Abstract
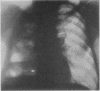
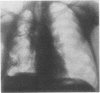
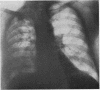
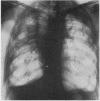
Pleural aspergillosis occurs mostly in established cases of pleural empyema with a broncho-pleural fistula. Ten such patients are reported here: in all, Aspergillus fumigatus infection was related to tuberculosis. In three cases with an active, sputum-positive tuberculous process the pleural empyema was a complication of spontaneous pneumothorax in two, and of lung resection in one. In two cases the empyema occurred as a complication of tuberculous pleuritis, but A. fumigatus infection was noted only after the sputum had become negative for tubercle bacilli. In five patients with inactive tuberculosis, the empyema was a late complication of pneumothorax therapy. The diagnosis of pleural aspergillosis is made on the basis of microscopical examination and culture of A. fumigatus in the pleural pus. The cultures were positive in seven of the 10 cases presented. In two cases in which the culture was negative microscopical examination of the pus revealed the presence of numerous fungal hyphae which was evidence of fungal necrosis. In one case the diagnosis was not made until necropsy. Serum precipitin tests with filtrates of A. fumigatus are further valuable evidence of aspergillous infection. Of 10 presented patients, this test was positive in all seven cases in which it was done. The treatment of pleural aspergillosis by local instillation of nystatin or amphotericin B was effective in six out of seven cases in which it was used.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARLOW D. Aspergillosis complicating pulmonary tuberculosis. Proc R Soc Med. 1954 Oct;47(10):877–877. doi: 10.1177/003591575404701009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOURCHON J., LANCESTRE G. ASPERGILLOME PLEURAL. J Fr Med Chir Thorac. 1964 Sep-Oct;18:679–688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREOUR P., LAUMONIER P., CARRE J. C., POTAUX L., MORVAN A. [On a voluminous intra-pleural aspergilloma]. J Fr Med Chir Thorac. 1963 May-Jun;17:419–425. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLEBIOWSKI A. K. Pleural aspergillosis following resection for pulmonary tuberculosis. Tubercle. 1958 Apr;39(2):111–112. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(58)80028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luizy J., Mathey J., Le Brigand H., Galey J. J. Technique d'irrigation pleurale sous dépression continue dans le traitement des pyothorax. (Premiers résultats cliniques) Rev Tuberc Pneumol (Paris) 1966 Apr;30(4):393–416. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD O., DIEUDONNE P., TARDIEU P. LES ASPERGILLOSES PULMONAIRES POST-OP'ERATOIRES. J Fr Med Chir Thorac. 1964 Jul-Aug;18:579–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOCHOCKY S. Infection of pneumonectomy space with Aspergillus fumigatus treated by "nystatin". Dis Chest. 1959 Nov;36:554–556. doi: 10.1378/chest.36.5.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TARDIEU P., DIEUDONNE P., MONOD O., ATCHOARENA J. B. ASPERGILLOMES PLEURAUX. J Fr Med Chir Thorac. 1964 Jul-Aug;18:591–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]