Abstract
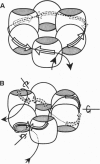
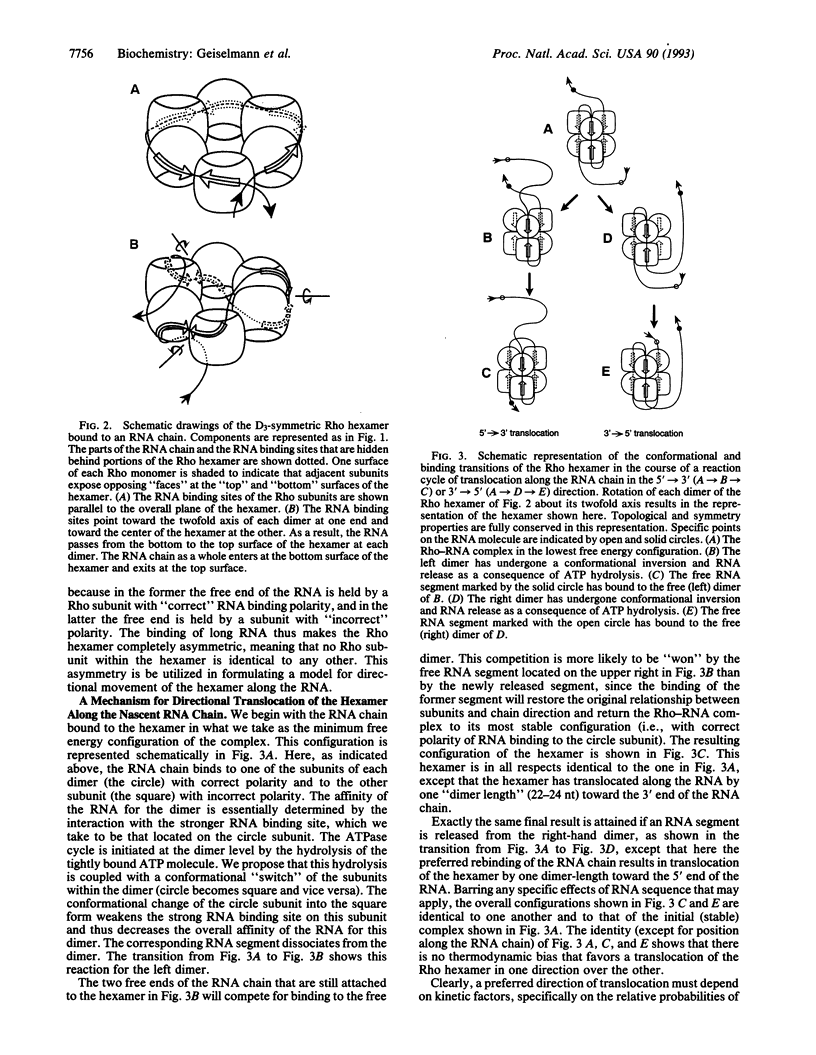
Transcription termination protein Rho of Escherichia coli interacts with newly synthesized RNA chains and brings about their release from elongation complexes paused at specific Rho-dependent termination sites. Rho is thought to accomplish this by binding to a specific Rho "loading site" on the nascent RNA and then translocating preferentially along the transcript in a 5'-->3' direction. On reaching the elongation complex, Rho releases the nascent RNA by a 5'-->3' RNA.DNA helicase activity. These translocation and helicase activities are driven by the RNA-dependent ATPase activity of Rho. In this paper we propose a mechanism for these processes that is based on the structure and properties of the Rho protein. Rho is a hexamer of identical subunits that are arranged as a trimer of asymmetric dimers with D3 symmetry. The binding of ATP and RNA to Rho also reflects this pattern; the Rho hexamer carries three strong and three weak binding sites for each of these entities. The asymmetric dimers of Rho correspond to functional dimers that can undergo conformational transitions driven by ATP hydrolysis. We propose that the quaternary structure of Rho coordinates the ATP-driven RNA binding and release processes to produce a biased random walk of the Rho hexamer along the RNA, followed by RNA.DNA helicase activity and transcript release. The proposed model may have implications for other hexameric DNA.DNA, RNA.DNA, and RNA.RNA helicases that function in replication and transcription.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alifano P., Rivellini F., Limauro D., Bruni C. B., Carlomagno M. S. A consensus motif common to all Rho-dependent prokaryotic transcription terminators. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90239-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear D. G., Andrews C. L., Singer J. D., Morgan W. D., Grant R. A., von Hippel P. H., Platt T. Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho has a two-domain structure in its activated form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1911–1915. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bear D. G., Hicks P. S., Escudero K. W., Andrews C. L., McSwiggen J. A., von Hippel P. H. Interactions of Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho with RNA. II. Electron microscopy and nuclease protection experiments. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 20;199(4):623–635. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer P. D. The binding change mechanism for ATP synthase--some probabilities and possibilities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jan 8;1140(3):215–250. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90063-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan C. A., Dombroski A. J., Platt T. Transcription termination factor rho is an RNA-DNA helicase. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):945–952. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90703-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan C. A., Steinmetz E. J., Spear P., Platt T. Specificity and efficiency of rho-factor helicase activity depends on magnesium concentration and energy coupling to NTP hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5440–5447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. Y., Galluppi G. R., Richardson J. P. Transcription termination at lambda tR1 is mediated by interaction of rho with specific single-stranded domains near the 3' end of cro mRNA. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1023–1028. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90701-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolan J. W., Marshall N. F., Richardson J. P. Transcription termination factor rho has three distinct structural domains. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5747–5754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski A. J., Brennan C. A., Spear P., Platt T. Site-directed alterations in the ATP-binding domain of rho protein affect its activities as a termination factor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18802–18809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski A. J., LaDine J. R., Cross R. L., Platt T. The ATP binding site on rho protein. Affinity labeling of Lys181 by pyridoxal 5'-diphospho-5'-adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18810–18815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dombroski A. J., Platt T. Structure of rho factor: an RNA-binding domain and a separate region with strong similarity to proven ATP-binding domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2538–2542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel D., Richardson J. P. Conformational alterations of transcription termination protein rho induced by ATP and by RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7389–7400. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farnham P. J., Platt T. A model for transcription termination suggested by studies on the trp attenuator in vitro using base analogs. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):739–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faus I., Richardson J. P. Structural and functional properties of the segments of lambda cro mRNA that interact with transcription termination factor Rho. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 5;212(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90304-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finger L. R., Richardson J. P. Stabilization of the hexameric form of Escherichia coli protein rho under ATP hydrolysis conditions. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 25;156(1):203–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90467-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galluppi G. R., Richardson J. P. ATP-induced changes in the binding of RNA synthesis termination protein Rho to RNA. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr 15;138(3):513–539. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80016-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiselmann J., Seifried S. E., Yager T. D., Liang C., von Hippel P. H. Physical properties of the Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. 2. Quaternary structure of the rho hexamer. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):121–132. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiselmann J., Yager T. D., Gill S. C., Calmettes P., von Hippel P. H. Physical properties of the Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. 1. Association states and geometry of the rho hexamer. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):111–121. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiselmann J., Yager T. D., von Hippel P. H. Functional interactions of ligand cofactors with Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. II. Binding of RNA. Protein Sci. 1992 Jul;1(7):861–873. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiselmann J., von Hippel P. H. Functional interactions of ligand cofactors with Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. I. Binding of ATP. Protein Sci. 1992 Jul;1(7):850–860. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogol E. P., Seifried S. E., von Hippel P. H. Structure and assembly of the Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho and its interaction with RNA. I. Cryoelectron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1127–1138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90923-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Restoration of termination by RNA polymerase mutations is rho allele-specific. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 5;129(2):295–304. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90283-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin D. J., Burgess R. R., Richardson J. P., Gross C. A. Termination efficiency at rho-dependent terminators depends on kinetic coupling between RNA polymerase and rho. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1453–1457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohman T. M. Escherichia coli DNA helicases: mechanisms of DNA unwinding. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Jan;6(1):5–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb00831.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowery-Goldhammer C., Richardson J. P. An RNA-dependent nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase (ATPase) associated with rho termination factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2003–2007. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowery C., Richardson J. P. Characterization of the nucleoside triphosphate phosphohydrolase (ATPase) activity of RNA synthesis termination factor p. II. Influence of synthetic RNA homopolymers and random copolymers on the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1381–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo I. A., Hough P. V., Wall J. S., Dodson M., Dean F. B., Hurwitz J. ATP-dependent assembly of double hexamers of SV40 T antigen at the viral origin of DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Apr 20;338(6217):658–662. doi: 10.1038/338658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McSwiggen J. A., Bear D. G., von Hippel P. H. Interactions of Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho with RNA. I. Binding stoichiometries and free energies. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 20;199(4):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90305-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Bear D. G., Litchman B. L., von Hippel P. H. RNA sequence and secondary structure requirements for rho-dependent transcription termination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3739–3754. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Bear D. G., von Hippel P. H. Rho-dependent termination of transcription. I. Identification and characterization of termination sites for transcription from the bacteriophage lambda PR promoter. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9553–9564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan W. D., Bear D. G., von Hippel P. H. Rho-dependent termination of transcription. II. Kinetics of mRNA elongation during transcription from the bacteriophage lambda PR promoter. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9565–9574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda T., Takanami M. Observations on the structure of the termination factor rho and its attachment to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):799–802. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reha-Krantz L. J., Hurwitz J. The dnaB gene product of Escherichia coli. I. Purification, homogeneity, and physical properties. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):4043–4050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisbig R. R., Hearst J. E. Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase transcriptional pause sites on SV40 DNA F1. Biochemistry. 1981 Mar 31;20(7):1907–1918. doi: 10.1021/bi00510a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Activation of rho protein ATPase requires simultaneous interaction at two kinds of nucleic acid-binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5760–5766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. P. Rho-dependent transcription termination. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 6;1048(2-3):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seifried S. E., Easton J. B., von Hippel P. H. ATPase activity of transcription-termination factor rho: functional dimer model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10454–10458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz E. J., Brennan C. A., Platt T. A short intervening structure can block rho factor helicase action at a distance. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18408–18413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt B. L. Escherichia coli transcription termination protein rho has three hydrolytic sites for ATP. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11130–11137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., von Hippel P. H. Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. I. ATPase activation by oligonucleotide cofactors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13940–13946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., von Hippel P. H. Escherichia coli transcription termination factor rho. II. Binding of oligonucleotide cofactors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13947–13955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yager T. D., von Hippel P. H. A thermodynamic analysis of RNA transcript elongation and termination in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 29;30(4):1097–1118. doi: 10.1021/bi00218a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Yager T. D. The elongation-termination decision in transcription. Science. 1992 Feb 14;255(5046):809–812. doi: 10.1126/science.1536005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Yager T. D. Transcript elongation and termination are competitive kinetic processes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2307–2311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]