Abstract
Background
Oncomelania hupensis is the unique intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum, which plays a crucial role in the transmission of schistosomiasis. The endemic area of S. japonicum is strictly consistent with the geographical distribution of O. hupensis.
Methods
A total of 24 populations of O. hupensis from four ecological landscapes were selected for analysis of genetic diversity by screening eight microsatellite DNA polymorphic loci.
Results
The number of alleles per locus ranged from 29 to 70 with an average of 45.625 and that of effective alleles were 18.5 to 45.8 with an average of 27.4. The observed (Ho) and expected (He) heterozygosities varied from 0.331 to 0.57 and from 0.888 to 0.974, respectively. The mean of polymorphism information content (PIC) for all populations was 0.940, appearing polymorphic for all loci. For the fixation index of F-Statistics, Fit and Fst were 54.95 and 37.62 %, respectively. Variation of O. hupensis chiefly exists among individuals, accounting for 60.58 % of the total variation determined by Analysis of Molecular Variation (AMOVA). Variation among individuals within populations, among populations within groups and among groups only accounted for 26.60, 8.04 and 4.78 %, respectively. This distribution of variation suggests that genetic differences principally originate from within-populations rather than among-populations. Moreover, UPGMA cluster analysis showed that the populations spreading within middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River (HBWH, JSYZ, JXNC, HNHS, JXJJ, AHWW, HBJL, JXDC, HNNX, JSYZJZ, ZJJH, AHNG and AHWJ) clustered together first, then gathered with the populations in the high mountains (SCMS, SCYA, SCPJ, YNEY, SCLS, YNWS and SCXC), coastal hills (FJFQ and FJFZ) and Karst landform (GXBS and GXYZ) successively.
Conclusion
This study provides novel insight into the theoretical source of genetic differentiation of Oncomelania hupensis in mainland China, which is critical for the epidemiological investigation and surveillance of S. japonicum.
Keywords: Oncomelania hupensis, Schistosoma japonicum, Microsatellites DNA, Polymorphism, Genetic differentiation
Background
Schistosomiasis, caused by Schistosoma japonicum, remains one of the most prevalent parasitic diseases and effects severe socio-economic and public health losses in China [1, 2]. Oncomelania hupensis is the unique intermediate host of S. japonicum, which plays a critical role in the transmission of Schistosomiasis japonica [1, 3]. The geographical distribution of O. hupensis coincides with the endemic area of S. japonicum [4], which is mainly found throughout the southern region of the Yangtze River basin [5, 6]. As a result, significant genetic differentiation leads to the formation of multiple geographical populations of O. hupensis [3]. Coincident with the endemic area for schistosomiasis, O. hupensis has been mainly found in four types of ecological landscapes giving rise to subspecies including:(1) O. h. hupensis largely in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River (among the provinces of Hunan, Hubei, Jiangxi, Anhui, Jiangsu and Zhejiang) (2) O. h. robertsoni in the mountainous region of Sichuan and Yunnan provinces (3) O. h. guangxiensis in the Karst landscape of Guangxi province and (4) O. h. tangi in the southeastern coastal region of Fujian province [7, 8]. Interestingly, obvious morphological differences have been identified among individuals from the same regional population [9–11]. For example, O. hupensis from upstream of Miaohe basin, which contains regions of swamps and lakes, have a ribbed shell while those from downstream have a smooth shell [12].
Microsatellite DNA, known as short tandem repeat (STR) or simple sequence repeat(SSR), occurs throughout the eukaryotic genome. Differences in repetitive sequence numbers allow for high polymorphism due to the ubiquitous occurrence, high copy numbers, high heterozygosity and easy detection within population [13]. Along with other genome mark technology, it has been widely applied to research examining genetic diversity and serves as an important molecular marker [14–17]. At present, microsatellites have been isolated from many different organisms [18–20]. Specifically, from 128 molluscs, a total of 3, 284 microsatellite sequences have been identified [21]. Although the microsatellite DNA library of O. hupensis was built recently [22], the microsatellite markers have not been used extensively in population genetic structure studies and genome mapping of O. hupensis in P.R. China [23–25]. To deepen our knowledge on the genetic diversity of the intermediate host snail, we developed a novel multiplex PCR method to screen and analyze the genetic diversity of O. hupensis using microsatellites loci among the four various ecological landscape populations in mainland China.
Methods
Snail sampling
A total of 24 populations of O. hupensis were sampled from four ecological landscape populations in mainland China covering: (1) the region of swamps and lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, (2) the mountainous region of the Sichuan and Yunnan provinces, (3) the littoral hill part of the Fujian province and (4) the karst landscape of Guangxi autonomous region (Fig. 1, Table 1).
Fig. 1.
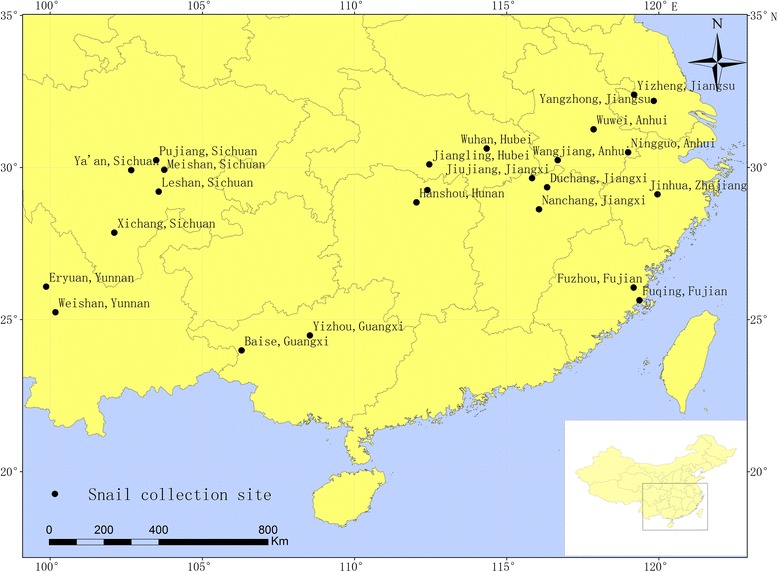
Illustration of geographical location of O. hupensis collection sites
Table 1.
