Abstract
Purpose
Umeclidinium/vilanterol (UMEC/VI) is a novel fixed dose combination of a long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist (LAMA) and a long-acting beta 2 receptor antagonist (LABA) agent. This analysis evaluated the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of UMEC/VI compared with tiotropium (TIO), from the Spanish National Health System (NHS) perspective.
Methods
A previously published linked equations cohort model based on the epidemiological longitudinal study ECLIPSE (Evaluation of COPD Longitudinally to Identify Predictive Surrogate End-points) was used. Patients included were COPD patients with a post-bronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) ≤70% and the presence of respiratory symptoms measured with the modified Medical Research Council dyspnea scale (modified Medical Research Council ≥2). Treatment effect, expressed as change in FEV1 from baseline, was estimated from a 24-week head-to-head phase III clinical trial comparing once-daily UMEC/VI with once-daily TIO and was assumed to last 52 weeks following treatment initiation (maximum duration of UMEC/VI clinical trials). Spanish utility values were derived from a published local observational study. Unitary health care costs (€2015) were obtained from local sources. A 3-year time horizon was selected, and 3% discount was applied to effects and costs. Results were expressed as cost/quality-adjusted life years (QALYs). Univariate and probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA) was performed.
Results
UMEC/VI produced additional 0.03 QALY and €590 vs TIO, leading to an ICER of €21,475/QALY. According to PSA, the probability of UMEC/VI being cost-effective was 80.3% at a willingness-to-pay of €30,000/QALY.
Conclusion
UMEC/VI could be considered as a cost-effective treatment alternative compared with TIO in symptomatic COPD patients from the Spanish NHS perspective.
Keywords: COPD, cost-effectiveness analysis, cost-utility analysis, umeclidinium/vilanterol, tiotropium
Introduction
COPD is a highly prevalent, chronic, progressive respiratory disease. In Spain, the EPISCAN study (the Epidemiologic Study of COPD in Spain) estimated a prevalence of 10.2% in people aged between 40 and 80 years.1 It is the fourth leading cause of death worldwide and is a major cause of chronic morbidity, above diseases such as diabetes or depression.2 Chronic, progressive dyspnea is one of the most prevalent symptoms of COPD, and it is estimated that approximately 50% of patients continue to have symptoms of dyspnea despite receiving treatment.3 The presence of dyspnea is associated with deterioration in the quality of life and increased mortality, regardless of exacerbations.4,5
In addition to the impact on the patient, COPD is also associated with a high consumption of health care resources and costs. In Spain, it is estimated that the annual mean health care cost of a COPD patient varies between €1,388 and €2,154, with the main components of cost being hospitalization (44%) and drug treatment (41%).6
The goal of COPD treatment is to reduce symptoms, reduce the frequency and severity of exacerbations, and improve the prognosis and quality of life of patients.7,8 Long-acting bronchodilators, which improve lung function and reduce symptoms, are the basis of COPD maintenance drug therapy.7 There are two types of bronchodilators, long-acting β2 receptor agonists (LABA) and long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonists (LAMA), which may be used alone or in combination. In patients with higher symptoms or in whom symptoms persist despite treatment, administration of an LAMA + LABA is recommended.7,8
Recently, the fixed-dose combination of the LAMA umeclidinium bromide (UMEC) and the LABA vilanterol (VI) (Anoro® Ellipta 55/22 μg, GlaxoSmithKline SA, Brentford, United Kingdom) indicated as once-daily maintenance bronchodilator treatment to relieve symptoms in adults patients with COPD9 has been marketed in Spain, providing a new alternative treatment for symptomatic patients.
Due to the humanistic and economic burden associated with COPD, treatment decisions should be based on the analysis of the expected clinical and economic benefits. Health care resources allocation demands a rational principle and the consequent priority setting. An economic evaluation allows for a comparative analysis of alternative actions in terms of costs and health outcomes, being considered as a valuable tool for decision-making. Efficiency measured in economic evaluations is concerned with the relation between resource inputs (costs) and either intermediate outputs or final health outcomes.10
The aim of this study was to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of once-daily UMEC/VI vs the most-frequently used treatment, the LAMA tiotropium (TIO) (Spiriva® Handihaler 18 μg, Boehringer Ingelheim SA, Ingelheim am Rhein, Germany), in symptomatic COPD patients from the perspective of the Spanish National Health System (NHS).
Materials and methods
The cost-effectiveness analysis was performed using a recently published validated model of COPD disease progression that allows comparing the long-term effects and costs of different treatment options.11 This model was adapted to the Spanish settings according to guidelines for health technology assessment in Spain and international recommendations.12,13 As no experimental or interventional research involving patients was applied, and no patient data was used, no ethical approval was required.
Disease progression model description
A qualitative conceptual model (CM) of COPD was developed to identify and describe qualitative causal relationships between disease attributes, progression, and outcomes.11 In order to do so, a literature review was performed to identify any prior published CM or literature reporting on the impact and association of COPD disease attributes. After critical analysis of the literature, a draft CM was developed based on the literature and expert opinion, and it was validated by a Delphi Panel. Delphi results were reviewed by a steering group of health economists, epidemiologists, and clinicians to determine the attributes, where sufficient evidence exists for use in economic modeling.11
Thus, the disease progression CM describes the associations between the demographic characteristics of patients, the central attributes of COPD representing disease progression (lung function, symptoms, exacerbations, and exercise tolerance), and their impact on health outcomes (expressed in terms of quality-adjusted life years [QALYs]) and costs.
