Abstract
Kidney disease is a well-known health disparity in the United States where African Americans are affected at higher rates compared with other groups such as European Americans and Mexican Americans. Common genetic variants in the myosin, heavy chain 9, non-muscle (MYH9) gene were initially identified as associated with non-diabetic end-stage renal disease in African Americans, and it is now understood that these variants are in strong linkage disequilibrium with likely causal variants in neighboring APOL1. Subsequent genome-wide and candidate gene studies have suggested that MYH9 common variants among others are also associated with chronic kidney disease and quantitative measures of kidney function in various populations. In a precision medicine setting, it is important to consider genetic effects or genetic associations that differ across racial/ethnic groups in delivering data relevant to disease risk or individual-level patient assessment. Kidney disease and quantitative trait-associated genetic variants have yet to be systematically characterized in multiple racial/ethnic groups. Therefore, to further characterize the prevalence of these genetic variants and their association with kidney related traits, we have genotyped 10 kidney disease or quantitative trait-associated single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (rs2900976, rs10505955, rs10502868, rs1243400, rs9305354, rs12917707, rs17319721, rs2467853, rs2032487, and rs4821480) in 14,998 participants from the population-based cross-sectional National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) III and 1999-2002 as part of the Epidemiologic Architecture for Genes Linked to Environment (EAGLE) study. In this general adult population ascertained regardless of health status (6,293 non-Hispanic whites, 3,013 non-Hispanic blacks, and 3,542 Mexican Americans), we observed higher rates of chronic kidney disease among non-Hispanic blacks compared with the other groups as expected. We performed single SNP tests of association using linear regressions assuming an additive genetic model adjusted for age, sex, diastolic blood pressure, systolic blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes status for several outcomes including creatinine (urinary), creatinine (serum), albumin (urinary), eGFR, and albumin-to-urinary creatinine ratio (ACR). We also tested for associations between each SNP and chronic kidney disease and albuminuria using logistic regression. Surprisingly, none of the MYH9 variants tested was associated with kidney diseases or traits in non-Hispanic blacks (p>0.05), perhaps attributable to the clinical heterogeneity of kidney disease in this population. Several associations were observed in each racial/ethnic group at p<0.05, but none were consistently associated in the same direction in all three groups. The lack of significant and consistent associations is most likely due to power highlighting the importance of the availability of large, diverse populations for genetic association studies of complex diseases and traits to inform precision medicine efforts in diverse patient populations.
1. Introduction
The kidney is an essential organ that excretes metabolic waste from blood to maintain fluid homeostasis, osmoregulation, blood pressure, and electrolyte balance – key processes for survival [1]. The health risks and financial burden of poor kidney health are well-documented (e.g. [2]). Also well-documented are the higher prevalence and incidence of kidney disease among African Americans compared with other racial/ethnic groups in the United States [3,4]. This is a tremendous health disparity that exists even after accounting for socioeconomic status, as evidenced by reports that have evaluated varying degrees of kidney disease and have detected significant risk in African Americans compared to European Americans even when distinct methods are implemented and when income is taken into account [5,6]. Recent admixture studies in African-descent populations with focal segmental glomerulosclerosis [7], nondiabetic end-stage disease (ESRD) [8], and other kidney disease have established a genetic basis that partially explains the observed racial/ethnic differences in the development and progression of these diseases [9].
Kidney disease is often symptom-free until it has significantly diminished the ability of the organ to function, and it is therefore crucial to identify genetic variants associated with biological indicators of kidney health. Kidney disease can be detected with biomarkers obtained through standardized blood tests that estimate renal function and by monitoring excretion of protein in the urine. Chronic kidney disease (CKD), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), albumin, and creatinine are clinical measures used to identify potential kidney failure. Numerous genetic variants have been implicated in studies of kidney disease and function [8,10-13]; however, not all of these variants have been evaluated in large, diverse population-based studies. To determine the utility of these variants for precision medicine settings, we asked the following: Do kidney trait-associated single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) allele frequencies differ across racial/ethnic groups? Can kidney trait and disease associations be generalized across populations?
To answer these questions, we as the Epidemiologic Architecture for Genes Linked to Environment (EAGLE), a study site of the Population Architecture using Genomics and Epidemiology I (PAGE) study [14], accessed the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys to evaluate the associations between kidney-related traits and ESRD-associated genetic variants across multiple racial/ethnic groups.
