Abstract
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is one of the most common causes of liver dysfunction worldwide, and its prevalence is highly associated with genetic susceptibility. The transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 (TM6SF2) E167K variant represents a general genetic determinant of hepatic triglyceride content and lobular inflammation, and its presence appears to be directly involved in the pathogenesis and development of NAFLD. Although this variant appears to be a novel powerful modifier in the development of NAFLD, whether it is associated with an increased risk of NAFLD-related liver fibrosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains to be determined. The aim of this review is to describe the functions of the TM6SF2 E167K variant and its association with NAFLD, with particular emphasis on the underlying mechanisms of its role in the development and progression of NAFLD. Additionally, the links between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and NAFLD-related liver fibrosis and HCC will be discussed.
Keywords: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, TM6SF2, E167K variant, Polymorphism
Introduction
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) represents one of the most common chronic liver diseases and has emerged as a prevalent public health concern worldwide.1,2 NAFLD can present as simple fatty liver, characterized by excess hepatic triglyceride content (HTGC) in the absence of excessive ethanol consumption,3 and is generally considered a benign pathological process. However, approximately 20% of NAFLD patients display hepatocellular injury and lobular inflammation, designated nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). NASH may even progress to liver cirrhosis and/or hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). These conditions have been demonstrated to confer increased liver-related mortality.4–6 Furthermore, NAFLD, which may be a hepatic manifestation of metabolic syndrome,7 can result in a variety of extrahepatic complications, including type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and cardiovascular disease (CVD).5
Generally, NAFLD is considered a complex disorder in which gene variants and environmental factors interact to determine disease phenotypes.8–10 The predisposition to accumulate hepatic triglycerides varies considerably among individuals, partly as a result of genetic susceptibility.11 Previously, genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have shown that a nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) in the patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3 (PNPLA3, also known as adiponutrin) gene, is significantly associated with the development and progression of NAFLD.12–18 The associated polymorphism encodes an isoleucine to methionine substitution at residue 148 (I148M). However, NAFLD is not caused by individual SNPs or genes but by multiple susceptibility genes. A recent exome-wide association study published as a letter in Nature Genetics identified a potential association between a transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 (TM6SF2) polymorphism (or rs58542926 c.449 C>T) and increased HTGC, as quantified by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H-MRS).19 The polymorphism resulted in a peptide in which glutamate is replaced with lysine at residue 167 (E167K). It has been reported that a variant within the neurocan (NCAN) gene (rs2228603 C>T), which is in strong linkage disequilibrium (D’=0.926, r2=0.798) with the TM6SF2 E167K variant, is also associated with radiologically and histologically characterized NAFLD in both GWAS20,21 and candidate-gene studies.22 Kozlitina and colleagues, for the first time, determined that the causative variant affecting HTGC was the TM6SF2 E167K variant and not NCAN,19 thereby explaining the association of the NCAN locus with altered lipid metabolism. Subsequently, several studies have investigated the link between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and NAFLD.23–25 This review summarizes current knowledge pertaining to the functions of the TM6SF2 E167K variant and its association with NAFLD. In particular, we focus on the underlying mechanisms of the variant in the development and progression of NAFLD. In addition, the associations between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and NAFLD-related liver fibrosis and HCC are discussed.