Associations between the attributes and health outcomes were quantified by Exuzides et al using non-linear regression models of random effects, known as risk equations, which were developed from the longitudinal epidemiological ECLIPSE (Evaluation of COPD Longitudinally to Identify Predictive Surrogate End-points) study.14–16 Risk equations represent and quantify associations between the central indicators of the disease and their impact on HRQoL and mortality. Risk equations were estimated for each of the central attributes defined in the CM: exacerbations (moderate and severe), lung function (measured by forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1]), COPD symptoms (dyspnea, cough, and/or sputum), and exercise capacity (measured by 6-minute walk test distance [6MWD]) (equations available in Exuzides et al16). They were estimated to predict the effect of baseline and longitudinal covariates on the dependent central attribute, on an annual basis. Across the risk equations, the baseline variables used were age, CVD comorbidities, “Other” comorbidities, smoking status, sex, body mass index, 6MWD, fibrinogen level, modified Medical Research Council (mMRC) grade, St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) score, and prior exacerbations. The predicted outcomes of the risk equations of central attributes were used as inputs into the final outcome equations for HRQoL (measured by SGRQ score) and mortality.16
These risk equations were brought together to estimate the progression of COPD in terms of the central attributes of the disease through to final health outcomes of (quality adjusted) life expectancy, and health service cost. The model was therefore implemented as a linked-equation model. The model starts with baseline prognostic factors and moves on to predicting the central attributes (lung function, exacerbation rate, symptoms, and exercise capacity). The baseline variables and longitudinal central associations are then used together, to predict the final health outcomes of HRQoL utility and survival.
Internal validation compared 3 years of predicted cohort experience with results from ECLIPSE. At 3 years, the model predicted a survival rate, an annual exacerbation rate, and an annual decline in FEV1, which fell within the confidence limits of the ECLIPSE data.
For adaptation to Spain, a time horizon of 3 years was selected, in line with previously published analyses.17 A discount rate of 3% was applied for future costs and effects occurring after the first year based on local recommendations.12 The study was made from the perspective of the Spanish NHS, which only takes direct health care costs into account.
The results of the cost-effectiveness analysis were expressed using the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of UMEC/VI vs TIO, calculated using the formula:
Compared options and study population
The LAMA TIO was selected as the reference comparator as it is the most-widely used treatment in Spain.18
According to the recommendations on LAMA + LABA combination therapy,7,8 COPD patients with moderate or severe impairment in lung function (post-bronchodilator FEV1 ≤70% of predicted normal values), with the presence of dyspnea (mMRC score ≥2) and a low risk of exacerbations were included. The remaining baseline characteristics of the patients with an impact on the estimated model results were defined using local studies and national statistics in order to be more representative of the Spanish population;19–21 in the cases where this was not possible, the best available published source was used (Table 1).
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the population included in the analysis
| Baseline characteristics | Base case | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Female (%) | 17 | Casanova et al19 |
| Male (%) | 83 | |
| Mean age (years) | 67 | Casanova et al19 |
| Body mass index | ||
| Low (%) | 4.6 | Casanova et al19 |
| Medium (%) | 60.3 | |
| High (%) | 35.1 | |
| ≥1 cardiovascular comorbidity (%) | 29 | Maleki-Yazdi et al22 |
| ≥1 other comorbidity (%) | 86 | |
| History of exacerbations, ≥1 (%) | 16.6 | |
| mMRC score ≥2 (%) | 100 | |
| Active smokers (%) | 29 | Casanova et al19 |
| Height (m) (mean) | 1.676 | Spanish National Health Survey21 |
| Fibrinogen (μg/mL) (mean) | 458.8 | Vestbo et al14 Agusti et al15 |
| Number of exacerbations in previous year (mean) | 0.27 | Maleki-Yazdi et al22 |
| Moderate/severe ratio | 80:20 | Hurst et al44 |
| SGRQ score (mean) | 42.7 | Almagro et al20 |
| Post-bronchodilator baseline FEV1 (%pred) (mean) | 46.4% | Maleki-Yazdi et al22 |
| Six-minute walk test (6MWT) (m) (mean) | 438 | Casanova et al19 |
Abbreviations: mMRC, modified Medical Research Council; SGRQ, St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
Clinical entry data
Effectiveness
The disease progression model allows estimating differences between treatments in terms of lung function (FEV1). Differences between UMEC/VI and TIO were determined according to the results of the 24-week phase III clinical trial that compared the efficacy of UMEC/VI and TIO in terms of trough FEV1.22 This clinical trial was a multicenter, randomized, blinded, double-dummy, parallel-group study that randomized 905 patients aged >40 years with moderate-to-very severe COPD and an established clinical history of COPD (defined by American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society guidelines). This study found an increase in trough FEV1 of 112 mL for UMEC/VI 55/22 μg compared with TIO 18 μg at 24 weeks of treatment. This difference in efficacy between treatments was applied during the first year of the time horizon, according to the study by Donohue et al,23 which showed the sustained effect of UMEC/VI on lung function at 52 weeks. As there is no published data for UMEC/VI beyond 52 weeks, a conservative scenario that assumed no difference in efficacy between the two treatments beyond that time was used.
Utilities
In the initial disease progression model,11,16 quality of life was obtained using an adjusted risk equation constructed using the SGRQ scores reported in the ECLIPSE study, and subsequently converted to utilities according to the algorithm of Starkie et al.24
In this analysis, for better adaptation to the Spanish environment, a new risk equation estimated utility values according to specific data on Spanish COPD patients obtained from an observational study that estimated utility scores in these patients.25,26 In this study, utility values were derived from the preference-based generic questionnaire EQ-5D-3L, applying weighted Spanish societal preferences, obtained from a multicenter, observational, cross-sectional study that included patients aged ≥40 years, with spirometrically confirmed COPD. The new risk equation was a saturated linear regression model explained by the variables from the observational study, which were considered to have an impact on both utility and the disease progression model (explanatory variables). These variables were sex, age, body mass index, comorbidities, smoking status, lung function, exacerbation history, symptoms measured by mMRC score, and the presence of cough and sputum (Table 2). All these variables were obtained directly from the local study except cough and sputum, which was assumed to correspond to a score of ≥3 in the first two dimensions of the COPD Assessment Test questionnaire collected in the local study.
