Abstract
The results obtained from two radiological methods of determining total lung capacity (TLC) (Kovach's parabo oid and Barnhard's ellipsoid) were compared with those obtained with the body plethysmograph. Determinations of TLC were made in four groups of subjects: group 1 consisted of 26 miners most of whom had simple pneumoconiosis; group 2 consisted of 12 normal subjects; group 3 consisted of eight subjects who had a variety of chest disease, but with no demonstrable parenchymal or pleural opacification; and group 4 consisted of 19 subjects with miscellaneous diseases, all showing demonstrable infiltration or opacification.
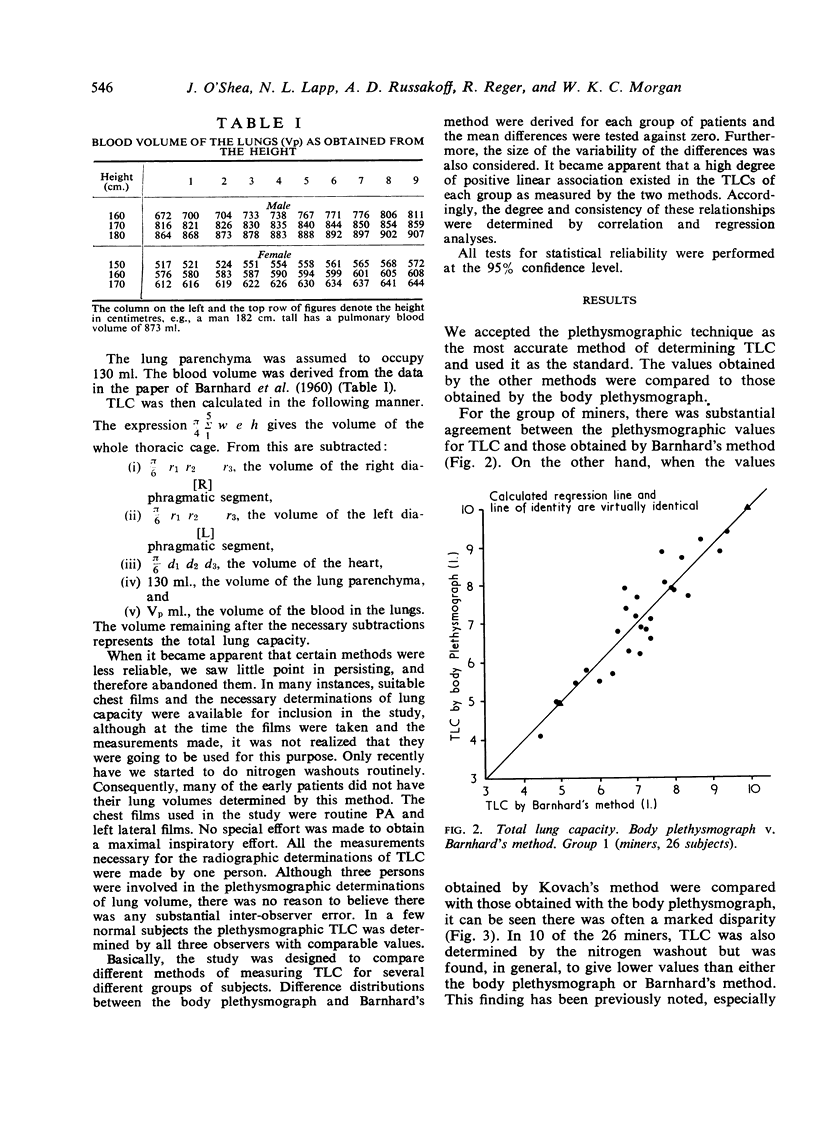
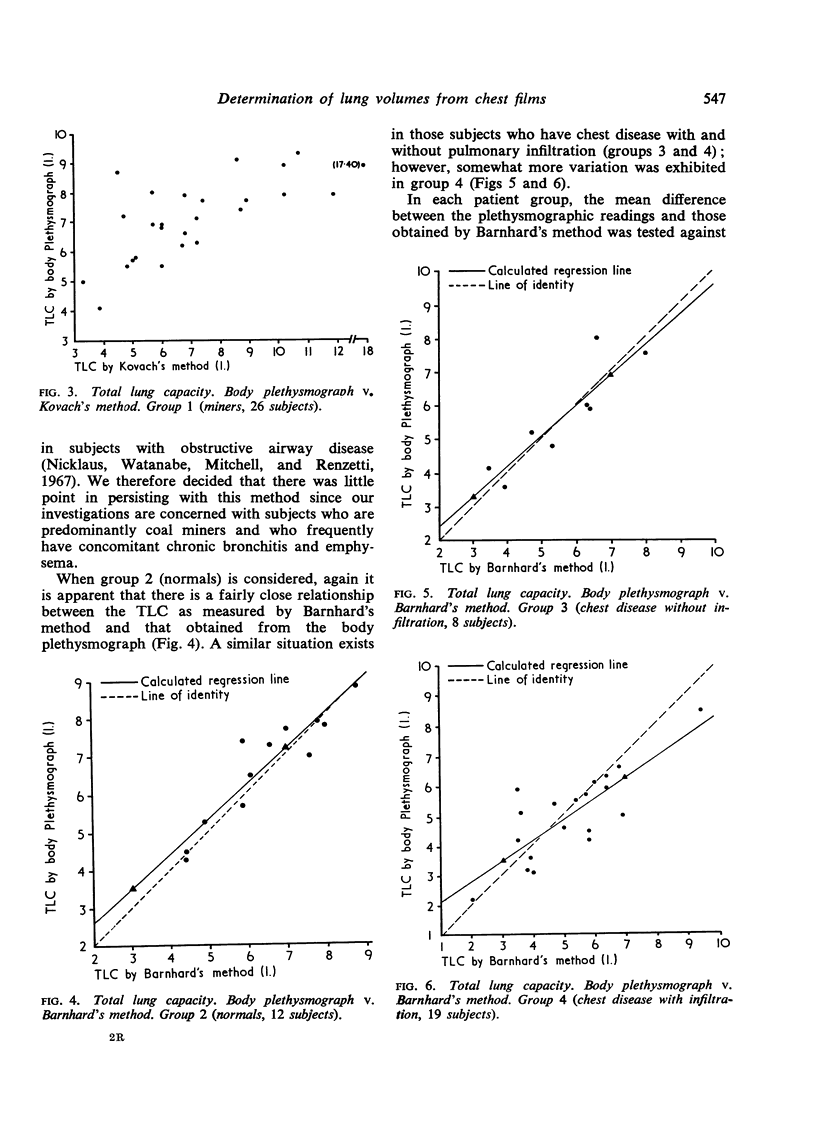
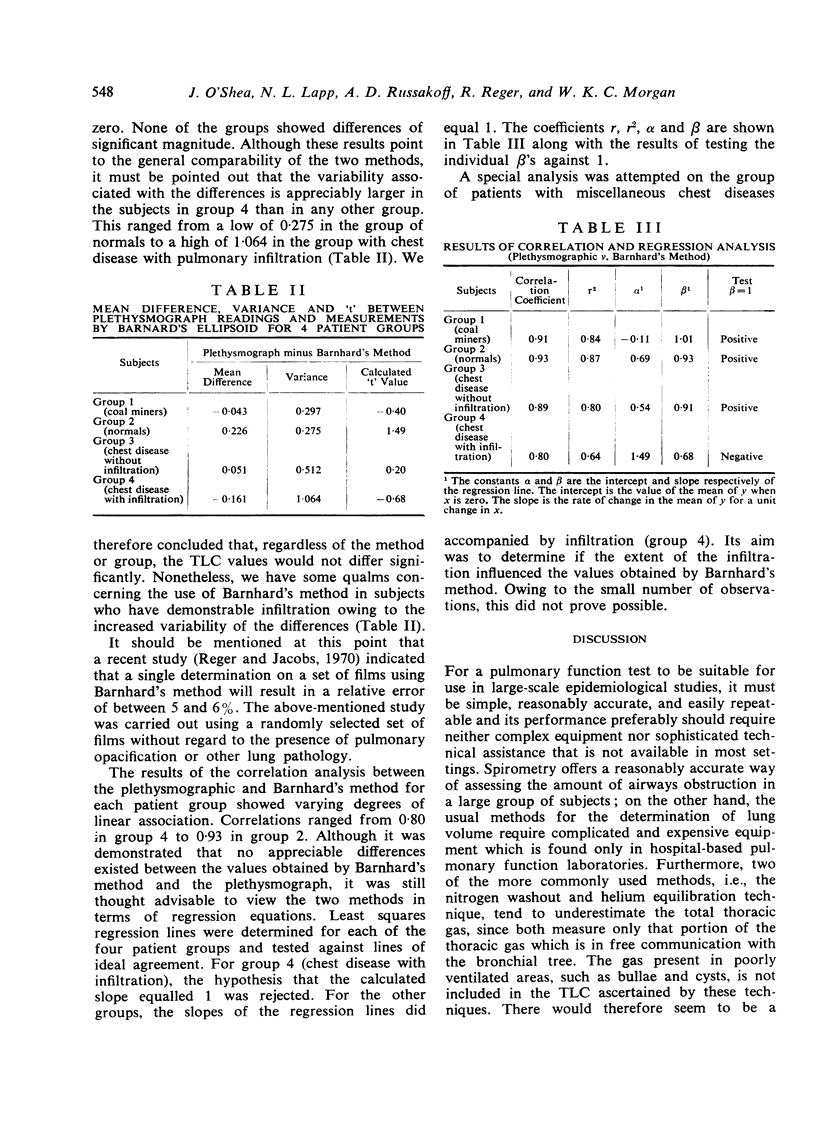
The values obtained by the method of Kovach and his colleagues often differed markedly from the plethysmographic determinations, and it became apparent that this method was not sufficiently accurate. On the other hand, the technique of Barnhard and his colleagues gave results that were essentially similar to, and as far as we can say interchangeable with, those obtained