Function of TM6SF2 gene and the TM6SF2 E167K variant
TM6SF2, a gene with unknown biological function, is located on chromosome 19 and encodes a protein containing 351 amino acids, with 7–10 transmembrane domains predicted by protein pattern and domain prediction software.26 TM6SF2 is highly expressed in the liver, small intestine, and kidney, whereas its levels are relatively lower in other tissues.19,27 Mahdessian et al. performed a protein subcellular localization study with confocal microscopy and observed that TM6SF2 protein was predominantly localized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC) in the human hepatoma cell lines, Huh7 and HepG2.26
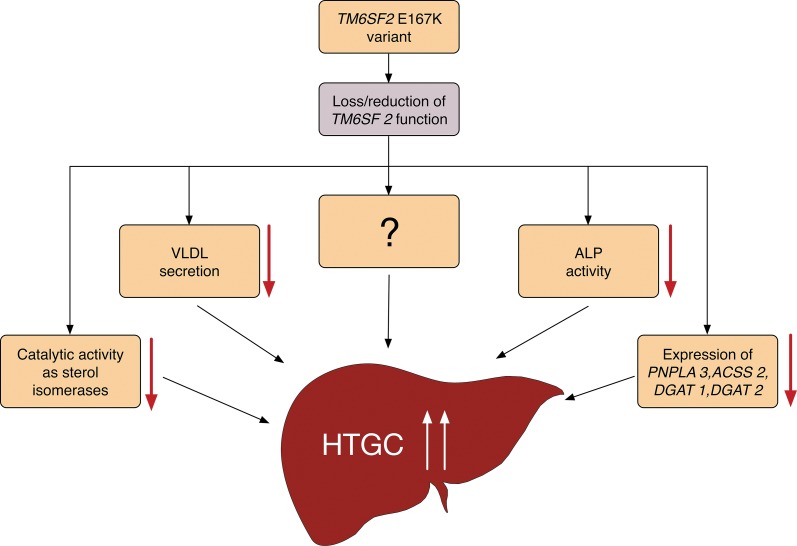
Identification of the physiological functions of the TM6SF2 gene is critical to understand the role of this gene in the development of diseases, such as NAFLD. However, the specific molecular functions of the TM6SF2 gene remain unclear, and, despite extensive investigation, no functionally characterized proteins have been identified. The TM6SF2 E167K variant (p.Glu167Lys substitution) has been demonstrated to reduce the expression of the TM6SF2 protein by 46% in Huh7 cells.19 In a study of histologically proven NAFLD patients, carriers of the TM6SF2 E167K variant had decreased mRNA and protein expression of TM6SF2 in the liver.25 Moreover, functional studies showed that TM6SF2 activity is crucial for the secretion of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL)19,26,28 and the activity of serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP).19 Kozlitina and colleagues reported that recombinant adeno-associated viral (AAV) vectors expressing short hairpin RNAs mediated >90% hepatic inhibition of TM6SF2 mRNA, accompanied with a 3-fold increase in HTGC and a 50% decrease in VLDL secretion, as well as a reduction in intestinal ALP activity.19 Furthermore, a subsequent study confirmed that TM6SF2 inhibition significantly reduced the expression of a number of genes (e.g. PNPLA3, ACSS2, DGAT1, and DGAT2) that play important roles in triglyceride synthesis and increased hepatic lipid droplet area and size.26 Sanchez-Pulido and Ponting identified a novel functional domain, the EXPERA domain, which may possess catalytic activities as sterol isomerases.29 In light of these findings, we speculate that the TM6SF2 E167K variant may act as a loss of function mutation that enhances the accumulation of lipid content in the liver (Fig. 1). Briefly, the TM6SF2 E167K variant is associated with a reduction in TM6SF2 function, which results in an increase in HTGC (by reducing VLDL secretion),19,26,28 ALP activity,19 expression of some lipid metabolism-related genes (e.g. PNPLA3, ACSS2, DGAT1, and DGAT2),26 catalytic activities of sterol isomerases,29 and/or other unidentified molecular mechanisms. However, the mechanism by which the TM6SF2 E167K variant impairs VLDL secretion has not yet been determined.
Fig. 1. Hypothetical molecular mechanism of hepatic triglyceride content accumulation associated with the TM6SF2 E167K variant.
ACSS2, acetyl-CoA short chain synthetase 2; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; DGAT1, diacylglycerol acyltransferase1; DGAT2, diacylglycerol acyltransferase2; HTGC, hepatic triglyceride content; PNPLA3, patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3; TM6SF2, transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2; VLDL, very-low-density lipoprotein.