Table 2.
Risk equation to incorporate Spanish utilities (linear regression model)
| Variables | Effect |
|---|---|
| Intercept | 0.8345 |
| Female (vs male) | −0.0875 |
| Low BMI (vs mean) | −0.0059 |
| High BMI (vs mean) | -0.0136 |
| Cardiovascular comorbidities (vs no) | −0.0074 |
| Other comorbidities (vs no) | −0.0074 |
| Smoker (vs ex-smoker) | −0.0244 |
| Age | 0.0012 |
| Number of exacerbations | −0.0291 |
| Post-bronchodilator FEV1 (%pred) | 0.0006 |
| mMRC 2–3 (vs 0–1) | −0.1541 |
| mMRC 4 (vs 0–1) | −0.5326 |
| Cough and sputum (vs no)a | −0.0672 |
Note:
Defined as answers ≥3 in the first two dimensions of the CAT (COPD Assessment Test) questionnaire.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; pred, predicted; mMRC, modified Medical Research Council.
Economic entry data
Costs were counted according to the number of exacerbations (moderate to severe), the costs of follow-up according to the frequency of dyspnea symptoms, and the cost of drug treatment. All costs were estimated in euros 2015 and were adapted from Spanish sources.
The pharmacologic costs associated with UMEC/VI and TIO were expressed in terms of the retail price plus value added tax (PTP+VAT)27 and were counted as the cost/day during the 3-year time horizon of the analysis.
To calculate the cost of exacerbations, a moderate exacerbation was defined as one requiring treatment with oral corticosteroids and/or antibiotics and a severe exacerbation as one requiring hospitalization. The costs associated with each episode were estimated from the resource use specified in the studies by Miravitlles et al,28,29 resulting in a cost of €70.86 for moderate exacerbations (considering drug costs, one visit to primary care, and one visit to emergency department for 4.3% of the patients), and €4,349.61 for severe exacerbations (considering one visit to primary care, one visit to emergency department, and 8 days of hospitalization).
There are no reported data on the annual cost associated with patient follow-up according to the frequency of dyspnea, although one UK study has estimated the costs of follow-up according to the severity of dyspnea measured by the mMRC score.30 For this reason, the following assumption of equivalence between the frequency of the symptoms of dyspnea and their severity was made:
Level 1: No symptoms per week = mMRC 0–1
Level 2: Symptoms several days per week = mMRC 2–3
Level 3: Symptoms almost daily = mMRC 4
Using this assumption, the annual cost for each level was calculated based on the annual cost of following a COPD patient in Spain,31 the distribution of the severity of dyspnea in Spain,19 and the distribution of costs in the study by Punekar et al (Table 3).30
Table 3.
Unitary costs of health care resources included in the analysis
| Type | Cost (€) | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Drug cost (PTP + VAT) | ||
| UMEC/VI – 55/22 umeclidinium/vilanterol powder for inhalation 30 doses | 70.25 | National Formulary |
| TIO – 18 μg tiotropium powder for inhalation 30 capsules | 49.06 | Listing27 |
| Cost per episode of exacerbation | ||
| Moderate exacerbation | 70.86 | Miravitlles et al28,29 |
| Severe exacerbation | 4,349.61 | |
| Annual cost of management according to symptoms | ||
| Dyspnea level 1: no symptoms per week = mMRC 0–1 | 511.18 | Punekar et al30 |
| Dyspnea stage 2: symptoms several days per week = mMRC 2–3 | 681.72 | Almagro et al20 |
| Dyspnea level 3: symptoms nearly every day = mMRC 4 | 901.7 | Sicras et al31 |
Abbreviations: PTP + VAT, retail price plus value added tax; UMEC/VI, umeclidinium and vilanterol; TIO, tiotropium; mMRC, modified Medical Research Council.
Uncertainty analysis
Deterministic and probabilistic sensitivity analyses were performed to evaluate the uncertainty of some parameters in the model results and to determine the robustness of the results.
In the deterministic sensitivity analyses, the influence of various parameters on the results of the model was estimated by individual modification. Table 4 shows the modified parameters and the new values used. In addition, to evaluate the uncertainty associated with the development of the new risk equation to obtain utilities, alternative equations were adjusted as shown in Tables S1–S3.
Table 4.
Deterministic sensitivity analysis values
| Parameter | Base case | Alternative values |
|---|---|---|
| Time horizon | 3 years | 1 year, 5 years |
| Baseline characteristics | Spanish population data, clinical development of UMEC/VI and ECLIPSE | Clinical development UMEC/VI and ECLIPSE |
| Efficacy data UMEC/VI vs TIO | 112 mL (81.144; P<0.001) (Maleki-Yazdi et al22) | 60 mL (10.109; P=0.018) (Decramer et al33) |
| Duration of efficacy | First year | First 6 months Entire time horizon (3 years) |
| Modeling of quality of life | Spanish utilities (M1) | SGRQ |
| Discount rate for costs and future events | 3% | (0%–5%) |
| Exacerbation unitary cost (moderate and severe) | Estimated from Miravitlles et al28,29 | (± 20%) |
| Follow-up cost according dyspnea levels (three levels of frequency) | Estimated from Sicras et al31 | (±20%) |
| Punekar et al30 | ||
| Almagro et al20 |
Abbreviations: UMEC/VI, umeclidinium and vilanterol; TIO, tiotropium; SGRQ, St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire; ECLIPSE, Evaluation of COPD Longitudinally to Identify Predictive Surrogate End-points.