2. Methods
2.1. Study population
The study population presented here is from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. NHANES are cross-sectional surveys of non-institutionalized Americans regardless of health status. Demographics and health data are collected via survey (self-identified), labs, and physical exams in the Mobile Examination Center by public health professionals. CDC collected biospecimens for DNA extraction from consenting participants between 1991 and 1994 (NHANES III), 1999-2000, and 2001-2002 (Continuous NHANES). All procedures were approved by the CDC Ethics Review Board and written informed consent was obtained from all participants. Because no identifying information was accessed by the investigators, Vanderbilt University’s Institutional Review Board determined that this study met the criteria for a “non-human subjects” determination.
Estimated glomerular filtration rate was calculated using the following equation: 175 × (standardized Scr-1.154) × (age-0.203) × (0.742 if female) × (1.212 if black), where Scr is standardized serum creatinine. Albuminuria as a binary trait was defined as either 1) urinary albumin-to-urinary creatinine ratio (ACR) ≥ 30 mg/g or 2) sex-specific thresholds (urinary ACR ≥ 17 mg/g in men and ≥ 25 mg/g in women). Chronic kidney disease was defined as eGFR <60 ml/min or the presence of albuminuria. Participants were considered to have type 2 diabetes if they answered “yes” to “Ever been told you have sugar/diabetes?” and “Are you now taking insulin?” or if they had fasting blood glucose levels >126 mg/dL.
2.2. SNP selection and genotyping
As part of the PAGE I study [14], we as the EAGLE study site selected candidate gene and genome-wide association study (GWAS)-associated variants in late 2009 (Table 1). A total of 11 SNPs (rs2900976, rs10505955, rs10502868, rs1243400, rs9305354, rs12917707, rs17319721, rs2467853, rs2032487, rs4821480, and rs4821481) were targeted for genotyping as part of a custom 96-OPA on the Illumina BeadXpress. In addition to genotyping experimental NHANES samples, we genotyped blind duplicates provided by CDC and HapMap controls (n=360). MYH9 rs4821481 was out of Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium in more than one NHANES III racial/ethnic group (at p<0.001) and was therefore dropped from subsequent analyses; all other SNPs passed quality control.
Table 1.
SNPs selected for targeted genotyping in NHANES and their previously reported associations.
| rs number (Coded allele) | Nearest gene (Location) | Associated phenotype (Population) | Reported genetic effect (p-value) | PubMed ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| ||||
| rs2900976 (NR) | DYSF-RPS20P10 (intergenic) | Albumin (Tuscans living in the Chianti region of Italy) | NR (1.4×10-6) | 18464913 |
|
| ||||
| rs10505955 (G) | BCAT1 (intronic) | Albumin (Korculans from Korcula, Croatia) | β = 0.10 (9.5×10-6) | 19260141 |
|
| ||||
| rs10502868 (G) | SLC14A2 (intronic) | Albumin (Korculans from Korcula, Croatia) | β = -0.40 (6.5×10-6) | 19260141 |
|
| ||||
| rs1243400 (NR) | - (chromosome 10) | Albumin, urinary (European Americans from Framingham, MA) | NR (4.8×10-6 based on FBAT) | 17903292 |
|
| ||||
| rs9305354 (NR) | LOC284825 (intergenic) | Albumin, urinary (European Americans from Framingham, MA) | NR (8.4×10-6 based on GEE) | 17903292 |
|
| ||||
| rs12917707 (G) | UMOD (5′ flanking) | Chronic kidney disease Glomerular filtration rate, estimated by serum creatinine (European-descent participants from multiple cohorts) | OR =1.25 (2.3×10-12) | 19430482 |
| β = 0.02 (5.2×10-16) | ||||
|
| ||||
| rs17319721 (A) | SHROOM3 (intronic) | Glomerular filtration rate, estimated by serum creatinine (European-descent participants from multiple cohorts) | β = -0.01 (1.2×10-12) | 19430482 |
|
| ||||
| rs2467853 (G) | SPATA5L1 (intronic) | Glomerular filtration rate, estimated by serum creatinine (European-descent participants from multiple cohorts) | β = -0.01 (6.2×10-14) | 19430482 |
|
| ||||
| rs2032487 (C ) | MYH9 (intronic) | End-stage renal disease, non-diabetic (African Americans) | OR = 2.19 (1.46×10-11, recessive genetic model) | 18794854 |
|
| ||||
| rs4821480 (T) | MYH9 (intronic) | End-stage renal disease, non-diabetic (African Americans) | OR = 2.29 (7.31×10-11, recessive genetic model) | 18794854 |
|
| ||||
| rs4821481 (T) | MYH9 (intronic) | End-stage renal disease, non-diabetic (African Americans) | OR = 2.25 (1.46×10-12, recessive genetic model) | 18794854 |
Abbreviations: beta (β); family-based association tests (FBAT); generalized estimating equations (GEE); not reported (NR); odds ratio (OR).
