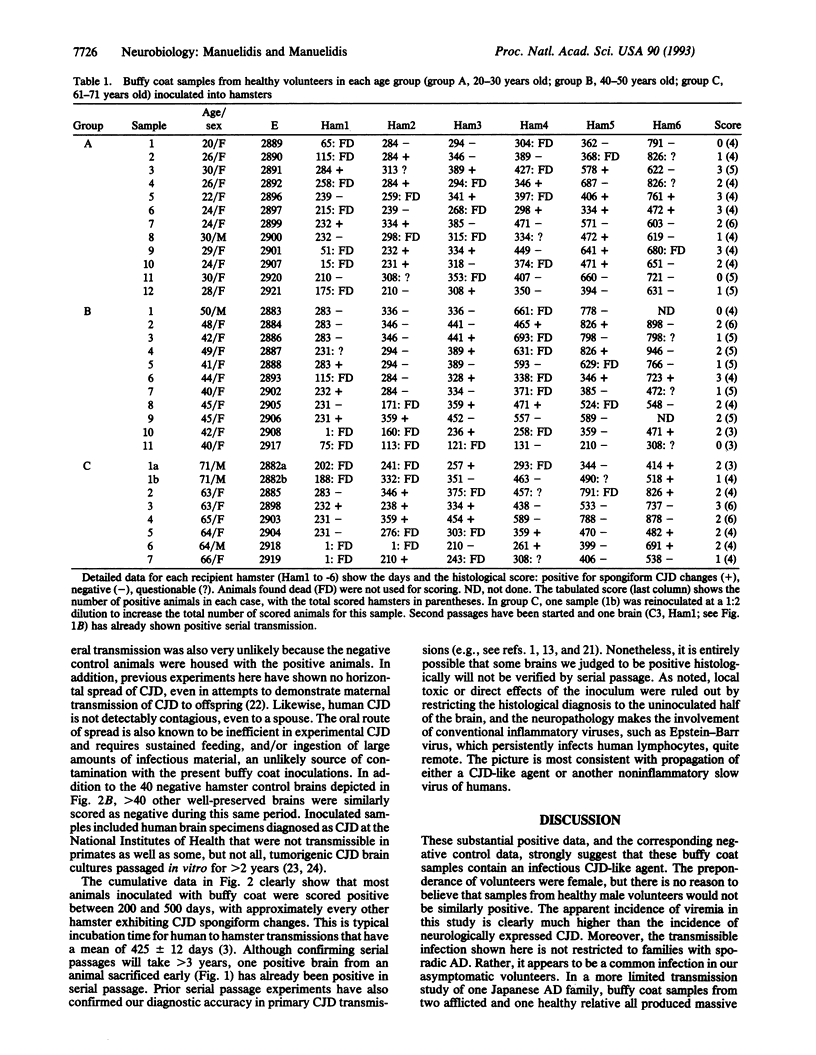
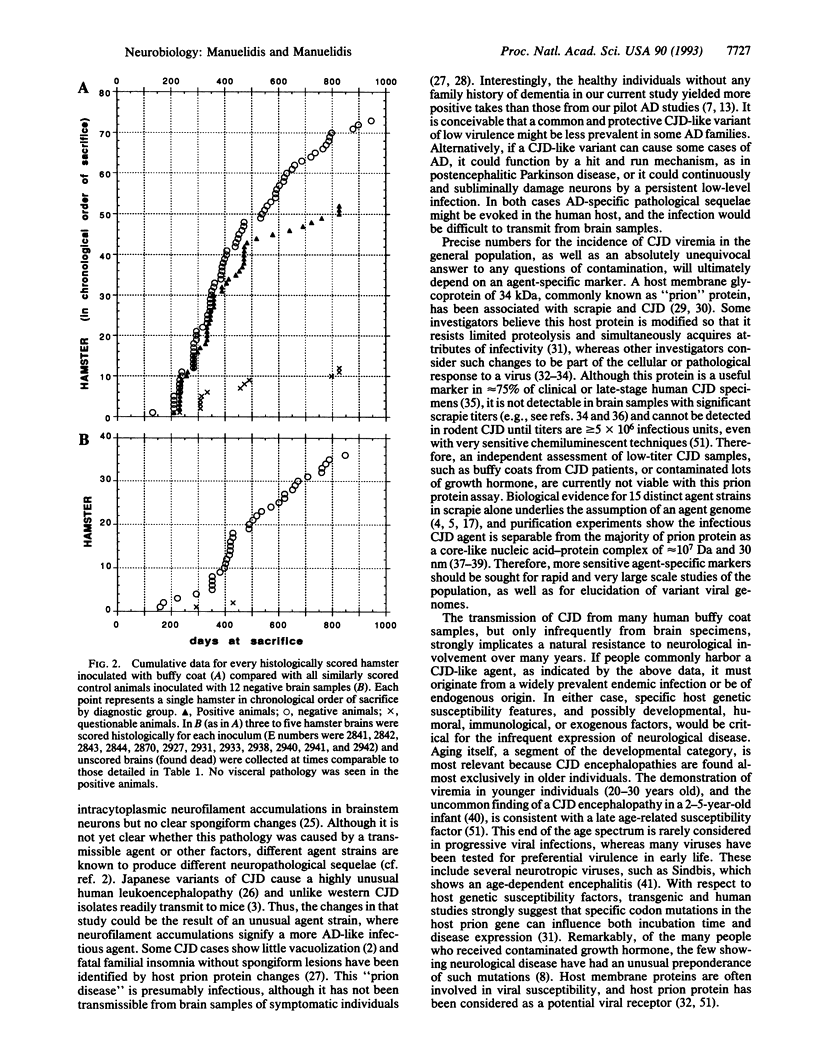
Abstract
The etiology of most human dementias is unknown. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD), a relatively uncommon human dementia, is caused by a transmissible virus-like agent. Molecular markers that are specific for the agent have not yet been defined. However, the infectious disease can be transmitted to rodents from both brain and infected buffy coat (blood) samples. To determine whether human CJD infections are more widespread than is apparent from the low incidence of neurological disease, we attempted to transmit CJD from buffy coat samples of 30 healthy volunteers who had no family history of dementing illness. Primary transmissions from 26 of 30 individuals produced CJD-like spongiform changes in the brains of recipient hamsters at 200-500 days postinoculation. This positive evidence of viremia was found for individuals in all age groups (20-30, 40-50, and 61-71 years old), whereas 12 negatively scored brain samples failed to produce similar changes in hamsters observed for > 900 days in the same setting. We suggest that a CJD agent endemically infects humans but only infrequently produces an infectious dementia. Disease expression is likely to be influenced by several host factors in combination with viral variants that have altered neurovirulence.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akowitz A., Manuelidis E. E., Manuelidis L. Protected endogenous retroviral sequences copurify with infectivity in experimental Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Arch Virol. 1993;130(3-4):301–316. doi: 10.1007/BF01309662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akowitz A., Sklaviadis T., Manuelidis E. E., Manuelidis L. Nuclease-resistant polyadenylated RNAs of significant size are detected by PCR in highly purified Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease preparations. Microb Pathog. 1990 Jul;9(1):33–45. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90038-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allsop D., Ikeda S., Bruce M., Glenner G. G. Cerebrovascular amyloid in scrapie-affected sheep reacts with antibodies to prion protein. Neurosci Lett. 1988 Oct 5;92(2):234–239. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(88)90067-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown P., Coker-Vann M., Pomeroy K., Franko M., Asher D. M., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Diagnosis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease by Western blot identification of marker protein in human brain tissue. N Engl J Med. 1986 Feb 27;314(9):547–551. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198602273140904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce M. E., McConnell I., Fraser H., Dickinson A. G. The disease characteristics of different strains of scrapie in Sinc congenic mouse lines: implications for the nature of the agent and host control of pathogenesis. J Gen Virol. 1991 Mar;72(Pt 3):595–603. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-72-3-595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang J., Rohwer R. G. Clostridium difficile infection in adult hamsters. Lab Anim Sci. 1991 Dec;41(6):548–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czub M., Braig H. R., Diringer H. Replication of the scrapie agent in hamsters infected intracerebrally confirms the pathogenesis of an amyloid-inducing virosis. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jul;69(Pt 7):1753–1756. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-7-1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. G., Fraser H., McConnell I., Outram G. W., Sales D. I., Taylor D. M. Extraneural competition between different scrapie agents leading to loss of infectivity. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):556–556. doi: 10.1038/253556a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. G., Fraser H., Outram G. W. Scrapie incubation time can exceed natural lifespan. Nature. 