Location of O. hupensis collection
| Collection site(Code) | Geomorphic feature | No. samples | Collection date | Longitude | Latitude |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ningguo, Anhui(AHNG) | swamps and lakes | 17 | 09/12/2012 | 30.5022° N | 118.9891° E |
| Wangjiang, Anhuui(AHWJ) | swamps and lakes | 20 | 09/12/2012 | 30.2423° N | 116.2814° E |
| Wuwei, Anhui(AHWW) | swamps and lakes | 18 | 09/12/2012 | 31.2571° N | 117.8573° E |
| Jiangling, Hubei(HBJL) | swamps and lakes | 18 | 06/14/2013 | 31.1034° N | 112.4631° E |
| Wuhan, Hubei(HBWH) | swamps and lakes | 17 | 05/11/2012 | 30.6749° N | 114.3865° E |
| Hanshou, Hunan(HNHS) | swamps and lakes | 16 | 03/18/2013 | 28.8592° N | 112.0378° E |
| Nanxian, Hunan(HNNX) | swamps and lakes | 11 | 03/18/2013 | 29.2581° N | 112.3972° E |
| Yizheng,Jiangsu(JSYZ) | swamps and lakes | 19 | 04/21/2013 | 32.3911° N | 119.1914° E |
| Yangzhong, Jiangsu(JSYZ) | swamps and lakes | 18 | 04/21/2013 | 32.1942° N | 119.8353° E |
| Duchang, Jiangxi(JXDC) | swamps and lakes | 19 | 04/14/2012 | 29.3562° N | 116.3324° E |
| Jiujiang, Jiangxi(JXJJ) | swamps and lakes | 15 | 04/14/2012 | 29.6517° N | 115.8356 °E |
| Nanchang, Jiangxi(JXNC) | swamps and lakes | 14 | 04/14/2012 | 28.6252° N | 116.0642°E |
| Jinhua, Zhejiang(ZJJH) | swamps and lakes | 16 | 06/23/2012 | 29.1044° N | 120.0052° E |
| Yaan, Sichuan(SCYA) | Mountains | 17 | 09/25/2012 | 29.8931° N | 102.6651° E |
| Leshan, Sichuan(SCLS) | Mountains | 16 | 09/25/2012 | 29.1722° N | 103.5759° E |
| Meishan, Sichuan(SCMS) | Mountains | 19 | 09/25/2012 | 29.8788° N | 104.0949° E |
| Xichang, Sichuan(SCXC) | Mountains | 20 | 09/27/2012 | 27.8632° N | 102.1134° E |
| Pujiang, Sichuan(SCPJ) | Mountains | 15 | 09/27/2012 | 30.2412° N | 103.4897° E |
| Eryuan, Yunnan(YNEY) | Mountains | 15 | 03/21/2013 | 26.0852° N | 112.0371° E |
| Weishan, Yunnan(YNWS) | Mountains | 12 | 03/21/2013 | 31.2573° N | 117.8574° E |
| Baise, Guangxi(GXBS) | Karst | 9 | 03/22/2013 | 23.9829° N | 106.1678° E |
| Yizhou, Guangxi(GXYZ) | Karst | 18 | 03/22/2013 | 24.4792° N | 108.5362° E |
| Fuqing, Fujian/ FJFQ) | Coastal hills | 20 | 04/17/2012 | 25.6374° N | 119.3652° E |
| Fuzhou, Fujian(FJFZ) | Coastal hills | 17 | 04/17/2012 | 25.9911° N | 119.1674° E |
DNA preparation
Ten to 20 O. hupensis samples were randomly chosen from each site, fed for 1 week and identified as infected or non-infected with S. japonicum by observation of cercariae emerging from the snails. Only non-infected snails were used in this study. After removal of the gut and digestive glands from the soft parts of the snails, the 30 mg muscle tissues from the pleopod of a single snail were digested for 3 hours at 56 °C with proteinase K (Amresco Inc. Solon, OH, USA) followed by the standard DNA extraction procedure [26] using mollusc DNA Kit (Omega, USA).
PCR amplification and detection of PCR products
The microsatellite DNA polymorphic loci were selected and evaluated from previous microsatellite loci library [22]. Two rounds of multiplex PCR reaction were developed including four microsatellite loci in each one, which were identified by different lengths and fluorescence peaks of 6-FAM, VIC, NED and PET labeled by (Sigma-aldrich London, UK). Primer sequences and information are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2.
Primers of the 8 microsatellite loci in O. hupensis
| Locus | Primer sequence (5′ → 3′) | Repeat motif | Annealing tempreture/(°C) | Allele size from field snails (bp) | NO. of mutilplex PCR | GenBank accession No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1-10 | Pf: TCACTCGGGTGTAATGCT | (GA)38 | 55 | 173–259 | 1 | GU204080 |
| Pr: TTTGTTACTGATGGTGGC | ||||||
| T4-25 | Pf: CAATAGTTCGACTCGGAAGA | (CT)35 | 52 | 142–228 | 1 | GU204084 |
| Pr: CGAGGTATGGCGTTGCTT | ||||||
| T4-22 | Pf: TATCCAAGAAGCCGAAAC | (CA)10 | 50 | 224–256 | 1 | GU204083 |
| Pr: GAGGAAAGCGAGGTAAGA | ||||||
| D11 | Pf: TTCAGTTGTCTTATTTCGTG | (TG)17 | 55 | 141–192 | 1 | GU204223 |
| Pr: TAGATGTTCACTGGTTTGTC | ||||||
| T5-11 | Pf: ACGCCAGTCTTGGTGTCA | (GT)14 | 55 | 153–210 | 2 | GU204092 |
| Pr: TACTTGGGCAGAAGGGTT | ||||||
| T6-17 | Pf: GCTGTCCTTTTACCAACTGC | (AC)8 | 55 | 192–248 | 2 | GU204108 |
| Pr: TATCAAAGGATTATGCCGAG | ||||||
| A18 | Pf: GCCGATGATACAAGACCC | (CT)18 | 60 | 131–256 | 2 | GU204047 |
| Pr: GAGAATCTCCAGGCACGC | ||||||
| C22 | Pf: CGGTACATCTGGATAGTGG | (CA)21 | 62 | 185–239 | 2 | GU204145 |
| Pr: TGCGAAACAGTTGCAGACAC |
The multiplex PCRs were developed using the Type-it Microsatellite PCR Kit (QiaGen, London, UK) with a 25 μl reaction system, including 2x Type-it Multiplex PCR Master Mix 12.5 μl, 10x primer mix 2 μl including four primers in each mix, template DNA 2 μl with less than 200 ng then add RNase-free water to 25 μl. The reaction conditions for PCR amplification were as follows: 95 °C, 5 min; 95 °C, 30 s, 60 °C, 60 s; 72 °C, 30 s, 30 cycles; 65 °C, 30 min for final extension. 1 μl of the PCR product was mixed with 0.6 μl of ROX and 8.4 μl ultrapure Hi-Di formamide, denatured at 95 °C for 5 min and detected using automatic genetic analyzer (3730XL, ABI, USA).