2.3. Statistical methods
All statistical tests were performed stratified by race/ethnicity. Race/ethnicity is self-reported in NHANES, which has been shown to be correlated with global genetic ancestry [15]. Single SNP tests of association were performed for each of the ten SNPs and the following quantitative trait outcomes among adults (17 years of age or older) using linear regression: creatinine (urinary), creatinine (serum), albumin (urinary), eGFR, and albumin-to-urinary creatinine ratio (ACR). Single SNP tests of association were also performed using logistic regression for albuminuria and chronic kidney disease. Non-normal quantitative trait distributions were natural log-transformed prior to analysis. All tests of association assumed an additive genetic model and were adjusted by age, sex, diastolic blood pressure, systolic blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes status. All analyses were performed unweighted using SAS v9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC) and the Analytic Data Research by Email (ANDRE) portal of the CDC Research Data Center in Hyattsville, MD [16]. Results from quantitative trait tests of association were plotted using Synthesis-View [17,18].
3. Results
Study population characteristics are given in Table 2. Overall half of the adult participants were non-Hispanic white and female. Both non-Hispanic black and Mexican American participants were younger on average compared with non-Hispanic white participants. As expected based on the known epidemiology [2], the labs associated with kidney function (creatinine) were worse in non-Hispanic blacks compared with the other two groups. More cases of chronic kidney disease were identified among non-Hispanic black participants compared with the other two groups. Conversely, more cases of albuminuria were identified among Mexican American participants compared with the other two groups (Table 2).
Table 2.
Study population characteristics.
| Non-Hispanic whites | Non-Hispanic blacks | Mexican Americans | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 6,293 | 3,013 | 3,542 |
| Female (%) | 3,385 (53.8%) | 1,652 (54.8%) | 1,761 (49.7%) |
| Age, in years | 53.24 (19.70) | 44.08 (17.27) | 44.00 (17.69) |
| ln(serum creatinine, mg/dL) | -0.10 (0.31) | 0.003 (0.32) | -0.20 (0.34) |
| ln(urinary creatinine, mg/dL) | 4.53 (0.75) | 4.97 (0.65) | 4.65 (0.73) |
| Albuminuria (%) | 14/5944 (0.2%) | 15/2779 (0.5%) | 34/3377 (1.0%) |
| Urinary albumin-to-urinary creatinine ratio (ACR) | 0.002 (0.05) | 0.006 (0.07) | 0.010 (0.10) |
| Urinary albumin, mg/mL | 33.20 (221.08) | 76.27 (454.86) | 77.06 (583.25) |
| eGFR | 50.78 (26.38) | 73.91 (52.74) | 48.24 (30.83) |
| CKD (%) | 1734/5940 (29.2%) | 1555/2796 (55.6%) | 922/3378 (27.3%) |
Means (+/- standard deviation) given unless otherwise noted.
The allele frequencies for the coded allele of each SNP are displayed in Figure 1 by race/ethnicity. Coded alleles for rs10502868, rs12917707, rs2032487, rs2467853, rs2900976, and rs4821480 were all more common in non-Hispanic blacks than non-Hispanic whites and Mexican Americans. Coded alleles for rs10505955, rs17319721, and rs9305354 were all more common in non-Hispanic whites than non-Hispanic blacks and Mexican Americans. Coded alleles for rs1243400 were more common in Mexican Americans than non-Hispanic blacks and non-Hispanic whites. Four of the SNPs characterized here (rs12917707, rs2032487, rs2467853, and rs4821480) are not included in the International HapMap Project Phase 3 [19] and therefore do not have reference allele frequency data available for comparison across populations. Of the remaining six SNPs, the majority of allele frequencies observed in NHANES were similar to those observed in HapMap populations with similar genetic ancestry [African Americans from Southwestern United States (ASW), European Americans from Utah (CEU), and Mexican Americans from Los Angeles, California (MEX)]. Of note is SLC14A2 rs10502868 where the MEX allele frequency (2%) was significantly higher compared with the frequency estimated in Mexican Americans from NHANES (0.001%). Also, MEX allele frequencies are not available for SHROOM3 rs17319721, common variant in Mexican Americans from NHANES (37%; Figure 1).