In the probabilistic sensitivity analysis (PSA) 10,000 simulations were performed using Monte Carlo methodology32 simultaneously modifying the coefficients of all risk equations (Cholesky decomposition was considered to maintain correlation effects), the baseline characteristics (beta and normal distributions) of the patients, and the difference in efficacy between treatments (normal distribution).
All model calculations were made using Microsoft Excel 2010.
Results
Base case
The results of the cost-effectiveness analysis of UMEC/VI vs TIO after 3 years of treatment are summarized in Table 5. Compared with TIO, the improvement in lung function observed with UMEC/VI resulted in an increase of 0.03 QALY. UMEC/VI treatment resulted in additional costs of €590, mainly due to the difference in the cost of drug treatment. This resulted in an ICER of €21,475/QALY.
Table 5.
Results of base case
| UMEC/VI | TIO | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Health outcomes (QALY) | 2.025 | 1.998 | |
| Costs | €6,215 | €5,625 | |
| ICER (€/QALY) | €21,475 |
Abbreviations: UMEC/VI, umeclidinium and vilanterol; TIO, tiotropium; ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio; QALY, quality-adjusted life year.
Uncertainty analysis
The tornado diagram (Figure 1) shows the results of the deterministic sensitivity analysis described in Table 5. The ICER ranges between €20,636 and €47,428. The parameters with the greatest impact were the modification of the utility values (ICER increases if the initial equation based on the ECLIPSE study is used), the difference in efficacy between treatments (ICER increases with a decreased difference in efficacy based on Decramer et al,33 the duration of the effect (ICER decreases with increasing duration), and the time horizon considered (ICER decreases with decreasing time horizon). The other parameters considered produced no changes in the ICER.
Figure 1.
Results of the sensitivity analysis.
Abbreviations: SGRQ, St George’s Respiratory Questionnaire; UMEC/VI, umeclidinium and vilanterol; TIO, tiotropium; Min, minimum; Max, maximum.
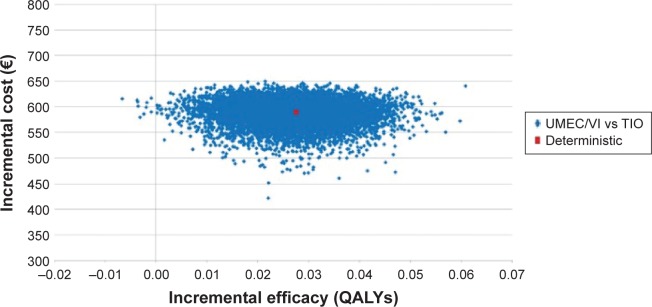
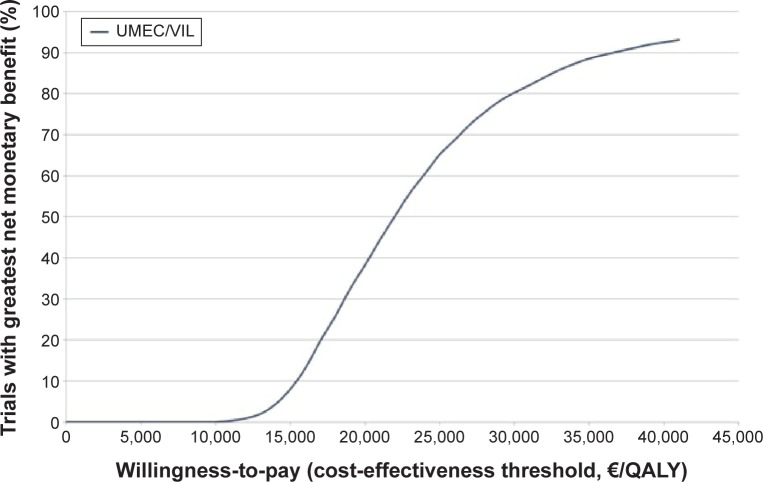
Figure 2 shows the cost-effectiveness plane with the results of the PSA: 99.9% of the simulations are located in the first quadrant, representing a higher cost and greater effectiveness of UMEC/VI vs TIO. Figure 3 shows the acceptability curve of the probability that UMEC/VI is cost-effective compared with TIO, the probability increases as the willingness to pay per QALY gained rises.
Figure 2.
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis results. Cost-effectiveness plane.
Abbreviations: QALYs, quality-adjusted life years; UMEC/VI, umeclidinium and vilanterol; TIO, tiotropium.
Figure 3.
Acceptability curve.
Abbreviations: QALY, quality-adjusted life year; UMEC/VIL, umeclidinium/vilanterol.
Discussion
In today’s health care environment, decision-making must be based not only on criteria of efficacy and safety, but also on those of efficiency. Cost-effectiveness analyses provide information on the economic value of a health intervention, generally in comparison with the mostfrequently used intervention. Thus, cost-effectiveness analyses are tools that may aid health care managers and decision makers make informed decisions. This analysis studied the economic value to the NHS of a new treatment, the combination of UMEC/VI vs TIO, the most widely used treatment for COPD in Spanish clinical practice.18
In the base case, the ICER of UMEC/VI is €21,475/QALY compared with TIO, suggesting that UMEC/VI may be considered as a cost-effective option vs TIO, as the ICER is below the threshold of €30,000/QALY generally accepted in Spain.34,35 In the PSA, UMEC/VI was a cost-effective option vs TIO in 80.3% of the simulations using the same threshold.
The QALY quantifies changes in utility over the life of the patient, and it has two components; quality and quantity of life, being the most accepted health-related utility measure. In the model developed, QALY difference observed between compared treatments was a consequence of different cumulative number of exacerbations over the time horizon analyzed, 6MWT results, percentage of patients with symptoms (dyspnea and cough and sputum), quality of life, and survival.