Association between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and NAFLD
In 2014, Kozlitina and colleagues explored for the first time genetic variants associated with predisposition to NAFLD in an exome-wide association study (the Dallas Heart Study).19 They observed that the TM6SF2 E167K variant, a nonsynonymous SNP, was a powerful determinant of HTGC in a multi-ancestry, multi-ethnic, and population-based cohort.19 Interestingly, the association between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and the hepatocyte triglyceride remodeling protein was independent of the effect of the PNPLA3 I148M variant,19 which was deemed a major common genetic modifier of NAFLD.30 In addition, the TM6SF2 E167K variant was strongly associated with increased levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT). The former variant did not, however, affect aspartate aminotransferase (AST), suggesting that the variant was associated with liver injury, since ALT is one of the most accurate markers of liver dysfunction.31
Several subsequent studies have verified the association between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and NAFLD in multi-ethnic groups, both in adults23–25,32,33 and children (Table 1).34 Wang et al.24 carried out a case-control, community-based study of 768 Chinese NAFLD patients and healthy controls and demonstrated that, despite its low frequency, the TM6SF2 E167K variant was significantly associated with NAFLD (p<0.001). This association remained significant upon occurrence of the PNPLA3 I148M (rs738409) polymorphism (p<0.001) and the NCAN rs2228603 polymorphism (p=0.001); the latter was also identified as a risk factor of NAFLD.20 Similarly, in an earlier study, Wong et al. reported that the TM6SF2 variant was detected in four out of 920 Chinese subjects. These four subjects had increased hepatic fat content, and two of them had NAFLD.32 These findings were replicated in a cohort of 300 Finnish subjects. The hepatic fat content in the analyzed subjects was significantly higher in carriers of the TM6SF2 variant than in noncarriers.33 In a study of 226 histopathologically proven NAFLD patients in Argentina, Sookoian and colleagues observed that the TM6SF2 E167K variant was closely associated with the degree of hepatic steatosis, as measured by liver biopsy; and the effect was independent of age, sex, body mass index (BMI), and PNPLA3 I148M polymorphism.25 More recently, a study of 1,074 European Caucasian patients with histologically characterized NAFLD of different stages showed that the TM6SF2 variant was associated with increased risk of pronounced steatosis (odds ratio [OR]=1.379, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.019–1.865; p=0.037).23
Table 1. Studies evaluating the association between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and non-alcohol fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
| Author and year | Ref. | Population/ethnicity/country | N | Age | Diagnosis criteria | Key findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kozlitina et al., 2014 | 19 | European/African/Hispanic | 2736 | Adult | 1H-MRS | Increase in HTGC and serum ALT; reduced VLDL secretion and ALP activity |
| Wong et al., 2014 | 32 | Chinese | 922 | Adult | 1H-MRS | Increased HTGC but not associated with severe liver injury |
| Zhou et al., 2014 | 33 | Finnish | 300 | Adult | 1H-MRS | Increased liver fat content |
| Wang et al., 2015 | 24 | Chinese | 768 | Adult | Ultrasonography | Increased NAFLD risk, independent of the PNPLA3 rs738409 and NCAN rs2228603 polymorphisms |
| Liu et al., 2014 | 23 | European | 349 | Adult | Liver biopsy | Associated with increased risk of greater steatosis |
| European | 725 | Adult | Liver biopsy | Confers significant greater NAFLD-related, hepatic fibrosis/cirrhosis, independent of PNPLA3 rs738409 polymorphism | ||
| European Caucasian | 99 | Adult | Liver biopsy | Increased risk of NAFLD-HCC | ||
| Dongiovanni et al., 2015 | 39 | European | 1201 | Adult, pediatric | Liver biopsy | Increased susceptibility to NASH and advanced fibrosis, independent of the PNPLA3 rs738409 but protects against cardiovascular disease |
| Sookoian et al., 2015 | 25 | Argentinean | 361 | Adult | Liver biopsy | Associated with the degree of liver steatosis but not lobular inflammation or fibrosis |
| Grandone et al., 2015 | 34 | Italian | 1010 | Pediatric | Ultrasonography | Associated with steatosis and higher ALT levels |
ALP, alkaline phosphatase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; 1H-MRS, hydrogen magnetic resonance spectroscopy; HTGC, hepatic triglyceride content; NCAN, neurocan; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; PNPLA3, patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3; TM6SF2, transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2; VLDL, very-low-density lipoprotein.