Analysis of microsatellite diversity
The accurate length of amplified fragments of microsatellite DNA loci were determined using Geneious software(Version 7.0.6) and subsequently exported as an Excel table. The raw data in the table were converted into a recognized format by Arlequin and Genepop using the toolkit of the Excel microsatellite toolkit. The data format which fits for Popgene were acquired by DataTrans 1.0. Various parameters of genetic difference within populations include: number of alleles (Na), number of efficient alleles (Ne), inbreeding coefficient (Fis), expected heterozygosity (He) and observed heterozygosity (Ho) were calculated. The degree of Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) and linkage disequilibrium (LD) were tested with Genepop 4.1.10. The frequency of null alleles within every population was calculated in Genepop. The index of genetic variation between populations (Fst), gene flow (Nm) and genetic distance [Fst/ (1-Fst)] were determined using Arlequin [27]. The correlation between genetic distance and geographical distance were tested with Mantel regression. Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) was processed through Popgene software, clustering analysis was determined by unweighted pair group method with arithmetic means (UPGMA) and the phylogenetic tree was modified with TreeView [28]. The polymorphism information content (PIC) was calculated according to the formula previously described [28].
Results
Gene scan
From the 24 populations of O. hupensis sampled, 396 specimens were scanned at the genetic level across eight polymorphic loci of microsatellite DNA. The lengths of amplified fragments for a total of 6,196 microsatellite DNA loci were obtained.
Genetic differences within populations
Results obtained from the analysis of the 24 populations of O. hupensis showed that the number of alleles per locus ranged from 29 to 70 with an average of 45.625, and that of effective alleles were 18.5 to 45.8 with an average of 27.4. The GXYZ and HNHS populations had the minimum and maximum average Na values, respectively. The average He within populations ranged from 0.888 to 0.974, and the average Ho ranged from 0.331 to 0.57. The populations with the highest and lowest Ho values were HNHS and GXYZ, respectively. The average PIC for all populations of O. hupensis was 0.940 (Tables 3, 4 and 5).
Table 3.
Coefficients of genetic diversity of O. hupensis at different loci (the populations of landscape of swamps and lakes)
| Populations | Index | Microsatellite loci | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1-10 | T4-25 | D11 | T4-22 | T5-11 | T6-27 | A18 | C22 | |||
| AHNG | Na | 13 | 12 | 7 | 8 | 14 | 9 | 11 | 10 | 10.500 |
| He | 0.863 | 0.815 | 0.806 | 0.774 | 0.927* | 0.847* | 0.929* | 0.941* | 0.863 | |
| Ho | 0.412 | 0.706 | 0.188 | 0.706 | 0.882 | 0.588 | 0.071 | 0.222 | 0.472 | |
| PIC | 0.948 | 0.938 | 0.913 | 0.902 | 0.927 | 0.932 | 0.948 | 0.949 | 0.932 | |
| AHWJ | Na | 13 | 15 | 4 | 2 | 8 | 6 | 8 | 1 | 7.125 |
| He | 0.918* | 0.936 | 0.406 | 0.258 | 0.749 | 0.549 | 0.777 | 0.000 | 0.574 | |
| Ho | 0.588 | 0.471 | 0.000 | 0.059 | 0.765 | 0.133 | 0.200 | 0.104 | 0.317 | |
| PIC | 0.967 | 0.927 | 0.987 | 0.923 | 0.937 | 0.927 | 0.914 | 0.972 | 0.944 | |
| AHWW | Na | 6 | 21 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 10 | 15 | 17 | 12.375 |
| He | 0.810 | 0.963* | 0.856 | 0.860 | 0.898 | 0.849 | 0.914* | 0.936 | 0.886 | |
| Ho | 0.091 | 0.444 | 0.353 | 0.278 | 0.389 | 0.611 | 0.412 | 0.647 | 0.403 | |
| PIC | 0.943 | 0.923 | 0.938 | 0.912 | 0.924 | 0.972 | 0.916 | 0.976 | 0.937 | |
| HBJL | Na | 12 | 19 | 15 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 13.500 |
| He | 0.913* | 0.961* | 0.939 | 0.904 | 0.879 | 0.938* | 0.895 | 0.930 | 0.920 | |
| Ho | 0.417 | 0.647 | 0.357 | 0.294 | 0.471 | 0.706 | 0.750 | 0.529 | 0.521 | |
| PIC | 0.947 | 0.933 | 0.937 | 0.890 | 0.927 | 0.928 | 0.968 | 0.972 | 0.939 | |
| HBWH | Na | 12 | 19 | 16 | 12 | 15 | 13 | 19 | 18 | 15.500 |
| He | 0.944 | 0.961* | 0.956* | 0.903 | 0.949* | 0.924 | 0.966* | 0.966* | 0.946 | |
| Ho | 0.272 | 0.533 | 0.467 | 0.667 | 0.533 | 0.733 | 0.733 | 0.600 | 0.567 | |
| PIC | 0.991 | 0.896 | 0.922 | 0.917 | 0.958 | 0.921 | 0.970 | 0.927 | 0.938 | |
| HNHS | Na | 16 | 21 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 8 | 20 | 18 | 16.375 |
| He | 0.952* | 0.974* | 0.927 | 0.907* | 0.952* | 0.798 | 0.962* | 0.956* | 0.929 | |
| Ho | 0.250 | 0.750 | 0.438 | 0.813 | 0.733 | 0.750 | 0.500 | 0.688 | 0.615 | |
| PIC | 0.956 | 0.973 | 0.974 | 0.932 | 0.941 | 0.931 | 0.952 | 0.938 | 0.950 | |
| HNNX | Na | 7 | 10 | 7 | 6 | 9 | 9 | 12 | 10 | 8.750 |
| He | 0.801 | 0.913 | 0.853 | 0.844* | 0.887 | 0.810 | 0.942* | 0.892 | 0.868 | |
| Ho | 0.091 | 0.818 | 0.200 | 0.364 | 0.636 | 0.545 | 0.500 | 0.909 | 0.508 | |
