and intraorbital osteomas: exploring the limits of the endoscopic approach. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012;138:498–504. doi: 10.1001/archoto.2012.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pons Y, Blancal JP, Vérillaud B, et al. Ethmoid sinus osteoma: diagnosis and management. Head Neck. 2013;35:201–204. doi: 10.1002/hed.22945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pagella F, Pusateri A, Matti E, et al. Transnasal endoscopic approach to symptomatic sinonasal osteomas. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2012;26:335–339. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2012.26.3782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Choi YC, Jeon EJ, Park YS. Ossifying fibroma arising in the right ethmoid sinus and nasal cavity. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2000;54:159–162. doi: 10.1016/s0165-5876(00)00349-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pirana S, Zerati F, Voegels R, et al. Psammomatoid ossifying fibroma. Rhinology. 2003;41:250–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.London SD, Schlosser RJ, Gross CW. Endoscopic management of benign sinonasal tumors: a decade of experience. Am J Rhinol. 2002;16:221–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Manes RP, Ryan MW, Batra PS, et al. Ossifying fibroma of the nose and paranasal sinuses. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013;3:161–168. doi: 10.1002/alr.21067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Engelbrecht V, Preis S, Hassler W, et al. CT and MRI of congenital sinonasal ossifying fibroma. Neuroradiology. 1999;41:526–529. doi: 10.1007/s002340050798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sontakke SA, Karjodkar FR, Umarji HR. Computed tomographic features of fibrous dysplasia of maxillofacial region. Imaging Sci Dent. 2011;41:23–28. doi: 10.5624/isd.2011.41.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kendi AT, Kara S, Altinok D, et al. Sinonasal ossifying fibroma with fluid-fluid levels on MR images. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003;24:1639–1641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Yang BT, Wang YZ, Wang XY, et al. Imaging study of ossifying fibroma with associated aneurysmal bone cyst in the paranasal sinus. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:3450–3455. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2012.05.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Efune G, Perez CL, Tong L, et al. Paranasal sinus and skull base fibro-osseous lesions: when is biopsy indicated for diagnosis? Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2012;2:160–165. doi: 10.1002/alr.20109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Slootweg PJ, El Mofty SK. Ossifying fibroma. In: Barnes L, Eveson JW, Reichart P, Sidransky D, editors. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and genetics of head and neck tumours. Lyon: IARC; 2005. pp. 319–320. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wang H, Sun X, Liu Q, et al. Endoscopic resection of sinonasal ossifying fibroma: 31 cases report at an institution. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2014;271:2975–2982. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-2972-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Castelnuovo P, Valentini V, Giovannetti F, et al. Osteomas of the maxillofacial district: endoscopic surgery versus open surgery. J Craniofac Surg. 2008;19:1446–1455. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e31818b417d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Savastano M, Guarda-Nardini L, Marioni G, et al. The bicoronal approach for the treatment of a large frontal sinus osteoma. A technical note. Am J Otolaryngol. 2007;28:427–429. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2006.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Smith TP. Embolization in the external carotid artery. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17:1897–1913. doi: 10.1097/01.RVI.0000247301.64269.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hufendiek K, Hufendiek K, Finkenzeller T, et al. Acute visual loss after preoperative embolization of an ethmoidal metastasis. Int Ophthalmol. 2012;32:165–169. doi: 10.1007/s10792-012-9525-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]