Recently, three studies have reported an inconsistent association between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and steatosis in the presence of chronic hepatitis C (CHC).35–37 Coppola et al. carried out a study in a cohort of 148 consecutive biopsy-proven CHC patients with different hepatitis C virus (HCV) genotypes and demonstrated that the score of liver steatosis (as assessed by a partially modified Kleiner scoring system for NAFLD35,38) was higher in patients with the TM6SF2 E167K variant (1.9±1.3) than in patients with the TM6SF2 167E allele (1.1±1.1, p=0.02).35 In agreement with Coppola’s study, Milano and colleagues established a link between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and severe steatosis (p=0.038). This finding was independent of age, gender, HCV-genotype 3, BMI, T2DM, alcohol intake, ancestry, and the PNPLA3 I148M polymorphism.36 However, in a large Caucasian cohort of 694 biopsied genotype 1 CHC patients, carriers of the TM6SF2 E167K variant exhibited a similar distribution of steatosis severity compared to non-carriers (p=0.63).37 This finding was in contrast to the two previous studies.35,36 Several factors may contribute to the conflicting results in these studies, including the different HCV genotypes, the number of enrolled patients, and differences in the histological assessments.
In a study of 1,010 obese children, the TM6SF2 E167K variant was reported to predispose children to NAFLD. In the same study, the TM6SF2 E167K variant was significantly associated with steatosis and higher levels of ALT.34 However, this association in children needs to be confirmed in well-designed studies that include larger and multiple ethnic pediatric NAFLD patients with matched healthy children.
TM6SF2 E167K variant in the progression of NAFLD/NASH
NASH is considered the potentially progressive and fatal form of NAFLD, which may result in dramatically increased risks of developing cirrhosis, HCC, and/or other end-stage liver diseases.4 Therefore, the prognosis of NAFLD patients is largely determined by whether or not NASH can be controlled or even reversed. The detailed pathogenesis of NASH, however, remains unclear, and thus, strategic management of NASH is still lacking.
Recent studies have explored the association between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and NASH.23,39 Liu et al. confirmed in a study of 349 biopsy-proven patients that the TM6SF2 E167K variant was associated with the severity of histological NASH (p=0.039) and a greater risk of NAFLD-related liver fibrosis (p<0.001). This result was independent of gender, age, BMI, T2DM, and the PNPLA3 I148M polymorphism.23 Furthermore, in a large cross-sectional cohort of 1,201 subjects with histologically confirmed NASH, Dongiovanni et al. observed that carriers of the TM6SF2 E167K variant had significantly increased susceptibility to NASH (OR=1.84, 95% CI: 1.23–2.79; p=0.003) and advanced fibrosis (OR=2.08, 95% CI: 1.20–3.55; p=0.008). These results were independent of the PNPLA3 I148M variant.39 However, the effect of the TM6SF2 E167K variant on fibrosis severity was abolished after conditioning for NASH. In addition, this study also showed, for the first time, the associations of this variant with hepatocellular ballooning (p=0.036), lobular necroinflammation (p=0.040), and the full spectrum of fibrosis severity (p=0.022).39
The association between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and fibrosis was not replicated in two recent studies.25,32 Sookoian and colleagues, recruited 226 histopathologically proven NAFLD patients and demonstrated that the TM6SF2 E167K variant was not associated with severity of fibrosis (OR=0.95; 95% CI: 0.66–1.36; p=0.77), lobular inflammation (OR=0.85; 95% CI: 0.60–1.20; p=0.34), or hepatocellular ballooning (OR=1.08; 95% CI: 0.78–1.50; p=0.64).25 Furthermore, Wong et al. performed a study on 920 Chinese patients and reported that carriers of the TM6SF2 E167K variant did not exhibit increased fibrosis relative to noncarriers. This was assessed using transient elastography.32 It is possible that the inconsistent results may be partially due to the low frequency of the TM6SF2 E167K variant in these two studies.25,32 The frequency of the variant was 0.4% and 8.6%, respectively, and only four and 15 patients with fibrosis were carriers of the TM6SF2 E167K variant, respectively. In conclusion, there is a minor association between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and fibrosis. However, further well-designed studies that include larger numbers and multiple ethnic NAFLD patients are required to evaluate fully this association.