| PIC | 0.936 | 0.976 | 0.926 | 0.927 | 0.956 | 0.912 | 0.951 | 0.936 | 0.941 | |
| JSYZ | Na | 7 | 18 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 10 | 12 | 13 | 11.875 |
| He | 0.909* | 0.961* | 0.806 | 0.924* | 0.926 | 0.905* | 0.915 | 0.937 | 0.910 | |
| Ho | 0.333 | 0.733 | 0.385 | 0.667 | 0.500 | 0.500 | 0.143 | 0.571 | 0.479 | |
| PIC | 0.897 | 0.918 | 0.973 | 0.899 | 0.973 | 0.948 | 0.940 | 0.918 | 0.933 | |
| JSYZJZ | Na | 6 | 21 | 8 | 13 | 16 | 11 | 18 | 17 | 13.750 |
| He | 0.817 | 0.954* | 0.859 | 0.894 | 0.910 | 0.889* | 0.943* | 0.938 | 0.901 | |
| Ho | 0.111 | 0.722 | 0.412 | 0.611 | 0.500 | 0.611 | 0.500 | 0.611 | 0.510 | |
| PIC | 0.949 | 0.972 | 0.936 | 0.879 | 0.910 | 0.980 | 0.938 | 0.938 | 0.938 | |
| JXDC | Na | 7 | 21 | 7 | 11 | 16 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 12.250 |
| He | 0.890 | 0.968* | 0.800 | 0.890 | 0.945* | 0.761 | 0.908 | 0.922 | 0.886 | |
| Ho | 0.143 | 0.733 | 0.385 | 0.467 | 0.867 | 0.533 | 0.133 | 0.667 | 0.491 | |
| PIC | 0.982 | 0.936 | 0.926 | 0.919 | 0.928 | 0.979 | 0.914 | 0.935 | 0.943 | |
| JXJJ | Na | 5 | 14 | 8 | 9 | 11 | 7 | 11 | 16 | 10.125 |
| He | 0.803 | 0.957* | 0.902 | 0.887 | 0.931 | 0.481 | 0.950* | 0.957* | 0.859 | |
| Ho | 0.167 | 0.545 | 0.667 | 0.636 | 0.727 | 0.455 | 0.500 | 0.818 | 0.564 | |
| PIC | 0.968 | 0.973 | 0.927 | 0.898 | 0.918 | 0.977 | 0.927 | 0.963 | 0.947 | |
| JXNC | Na | 6 | 17 | 9 | 8 | 9 | 7 | 7 | 12 | 9.375 |
| He | 0.911* | 0.993* | 0.908* | 0.869* | 0.915 | 0.824 | 0.856 | 0.948 | 0.903 | |
| Ho | 0.200 | 0.889 | 0.500 | 0.333 | 0.444 | 0.778 | 0.111 | 0.667 | 0.490 | |
| PIC | 0.953 | 0.911 | 0.890 | 0.915 | 0.937 | 0.967 | 0.917 | 0.967 | 0.932 | |
| ZJJH | Na | 3 | 14 | 1 | 7 | 16 | 0 | 12 | 6 | 7.375 |
| He | 0.800 | 0.940* | 0.000 | 0.764 | 0.948* | 0.000 | 0.915 | 0.720 | 0.636 | |
| Ho | 0.000 | 0.625 | - | 0.563 | 0.813 | - | 0.500 | 0.438 | 0.490 | |
| PIC | 0.946 | 0.927 | 0.917 | 0.908 | 0.918 | 0.952 | 0.978 | 0.962 | 0.939 | |
- Relevant data unavailable
*Statistically significant deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (P < 0.01)
Table 4.
Coefficients of genetic diversity of O. hupensis at different loci (the populations of landscape of mountains)
| Populations | Index | Microsatellite loci | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1-10 | T4-25 | D11 | T4-22 | T5-11 | T6-27 | A18 | C22 | |||
| SCLS | Na | 13 | 12 | 7 | 8 | 14 | 9 | 11 | 10 | 10.500 |
| He | 0.863 | 0.815 | 0.806 | 0.774 | 0.927 | 0.847 | 0.929 | 0.941* | 0.863 | |
| Ho | 0.412 | 0.706 | 0.188 | 0.706 | 0.882 | 0.588 | 0.071 | 0.222 | 0.472 | |
| PIC | 0.948 | 0.927 | 0.971 | 0.909 | 0.929 | 0.972 | 0.927 | 0.938 | 0.945 | |
| SCMS | Na | 15 | 15 | 12 | 10 | 16 | 10 | 21 | 14 | 14.125 |
| He | 0.925* | 0.924 | 0.892 | 0.863 | 0.941 | 0.865 | 0.964* | 0.899 | 0.909 | |
| Ho | 0.563 | 0.700 | 0.474 | 0.263 | 0.850 | 0.350 | 0.550 | 0.650 | 0.550 | |
| PIC | 0.983 | 0.924 | 0.912 | 0.965 | 0.901 | 0.908 | 0.967 | 0.961 | 0.944 | |
| SCPJ | Na | 6 | 9 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 5 | 9 | 2 | 6.000 |
| He | 0.748 | 0.883 | 0.800 | 0.446 | 0.763 | 0.580 | 0.742 | 0.667 | 0.704 | |
| Ho | 0.308 | 0.769 | 0.385 | 0.077 | 0.538 | 0.500 | 0.385 | 0.000 | 0.370 | |
| PIC | 0.981 | 0.959 | 0.923 | 0.932 | 0.972 | 0.971 | 0.927 | 0.940 | 0.951 | |
| SCXC | Na | 3 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 3.875 |
| He | 0.567 | 0.816 | 0.743 | 0.067 | 0.395 | 0.000 | 0.559 | 0.618 | 0.471 | |
| Ho | 0.000 | 0.467 | 0.800 | 0.067 | 0.400 | - | 0.067 | 0.733 | 0.362 | |
| PIC | 0.974 | 0.979 | 0.890 | 0.910 | 0.969 | 0.918 | 0.976 | 0.978 | 0.949 | |
| SCYA | Na | 9 | 13 | 5 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 7 | 0 | 5.875 |
| He | 0.869* | 0.909 | 0.756 | 0.536 | 0.732 | 0.538 | 0.802 | 0.000 | 0.643 | |
| Ho | 0.688 | 0.938 | 0.750 | 0.267 | 0.375 | 0.500 | 0.250 | - | 0.538 | |
| PIC | 0.916 | 0.928 | 0.910 | 0.912 | 0.890 | 0.935 | 0.979 | 0.966 | 0.957 | |
| YNEY | Na | 8 | 9 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 3.875 |
| He | 0.818 | 0.846 | 0.000 | 0.251 | 0.191 | 0.667 | 0.251 | 0.000 | 0.378 | |
| Ho | 0.133 | 0.333 | - | 0.133 | 0.067 | 0.000 | 0.067 | - | 0.107 | |
| PIC | 0.972 | 0.899 | 0.926 | 0.930 | 0.929 | 0.927 | 0.972 | 0.967 | 0.941 | |
| YNWS | Na | 6 | 8 | 6 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 1 | 5.375 |
| He | 0.779 | 0.862 | 0.801 | 0.159 | 0.833 | 0.500 | 0.848 | 0.000 | 0.598 | |
| Ho | 0.333 | 0.750 | 0.500 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 0.417 | 0.727 | - | 0.485 | |
| PIC | 0.954 | 0.901 | 0.927 | 0.915 | 0.928 | 0.926 | 0.981 | 0.958 | 0.946 | |
- Relevant data unavailable
*Statistically significant deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (P < 0.01)
Table 5.