by the body plethysmograph in groups 1, 2, and 3. In subjects with marked pulmonary opacification or infiltration, the disparity between Barnhard's method and the plethysmograph tended to be more sizeable. It was concluded that Barnhard's method for determining total lung capacity is accurate and could be applied to epidemiological surveys.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNHARD H. J., PIERCE J. A., JOYCE J. W., BATES J. H. Roentgenographic determination of total lung capacity. A new method evaluated in health, emphysema and congestive heart failure. Am J Med. 1960 Jan;28:51–60. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(60)90222-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBOIS A. B., BOTELHO S. Y., BEDELL G. N., MARSHALL R., COMROE J. H., Jr A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume: a comparison with a nitrogen washout method for measuring functional residual capacity in normal subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Mar;35(3):322–326. doi: 10.1172/JCI103281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling R. C., Cournand A., Richards D. W. STUDIES ON THE INTRAPULMONARY MIXTURE OF GASES. III. AN OPEN CIRCUIT METHOD FOR MEASURING RESIDUAL AIR. J Clin Invest. 1940 Jul;19(4):609–618. doi: 10.1172/JCI101163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaensler E. A., Wright G. W. Evaluation of respiratory impairment. Arch Environ Health. 1966 Feb;12(2):146–189. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1966.10664355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurtado A., Fray W. W. STUDIES OF TOTAL PULMONARY CAPACITY AND ITS SUB-DIVISIONS. II. CORRELATION WITH PHYSICAL AND RADIOLOGICAL MEASUREMENTS. J Clin Invest. 1933 Sep;12(5):807–823. doi: 10.1172/JCI100541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACH J. C., AVEDIAN V., MORALES G., POULOS P. Lung compartment determination. J Thorac Surg. 1956 Apr;31(4):452–457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklaus T. M., Watanabe S., Mitchell M. M., Renzetti A. D., Jr Roentgenologic, physiologic and structural estimations of the total lung capacity in normal and emphysematous subjects. Am J Med. 1967 Apr;42(4):547–553. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