Figure 1. Coded allele frequency of kidney disease or trait-associated SNPs by race/ethnicity.
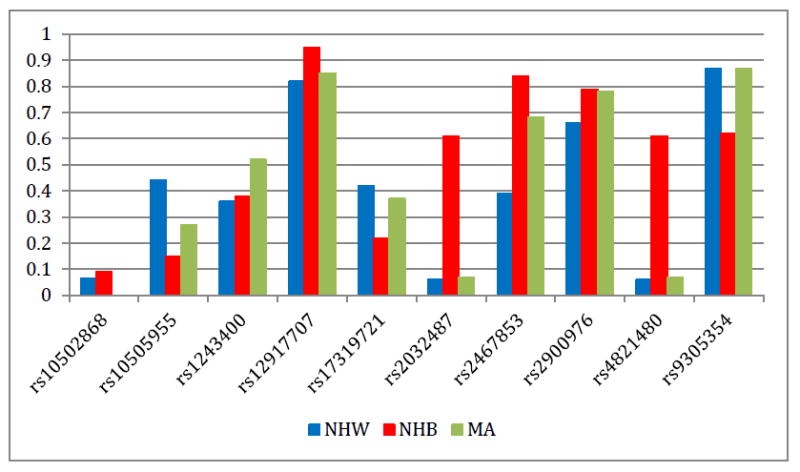
Allele frequencies (y-axis) are given for each of the ten SNPs genotyped in NHANES (x-axis) for each race/ethnicity. Race/ethnicity is color-coded (blue for non-Hispanic whites, red for non-Hispanic blacks, and green for Mexican Americans). Allele frequencies displayed here were calculated based on NHANES III and NHANES 1999-2002 frequencies combined.
Test of association p-values and directions of genetic effect are displayed in Figure 2 for each SNP and trait across each population sample. Eight of the genotyped SNPs were associated (at p<0.05) with at least one trait in at least one population. Of these, three SNPs were limited to association with one trait in one population: 1) DYSF-RPS20P10 rs2900976 was associated with natural log transformed creatinine in non-Hispanic blacks (β = -0.022), 2) SHROOM3 rs17319721 was associated with natural log transformed creatinine in non-Hispanic whites (β = 0.011), and 3) LOC284825 rs9305354 was associated with natural log transformed urinary creatinine in non-Hispanic blacks (β = -0.047). Three SNPs were associated with multiple traits in non-Hispanic whites: 1) UMOD rs12917707 was associated with natural log transformed creatinine and eGFR (β = 0.016 and 1.209, respectively), 2) MYH9 rs4821480 was associated with natural log transformed creatinine, albumin-creatinine ratio, and CKD (β = 0.023, 0.180, and odds ratio = 1.305 and 95% confidence interval 1.053 – 1.617, respectively), and 3) MYH9 rs2032487 was associated with natural log transformed creatinine, eGFR, albumin-creatinine ratio, and CKD (β = 0.030, 1.963, 0.196, and odds ratio = 1.340 and 95% confidence interval 1.076 – 1.669, respectively).
Figure 2. Results of tests of association are displayed using Synthesis-View by SNP, quantitative trait, and race/ethnicity.