Coefficients of genetic diversity of O. hupensis at different loci (the populations of landscape of karst and coastal hills)
| Populations | Index | Microsatellite loci | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1-10 | T4-25 | D11 | T4-22 | T5-11 | T6-27 | A18 | C22 | |||
| GXBS | Na | 0 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 5 | 3.000 |
| He | 0.000 | 0.601 | 0.739 | 0.667 | 0.788 | 0.503 | 0.582 | 0.739* | 0.577 | |
| Ho | - | 0.556 | 0.444 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.667 | 0.111 | 0.222 | 0.286 | |
| PIC | 0.957 | 0.898 | 0.918 | 0.904 | 0.944 | 0.920 | 0.972 | 0.971 | 0.936 | |
| GXYZ | Na | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1.25 |
| He | 0.506 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.315 | 0.000 | 0.103 | |
| Ho | 0.063 | - | - | - | - | - | 0.375 | - | 0.055 | |
| PIC | 0.946 | 0.912 | 0.937 | 0.901 | 0.891 | 0.921 | 0.969 | 0.964 | 0.931 | |
| FJFZ | Na | 9 | 8 | 7 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 0 | 5.125 |
| He | 0.861 | 0.698 | 0.861 | 0.000 | 0.705 | 0.714 | 0.754 | 0.000 | 0.574 | |
| Ho | 0.364 | 0.692 | 0.364 | - | 0.538 | 0.769 | 0.231 | - | 0.493 | |
| PIC | 0.947 | 0.914 | 0.925 | 0.921 | 0.923 | 0.931 | 0.902 | 0.978 | 0.930 | |
| FJFQ | Na | 10 | 10 | 6 | 5 | 12 | 4 | 13 | 6 | 8.250 |
| He | 0.786 | 0.832 | 0.864 | 0.498 | 0.826 | 0.800* | 0.805 | 0.377 | 0.724 | |
| Ho | 0.222 | 0.158 | 0.167 | 0.444 | 0.842 | 0.667 | 0.842 | 0.053 | 0.424 | |
| PIC | 0.886 | 0.960 | 0.927 | 0.908 | 0.922 | 0.907 | 0.908 | 0.922 | 0.918 | |
- Relevant data unavailable
*Statistically significant deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (P < 0.01)
Significant deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) was observed: 47 out of 192 (24.48 %) possible single exact locus tests (P < 0.01).No significant linkage disequilibrium was found between all pairs of the eight loci examined (P < 0.01), which indicated the independent behaviour of all loci. Analysis with Genepop software showed the possible occurrence of null alleles, which may lead to deviations from HWE and result in exaggerated levels of genetic differentiation [26, 29, 30]. Null alleles may be due to flank sequence variation decreasing primer annealing efficiency, allele drop out or DNA quality [23, 31].
Genetic differences among individuals
Fit and Fst values were 54.95 and 37.62 %, respectively. This suggests that genetic differences mainly exist within populations rather than among those with unbalanced differentiation degrees (Table 6).
Table 6.
F-Statistics and gene flow for all loci
| Locus | Sample Size | Fis | Fit | Fst | Nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1-10 | 396 | 0.6107 | 0.7534 | 0.3665 | 0.4321 |
| T4-25 | 396 | 0.0569 | 0.3253 | 0.2846 | 0.6284 |
| D11 | 396 | 0.3852 | 0.6297 | 0.3977 | 0.3786 |
| T4-22 | 396 | 0.3883 | 0.6821 | 0.4803 | 0.2705 |
| T5-11 | 396 | 0.0883 | 0.3750 | 0.3144 | 0.5451 |
| T6-27 | 396 | −0.0044 | 0.4410 | 0.4435 | 0.3138 |
| A18 | 396 | 0.4368 | 0.6229 | 0.3304 | 0.5067 |
| C22 | 396 | 0.2437 | 0.5459 | 0.3996 | 0.3756 |
| Mean | 396 | 0.2721 | 0.5459 | 0.3762 | 0.4146 |
Mantel’s test of regression showed that the correlation (41.97 %) between geographic distance and genetic distance among populations is positive (R2 = 0.1011, P < 0.05) and genetic distribution of all populations accorded with the Isolation-by-distance Model (Fig. 2, Tables 7 and 8).
Fig. 2.
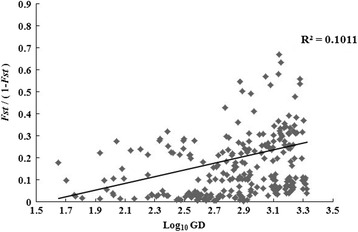
Analysis on the relationship between genetic distance and geographic distance
Table 7.
FST and geographic distance among paired O. hupensis populations of landscape of swamps and lakes
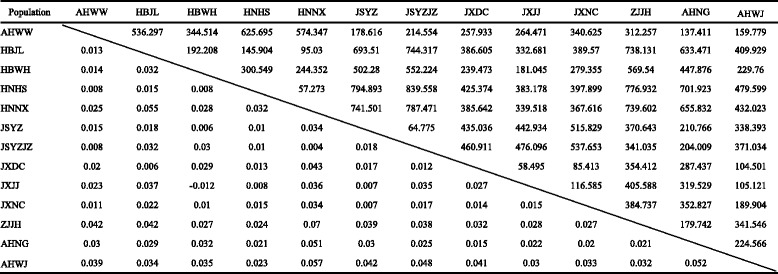
Lower triangule and upper triangule represent Fst and geographic distance (GD) / km, respectively
Table 8.