Even if there is a link between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and NASH/fibrosis, the underlying specific mechanism by which the TM6SF2 E167K variant plays a role in NASH/fibrosis remains unclear. Several studies have confirmed that dietary cholesterol and dysregulated cholesterol metabolism play a crucial role in the development and severity of hepatic inflammation and NASH.41,42 However, another study demonstrated that accumulation of hepatic triglyceride may not be directly hepatotoxic in mice with methionine and choline diet-induced NASH.40 In addition, Marí et al. reported that mitochondrial free cholesterol accumulation participated in the development of NASH as a first hit, by sensitizing hepatocytes to inflammatory cytokine-mediated death through the depletion of mitochondrial glutathione.43 Free cholesterol has been shown to sensitize the main source of extracellular matrix in fibrosis,44 hepatic stellate cells, to transforming growth factor β-mediated activation through enhancement of Toll-like receptor 4 signaling, resulting in exacerbation of hepatic fibrosis.45 Based on the available findings, the TM6SF2 E167K variant may contribute to the development and progression of NASH and/or NAFLD-associated hepatic fibrosis. This is likely to occur following the regulation of cholesterol metabolism and not the accumulation of triglyceride. However, whether progressive liver disease is related to cholesterol and/or triglyceride retention needs to be further investigated.
Finally, Liu and colleagues reported that the TM6SF2 E167K variant also confers increased predisposition to NAFLD-related HCC (OR=1.922, 95% CI: 1.31–2.81; p<0.001).23 However, this association was not apparent when risk factors, including gender, age, presence of T2DM, and cirrhosis, were considered (p=0.42). However, it should be noted that this study recruited only 99 Northern European Caucasian patients, where TM6SF2 E167K is a low-frequency (i.e. minor allele frequency) variant. Thus, further investigation including a larger cohort of NAFLD-related HCC subjects is required to investigate the potential association.
Clinical implications and future research directions
As described above, a potential association between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and NAFLD has been revealed.19,23–25,32–34,39 Several studies have established that carriers of the TM6SF2 E167K variant are protected from CVD.28,39 Holmen and colleagues demonstrated that the TM6SF2 E167K variant was associated with lower circulating lipoprotein levels. The TM6SF2 E167K variant also protected against myocardial infarction (MI) in a cross-sectional study (OR=0.87, 95% CI: 0.79–0.93, p=0.005).28 Moreover, Dongiovanni et al. carried out a study in a large, prospective cohort and confirmed that the E167K carriers had a lower risk of developing carotid plaques (OR=0.49; 95% CI: 0.25–0.94) as well as a lower incidence of CVD (hazard ratio: 0.61; 95% CI: 0.39–0.95).39
The underlying mechanism linking the TM6SF2 E167K variant to an increased risk of NAFLD, but decreased risk of CVD, remains to be determined. In the future, larger well-designed studies, including multiple ethnic groups, are required to confirm the association between the TM6SF2 E167K variant and NAFLD and/or NAFLD-related metabolic syndrome (including CVD). Moreover, TM6SF2 E167K transgenic mouse models may help to explore further the physiological and pathophysiological role of this gene in the development and progression of NAFLD, providing valuable experimental data for potential therapeutic targets.
Conclusions
The TM6SF2 E167K variant, despite the low frequency of the minor allele, appears to be a novel powerful modifier associated with the development of NAFLD. Whether or not the variant is associated with an increased risk of NAFLD-related fibrosis and HCC remains to be determined. Identification of the TM6SF2 E167K variant contribution to NAFLD should help in the development of new genetic predictors for early diagnosis of NAFLD, allowing for implementation of early preventive and therapeutic strategies for NAFLD in high-risk populations. However, further investigation is required to understand the underlying mechanisms involved in this process, thus facilitating the development of clinical applications.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Qingdao Livelihood, Science and Technology Project, China (14-2-3-17-nsh) and Qingdao Key Health Discipline Development Fund. In addition, this project was supported by the Medjaden Academy & Research Foundation for Young Scientists (Grant No. MJA20150831).