1975 Aug 28;256(5520):732–733. doi: 10.1038/256732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. G., Young G. B., Stamp J. T., Renwick C. C. An analysis of natural scrapie in Suffolk sheep. Heredity (Edinb) 1965 Nov;20(4):485–503. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1965.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H. Sustained viremia in experimental hamster scrapie. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1984;82(1-2):105–109. doi: 10.1007/BF01309373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. T., McFarland H. F., Levy S. E. Age-dependent resistance to viral encephalitis: studies of infections due to Sindbis virus in mice. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):257–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H., Walker C. A., Fraser H. The genomic identity of different strains of mouse scrapie is expressed in hamsters and preserved on reisolation in mice. J Gen Virol. 1989 Aug;70(Pt 8):2017–2025. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-8-2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda Y., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Amyx H. L., Gajdusek D. C. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in mice: persistent viremia and preferential replication of virus in low-density lymphocytes. Infect Immun. 1983 Jul;41(1):154–161. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.1.154-161.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little B. W., Brown P. W., Rodgers-Johnson P., Perl D. P., Gajdusek D. C. Familial myoclonic dementia masquerading as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol. 1986 Aug;20(2):231–239. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manetto V., Medori R., Cortelli P., Montagna P., Tinuper P., Baruzzi A., Rancurel G., Hauw J. J., Vanderhaeghen J. J., Mailleux P. Fatal familial insomnia: clinical and pathologic study of five new cases. Neurology. 1992 Feb;42(2):312–319. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.2.312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis E. E., Fritch W. W., Kim J. H., Manuelidis L. Immortality of cell cultures derived from brains of mice and hamsters infected with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):871–875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis E. E., Gorgacs E. J., Manuelidis L. Viremia in experimental Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Science. 1978 Jun 2;200(4345):1069–1071. doi: 10.1126/science.349691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
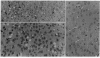
- Manuelidis E. E., Gorgacz E. J., Manuelidis L. Interspecies transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease to Syrian hamsters with reference to clinical syndromes and strains of agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3432–3436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis E. E., Kim J. H., Mericangas J. R., Manuelidis L. Transmission to animals of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease from human blood. Lancet. 1985 Oct 19;2(8460):896–897. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis E. E., Manuelidis L. Experiments on maternal transmission of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in guinea pigs. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1979 Feb;160(2):233–236. doi: 10.3181/00379727-160-40425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis E. E., Manuelidis L. Search for a transmissible agent in Alzheimer's disease: studies of human buffy coat. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1991;172:275–280. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76540-7_16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis E. E., Manuelidis L. Suggested links between different types of dementias: Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Alzheimer disease, and retroviral CNS infections. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord. 1989 Spring-Summer;3(1-2):100–109. doi: 10.1097/00002093-198903010-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Murdoch G., Manuelidis E. E. Potential involvement of retroviral elements in human dementias. Ciba Found Symp. 1988;135:117–134. doi: 10.1002/9780470513613.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Sklaviadis T., Manuelidis E. E. Evidence suggesting that PrP is not the infectious agent in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):341–347. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Tesin D. M., Sklaviadis T., Manuelidis E. E. Astrocyte gene expression in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5937–5941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Valley S., Manuelidis E. E. Specific proteins associated with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and scrapie share antigenic and carbohydrate determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4263–4267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch G. H., Sklaviadis T., Manuelidis E. E., Manuelidis L. Potential retroviral RNAs in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1477–1486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1477-1486.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleszak E. L., Murdoch G., Manuelidis L., Manuelidis E. E. Growth factor production by Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease cell lines. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3103–3108. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3103-3108.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted R. A., Langley R., Roelke M. E., Goeken R. M., Adger-Johnson D., Goff J. P., Albert J. P., Packer C., Laurenson M. K., Caro T. M. Worldwide prevalence of lentivirus infection in wild feline species: epidemiologic and phylogenetic aspects. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):6008–6018. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.6008-6018.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren R. B., Moss E. G., Racaniello V. R. Identification of two determinants that attenuate vaccine-related type 2 poliovirus. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1377–1382. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1377-1382.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryden E. B., Lipman N. S., Taylor N. S., Rose R., Fox J. G. Clostridium difficile typhlitis associated with cecal mucosal hyperplasia in Syrian hamsters. Lab Anim Sci. 1991 Dec;41(6):553–558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklaviadis T. K., Manuelidis L., Manuelidis E. E. Physical properties of the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease agent. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1212–1222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1212-1222.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklaviadis T., Dreyer R., Manuelidis L. Analysis of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease infectious fractions by gel permeation chromatography and sedimentation field flow fractionation. Virus Res. 1992 Dec;26(3):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(92)90016-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda M., Nishimura T., Kudo T., Tanimukai S., Tada K. Buffy coat from families of Alzheimer's disease patients produces intracytoplasmic neurofilament accumulation in hamster brain. Brain Res. 1991 Jun 14;551(1-2):319–321. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)90949-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi J., Ohta M., Koga M., Sato Y., Kuroiwa Y. Transmission of chronic spongiform encephalopathy with kuru plaques from humans to small rodents. Ann Neurol. 1979 Jun;5(6):581–584. doi: 10.1002/ana.410050616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xi Y. G., Ingrosso L., Ladogana A., Masullo C., Pocchiari M. Amphotericin B treatment dissociates in vivo replication of the scrapie agent from PrP accumulation. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):598–601. doi: 10.1038/356598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]