FST and geographic distance among paired O. hupensis populations of landscape of mountains, karst and Coastal hills
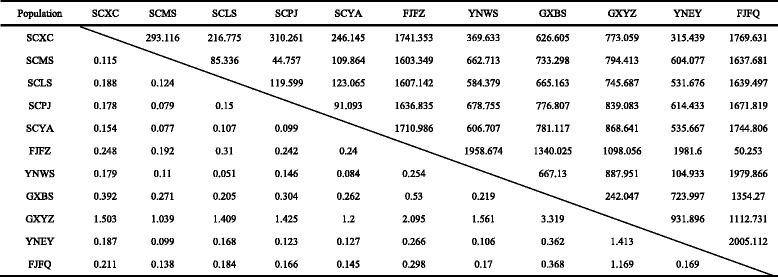
Lower triangule and upper triangule represent Fst and geographic distance (GD) / km, respectively
Genetic parameters of the four groups from different landscapes (i.e. lakes and marshes, high mountains, Karst and coastal Hills) showed that Na ranged from 2.063 to 11.452, He from 0.465 to 0.852 and Ho from 0.274 to 0.492. The group from the Karst landscape had the lowest value in all three indices, which indicated its low differentiation degree. AMOVA displayed that variations of O. hupensis mainly exists among individuals, which accounted for 60.58 % of total variations, and that of among individuals within populations, among populations within groups and among groups were only 26.60, 8.04 and 4.78 %, respectively (Table 9). This suggests that there is no significant genetic differentiation among groups.
Table 9.
Analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) for the Oncomelania hupensis
| Source of variation | Degree of freedom | Sum of squares | Variance components | Percentage of variation/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Among group | 3 | 15.653 | 0.02386 | 4.78 |
| Among populations within groups | 20 | 35.115 | 0.04015 | 8.04 |
| Among individuals within populations | 333 | 189.196 | 0.13282 | 26.60 |
| Within individuals | 357 | 108.000 | 0.30252 | 60.58 |
| Total | 713 | 347.964 | 0.49935 |
UPGMA cluster analysis for the 24 O. hupensis populations based genetic distance showed that the populations spread in the landscape of middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River (HBWH, JSYZ, JXNC, HNHS, JXJJ, AHWW, HBJL, JXDC, HNNX, JSYZJZ, ZJJH, AHNG and AHWJ) clustered together first and then gathered with the populations of high mountains (SCMS, SCYA, SCPJ, YNEY, SCLS, YNWS and SCXC), coastal hills (FJFQ and FJFZ) and Karst land form (GXBS and GXYZ) successively (Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
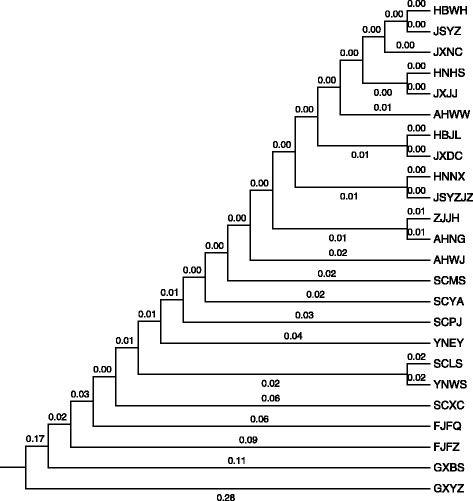

UPGMA cluster analysis of 24 O. hupensis populations
Discussion
Oncomelania hupensis is the sole intermediate host for transmitting Schistosoma japonicum in mainland China [32], and it is widely distributed in the southern region of the Yangtze River valley. Significant genetic variations have developed in O. hupensis from different geographic populations due to their distribution range, complexity of breeding environment and geographical location.
In this research, The genetic differentiation of four different landscape groups of O. hupensis were studied through eight screened polymorphic microsatellite DNA loci. This information is pertinent because it further improve our understanding on the effect of genetic diversities on the distribution of O. hupensis. This will ultimately help boost our surveillance activities and also strengthen the control of schistosomiasis transmission in China. genetic indices were tested aross eight microsatellite DNA loci. The mean Fis value for the 24 populations examined was 0.272, indicating a deficiency of heterozygotes and frequent inbreeding within populations, which is likely due to the small range of activity of O. hupensis. A total of 47 microsatellite DNA loci deviated from the Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium demonstrating a serious lack of heterozygotes. Possible explanations that may account for this include: activities of migration and inbreeding, drug pressure, gene mutation and null alleles. However, it is currently unclear which one is the dominant factor contributing to this phenomenon [33]. No significant linkage disequilibrium was found between all pairs of the eight loci, clearly showing the independent behaviour of all loci. Null alleles were found at all eight polymorphic loci. This may be due to: 1) mismatching of primer pairs: mutations in microsatellite DNA sites critical for binding with primers leads to abnormal amplification 2) losses of large alleles: the superiority of short alleles restrict amplification of long fragments or 3) differences in DNA quality: unevenness of templates character obstruct amplification in some loci [26, 31, 34]. Null alleles could implicate genetic diversity parameters for populations such as excess of homozygote individuals, reduction of Ho and He and increase of genetic distance and Fis; moreover, it leads to inaccuracy of parent analysis [30–37].
The abundance of the number of heterozygotes and the amount of genetic information in a population is directly proportional to the PIC value [38, 39]. Result shows that PIC was greater than 0.5 at every locus, and the mean value (0.947) from all populations was higher than (0.764) obtained from previous result [23]. This signifies that all the eight loci screened were highly polymorphic.
Furthermore, this study reveals that the average Fst for all loci was 0.376, which means that 37.6 % of genetic variation was among populations and 72.4 % was among individuals within populations. The analysis of AMOVA displayed that genetic variation among individuals (60.58 %) were far higher than that within populations (26.60 %), while among populations and among groups are (8.04 %) and (4.78 %) respectively. This implies that, genetic diversity is strongly derived from among-individuals rather than among-populations. However, the average Fst (0.376) and genetic variation among populations (8.04 %) were higher than values obtained from the previous results (0.048 and 4.8 %) respectively, revealing genetic variation among populations increased along with geographical distance [23]. The Mantel test demonstrated an apparent positive correlation between genetic distance and geographical distance. The genetic structure between geographical populations is embodied with some degree of independence. For example, the geographical distance between the HBWH and JSYZ populations located in the lake region was far, but with low degree of variation. This could possibly be related to the genetic differentiation principally being among individuals within populations rather than among geographic locations for the populations in Lakes and Marshes landscape.