Various international and Spanish economic evaluations of COPD have been made.17,36–39 The efficiency of TIO has been evaluated in several studies,36–38 which have found it is a cost-effective treatment compared with other bronchodilators, such as ipratropium or salmeterol. When comparing the present analysis with those already published, it can be concluded that both methods, population, outcomes, and costs included are similar with the considered ones in the model here explained.17
The present analysis is the first to determine the cost-effectiveness of the combination of two bronchodilators compared with monotherapy in the Spanish setting. The same analysis has been carried out in the UK with similar results, showing that UMEC/VI has a high probability of being cost effective vs TIO at £30,000/QALY.40 Recently, a cost-effectiveness analysis of combined treatment with indacaterol + glycopyrronium from the perspective of the Swedish NHS has been published.41 Although in this study the comparators used were a free combination or the combination of an inhaled corticosteroid + LABA, the results support the efficient use of LAMA + LABA treatment in symptomatic patients.
Model selection is a critical factor in cost-effectiveness analyses, since the model must accurately represent the disease studied. Generally, the models used in COPD are based exclusively on pulmonary function as the basis for the transition between different health states.17 The present analysis used a previously published model of disease progression11 that incorporates exacerbations, symptoms, and exercise capacity as measures of the progression of COPD. This wider focus on the progression of COPD is in line with the latest definitions of the disease based on a multidimensional assessment that goes beyond lung function.7,8
The population included in the analysis was symptomatic COPD patients with moderate-to-very severe FEV1 impairment but with low risk of exacerbations. The use of LAMA + LABA combination treatment is recommended in patients with higher symptoms or in whom symptoms or obvious limitations in exercise persist despite receiving monotherapy.7,8 The results obtained here support this recommendation, with UMEC/VI being an efficient treatment option compared with monotherapy with TIO.
The development of a new risk equation to incorporate Spanish utilities has various positive points. First, it allows better adaptation to the Spanish setting and makes the results more robust, being the first published Spanish analysis that incorporates utility values of Spanish COPD patients. In addition, in the initial disease progression model, utility was obtained by mapping of the SGRQ; although this technique is useful and commonly used, using utility scores obtained directly from generic patient questionnaires is recommended whenever possible.25 The study used to obtain utilities25,26 did not collect the same variables as those included in the initial equation of the disease progression model. This might be considered as a limitation, but the new risk equation included all available relevant variables, and therefore provides the best explanation of the variance in utility observed in Spanish patients. To evaluate the uncertainty of including Spanish utilities, sensitivity analysis with alternative equations for obtaining utilities was made. The results obtained, shown in Table S3, were very similar, except for the M2 equation that did not take into account the effect of lung function and therefore could not distinguish effects between treatments. With respect to the initial risk equation based on the SGRQ, variations in FEV1 showed less direct impact on utility.
Despite the advantages identified, the analysis had some limitations. First, the time horizon used and the limitations of long-term extrapolations from studies of limited duration should be taken into account, particularly with respect to the duration of the effect on the improvement in lung function observed in clinical trials. Some models with a lifetime horizon assume that the benefits in lung function observed at the beginning of treatment are maintained over time.17,42 Although some studies indicate that improvements in lung function may last up to 3 years,43 this benefit has not been demonstrated in long-term studies. Therefore, most reported cost-effectiveness analyses17 use a time horizon between 1 and 3 years, maintaining the treatment effect during this time. In the present analysis, a time horizon of 3 years was selected, and a more conservative strategy was adopted in which difference in efficacy between treatments was maintained for only the first 12 months, which corresponds to the maximum duration of studies of UMEC/VI, while the costs associated with pharmacological treatment were maintained for 3 years.
Another limitation of economic evaluations is related to the quality of data. In this case, local Spanish data sources were used when available or, in their absence, the best available evidence. All assumptions were validated by the authors, and a sensitivity analysis was made to evaluate uncertainty.
Conclusion
The results of this cost-effectiveness analysis show that treatment with UMEC/VI in symptomatic COPD patients is a cost-effective option compared with TIO from the perspective of Spanish NHS, as the ICER was below the threshold commonly accepted in Spain to consider interventions as efficient.
Supplementary materials
Table S1.
Risk equations developed for utility estimation
| Risk equation | Scenario | Description |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | Base case | Saturated linear regression model |
| M2 | Sensitivity analysis | Reduction in number of variables according to goodness of fit index AIC |
| M3 | Sensitivity analysis | Grouping of frequency and severity of dyspnea: mMRC2 (vs 0–1) and mMRC3–4 (vs 0–1) |
| M4 | Sensitivity analysis | Variable cough and sputum = score ≥2 in first two items of CAT |
| M5 | Sensitivity analysis | Variable cough and sputum = score ≥4 in first two items of CAT |
Abbreviations: AIC, Akaike information criterion; mMRC, modified Medical Research Council; CAT, COPD Assessment Test.
Table S2.
Variables considered in each of the risk equations
| Base-case sensitivity analysis
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect
| |||||
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | |
| Intercept | 0.8345 | 0.9158 | 0.8526 | 0.8345 | 0.8148 |
| Female (vs male) | −0.0875 | −0.0902 | −0.0819 | −0.0875 | −0.0749 |
| Low BMI (vs mean) | −0.0059 | – | −0.0870 | −0.0059 | −0.0153 |
| High BMI (vs mean) | −0.0136 | – | −0.0305 | −0.0136 | −0.0197 |
| Cardiovascular comorbidities (vs no) | −0.0074 | – | −0.0407 | −0.0074 | −0.0023 |
| Other comorbidities (vs no) | −0.0074 | – | −0.0169 | −0.0074 | −0.0091 |
| Smoker (vs ex-smoker) | −0.0244 | – | −0.0488 | −0.0244 | −0.0338 |
| Age | 0.0012 | – | 0.0012 | 0.0012 | 0.0010 |
| Number of exacerbations | −0.0291 | −0.0298 | −0.0338 | −0.0291 | −0.0316 |
| FEV1 (%) post-bronchodilator | 0.0006 | – | 0.0004 | 0.0006 | 0.0008 |
| mMRC 2–3 (vs 0–1)a | −0.1541 | −0.1606 | −0.1089 | −0.1541 | −0.1573 |
| mMRC 4 (vs 0–1)a | −0.5326 | −0.5390 | −0.3041 | −0.5326 | −0.5275 |
| Cough and sputum (vs no)b | −0.0672 | −0.0581 | −0.0600 | −0.0672 | −0.0776 |
Notes:
In M3, grouping is mMRC 2 (vs 0–1) and mMRC 3–4 (vs 0–1).
