FIG. 8.
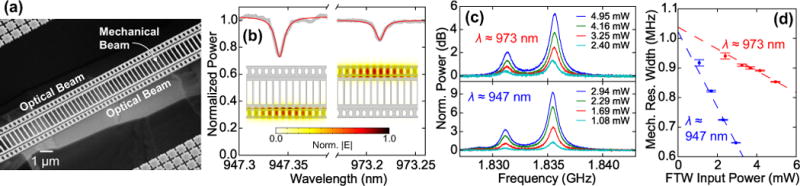
(a) SEM image of fabricated O-M-O device. (b) Separately-measured optical spectra of O-M-O device. Data are in gray, and Lorentzian fits are in red. The 947.34 nm mode (“bottom” beam) has intrinsic Qo = (1.1 ± 0.1) × 105, and the 973.21 nm mode (“top” beam) has intrinsic Qo = (1.05 ± 0.02) × 105. (insets) FEM simulations of the optical slot modes associated with bottom and top optical beams. (c) Mechanical spectra measured at different FTW input optical powers. Top spectra were acquired while optically coupled to the top beam, and bottom spectra were acquired while optically coupled to the bottom beam. (d) γm,eff/(2π) as measured via the top optical mode (red) and the bottom optical mode (blue) with respect to FTW input power. Dashed lines show weighted linear fits of γm,eff/(2π). Error bars represent the uncertainty in the fit of the mechanical spectra to a Lorentzian.