Abbreviations
- 1H-MRS
proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy
- AAV
adeno-associated virus
- ALP
alkaline phosphatase
- ALT
alanine aminotransferase
- AST
aspartate aminotransferase
- CVD
cardiovascular disease
- ER
endoplasmic reticulum
- ERGIC
ER-Golgi intermediate compartment
- GWAS
genome wide association studies
- HCC
hepatocellular carcinoma
- HTGC
hepatic triglyceride content
- MI
myocardial infarction
- NAFLD
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- NASH
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- NCAN
neurocan
- PNPLA3
patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing 3
- SNP
single nucleotide polymorphism
- T2DM
type 2 diabetes mellitus
- TM6SF2
transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2
- VLDL
very-low-density lipoprotein
References
- 1.Loomba R, Sanyal AJ. The global NAFLD epidemic. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:686–690. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.171. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hyysalo J, Männistö VT, Zhou Y, Arola J, Kärjä V, Leivonen M, et al. A population-based study on the prevalence of NASH using scores validated against liver histology. J Hepatol. 2014;60:839–846. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.12.009. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gao X, Fan JG. Diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and related metabolic disorders: consensus statement from the Study Group of Liver and Metabolism, Chinese Society of Endocrinology. J Diabetes. 2013;5:406–415. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12056. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.12056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.LaBrecque DR, Abbas Z, Anania F, Ferenci P, Khan AG, Goh KL, et al. World Gastroenterology Organisation global guidelines: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014;48:467–473. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000116. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000000116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Anstee QM, Targher G, Day CP. Progression of NAFLD to diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease or cirrhosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:330–344. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.41. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Oda K, Uto H, Mawatari S, Ido A. Clinical features of hepatocellular carcinoma associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a review of human studies. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2015;8:1–9. doi: 10.1007/s12328-014-0548-5. doi: 10.1007/s12328-014-0548-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chalasani N, Younossi Z, Lavine JE, Diehl AM, Brunt EM, Cusi K, et al. The diagnosis and management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: practice guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, American College of Gastroenterology, and the American Gastroenterological Association. Hepatology. 2012;55:2005–2023. doi: 10.1002/hep.25762. doi: 10.1002/hep.25762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hirschhorn JN, Gajdos ZK. Genome-wide association studies: results from the first few years and potential implications for clinical medicine. Annu Rev Med. 2011;62:11–24. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.091708.162036. doi: 10.1146/annurev.med.091708.162036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Anstee QM, Day CP. The genetics of NAFLD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:645–655. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.182. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2013.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marzuillo P, Grandone A, Perrone L, Miraglia Del Giudice E. Understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms in the pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The role of genetics. World J Hepatol. 2015;7:1439–1443. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i11.1439. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i11.1439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dongiovanni P, Anstee QM, Valenti L. Genetic predisposition in NAFLD and NASH: impact on severity of liver disease and response to treatment. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19:5219–5238. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990381. doi: 10.2174/13816128113199990381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Romeo S, Kozlitina J, Xing C, Pertsemlidis A, Cox D, Pennacchio LA, et al. Genetic variation in PNPLA3 confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1461–1465. doi: 10.1038/ng.257. doi: 10.1038/ng.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Rotman Y, Koh C, Zmuda JM, Kleiner DE, Liang TJ. NASH CRN. The association of genetic variability in patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3 (PNPLA3) with histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;52:894–903. doi: 10.1002/hep.23759. doi: 10.1002/hep.23759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zain SM, Mohamed R, Mahadeva S, Cheah PL, Rampal S, Basu RC, et al. A multi-ethnic study of a PNPLA3 gene variant and its association with disease severity in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hum Genet. 