In M4 and M5, cough and sputum are considered as equivalent to the score in the first two items of CAT ≥2 and ≥4, respectively.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; mMRC, modified Medical Research Council; –, variable not considered in the model.
Table S3.
Results obtained considering risk equations developed for utility estimation
| UMEC/VI
|
TIO
|
UMEC/VI vs TIO
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QALY | Cost (€) | QALY | Cost (€) | ΔQALY | ΔCost (€) | ICER (€/QALY) | |
| Base case | |||||||
| M1 | 2.025 | 6,215 | 1.998 | 5,625 | +0.0275 | +590.1 | 21,475 |
| M2 | 2.043 | 6,215 | 2.039 | 5,625 | +0.0048 | +590.1 | 123,425 |
| M3 | 2.021 | 6,215 | 1.994 | 5,625 | +0.0271 | +590.1 | 21,794 |
| M4 | 2.028 | 6,215 | 1.999 | 5,625 | +0.0288 | +590.1 | 20,456 |
| M5 | 2.024 | 6,215 | 1.997 | 5,625 | +0.0271 | +590.1 | 21,759 |
Abbreviations: UMEC/VI, umeclidinium and vilanterol; TIO, tiotropium; QALY, quality-adjusted life years; ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Carles Forné for his contribution to the development of the risk equation for incorporation Spanish utilities, and Yogesh Punekar for his contribution to the development of the analysis and his comments on earlier versions of this manuscript. This analysis was funded by GlaxoSmithKline (protocol code HO-14-15747).
Footnotes
Author contributions
M Miravitlles participated, as a leading investigator, in the design of the study, model adaptation, contributed to the review of the results and its discussion, and participated actively in the manuscript review. JB Gáldiz and F Garcia-Rio participated as an expert panel adapting the model inputs, reviewing the manuscript and discussing the results contributing with fruitful comments. A Huerta Hernandez, D Carcedo Rodriguez, and A Villacampa Lordan designed the study, reviewed the literature, adapted the model, and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors contributed toward data analysis, drafting and revising the paper and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Disclosure
M Miravitlles has received speaker fees from Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Menarini, Grifols, and Novartis, and consulting fees from Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, Gebro Pharma, CLS Behring, Cipla, MediImmune, Takeda, Novartis, and Grifols. JB Gáldiz has received speaker fees from Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, GlaxoSmithKline, Menarini, Grifols, and Novartis. F Garcia-Rio has received speaker fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Menarini, MundiPharma, Novartis, and Rovi, and consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis. A Huerta Hernandez is employed by and holds stocks of GlaxoSmithKline. A Villacampa Lordan and D Carcedo are employees of Oblikue Consulting, an independent consulting firm who received funding to carry out this analysis.
References
- 1.Miravitlles M, Soriano JB, Garcia-Rio R, et al. Prevalence of COPD in Spain: impact of undiagnosed COPD on quality of life and daily life activities. Thorax. 2009;64(10):863–868. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.115725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Murray CJ, Vos T, Lozano R, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990–2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380(9859):2197–2223. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dransfield MT, Bailey W, Crater G, Emmett A, O’Dell DM, Yawn B. Disease severity and symptoms among patients receiving monotherapy for COPD. Prim Care Respir J. 2011;20(1):46–53. doi: 10.4104/pcrj.2010.00059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nishimura K, Izumi J, Tsukina M, Oga J. Dyspnea is a better predictor of 5-year survival than airway obstruction in patients with COPD. Chest. 2002;121(5):1434–1440. doi: 10.1378/chest.121.5.1434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Burgel PR, Escamilla R, Perez T, et al. Impact of comorbidities on COPD-specific health related quality of life. Respir Med. 2013;107(2):233–241. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2012.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Miravitlles M, Murio C, Guerrero T, Gisbert R. Cost of chronic bronchitis and COPD. A 1-year follow-up study. Chest. 2003;123(3):784–791. doi: 10.1378/chest.123.3.784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Goldcopd.org [homepage on the internet] Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and prevention of COPD, Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) 2014. [Accessed July 1, 2015]. Available from: http://www.goldcopd.org.
- 8.Miravitlles M, Soler-Cataluña JJ, Calle M, et al. Spanish Guidelines for COPD (GesEPOC) Arch Bronconeumol. 2014;50(Suppl 1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/S0300-2896(14)70070-5. Update 2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Ministry of Health, Equality and Social Policy [Anoro® 55/22 mcg powder for inhalation] Data Sheet. [database on the Internet] [Accessed July 1, 2015]. Available from: http://www.aemps.gob.es/cima/fichasTecnicas.do?metodo=detalleForm.Spanish.