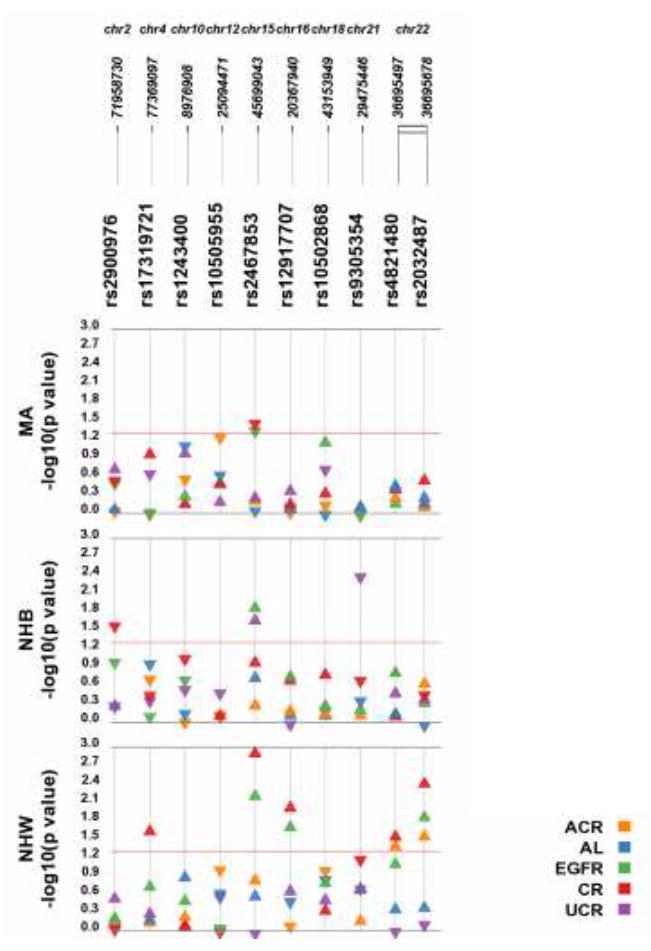
Plotted are the p-values (y-axis is –log of the p-value). The triangles denote the direction of the genetic effect. The red line is a p-value threshold of 0.05. Abbreviations: Albumin-creatinine ratio (ACR); albumin (AL), estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate (eGFR), serum creatinine (CR), urinary creatinine (uCR); non-Hispanic white (NHW), non-Hispanic black (NHB), Mexican American (MA).
SNP rs1243400 on chromosome 10 was associated with CKD in non-Hispanic whites and non-Hispanic blacks, though in opposite directions of effect for the same coded allele (odds ratio = 1.182; 95% confidence interval = 1.064 – 1.313 and odds ratio = 0.851; 95% confidence interval 0.74 - 0.98, respectively). SPATA5L1 rs2467853 was associated with several traits in all three populations, with natural log transformed creatinine in non-Hispanic whites and Mexican Americans (β = 0.016 and - 0.017, respectively), with eGFR in non-Hispanic whites and non-Hispanic blacks (β = 1.137 and 4.115, respectively), with natural log transformed urinary creatinine in non-Hispanic blacks (β = 0.050), with eGFR in Mexican Americans (β = 1.407), and with CKD in non-Hispanic whites (odds ratio = 1.135; 95% confidence interval 1.026 – 1.257).
4. Discussion
We tested ten kidney disease and trait-associated SNPs for an association with CKD and kidney traits in non-Hispanic whites, non-Hispanic blacks, and Mexican Americans ascertained regardless of health status for a national survey. As might be expected based on the SNP selection criteria, we observed eight associations with at least one trait in at least one population at p<0.05 in this diverse epidemiologic survey. No one SNPs was associated for the same trait or outcome across all three populations tested. However, we did observe that SNPs such as those in MYH9 were associated with several traits and outcomes in a single population.
That the MYH9 SNPs were associated with several traits/outcomes in non-Hispanic whites is not surprising, given the previous reports in the literature [20]. Surprising, however, is the lack of association of these SNPs in non-Hispanic blacks and Mexican Americans given the strong linkage disequilibrium between the MYH9 SNPs and APOL1 variants that are strongly associated with kidney disease in African Americans. In the present study, the three MYH9 SNPs targeted for genotyping are in strong linkage disequilibrium with one another in all three racial/ethnic groups (r2 ranging from 0.86 – 1.0). Reports have implicated APOL1 as the driving cause of racial/ethnic disparity in kidney disease [21], though other functional studies suggest MYH9 remains relevant to kidney disease risk [22]. The lack of association may be attributable to the combination of heterogeneous kidney diseases among individuals in the Mexican American and non-Hispanic black samples.
Affordability and representation are among the ten things that must be addressed in order to achieve precision medicine [23]. Ideally, genetic variants selected for clinical genotyping are relevant to all populations tested, and therefore efficient in providing potentially healthcare-related data even at the individual patient level. To achieve this goal, it is crucial that variants selected for genotyping have relevancy to traits in multiple populations, not just European-descent individuals.