2012;131:1145–1152. doi: 10.1007/s00439-012-1141-y. doi: 10.1007/s00439-012-1141-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Trépo E, Nahon P, Bontempi G, Valenti L, Falleti E, Nischalke HD, et al. Association between the PNPLA3 (rs738409 C>G) variant and hepatocellular carcinoma: Evidence from a meta-analysis of individual participant data. Hepatology. 2014;59:2170–2177. doi: 10.1002/hep.26767. doi: 10.1002/hep.26767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Xu R, Tao A, Zhang S, Deng Y, Chen G. Association between patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene (PNPLA3) polymorphisms and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a huge review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:9284. doi: 10.1038/srep09284. doi: 10.1038/srep09284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sookoian S, Castaño GO, Burgueño AL, Gianotti TF, Rosselli MS, Pirola CJ. A nonsynonymous gene variant in the adiponutrin gene is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease severity. J Lipid Res. 2009;50:2111–2116. doi: 10.1194/jlr.P900013-JLR200. doi: 10.1194/jlr.P900013-JLR200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sookoian S, Pirola CJ. Meta-analysis of the influence of I148M variant of patatin-like phospholipase domain containing 3 gene (PNPLA3) on the susceptibility and histological severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2011;53:1883–1894. doi: 10.1002/hep.24283. doi: 10.1002/hep.24283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kozlitina J, Smagris E, Stender S, Nordestgaard BG, Zhou HH, Tybjærg-Hansen A, et al. Exome-wide association study identifies a TM6SF2 variant that confers susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Genet. 2014;46:352–356. doi: 10.1038/ng.2901. doi: 10.1038/ng.2901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Speliotes EK, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Wu J, Hernaez R, Kim LJ, Palmer CD, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies variants associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease that have distinct effects on metabolic traits. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1001324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1001324. Epub. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shang XR, Song JY, Liu FH, Ma J, Wang HJ. GWAS-Identified Common Variants With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Chinese Children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015;60:669–674. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000662. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hernaez R, McLean J, Lazo M, Brancati FL, Hirschhorn JN, Borecki IB, et al. Association between variants in or near PNPLA3, GCKR, and PPP1R3B with ultrasound-defined steatosis based on data from the third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;11:1183–1190. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.02.011. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.02.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liu YL, Reeves HL, Burt AD, Tiniakos D, McPherson S, Leathart JB, et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 influences hepatic fibrosis progression in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4309. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5309. doi: 10.1038/ncomms5309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang X, Liu Z, Peng Z, Liu W. The TM6SF2 rs58542926 T allele is significantly associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese. J Hepatol. 2015;62:1438–1439. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.01.040. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2015.01.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sookoian S, Castaño GO, Scian R, Mallardi P, Fernández Gianotti T, et al. Genetic variation in transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 and the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and histological disease severity. Hepatology. 2015;61:515–525. doi: 10.1002/hep.27556. doi: 10.1002/hep.27556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mahdessian H, Taxiarchis A, Popov S, Silveira A, Franco-Cereceda A, Hamsten A, et al. TM6SF2 is a regulator of liver fat metabolism influencing triglyceride secretion and hepatic lipid droplet content. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:8913–8918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323785111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1323785111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dezso Z, Nikolsky Y, Sviridov E, Shi W, Serebriyskaya T, Dosymbekov D, et al. A comprehensive functional analysis of tissue specificity of human gene expression. BMC Biol. 2008;6:49. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-6-49. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-6-49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Holmen OL, Zhang H, Fan Y, Hovelson DH, Schmidt EM, Zhou W, et al. Systematic evaluation of coding variation identifies a candidate causal variant in TM6SF2 influencing total cholesterol and myocardial infarction risk. Nat Genet. 2014;46:345–351. doi: 10.1038/ng.2926. doi: 10.1038/ng.2926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sanchez-Pulido L, Ponting CP. TM6SF2 and MAC30, new enzyme homologs in sterol metabolism and common metabolic disease. Front Genet. 