- 10.Catalá-López F, García-Altés A, Alvarez-Martín E, Gènova-Maleras R, Morant-Ginestar C, Parada A. Burden of disease and economic evaluation of healthcare interventions: are we investigating what really matters? BMC Health Serv Res. 2011;11:75. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-11-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gonzalez-McQuire S, Tabberer M, Muellerova H, Briggs A, Lomas D, Rutten-van Mölken M. Development of a conceptual model for use in economic modeling of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Value Health. 2012;15(7):A470. doi: 10.1177/0272989X16662009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lopez-Bastida J, Oliva J, Antoñanzas F, et al. A proposed guideline for economic evaluation of health technologies. Gac Sanit. 2010;24(2):154–170. doi: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2009.07.011. Spanish. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.McGahn WF, Maiwenn AL, Doshi JA, Kamae I, Marx SE, Rindress D. The ISPOR good practice for quality improvement of cost-effectiveness research task force report. Value Health. 2009;12(8):1086–1099. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4733.2009.00605.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vestbo J, Anderson W, Coxson HO, et al. Evaluation of COPD longitudinally to identify predictive surrogate end-points (ECLIPSE) Eur Respir J. 2008;31(4):869–873. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00111707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Agusti A, Calverley PM, Celli B, et al. Characterisation of COPD heterogeneity in the ECLIPSE cohort. Respir Res. 2010;11:122. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-11-122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Exuzides A, Colby C, Briggs A, et al. Statistical modeling of disease progression for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease using data from the ECLIPSE Study. Med Decis Making. 2015 Oct 8; doi: 10.1177/0272989X15610781. Epub. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rutten-van Mölken MP, Goossens LM. Cost effectiveness of pharmacological maintenance treatment for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a review of the evidence and methodological issues. Pharmacoeconomics. 2012;30(4):271–302. doi: 10.2165/11589270-000000000-00000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.IMS Heath databases [Medical dispensing database] Total annual moving (MAT) April 2014–2015. [Accessed December 17, 2015]. Available from: http://www.imshealth.com.
- 19.Casanova C, Marin JM, Martinez-Gonzalez C, et al. New GOLD classification: longitudinal data on group assignment. Respir Res. 2014;15:3. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-15-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Almagro P, Martinez-Camblor P, Soriano JB, et al. Finding the best thresholds of FEV1 and dyspnea to predict 5-year survival in COPD patients: the COCOMICS study. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e89866. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ministry of Health, Equality and Social Policy [Spanish National Health Survey 2011–12] [Accessed July 1, 2015]. [database on the Internet]. Available from: http://www.msssi.gob.es/estadEstudios/estadisticas/encuestaNacional/encuesta2011.htm. Spanish.
- 22.Maleki-Yazdi MR, Kaelin T, Richard N, Zvarich M, Church A. Efficacy and safety of umeclidinium/vilanterol 62.5/25 mcg and tiotropium 18 mcg in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: results of a 24-week, randomized, controlled trial. Respir Med. 2014;108(12):1752–1760. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2014.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Donohue JF, Niewoehner D, Brooks J, O’Dell D, Church A. Safety and tolerability of once-daily umeclidinium/vilanterol 125/25 mcg and umeclidinium 125 mcg in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: results from a 52-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Respir Res. 2014;15:78. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-15-78. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Starkie HJ, Briggs AH, Chambers MG, Jones P. Predicting EQ-5D values using the SGRQ. Value Health. 2011;14(2):354–360. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2010.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Miravitlles M, Huerta A, Fernandez-Villar J. Generic utilities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients stratified according to different staging systems. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2014;12:120. doi: 10.1186/s12955-014-0120-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Miravitlles M, Huerta A, Valle M, et al. Clinical variables impacting on the estimation of utilities in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:367–377. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S76397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ministry of Health, Equality and Social Policy [Catalogue of sanitarian products included in the Spanish National Health System pharmaceutical provision] Apr, 2015. [Accessed July 1, 2015]. [database on the Internet]. Available from: http://www.msssi.gob.es/profesionales/nomenclator.do. Spanish.
- 28.Miravitlles M, Murio C, Guerrero T, Gisbert R, DAFNE Study Group Pharmacoeconomic evaluation of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis and COPD. Chest. 2002;121(5):1449–1455. doi: 10.1378/chest.121.5.1449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Miravitlles M, Garcia-Polo C, Domenech A, Villegas G, Conget F, de la Roza C. Clinical outcomes and cost analysis of exacerbations in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lung. 2013;191(5):523–530. doi: 10.1007/s00408-013-9487-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Punekar YS, Shukla A, Müllerova H. COPD management costs according to the frequency of COPD exacerbations in UK primary care. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2014;9:65–73. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S54417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Sicras A, Huerta A, Navarro R, Ibañez J. Use of resources and costs associated with the exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a retrospective population-based study. Semergen. 2014;40(4):189–197. doi: 10.1016/j.semerg.2013.10.002. Spanish. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Briggs AH. Handling uncertainty in cost-effectiveness models. Pharmacoeconomics. 