Arguably, precision medicine will also be more efficiently achieved with the addition and expansion of discovery studies that assess the impact of genetic variation in all populations and racial/ethnic backgrounds. The MYH9-APOL1 variants, which have a much greater impact in individuals of African ancestry, are an example of precision medicine targets that will streamline the process of identifying patients at greater risk for developing kidney disease, and also identifying donor kidneys that are more likely to survive [24].
The present study had numerous weaknesses and strengths. Despite the overall large sample size of Genetic NHANES (n = 14,998), the present study was limited to adult participants with kidney traits available for analysis. As a result, the sample size of participants with CKD was modest resulting in lower statistical power to replicate known genetic associations. Additionally, not all participants with CKD will progress to end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis. An assessment of end-stage renal disease as opposed to the more general CKD may have allowed the detection and replication of genetic associations observed for MYH9 in African Americans. Additionally, evaluating a specific subset of kidney disease (diabetic nephropathy, focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, HIV-associated nephropathy, etc.) would likely also yield more harmonized results. Likewise, protein in the urine (proteinuria or albuminuria, depending upon method of measurement) is the diagnostic hallmark and indicator of kidney dysfunction [1]; however, this was an uncommon condition in the present study resulting in low statistical power.
Despite these limitations, the present study had several strengths including the availability of multiple kidney disease and quantitative traits as well as three racial/ethnic groups from the United States. Large prospective studies and clinical-based repositories will be required to realize the vision of precision medicine particularly for health disparities across diverse populations. The current governmental support for focus on precision medicine heralds the necessity of studies such as the one presented herein. In a precision medicine setting, it is crucial to realize the different genetic effects and associations that can be observed in racial/ethnic populations. Kidney disease is a well-known example of health disparities with a strong, known genetic component influencing disease risk (MYH9-APOL1) and, while a genetic basis for the disparate rates of kidney diseases across racial/ethnic groups is widely recognized, research such as this is necessary to systematically characterize genome-wide and candidate gene identified genetic variants across diverse populations.
Acknowledgments
Genotyping for NHANES was supported in part by The Population Architecture Using Genomics and Epidemiology (PAGE) I study, which was funded by the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI/NIH U01HG004798). EAGLE would like to thank Dr. Geraldine McQuillan and Jody McLean for their help in accessing the Genetic NHANES data. The Vanderbilt University Center for Human Genetics Research, Computational Genomics Core provided computational and/or analytical support for this work. The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the National Institutes for Health or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. JNCB is supported by a PhRMA Informatics Fellowship.
Contributor Information
JESSICA N. COOKE BAILEY, Institute for Computational Biology, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Case Western Reserve University, Wolstein Research Building, 2103 Cornell Road, Suite 2527, Cleveland, OH 44106, USA, jnc43@case.edu
SARAH WILSON, Center for Human Genetics, Vanderbilt University, 519 Light Hall, 2215 Garland Avenue, Nashville, TN 37232, USA, sarah.wilson928@gmail.com.
KRISTIN BROWN-GENTRY, Center for Human Genetics Research, Vanderbilt University, 519 Light Hall, 2215 Garland Avenue, Nashville, TN 37232, USA, brownkd1908@yahoo.com.
ROBERT GOODLOE, Center for Human Genetics Research, Vanderbilt University, 519 Light Hall, 2215 Garland Avenue, Nashville, TN 37232, USA, robert.goodloe@gmail.com.
DANA C. CRAWFORD, Institute for Computational Biology, Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Case Western Reserve University, Wolstein Research Building, 2103 Cornell Road, Suite 2527, Cleveland, OH 44106, USA, dana.crawford@case.edu
References
- 1.Scott RP, Quaggin SE. The cell biology of renal filtration. The Journal of Cell Biology. 2015;209:199–210. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201410017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.USRDS Coordinating Center. United States Renal Data System. ( www.usrds.org). Accessed July 24, 2015.