2014;5:439. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00439. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ruhanen H, Perttilä J, Hölttä-Vuori M, Zhou Y, Yki-Järvinen H, Ikonen E, et al. PNPLA3 mediates hepatocyte triacylglycerol remodelling. J Lipid Res. 2014;55:739–746. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M046607. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M046607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chen LZ, Xin YN, Geng N, Jiang M, Zhang DD, Xuan SY. PNPLA3 I148M variant in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Demographic and ethnic characteristics and the role of the variant in nonalcoholic fatty liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:794–802. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.794. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wong VW, Wong GL, Tse CH, Chan HL. Prevalence of the TM6SF2 variant and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese. J Hepatol. 2014;61:708–709. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.04.047. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.04.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhou Y, Llauradó G, Orešič M, Hyötyläinen T, Orho-Melander M, Yki-Järvinen H. Circulating triacylglycerol signatures and insulin sensitivity in NAFLD associated with the E167K variant in TM6SF2. J Hepatol. 2015;62:657–663. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.010. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Grandone A, Cozzolino D, Marzuillo P, Cirillo G, Di Sessa A, Ruggiero L, et al. TM6SF2 Glu167Lys polymorphism is associated with low levels of LDL-cholesterol and increased liver injury in obese children. Pediatr Obes. 2015 Apr 20; doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12032. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Coppola N, Rosa Z, Cirillo G, Stanzione M, Macera M, Boemio A, et al. TM6SF2 E167K variant is associated with severe steatosis in chronic hepatitis C, regardless of PNPLA3 polymorphism. Liver Int. 2015;35:1959–1963. doi: 10.1111/liv.12781. doi: 10.1111/liv.12781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Milano M, Aghemo A, Mancina RM, Fischer J, Dongiovanni P, De Nicola S, et al. Transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 gene E167K variant impacts on steatosis and liver damage in chronic hepatitis C patients. Hepatology. 2015;62:111–117. doi: 10.1002/hep.27811. doi: 10.1002/hep.27811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Petta S, Maida M, Grimaudo S, Pipitone RM, Macaluso FS, Cabibi D, et al. TM6SF2 rs58542926 is not associated with steatosis and fibrosis in large cohort of patients with genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C. Liver Int. 2015 Jul 17; doi: 10.1111/liv.12918. doi: 10.1111/liv.12918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, et al. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2005;41:1313–1221. doi: 10.1002/hep.20701. doi: 10.1002/hep.20701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Dongiovanni P, Petta S, Maglio C, Fracanzani AL, Pipitone R, Mozzi E, et al. Transmembrane 6 superfamily member 2 gene variant disentangles nonalcoholic steatohepatitis from cardiovascular disease. Hepatology. 2015;61:506–514. doi: 10.1002/hep.27490. doi: 10.1002/hep.27490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yamaguchi K, Yang L, McCall S, Huang J, Yu XX, Pandey SK, et al. Inhibiting triglyceride synthesis improves hepatic steatosis but exacerbates liver damage and fibrosis in obese mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2007;45:1366–1374. doi: 10.1002/hep.21655. doi: 10.1002/hep.21655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wouters K, van Gorp PJ, Bieghs V, Gijbels MJ, Duimel H, Lütjohann D, et al. Dietary cholesterol, rather than liver steatosis, leads to hepatic inflammation in hyperlipidemic mouse models of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2008;48:474–486. doi: 10.1002/hep.22363. doi: 10.1002/hep.22363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Min HK, Kapoor A, Fuchs M, Mirshahi F, Zhou H, Maher J, et al. Increased hepatic synthesis and dysregulation of cholesterol metabolism is associated with the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell Metab. 2012;15:665–674. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.004. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2012.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Marí M, Caballero F, Colell A, Morales A, Caballeria J, Fernandez A, et al. Mitochondrial free cholesterol loading sensitizes to TNF- and Fas-mediated steatohepatitis. Cell Metab. 2006;4:185–198. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.07.006. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1655–1669. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.003. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Teratani T, Tomita K, Suzuki T, Oshikawa T, Yokoyama H, Shimamura K, et al. A high-cholesterol diet exacerbates liver fibrosis in mice via accumulation of free cholesterol in hepatic stellate cells. Gastroenterology. 2012;142:152–164. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.09.049. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.09.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]