2000;17(5):479–500. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200017050-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Decramer M, Anuzeto A, Kerwin E, et al. Efficacy and safety of umeclidinium plus vilanterol versus tiotropium, vilanterol, or umeclidinium monotherapy over 24 weeks in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: results from two multicenter, blinded, randomized controlled trials. Lancet Respir Med. 2014;2(6):472–486. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sacristan JA, Oliva J, Del Llano J, Prieto L, Pinto JL. What is an efficient health technology in Spain? Gac Sanit. 2002;16(4):334–343. doi: 10.1016/s0213-9111(02)71933-x. Spanish. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.De Cock E, Miravitlles M, Gonzalez-Juanatey JR, Azanza-Perea JR. Threshold value of the cost per year of life gained to recommend the adoption of health technologies in Spain: evidence from a review. Pharmacoeconomics. 2007;4(3):97–107. Spanish. [Google Scholar]
- 36.De Lucas P, Miravitlles M, Rodriguez JM, de Miguel J, Lopez S, Sanchez G. Cost-effectiveness analysis of tiotropium versus ipratropium in the treatment of COPD patients. Pharmacoeconomics. 2004;1(3):123–130. Spanish. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Rutten-van Mölken MP, Oostenbrink JB, Miravitlles M, Monz BU. Modelling the 5-year cost-effectiveness of tiotropium, salmeterol and ipratropium for the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Spain. Eur J Health Econ. 2007;8(2):123–135. doi: 10.1007/s10198-007-0039-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Brosa M, Diaz-Cerezo S, Miravitlles M, Gonzalez-Rojas N, Nieves D. Cost-effectiveness analysis of tiotropium in the treatment of COPD in Spain. Pharmacoeconomics. 2010;7(1):3–12. Spanish. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Brosa M, Perez-Alcantara F, Borderias-Clau L, Galdiz-Iturri JB, Riera-Febrer M, Figueres-Sabate M. Cost-utility anaysis of indacaterol versus tiotropium in the treatment of COPD in Spain. Pharmacoeconomics. 2013;10:89–97. Spanish. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Punekar YS, Roberts G, Ismaila A, O’Leay M. Cost-effectiveness of umeclidinium/vilanterol combination therapy among symptomatic COPD patients. Value Health. 2014;17(7):A595. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2014.08.2053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Price D, Keininger D, Costa-Scharplatz M, et al. Cost-effectiveness of the LAMA/LABA dual bronchodilator indacaterol/glycopirronium in a Swedish healthcare setting. Respir Med. 2014;108(12):1786–1793. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2014.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hoogendoorn M, Feenstra TL, Asukai Y, et al. Cost-effectiveness models for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: cross-model comparison of hypothetical treatment scenarios. Value Health. 2014;17(5):525–536. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2014.03.1721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Calverley PM, Anderson JA, Celli B, et al. Salmeterol and fluticasone propionate and survival in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(8):775–789. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa063070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hurst JR, Vestbo J, Anzueto A, Locantore N, et al. Susceptibility to exacerbation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(12):1128–1138. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0909883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1.
Risk equations developed for utility estimation
| Risk equation | Scenario | Description |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | Base case | Saturated linear regression model |
| M2 | Sensitivity analysis | Reduction in number of variables according to goodness of fit index AIC |
| M3 | Sensitivity analysis | Grouping of frequency and severity of dyspnea: mMRC2 (vs 0–1) and mMRC3–4 (vs 0–1) |
| M4 | Sensitivity analysis | Variable cough and sputum = score ≥2 in first two items of CAT |
| M5 | Sensitivity analysis | Variable cough and sputum = score ≥4 in first two items of CAT |
Abbreviations: AIC, Akaike information criterion; mMRC, modified Medical Research Council; CAT, COPD Assessment Test.
Table S2.
Variables considered in each of the risk equations
| Base-case sensitivity analysis
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect
| |||||
| M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | M5 | |
| Intercept | 0.8345 | 0.9158 | 0.8526 | 0.8345 | 0.8148 |
| Female (vs male) | −0.0875 | −0.0902 | −0.0819 | −0.0875 | −0.0749 |
| Low BMI (vs mean) | −0.0059 | – | −0.0870 | −0.0059 | −0.0153 |
| High BMI (vs mean) | −0.0136 | – | −0.0305 | −0.0136 | −0.0197 |
| Cardiovascular comorbidities (vs no) | −0.0074 | – | −0.0407 | −0.0074 | −0.0023 |
| Other comorbidities (vs no) | −0.0074 | – | −0.0169 | −0.0074 | −0.0091 |
| Smoker (vs ex-smoker) | −0.0244 | – | −0.0488 | −0.0244 | −0.0338 |
| Age | 0.0012 | – | 0.0012 | 0.0012 | 0.0010 |
| Number of exacerbations | −0.0291 | −0.0298 | −0.0338 | −0.0291 | −0.0316 |
| FEV1 (%) post-bronchodilator | 0.0006 | – | 0.0004 | 0.0006 | 0.0008 |
| mMRC 2–3 (vs 0–1)a | −0.1541 | −0.1606 | −0.1089 | −0.1541 | −0.1573 |
| mMRC 4 (vs 0–1)a | −0.5326 | −0.5390 | −0.3041 | −0.5326 | −0.5275 |
| Cough and sputum (vs no)b | −0.0672 | −0.0581 | −0.0600 | −0.0672 | −0.0776 |
Notes:
In M3, grouping is mMRC 2 (vs 0–1) and mMRC 3–4 (vs 0–1).
In M4 and M5, cough and sputum are considered as equivalent to the score in the first two items of CAT ≥2 and ≥4, respectively.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; mMRC, modified Medical Research Council; –, variable not considered in the model.
Table S3.
Results obtained considering risk equations developed for utility estimation
| UMEC/VI
|
TIO
|
UMEC/VI vs TIO
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QALY | Cost (€) | QALY | Cost (€) | ΔQALY | ΔCost (€) | ICER (€/QALY) | |
| Base case | |||||||
| M1 | 2.025 | 6,215 | 1.998 | 5,625 | +0.0275 | +590.1 | 21,475 |
| M2 | 2.043 | 6,215 | 2.039 | 5,625 | +0.0048 | +590.1 | 123,425 |
| M3 | 2.021 | 6,215 | 1.994 | 5,625 | +0.0271 | +590.1 | 21,794 |
| M4 | 2.028 | 6,215 | 1.999 | 5,625 | +0.0288 | +590.1 | 20,456 |
| M5 | 2.024 | 6,215 | 1.997 | 5,625 | +0.0271 | +590.1 | 21,759 |
Abbreviations: UMEC/VI, umeclidinium and vilanterol; TIO, tiotropium; QALY, quality-adjusted life years; ICER, incremental cost-effectiveness ratio.