- 3.Cowie CC, Port FK, Wolfe RA, SAVAGE PJ, Moll PP, Hawthorne VM. Disparities in Incidence of Diabetic End-Stage Renal Disease According to Race and Type of Diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1989;321:1074–1079. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Williams WW, Pollak MR. Health Disparities in Kidney Disease--Emerging Data from the Human Genome. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:2260–2261. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1312797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lipworth L, Mumma MT, Cavanaugh KL, Edwards TL, Ikizler TA, Tarone R, et al. Incidence and Predictors of End Stage Renal Disease among Low-Income Blacks and Whites. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e48407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McClellan WM, Newsome BB, McClure LA, Howard G, Volkova N, Audhya P, et al. Poverty and Racial Disparities in Kidney Disease: The REGARDS Study. American Journal of Nephrology. 2010;32:38–46. doi: 10.1159/000313883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kopp JB, Smith MW, Nelson GW, Johnson RC, Freedman BI, Bowden DW, et al. MYH9 is a major-effect risk gene for focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1175–1184. doi: 10.1038/ng.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kao WHL, Klag MJ, Meoni LA, Reich D, Berthier-Schaad Y, Li M, et al. MYH9 is associated with nondiabetic end-stage renal disease in African Americans. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1185–1192. doi: 10.1038/ng.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Parsa A, Kao WHL, Xie D, Astor BC, Li M, Hsu Cy, et al. Population stratification in the context of diverse epidemiologic surveys sans genome-wide data. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:2183–2196. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Melzer D, Perry JRB, Hernandez D, Corsi AM, Stevens K, Rafferty I, et al. A Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Protein Quantitative Trait Loci (pQTLs) PLoS Genet. 2008;4:e1000072. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zemunik T, Boban M, Lauc G, Jankovic S, Rotim K, Vatavuk Z, et al. Genome-wide association study of biochemical traits in Korcula Island, Croatia. Croat Med J. 2009;50:23–33. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2009.50.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hwang SJ, Yang Q, Meigs JB, Pearce EN, Fox CS. A genome-wide association for kidney function and endocrine-related traits in the NHLBI’s Framingham Heart Study. BMC Med Genet. 2007;8:S10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-8-S1-S10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kottgen A, Glazer NL, Dehghan A, Hwang SJ, Katz R, Li M, et al. Multiple loci associated with indices of renal function and chronic kidney disease. Nat Genet. 2009;41:712–717. doi: 10.1038/ng.377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Matise TC, Ambite JL, Buyske S, Carlson CS, Cole SA, Crawford DC, et al. The Next PAGE in Understanding Complex Traits: Design for the Analysis of Population Architecture Using Genetics and Epidemiology (PAGE) Study. American Journal of Epidemiology. 2011;174:849–859. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwr160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Oetjens MT, Brown-Gentry K, Goodloe R, Dilks HH, Crawford DC. Population stratification in the context of diverse epidemiologic surveys sans genome-wide data. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00076. (submitted) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bush WS, Boston J, Pendergrass SA, Dumitrescu L, Goodloe R, Brown-Gentry K, et al. Enabling high-throughput genotype-phenotype associations in the Epidemiology Architecture for Genes Linked to Environment (EAGLE) project as part of the Population Architecture using Genomics and Epidemiology (PAGE) study. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2013;18:373–384. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pendergrass S, Dudek SM, Roden DM, Crawford DC, Ritchie MD. Visual integration of results from a large DNA biobank (BioVU) using synthesis-view. Pac Symp Biocomput. 2011:265–275. doi: 10.1142/9789814335058_0028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pendergrass S, Dudek S, Crawford D, Ritchie M. Synthesis-View: visualization and interpretation of SNP association results for multi-cohort, multi-phenotype data and meta-analysis. BioData Mining. 2010;3:10. doi: 10.1186/1756-0381-3-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Integrating common and rare genetic variation in diverse human populations. Nature. 2010;467:52–58. doi: 10.1038/nature09298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Cooke JN, Bostrom MA, Hicks PJ, Ng MCY, Hellwege JN, Comeau ME, et al. Polymorphisms in MYH9 are associated with diabetic nephropathy in European Americans. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation. 2012;27:1505–1511. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfr522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Quaggin SE, George AL. Apolipoprotein L1 and the Genetic Basis for Racial Disparity in Chronic Kidney Disease. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology. 2011;22:1955–1958. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2011090932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Anderson BR, Howell DN, Soldano K, Garrett ME, Katsanis N, Telen MJ, et al. In vivo Modeling Implicates APOL1 in Nephropathy: Evidence for Dominant Negative Effects and Epistasis under Anemic Stress. PLoS Genet. 2015;11:e1005349. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1005349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kohane IS. Ten things we have to do to achieve precision medicine. Science. 2015;349:37–38. doi: 10.1126/science.aab1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Freedman BI, Julian BA. Should kidney donors be genotyped for APOL1 risk alleles? Kidney Int. 2015;87:671–673. doi: 10.1038/ki.2015.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