The phylogenetic tree constructed by UPGMA also showed that populations in neighboring geographical locations generally cluster together, which was consistent with the Mantel test results. The cluster sequence of geographical populations showed us that the population from the karst landscape of Guangxi autonomous region maybe the most original one, then the population from the littoral hill part of the Fujian province, the population from the mountainous region of the Sichuan and Yunnan provinces and the population from the region of swamps and lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, respectively. Regarding as the largest population spread throughout the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River [7], the populations from different provinces also crossed cluster, these include, between Hubei and Jiangsu, Hunan and Jiangxi, and Zhejiang and Anhui, which may be as a result of O. hupensis spreading along the river within the large population, or gene drifting for surged water flow in the lakes and marshes landscape [34]. Then this branch clustered with the populations of Sichuan and Yunnan province successively. Furthermore, the major branch clustered with the populations of Fujian and Guangxi province in turn, this agrees with the conclusion of four landscape populations relationships from previous studies using SSR-PCR [40] and DNA sequence markers [7, 41, 42].
Conclusion
This study has shown that the genetic diversity of O. hupensis, an important snail intermediate host of S. japonicum in China mainly originates from among-individuals rather than among-populations. It also reveals that the populations within subspecies have closer consanguinity than between subspecies in the mass, nevertheless, genetic variations exist within subspecies. These findings further provide important information on genetic structure of O. hupensis and strengthen our knowledge about diffusion trend and tracking to the source of Oncomelania in mainland China. Ultimately, these findings will help us develop more effective guidelines for controlling the spread and distribution of Oncomelania and consequently prevent the transmission of Schistosomiasis in China. Our data offers a better understanding of the genetic differentiation of Oncomelania hupensis, enhancing our ability to effective and efficient surveillance of Schistosomiasis.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81101280),the National Special Science and Technology Project for Major Infectious Diseases of China (Grant No. 2012ZX10004-220 and 2012ZX10004-201), Public Health Overseas Fund, Bureau of Health, Shanghai (No. GWHW201216), China-UK Global Health Support Programme (Grant No.: GHSP-CS-OP1-01)
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they do not have competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
WG, SL and BW conceived the study; WG, BW and SL performed the field collection, statistical analyses and wrote the manuscript; MA, BW, DR and XZ revised the manuscript and gave approval of the version to be published. All the authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Contributor Information
Wei Guan, Email: sg690287@sina.cn.
Shi-Zhu Li, Email: Lisz@chinacdc.cn.
Eniola Michael Abe, Email: abeeniola11@gmail.com.
Bonnie L. Webster, Email: bonw@nhm.ac.uk
David Rollinson, Email: dr@nhm.ac.uk.
Xiao-Nong Zhou, Email: zhouxn1@chinacdc.cn.
References
- 1.Wang L, Utzinger J, Zhou XN. Schistosomiasis control: experiences and lessons from China. Lancet. 2008;372:1793–5. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61358-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Li SZ, Luz A, Wang XH, Xu LL, Wang Q, Qian YJ, et al. Schistosomiasis in China: acute infections during 2005–2008. Chin Med J (Engl) 2009;122:1009–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Utzinger J, Zhou XN, Chen MG, Bergquist R. Conquering schistosomiasis in China: the long march. Acta Trop. 2005;96:69–96. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2005.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wang LD, Chen HG, Guo JG, Zeng XL, Hong XL, Xiong JJ, et al. A strategy to control transmission of Schistosoma japonicum in China. N Engl J Med. 2009;360:121–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0800135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Attwood SW, Upatham ES, Zhang YP, Yang ZQ, Southgate VR. A DNA-sequence based phylogeny for triculine snails (Gastropoda: Pomatiopsidae: Triculinae), intermediate hosts for Schistosoma (Trematoda:Digenea): Phylogeography and the origin of Neotricula. J Zool. 2004;262:47–56. doi: 10.1017/S0952836903004424. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhou YB, Zhao GM, Peng WX. Spatial genetic correlation analyses of Schistosome japonicum intermediate hosts within Oncomelania hupensis (Gastropoda: Rissooidea) from mainland China based on amplified fragment length polymorphisms. Fudan Univ J Med Sci. 2007;34:207–12. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Li SZ, Wang YX, Yang K, Liu Q, Wang Q, Zhang Y, et al. Landscape genetics: the correlation of spatial and genetic distances of Oncomelania hupensis, the intermediate host snail of Schistosoma japonicum in mainland China. Geospat Health. 2009;3:221–31. doi: 10.4081/gh.2009.222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhou YB, Yang MX, Zhao GM, Wei JG, Jiang QW. Oncomelania hupensis (Gastropoda: Rissooidea), intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum in China: genetics, molecular phylogeny based on amplified fragment length polymorphisms. Malacologia. 2007;49:367–82. doi: 10.4002/0076-2997-49.2.367. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Davis GM, Zhang Y, Hua GY, Spolsky C. Population genetics and systematic status of Oncomelania hupensis (Gastropoda: Pomatiopsidae) throughout China. Malacologia. 1995;37:133–56. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Li SZ, Wang Q, Qian YJ, Zhang Y, Zhou XN. Subspecies differentiation of Oncomelania hupensis in Mainland of China. Chin J Schisto Control. 2009;21:150–3. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhou YB, Jiang QW, Zhao GM, Yuan HC. Subspecies differentiation of Oncomelania hupensis from Mainland China. Chin J Schisto Control. 2007;19:485–7. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Shi CH, Wilke T, Davis GM, Xia MY, Qiu CP. Population genetics, micro-phylogeography, ecology, and infectivity of Chinese Oncomelania hupensis hupensis (Gastropoda: Rissooidea: Pomatiopsidae) in the Miao River system: is there a relationship to shell sculpture? Malacologia. 2002;44:333–47. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schlotteröer C, Amos B, Tautz D. Conservation of polymorphic simple sequence loci in cetacean species. Nature. 1991;354:63–5. doi: 10.1038/354063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Guo W, Shen ZR. The application of microsatellite DNA markers in entomology. Biotechnology. 2004;14:60–1. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Penaa HFJ, Vitalianoa SN, Beltrameb MAV, Pereirac FEL, Gennaria SM, Soaresa RM. PCR-RFLP genotyping of Toxoplasma gondii from chickens from EspíritoSanto state, Southeast region, Brazil: New genotypes and a new SAG3 marker allele. Vet Parasitol. 2013;192:111–7. doi: 10.1016/j.vetpar.2012.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Webster BL, Webster JP, Gouvras AN, Garba A, Lamine MS, Diaw OT, et al. DNA 'barcoding' of Schistosoma mansoni across sub-Saharan Africa supports substantial within locality diversity and geographical separation of genotypes. Acta Trop. 2013;128:250–60. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2012.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Webster BL, Culverwell CL, Khamis IS, Mohammed KA, Rollinson D, Stothard JR. DNA barcoding of Schistosoma haematobium on Zanzibar reveals substantial genetic diversity and two major phylogenetic groups. Acta Trop. 2013;128:206–17. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2012.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Feng QQ, Sui ZH, Zhang XC, Kong FN. Study on microsatellite markers of Gracilaria lemaneiformis. P Ocean Univ Chin. 2010;40:77–81. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhang YP, Wang W, Su B, Fan ZY, Zhang HM, He TM. Screening and application on microsatellite makers of the giant panda. Zoological Res. 1995;16:301–6. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang L, Fan Y, Ma YJ. Isolation of Microsatellite DNA and the Polymorphic Locus Screening from Phlebotomus chinensis (Diptera: Psychodidae) Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis. 2009;27:503–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Li SZ, Wang YX, Ma YJ, Wang Q, Liu Q, Wu Y. Isolation and charaterization of polymorphic microsatellite markers of Oncomelania hupensis. Chin J Schisto Control. 2010;22:122–5. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Li Z, Li SZ, Wang Q, Qian YJ, Liu Q, Yang P. Isolation and characterization of 15 new microsatellite markers in Oncomelania hupensis, the snail intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum in mainland China. Int J MolSci. 2012;13:5844–50. doi: 10.3390/ijms13055844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhou YB, Zhao GM, Wei JG, Jiang QW. Genetic diversity in 19 Chinese populations of Oncomelania hupensis (Gastropoda: Rissooidea) detected by simple sequence repeat-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Chin J Epidemiol. 2007;28:859–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li SZ, Zhang L, Liu Q, Lv S, Wang Q, Qian YJ. Study on the Genetic Differences among Oncomelania hupensis Population in Middle and Lower Reaches of Yangtze River using Microsatellite DNA Markers. Chin J Parasitol Parasit Dis. 2012;30:268–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cui B, Guan W, You P, Li SZ. Fine-scale population genetic structure of Oncomelania hupensis based on microsatellite DNA markers. Chin J Zoonoses. 2014;30:701–8. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ma L, Li SZ, Yang P, You P, Zhou XN. Comparison of five different methods of extracting genomic DNA from Oncomelania hupensis. Chin J Pathogen Biol. 2011;6:129–32. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S. Arlequin (version 3.0): an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform Online. 2007;1:47–50. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Khan HA, Arif IA, Bahkali AH, Al Farhan AH, AlHomaidan AA. Bayesian, maximum parsimony and UPGMA models for inferring the phylogenies of antelopes using mitochondrial markers. Evol Bioinform Online. 2008;4:263–70. doi: 10.4137/ebo.s934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.DeSousa SN, Finkeldey R, Gailing O. Experimental verification of microsatellite null alleles in Norway spruce (Picea abies [L.] Karst.): Implications for population genetic studies. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 2005;23:113–9. doi: 10.1007/BF02772701. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chapuis MP, Estoup A. Microsatellite null alleles and estimation of population differentiation. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:621–31. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msl191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wen YF, Uchiyama K, Han WJ, Ueno S, Xie WD, Xu GB. Null alleles in microsatellite markers. Bio diversity Science. 2013;21:117–26. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Davis GM, Zhang Y, Guo YH, Spolsky C. Systematic status of Oncomelania Hupensis (Gastropoda: Pomatiopsidae) throughout China. Stud Mar Sin. 1997;39:89–95. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhou YB, Zhao GM, Wei JG, Jiang QW. Study on the genetic diversty among populations of schistosome intermediate hosts within Oncomelania hupensis (Gastropoda: Pomatiopsidae) in mainland China. Chin J Epidemiol. 2006;27:865–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dakin EE, Avise JC. Microsatellite null alleles in parentage analysis. Heredity. 2004;93:504–9. doi: 10.1038/sj.hdy.6800545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lemer S, Rochel E, Planes S. Correction method for null alleles in species with variable microsatellite flanking regions, a case study of the black-lipped pearl oyster Pinctada margaritifera. J Hered. 2011;102:243–6. doi: 10.1093/jhered/esq123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jones AG, Ardren WR. Methods of parentage analysis in natural populations. Mol Ecol. 2003;12:2511–23. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-294X.2003.01928.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Moriguchi Y, Taira H, Tani N, Tsumura Y. Variation of paternal contribution in a seed orchard of Cryptomeria japonica determined using microsatellite markers. Can J For Res. 2004;34:1683–90. doi: 10.1139/x04-029. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liao XL, Yu XM, Tan DQ, Tong JG. Microsatellite DNA analysis of genetic diversity of grass carp in Yangtze River system. Acta Hydrobiol Sin. 2005;29:113–9. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yan LN, Zhang DX. Effects of sample size on various genetic diversity measures in population genetic study with microsatellite DNA markers. Acta Zool Sin. 2004;50:279–90. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Niu AO, Xiong YW. Studies on the genetic variation of Oncomelania hupensis with SSR-PCR. Chin J Parasit Dis Control. 2002;15:230–3. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhao QP, Jiang MS, Littlewood DT, Nie P. Distinct genetic diversity of Oncomelania hupensis, intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum in mainland China as revealed by ITS sequences. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2010;4:e611. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Attwood SW, Ibaraki M, Saitoh Y, Nihei N,Janies DA, Comparative Phylogenetic Studies on Schistosoma japonicum and Its Snail Intermediate Host Oncomelania hupensis: Origins, Dispersal and Coevolution. PLoS Negl Trop Dis,2015;9(7):e0003935. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0003935 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]


